元学习器示例 - 训练、估计、验证、可视化
介绍
在本笔记本中,我们将生成一些合成数据,以演示如何使用各种元学习算法来估计个体处理效果和平均处理效果,并带有置信区间。
[1]:
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
[2]:
from causalml.inference.meta import LRSRegressor
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_clustering.py:35: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _pt_shuffle_rec(i, indexes, index_mask, partition_tree, M, pos):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_clustering.py:54: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def delta_minimization_order(all_masks, max_swap_size=100, num_passes=2):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_clustering.py:63: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _reverse_window(order, start, length):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_clustering.py:69: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _reverse_window_score_gain(masks, order, start, length):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_clustering.py:77: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _mask_delta_score(m1, m2):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/links.py:5: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def identity(x):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/links.py:10: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _identity_inverse(x):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/links.py:15: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def logit(x):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/links.py:20: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _logit_inverse(x):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_masked_model.py:363: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _build_fixed_single_output(averaged_outs, last_outs, outputs, batch_positions, varying_rows, num_varying_rows, link, linearizing_weights):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_masked_model.py:385: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _build_fixed_multi_output(averaged_outs, last_outs, outputs, batch_positions, varying_rows, num_varying_rows, link, linearizing_weights):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_masked_model.py:428: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _init_masks(cluster_matrix, M, indices_row_pos, indptr):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/utils/_masked_model.py:439: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _rec_fill_masks(cluster_matrix, indices_row_pos, indptr, indices, M, ind):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/maskers/_tabular.py:186: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _single_delta_mask(dind, masked_inputs, last_mask, data, x, noop_code):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/maskers/_tabular.py:197: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _delta_masking(masks, x, curr_delta_inds, varying_rows_out,
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/tqdm/auto.py:22: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
from .autonotebook import tqdm as notebook_tqdm
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/maskers/_image.py:175: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def _jit_build_partition_tree(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, zmin, zmax, total_ywidth, total_zwidth, M, clustering, q):
/Users/jeong/miniconda3/envs/causalml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/shap/explainers/_partition.py:676: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def lower_credit(i, value, M, values, clustering):
The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
[3]:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import statsmodels.api as sm
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
import warnings
from causalml.inference.meta import LRSRegressor
from causalml.inference.meta import XGBTRegressor, MLPTRegressor
from causalml.inference.meta import BaseXRegressor, BaseRRegressor, BaseSRegressor, BaseTRegressor
from causalml.match import NearestNeighborMatch, MatchOptimizer, create_table_one
