如何为模仿学习/离线训练构建数据管道¶
概述¶
一般来说,模仿学习或离线训练的数据管道主要包含三个步骤:
训练一个专家策略。
生成数据。在这一步中,使用之前的专家来生成演示数据。
模仿学习 / 离线训练。最后,给定生成的专家数据,我们可以进行相应的模仿学习或离线训练。
为了更好地说明这个流程,我们举两个例子:行为克隆(BC)和通过观察的逆强化学习从次优演示中推断(TREX)。这两种算法的流程如下所示。
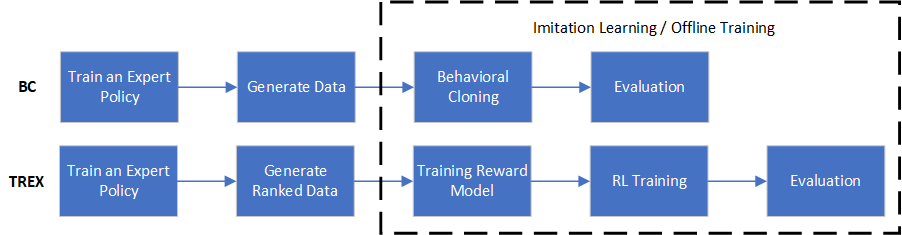
接下来,我们将详细介绍如何实现这两种算法的管道。
训练一个专家策略¶
在这一步中,我们将训练一个专家策略,这与标准的强化学习过程没有区别。例如,要在cartpole上执行PPO,我们可以使用:
from copy import deepcopy from easydict import EasyDict from dizoo.classic_control.cartpole.config.cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_config import cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_config,\ cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_create_config from ding.entry import serial_pipeline_bc, collect_demo_data, serial_pipeline config = [deepcopy(cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_config), deepcopy(cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_create_config)] config[0].policy.learn.learner.hook.save_ckpt_after_iter = 100 expert_policy = serial_pipeline(config, seed=0)
生成数据¶
在这一步中,专家策略将生成演示数据。
对于不同的模仿学习或离线训练算法,示范数据的格式可能不同。如果我们只需要状态-动作对(例如BC),则可以轻松生成示范数据,如下所示:
collect_count = 10000 # number of transitions to collect expert_data_path = 'expert_data_ppo_bc.pkl' # data path to be saved state_dict = expert_policy.collect_mode.state_dict() collect_config = [deepcopy(cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_config), deepcopy(cartpole_ppo_offpolicy_create_config)] collect_config[0].exp_name = 'test_serial_pipeline_bc_ppo_collect' collect_demo_data( collect_config, seed=0, state_dict=state_dict, expert_data_path=expert_data_path, collect_count=collect_count )
因为收集配置与专家配置几乎相同,我们直接修改原始配置。
然而,对于TREX,数据生成过程更为复杂,如下所示:
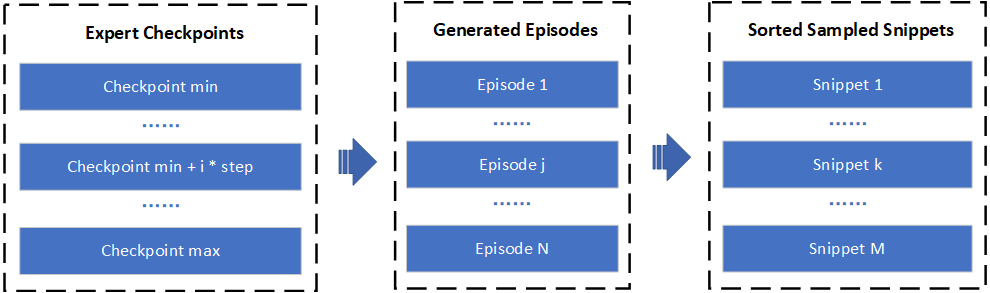
首先,我们加载不同的专家模型以生成各种示范片段。然后,这些片段将被采样成具有较短序列长度的片段,并根据它们的总回报进行排序。
在我们的实现中,上述过程包含在一个函数中。收集TREX数据的方法是:
from ding.entry.application_entry_trex_collect_data import trex_collecting_data from dizoo.classic_control.cartpole.config.cartpole_trex_offppo_config import cartpole_trex_offppo_config,\ cartpole_trex_offppo_create_config exp_name = 'test_serial_pipeline_trex_collect' collect_config = [deepcopy(cartpole_trex_offppo_config), deepcopy(cartpole_trex_offppo_create_config)] collect_config[0].exp_name = exp_name collect_config[0].reward_model.data_path = exp_name collect_config[0].reward_model.reward_model_path = exp_name + '/cartpole.params' # path for saving TREX reward model collect_config[0].reward_model.expert_model_path = config[0].exp_name args = EasyDict({'cfg': deepcopy(collect_config), 'seed': 0, 'device': 'cpu'}) trex_collecting_data(args=args)
模仿学习 / 离线训练¶
最后在这一步中,我们将使用生成的演示数据进行模仿学习/离线训练。对于BC,我们可以使用:
from dizoo.classic_control.cartpole.config.cartpole_bc_config import cartpole_bc_config,\ cartpole_bc_create_config il_config = [deepcopy(cartpole_bc_config), deepcopy(cartpole_bc_create_config)] _, converge_stop_flag = serial_pipeline_bc(il_config, seed=0, data_path=expert_data_path) assert converge_stop_flag
对于TREX,我们可以使用:
from ding.entry import serial_pipeline_preference_based_irl serial_pipeline_preference_based_irl(collect_config, seed=0, max_train_iter=1)
值得注意的是,我们将所有特定于算法的代码集成到每个serial_pipeline中。
对于BC,这个过程包括克隆专家行为和对结果进行评估。对于TREX,训练一个奖励模型来预测观察的奖励。然后应用RL算法以最大化预测的奖励,并最终进行评估。这个过程的关键是用预测的奖励替换真实的奖励:
def estimate(self, data: list) -> List[Dict]: """ Overview: Estimate reward by rewriting the reward key in each row of the data. Arguments: - data (:obj:`list`): the list of data used for estimation, with at least \ ``obs`` and ``action`` keys. Effects: - This is a side effect function which updates the reward values in place. """ train_data_augmented = self.reward_deepcopy(data) res = collect_states(train_data_augmented) res = torch.stack(res).to(self.device) with torch.no_grad(): sum_rewards, sum_abs_rewards = self.reward_model.cum_return(res, mode='batch') for item, rew in zip(train_data_augmented, sum_rewards): item['reward'] = rew return train_data_augmented