回调函数:观察、定制与控制智能体行为
简介:什么是回调函数及其使用价值?
回调是ADK的核心功能,它提供了一种强大的机制来介入智能体的执行过程。通过回调,您可以在特定预定义点观察、定制甚至控制智能体的行为,而无需修改ADK框架的核心代码。
它们是什么? 本质上,回调函数是您定义的标准Python函数。当您创建智能体时,将这些函数与智能体关联。ADK框架会在智能体生命周期的关键阶段自动调用您的函数,例如:
- 在智能体的主要处理逻辑运行之前或之后。
- 在向大型语言模型(LLM)发送请求之前,或从LLM接收响应之后。
- 在执行工具(如Python函数或其他智能体)之前或完成之后。
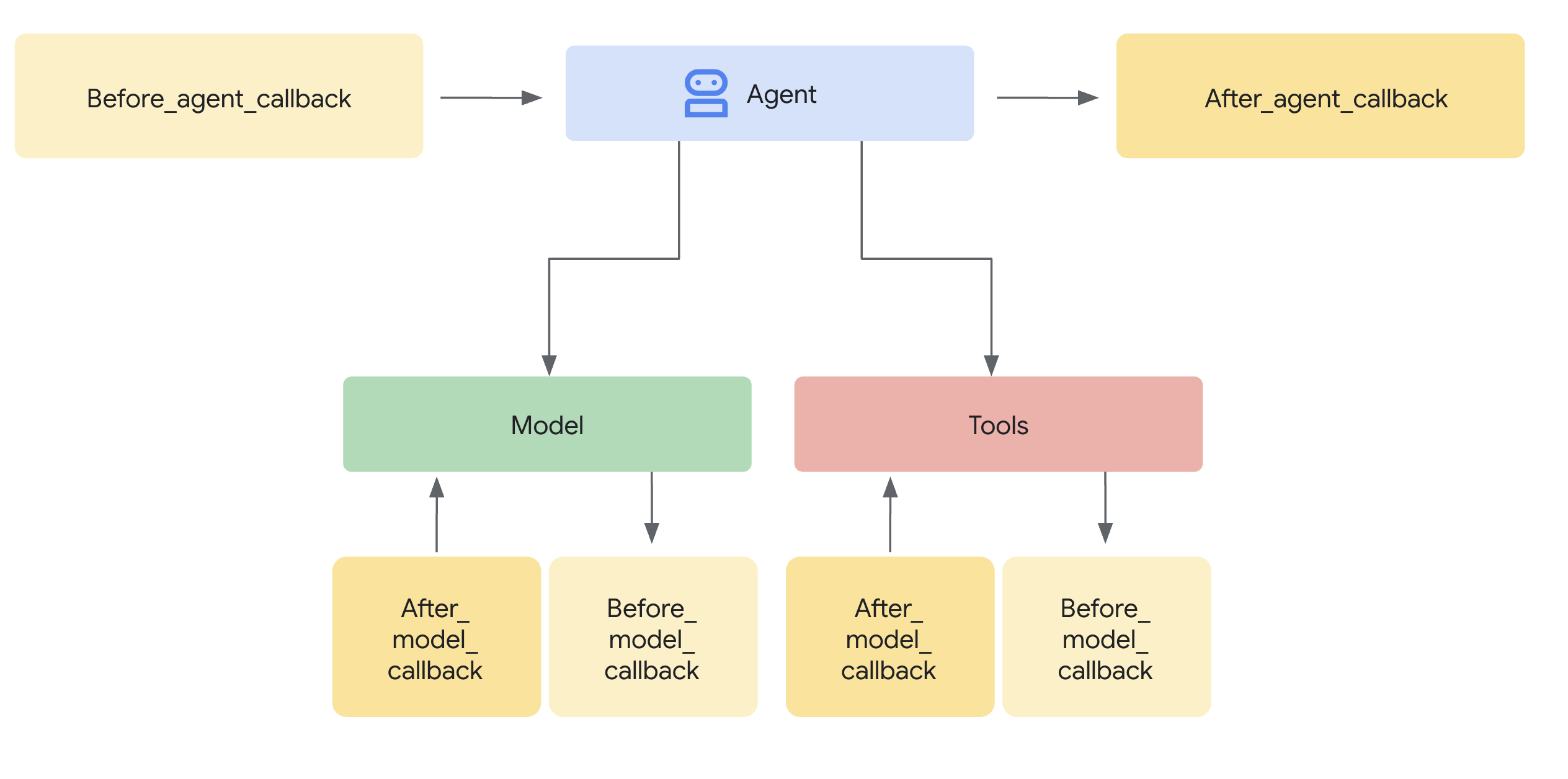
为什么使用它们? 回调机制提供了极大的灵活性,并能实现高级智能体功能:
- 观察与调试:在关键步骤记录详细信息以便监控和故障排除。
- 自定义与控制:根据您的逻辑修改流经智能体的数据(如LLM请求或工具结果),甚至完全绕过某些步骤。
- 实现防护栏: 强制执行安全规则、验证输入/输出,或防止不允许的操作。
- 管理状态:在执行过程中读取或动态更新智能体的会话状态。
- 集成与增强:触发外部操作(API调用、通知)或添加缓存等功能。
如何添加它们? 当您创建Agent或LlmAgent实例时,通过将您定义的Python函数作为参数传递给智能体的构造函数(__init__)来注册回调。
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from typing import Optional
# --- Define your callback function ---
def my_before_model_logic(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
print(f"Callback running before model call for agent: {callback_context.agent_name}")