from causalml.propensity import ElasticNetPropensityModel
from causalml.dataset import *
from causalml.metrics import *
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
%matplotlib inline
Failed to import duecredit due to No module named 'duecredit'
[4]:
import importlib
print(importlib.metadata.version('causalml') )
0.15.1.dev0
第一部分:使用合成数据的示例工作流程
生成合成数据
我们已经实现了4种生成合成数据的模式(由输入参数
mode指定)。有关这些数据生成过程的更多详细信息,请参阅参考资料部分。
[5]:
# Generate synthetic data using mode 1
y, X, treatment, tau, b, e = synthetic_data(mode=1, n=10000, p=8, sigma=1.0)
计算平均处理效果 (ATE)
元学习器可以通过调用基础学习器类并提供sklearn/xgboost回归器类作为输入来实例化。或者,我们提供了一些现成的学习器,这些学习器已经继承了各自基础学习器类的能力。这更加抽象,使得这些工具能够快速且易于使用。
[6]:
# Ready-to-use S-Learner using LinearRegression
learner_s = LRSRegressor()
ate_s = learner_s.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print(ate_s)
print('ATE estimate: {:.03f}'.format(ate_s[0][0]))
print('ATE lower bound: {:.03f}'.format(ate_s[1][0]))
print('ATE upper bound: {:.03f}'.format(ate_s[2][0]))
# After calling estimate_ate, add pretrain=True flag to skip training
# This flag is applicable for other meta learner
ate_s = learner_s.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, pretrain=True)
print(ate_s)
print('ATE estimate: {:.03f}'.format(ate_s[0][0]))
print('ATE lower bound: {:.03f}'.format(ate_s[1][0]))
print('ATE upper bound: {:.03f}'.format(ate_s[2][0]))
(array([0.72721128]), array([0.67972656]), array([0.77469599]))
ATE estimate: 0.727
ATE lower bound: 0.680
ATE upper bound: 0.775
(array([0.72721128]), array([0.67972656]), array([0.77469599]))
ATE estimate: 0.727
ATE lower bound: 0.680
ATE upper bound: 0.775
[7]:
# Ready-to-use T-Learner using XGB
learner_t = XGBTRegressor()
ate_t = learner_t.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('Using the ready-to-use XGBTRegressor class')
print(ate_t)
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in XGB
learner_t = BaseTRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
ate_t = learner_t.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('\nUsing the BaseTRegressor class and using XGB (same result):')
