异步任务队列¶
许多模型推理最好作为长时间运行的操作来处理。BentoML中的任务允许您在后台执行这些长时间运行的工作负载,并在稍后时间检索结果。
本文档解释了如何定义和调用任务端点。
概述¶
任务非常适合那些不需要立即获取推理结果的场景,例如:
批处理: 在单个批次中处理大量数据或计算。
视频或图像生成: 创建或处理可能需要大量时间的媒体文件。
同步等待此类任务可能会导致效率低下,调用者在大部分时间内保持空闲。使用BentoML任务,您可以先发送提示,然后异步获取结果。
以下是使用 BentoML 任务的一般工作流程:
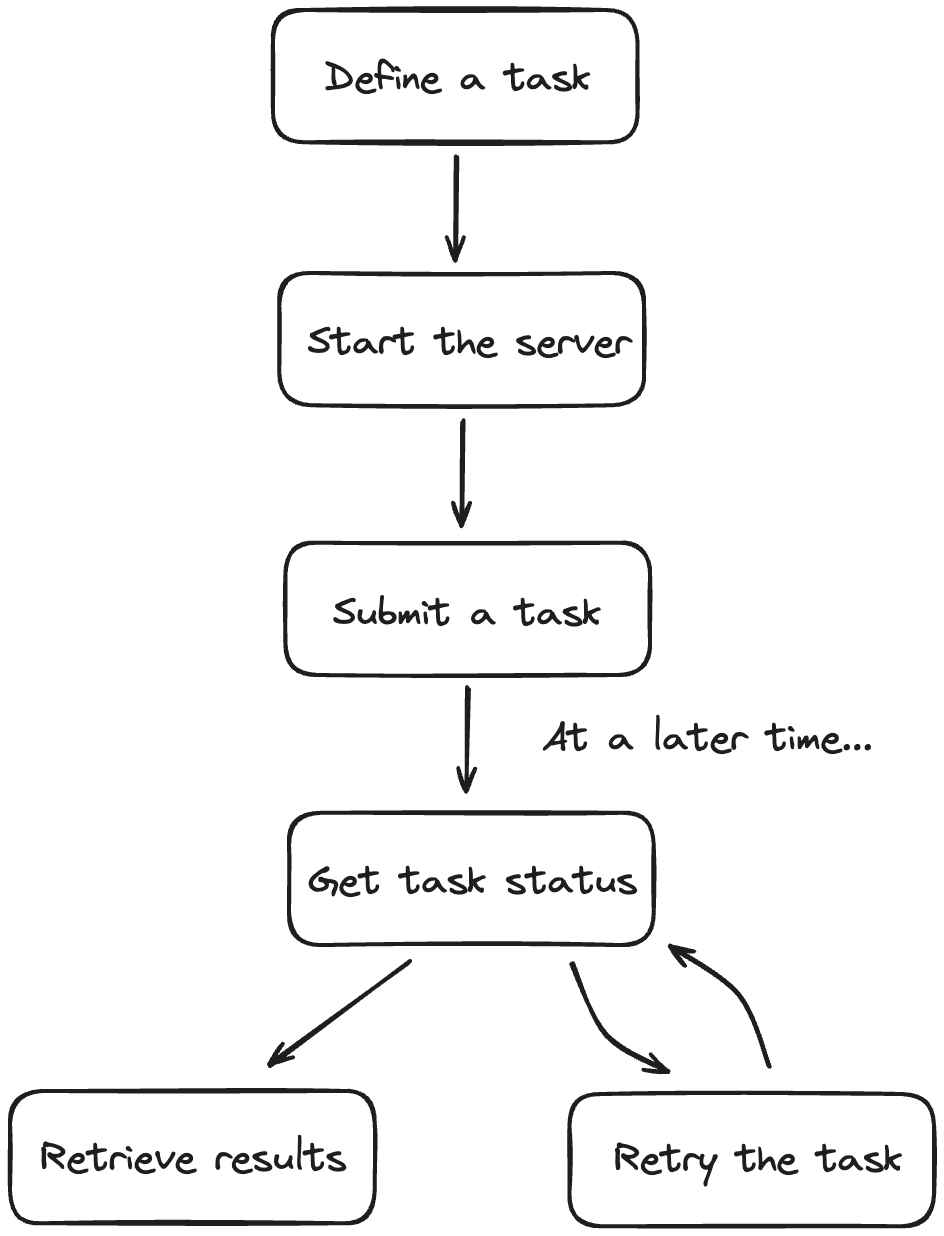
定义一个任务端点¶
您可以在服务构造函数中使用@bentoml.task装饰器定义任务端点。以下是一个示例:
import bentoml
from PIL.Image import Image
@bentoml.service
class ImageGenerationService:
@bentoml.task
def long_running_image_generation(self, prompt: str) -> Image:
# Process the prompt in a long-running process
return image
BentoML 自动暴露了几个端点供客户端管理任务,例如任务提交和状态检索。
调用任务端点¶
BentoML 任务通过任务队列风格的 API 端点进行管理。您可以通过提交请求创建客户端与端点进行交互,专用的工作进程将监视队列以获取新任务。可以使用 SyncHTTPClient 和 AsyncHTTPClient 客户端来调用任务端点。
以下是使用同步客户端提交任务的方法:
import bentoml
prompt = "a scenic mountain view that ..."
client = bentoml.SyncHTTPClient('http://localhost:3000')
# The arguments are the same as the Service method, just call with `.submit()`
task = client.long_running_image_generation.submit(prompt=prompt)
print("Task submitted, ID:", task.id)
一旦任务提交,客户端会收到一个任务ID,该ID可用于跟踪任务状态并在稍后时间检索结果。以下是一个示例:
# Use the following code at a later time
status = task.get_status()
if status.value == 'success':
print("The task runs successfully. The result is", task.get())
elif status.value == 'failure':
print("The task run failed.")
else:
print("The task is still running.")
如果任务失败或需要使用相同的参数重新运行任务,请使用 retry():
status = task.get_status()
if status.value == 'failure':
print("Task failed, retrying...")
new_task = task.retry()
new_status = new_task.get_status()
print("New task status:", new_status.value)
欲了解更多信息,请参阅调用API端点。