# ... your custom logic here ...
return None # Allow the model call to proceed
# --- Register it during Agent creation ---
my_agent = LlmAgent(
name="MyCallbackAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash", # Or your desired model
instruction="Be helpful.",
# Other agent parameters...
before_model_callback=my_before_model_logic # Pass the function here
)
回调机制:拦截与控制
当ADK框架遇到可以运行回调的点时(例如,在调用LLM之前),它会检查是否为该智能体提供了相应的回调函数。如果提供了,框架将执行您的函数。
上下文是关键: 您的回调函数并非孤立调用。框架会提供特殊的上下文对象(CallbackContext 或 ToolContext)作为参数。这些对象包含关于智能体当前执行状态的重要信息,包括调用详情、会话状态,以及可能对工件或内存等服务的引用。您可以通过这些上下文对象来理解当前情况并与框架交互。(详见专门的"上下文对象"章节)。
控制流程(核心机制):回调最强大的方面在于它们的返回值如何影响智能体的后续行动。这就是你拦截和控制执行流程的方式:
-
return None(允许默认行为):- 这是标准方式,用于表示您的回调已完成其工作(例如日志记录、检查、对可变输入参数如
llm_request进行轻微修改),且ADK智能体应继续正常操作。 - 对于
before_*回调函数(before_agent、before_model、before_tool),返回None表示将继续执行后续步骤(运行智能体逻辑、调用大语言模型、执行工具)。 - 对于
after_*回调函数(after_agent、after_model、after_tool),返回None意味着将直接使用前一步骤生成的结果(智能体的输出、大语言模型的响应、工具的结果)。
- 这是标准方式,用于表示您的回调已完成其工作(例如日志记录、检查、对可变输入参数如
-
return(覆盖默认行为):- 返回特定类型的对象(而非
None)是覆盖ADK智能体默认行为的方式。框架将使用你返回的对象,并跳过原本会执行的步骤,或替换刚生成的结果。 before_agent_callback→types.Content: 跳过智能体的主要执行逻辑(_run_async_impl/_run_live_impl)。返回的Content对象会立即被视为智能体本轮交互的最终输出。适用于直接处理简单请求或实施访问控制。before_model_callback→LlmResponse: 跳过对外部大语言模型的调用。返回的LlmResponse对象会被当作LLM的实际响应进行处理。非常适合实现输入防护栏、提示验证或提供缓存响应。before_tool_callback→dict: 跳过实际工具函数(或子智能体)的执行。返回的dict会被用作工具调用的结果,通常随后传回给LLM。非常适合验证工具参数、应用策略限制或返回模拟/缓存的工具结果。after_agent_callback→types.Content: 替换智能体运行逻辑刚刚生成的Content。after_model_callback→LlmResponse: 替换从大语言模型接收到的LlmResponse。适用于净化输出、添加标准免责声明或修改大语言模型的响应结构。after_tool_callback→dict: 替换工具返回的dict结果。允许在将工具输出发送回LLM之前进行后处理或标准化。
- 返回特定类型的对象(而非
概念性代码示例(防护栏):
这个示例展示了使用before_model_callback实现防护栏的常见模式。
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from typing import Optional
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
GEMINI_2_FLASH="gemini-2.0-flash"
# --- Define the Callback Function ---
def simple_before_model_modifier(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
"""Inspects/modifies the LLM request or skips the call."""
agent_name = callback_context.agent_name
print(f"[Callback] Before model call for agent: {agent_name}")
# Inspect the last user message in the request contents
last_user_message = ""
if llm_request.contents and llm_request.contents[-1].role == 'user':
if llm_request.contents[-1].parts:
last_user_message = llm_request.contents[-1].parts[0].text
print(f"[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '{last_user_message}'")
# --- Modification Example ---
# Add a prefix to the system instruction
original_instruction = llm_request.config.system_instruction or types.Content(role="system", parts=[])
prefix = "[Modified by Callback] "
# Ensure system_instruction is Content and parts list exists
if not isinstance(original_instruction, types.Content):
# Handle case where it might be a string (though config expects Content)
original_instruction = types.Content(role="system", parts=[types.Part(text=str(original_instruction))])
if not original_instruction.parts:
original_instruction.parts.append(types.Part(text="")) # Add an empty part if none exist
# Modify the text of the first part
modified_text = prefix + (original_instruction.parts[0].text or "")
original_instruction.parts[0].text = modified_text
llm_request.config.system_instruction = original_instruction
print(f"[Callback] Modified system instruction to: '{modified_text}'")
# --- Skip Example ---
# Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if "BLOCK" in last_user_message.upper():
print("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.")
# Return an LlmResponse to skip the actual LLM call
return LlmResponse(
content=types.Content(
role="model",
parts=[types.Part(text="LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")],
)
)
else:
print("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.")
# Return None to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return None
# Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback
my_llm_agent = LlmAgent(
name="ModelCallbackAgent",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="You are a helpful assistant.", # Base instruction
description="An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback",
before_model_callback=simple_before_model_modifier # Assign the function here
)
APP_NAME = "guardrail_app"
USER_ID = "user_1"
SESSION_ID = "session_001"
# Session and Runner
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=my_llm_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
# Agent Interaction
def call_agent(query):
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
events = runner.run(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
call_agent("callback example")
通过理解返回None与返回特定对象之间的机制差异,您可以精确控制智能体的执行路径,使回调成为使用ADK构建复杂可靠智能体的关键工具。