print(ate_t)
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in LinearRegression
learner_t = BaseTRegressor(learner=LinearRegression())
ate_t = learner_t.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('\nUsing the BaseTRegressor class and using Linear Regression (different result):')
print(ate_t)
Using the ready-to-use XGBTRegressor class
(array([0.55539207]), array([0.53185148]), array([0.57893267]))
Using the BaseTRegressor class and using XGB (same result):
(array([0.55539207]), array([0.53185148]), array([0.57893267]))
Using the BaseTRegressor class and using Linear Regression (different result):
(array([0.71740976]), array([0.67655445]), array([0.75826507]))
[8]:
# X Learner with propensity score input
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in XGB
learner_x = BaseXRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
ate_x = learner_x.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e)
print('Using the BaseXRegressor class and using XGB:')
print(ate_x)
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in LinearRegression
learner_x = BaseXRegressor(learner=LinearRegression())
ate_x = learner_x.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e)
print('\nUsing the BaseXRegressor class and using Linear Regression:')
print(ate_x)
Using the BaseXRegressor class and using XGB:
(array([0.52239345]), array([0.50279387]), array([0.54199302]))
Using the BaseXRegressor class and using Linear Regression:
(array([0.71740976]), array([0.67655445]), array([0.75826507]))
[9]:
# X Learner without propensity score input
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in XGB
learner_x = BaseXRegressor(XGBRegressor())
ate_x = learner_x.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('Using the BaseXRegressor class and using XGB without propensity score input:')
print(ate_x)
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in LinearRegression
learner_x = BaseXRegressor(learner=LinearRegression())
ate_x = learner_x.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('\nUsing the BaseXRegressor class and using Linear Regression without propensity score input:')
print(ate_x)
Using the BaseXRegressor class and using XGB without propensity score input:
(array([0.52348025]), array([0.50385245]), array([0.54310804]))
Using the BaseXRegressor class and using Linear Regression without propensity score input:
(array([0.71740976]), array([0.67655445]), array([0.75826507]))
[10]:
# R Learner with propensity score input
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in XGB
learner_r = BaseRRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
ate_r = learner_r.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e)
print('Using the BaseRRegressor class and using XGB:')
print(ate_r)
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in LinearRegression
learner_r = BaseRRegressor(learner=LinearRegression())
ate_r = learner_r.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e)
print('Using the BaseRRegressor class and using Linear Regression:')
print(ate_r)
Using the BaseRRegressor class and using XGB:
(array([0.51551318]), array([0.5150305]), array([0.51599587]))
Using the BaseRRegressor class and using Linear Regression:
(array([0.51503495]), array([0.51461987]), array([0.51545004]))
[11]:
# R Learner with propensity score input and random sample weight
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in XGB
learner_r = BaseRRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
sample_weight = np.random.randint(1, 3, len(y))
ate_r = learner_r.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e, sample_weight=sample_weight)
print('Using the BaseRRegressor class and using XGB:')
print(ate_r)
Using the BaseRRegressor class and using XGB:
(array([0.48910448]), array([0.48861819]), array([0.48959077]))
[12]:
# R Learner without propensity score input
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in XGB
learner_r = BaseRRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
ate_r = learner_r.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('Using the BaseRRegressor class and using XGB without propensity score input:')
print(ate_r)
# Calling the Base Learner class and feeding in LinearRegression
learner_r = BaseRRegressor(learner=LinearRegression())
ate_r = learner_r.estimate_ate(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
print('Using the BaseRRegressor class and using Linear Regression without propensity score input:')
print(ate_r)
Using the BaseRRegressor class and using XGB without propensity score input:
(array([0.45400543]), array([0.45352042]), array([0.45449043]))
Using the BaseRRegressor class and using Linear Regression without propensity score input:
(array([0.59802659]), array([0.59761147]), array([0.5984417]))
7. 计算个体治疗效果 (ITE/CATE)
CATE代表条件平均处理效应。
[13]:
# S Learner
learner_s = LRSRegressor()
cate_s = learner_s.fit_predict(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
# T Learner
learner_t = BaseTRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
cate_t = learner_t.fit_predict(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
# X Learner with propensity score input
learner_x = BaseXRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
cate_x = learner_x.fit_predict(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e)
# X Learner without propensity score input
learner_x_no_p = BaseXRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
cate_x_no_p = learner_x_no_p.fit_predict(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
# R Learner with propensity score input
learner_r = BaseRRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
cate_r = learner_r.fit_predict(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y, p=e)
# R Learner without propensity score input
learner_r_no_p = BaseRRegressor(learner=XGBRegressor())
cate_r_no_p = learner_r_no_p.fit_predict(X=X, treatment=treatment, y=y)
[14]:
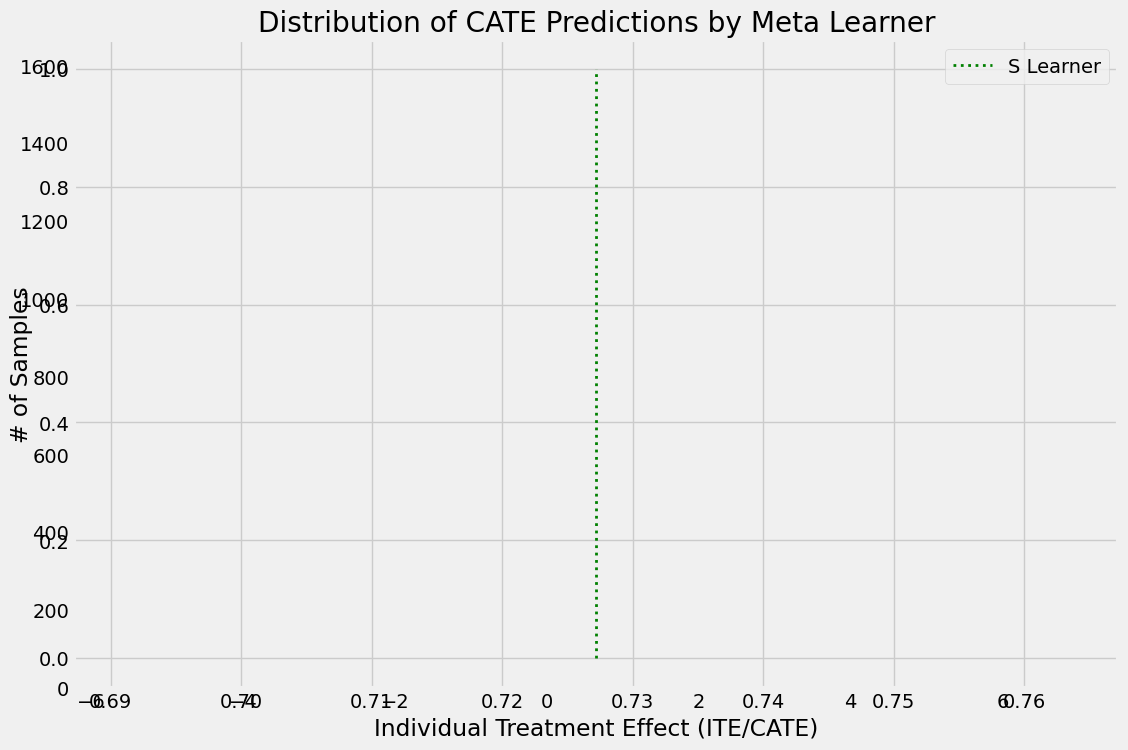
alpha=0.2
bins=30
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.hist(cate_t, alpha=alpha, bins=bins, label='T Learner')
plt.hist(cate_x, alpha=alpha, bins=bins, label='X Learner')
plt.hist(cate_x_no_p, alpha=alpha, bins=bins, label='X Learner (no propensity score)')
plt.hist(cate_r, alpha=alpha, bins=bins, label='R Learner')
plt.hist(cate_r_no_p, alpha=alpha, bins=bins, label='R Learner (no propensity score)')
plt.vlines(cate_s[0], 0, plt.axes().get_ylim()[1], label='S Learner',
linestyles='dotted', colors='green', linewidth=2)
plt.title('Distribution of CATE Predictions by Meta Learner')
plt.xlabel('Individual Treatment Effect (ITE/CATE)')
plt.ylabel('# of Samples')
_=plt.legend()
第B部分:验证元学习器的准确性
我们将基于A部分中的相同合成数据生成方法(simulate_nuisance_and_easy_treatment)来验证元学习器的性能。
[15]:
train_summary, validation_summary = get_synthetic_summary_holdout(simulate_nuisance_and_easy_treatment,
n=10000,
valid_size=0.2,
k=10)
[16]:
train_summary
[16]:
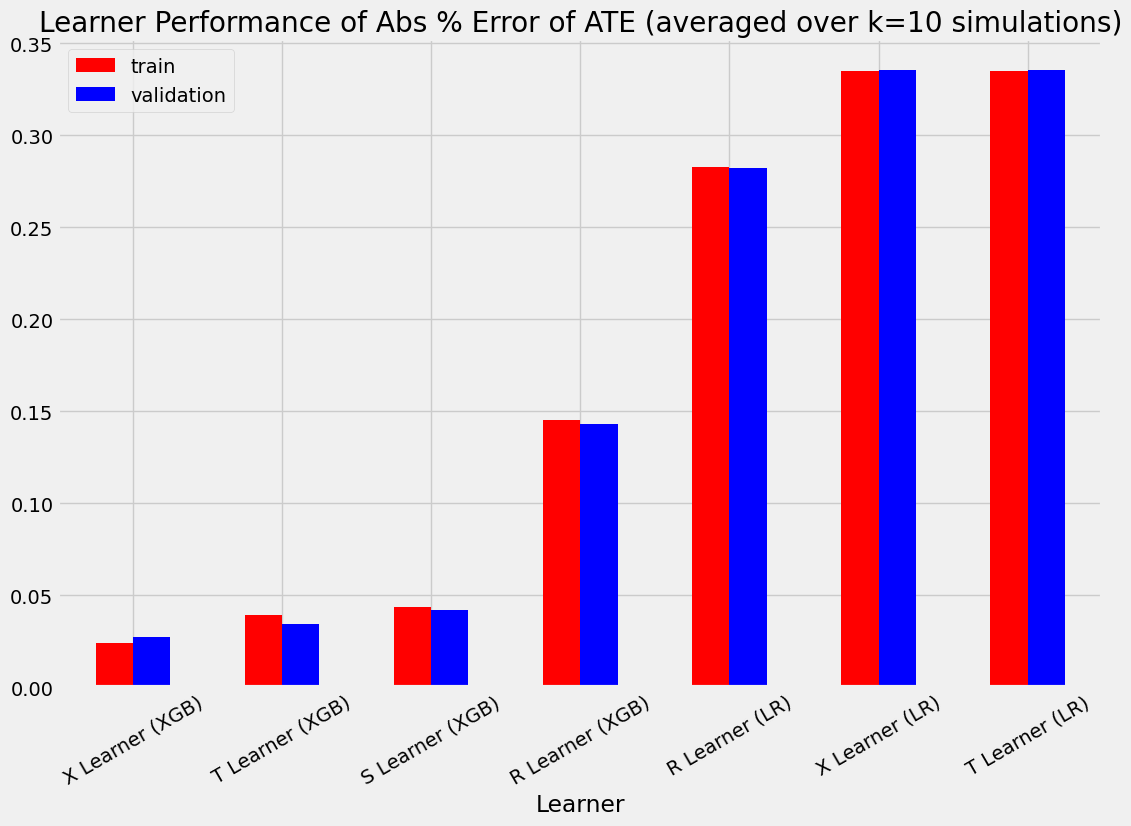
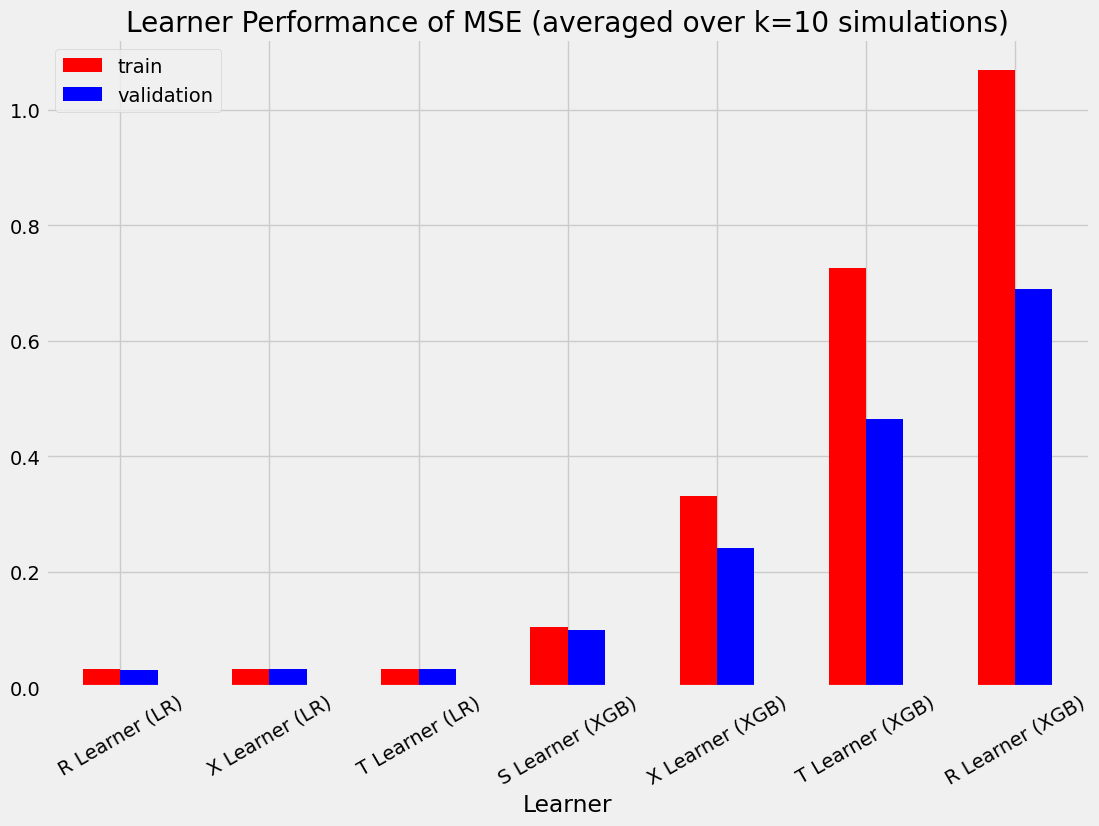
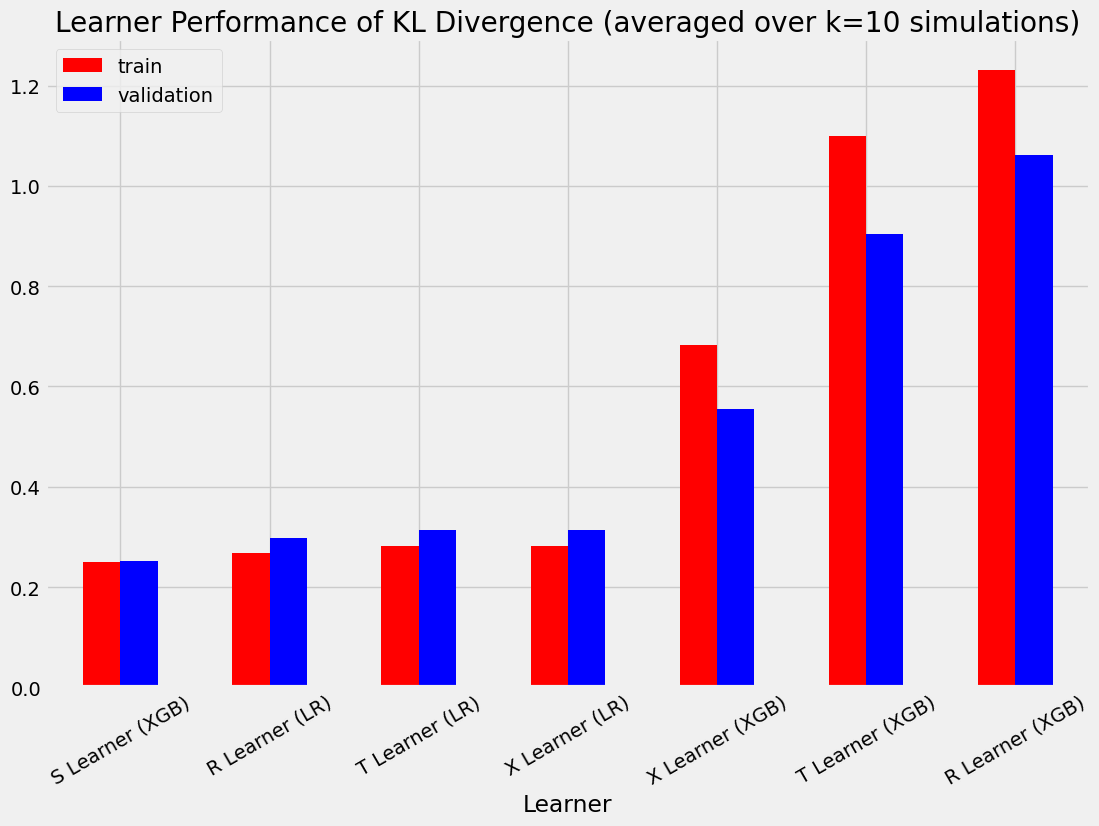
| ATE的绝对百分比误差 | 均方误差 | KL散度 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实际值 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| S Learner (LR) | 0.349749 | 0.072543 | 3.703728 |
| S Learner (XGB) | 0.043545 | 0.103968 | 0.249110 |
| T Learner (LR) | 0.334790 | 0.031673 | 0.282270 |
| T 学习器 (XGB) | 0.039432 | 0.726171 | 1.099338 |
| X 学习器 (LR) | 0.334790 | 0.031673 | 0.282270 |
| X 学习器 (XGB) | 0.024209 | 0.331760 | 0.682191 |
| R 学习器 (LR) | 0.282719 | 0.031079 | 0.267950 |
| R 学习器 (XGB) | 0.145131 | 1.068164 | 1.230508 |
[17]:
validation_summary
[17]:
| ATE的绝对百分比误差 | 均方误差 | KL散度 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实际值 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| S Learner (LR) | 0.354242 | 0.072989 | 3.797245 |
| S Learner (XGB) | 0.041916 | 0.098853 | 0.251344 |
| T Learner (LR) | 0.335444 | 0.031613 | 0.314690 |
| T Learner (XGB) | 0.034209 | 0.465331 | 0.904251 |
| X 学习器 (LR) | 0.335444 | 0.031613 | 0.314690 |
| X 学习器 (XGB) | 0.027473 | 0.241996 | 0.554173 |
| R 学习器 (LR) | 0.282196 | 0.030891 | 0.298666 |
| R 学习器 (XGB) | 0.143055 | 0.689088 | 1.061381 |
[18]:
scatter_plot_summary_holdout(train_summary,
validation_summary,
k=10,
label=['Train', 'Validation'],
drop_learners=[],
drop_cols=[])

[19]:
bar_plot_summary_holdout(train_summary,
validation_summary,
k=10,
drop_learners=['S Learner (LR)'],
drop_cols=[])
[20]:
# Single simulation
train_preds, valid_preds = get_synthetic_preds_holdout(simulate_nuisance_and_easy_treatment,
n=50000,
valid_size=0.2)
[21]:
#distribution plot for signle simulation of Training
distr_plot_single_sim(train_preds, kind='kde', linewidth=2, bw_method=0.5,
drop_learners=['S Learner (LR)',' S Learner (XGB)'])
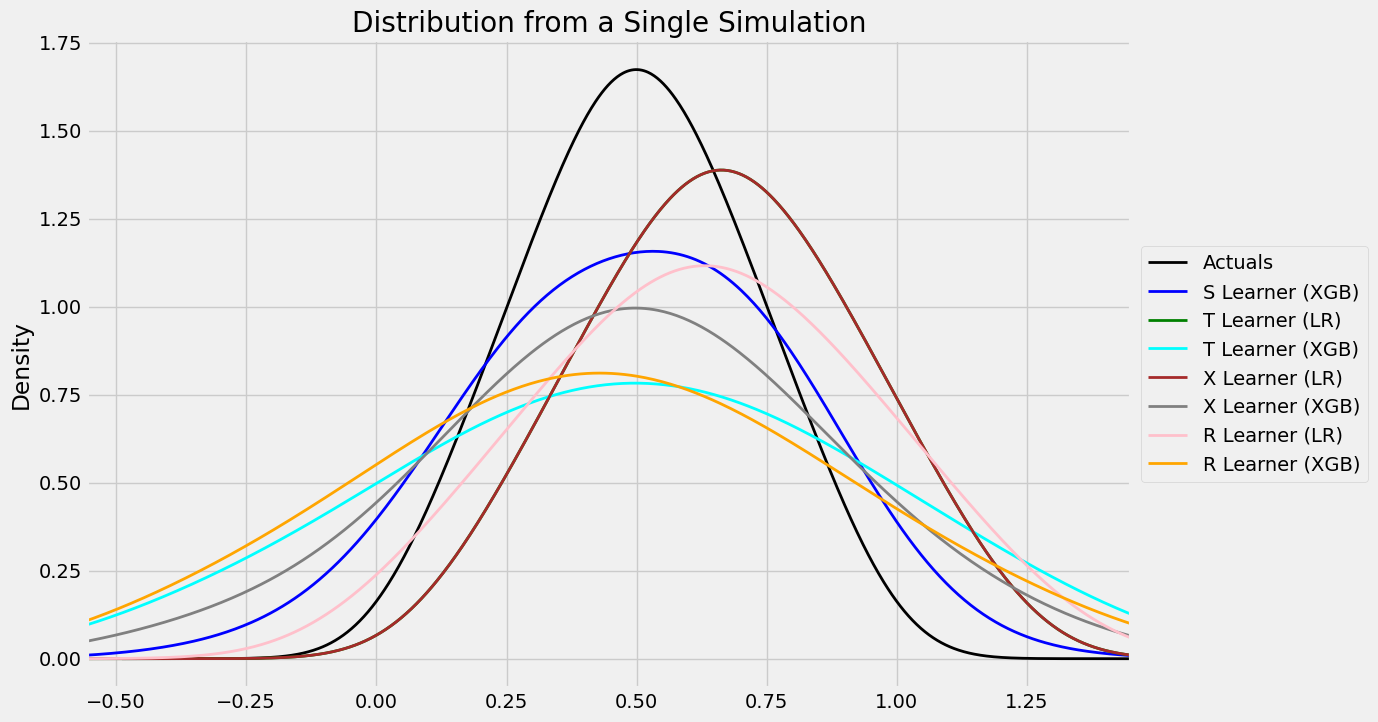
[22]:
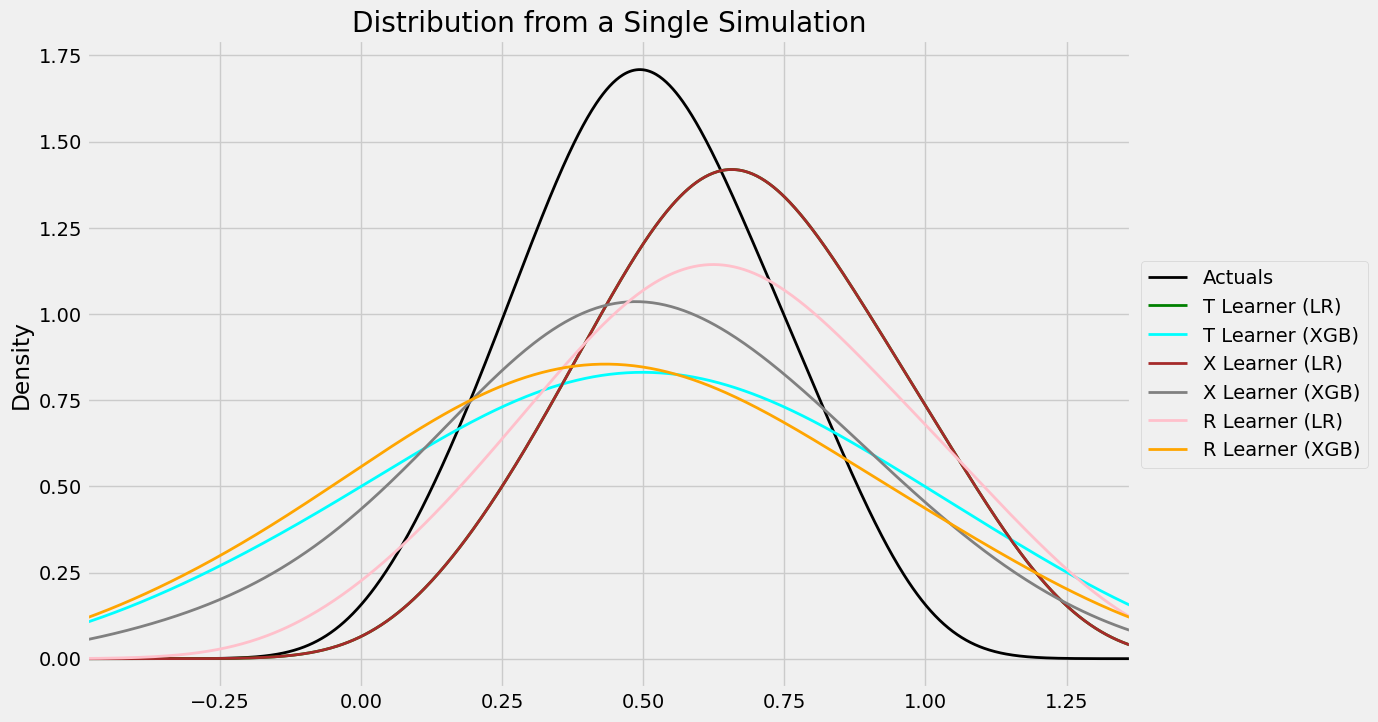
#distribution plot for signle simulation of Validaiton
distr_plot_single_sim(valid_preds, kind='kde', linewidth=2, bw_method=0.5,
drop_learners=['S Learner (LR)', 'S Learner (XGB)'])
[23]:
# Scatter Plots for a Single Simulation of Training Data
scatter_plot_single_sim(train_preds)

[24]:
# Scatter Plots for a Single Simulation of Validaiton Data
scatter_plot_single_sim(valid_preds)
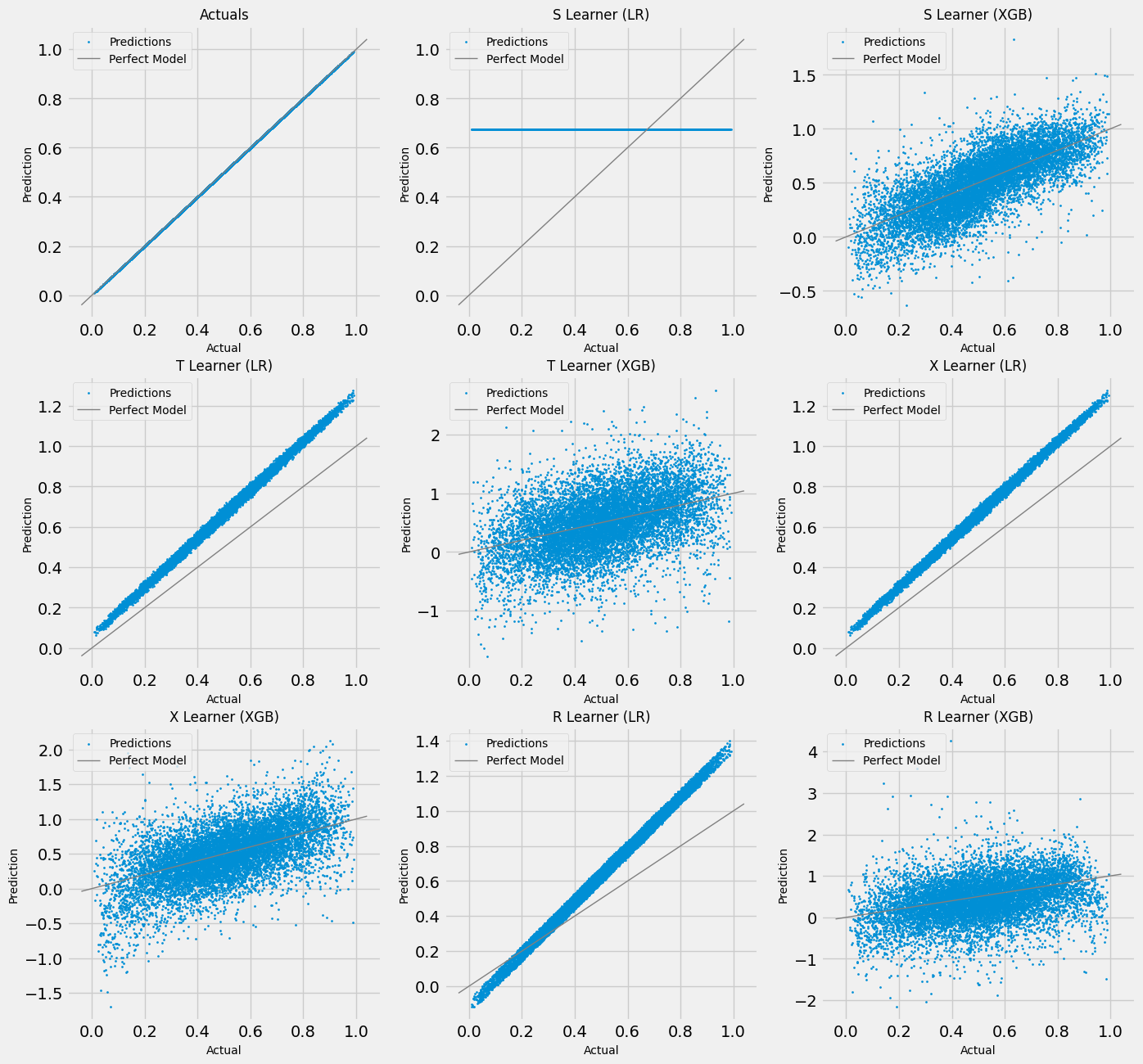
[25]:
# Cumulative Gain AUUC values for a Single Simulation of Training Data
get_synthetic_auuc(train_preds, drop_learners=['S Learner (LR)'])
[25]:
| 学习者 | 累计增益AUUC | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 实际值 | 4.934321e+06 |
| 2 | T 学习器 (LR) | 4.932595e+06 |
| 4 | X 学习器 (LR) | 4.932595e+06 |
| 6 | R 学习器 (LR) | 4.931463e+06 |
| 1 | S Learner (XGB) | 4.707889e+06 |
| 5 | X 学习器 (XGB) | 4.507384e+06 |
| 3 | T 学习器 (XGB) | 4.389641e+06 |
| 7 | R 学习器 (XGB) | 4.309501e+06 |
| 8 | 随机 | 4.002357e+06 |
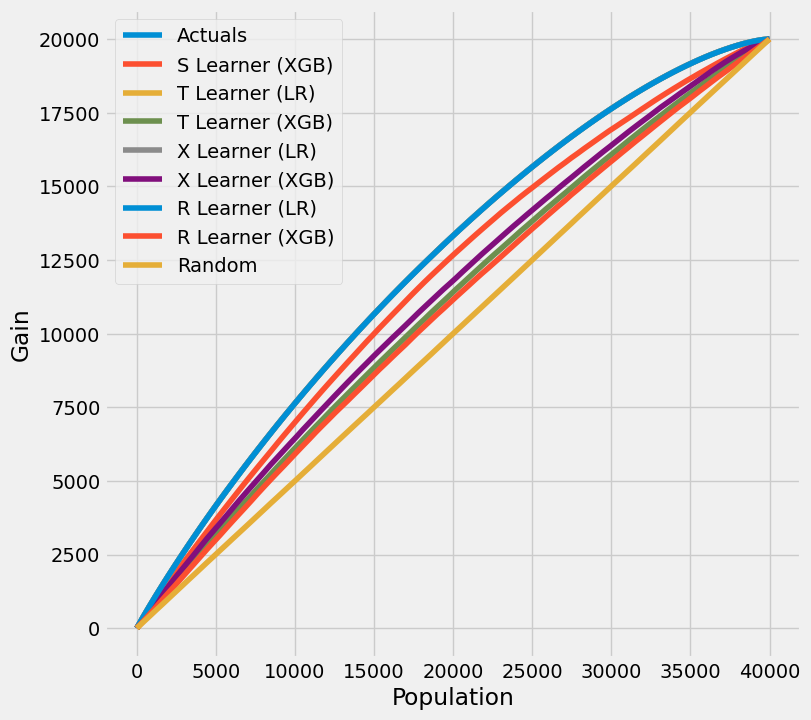
[26]:
# Cumulative Gain AUUC values for a Single Simulation of Validaiton Data
get_synthetic_auuc(valid_preds, drop_learners=['S Learner (LR)'])
[26]:
| 学习者 | 累计增益AUUC | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 实际值 | 308122.561368 |
| 2 | T 学习器 (LR) | 308013.995722 |
| 4 | X 学习器 (LR) | 308013.995722 |
| 6 | R 学习器 (LR) | 307941.890461 |
| 1 | S Learner (XGB) | 294216.363545 |
| 5 | X 学习器 (XGB) | 283752.122952 |
| 3 | T 学习器 (XGB) | 276230.885568 |
| 7 | R 学习器 (XGB) | 271316.357530 |
| 8 | 随机 | 250262.193393 |
