! [ -e /content ] && pip install -Uqq fastai # 在Colab上升级fastai视觉增强
::: {#cell-2 .cell 0=‘d’ 1=‘e’ 2=‘f’ 3=‘a’ 4=‘u’ 5=‘l’ 6=‘t’ 7=’_’ 8=‘e’ 9=‘x’ 10=‘p’ 11=’ ’ 12=‘v’ 13=‘i’ 14=‘s’ 15=‘i’ 16=‘o’ 17=‘n’ 18=‘.’ 19=‘a’ 20=‘u’ 21=‘g’ 22=‘m’ 23=‘e’ 24=‘n’ 25=‘t’}
### 默认类级别 3:::
在计算机视觉中应用数据增强的变换
from __future__ import annotations
from fastai.data.all import *
from fastai.vision.core import *
from fastai.vision.data import *在当今快节奏的世界中,时间管理已成为一项至关重要的技能。无论是在职场还是个人生活中,有效地管理时间都能显著提升生产力和生活质量。首先,制定明确的目标是时间管理的基础。这些目标应具体、可衡量、可实现、相关且有时限,即SMART原则。其次,优先级排序是关键。使用艾森豪威尔矩阵等工具,将任务分为重要且紧急、重要但不紧急、紧急但不重要以及既不紧急也不重要四类,有助于集中精力处理真正重要的事务。此外,避免拖延也是时间管理的重要一环。通过设定小目标、分解任务以及使用番茄工作法等技巧,可以有效克服拖延症。最后,定期回顾和调整时间管理策略,确保其适应不断变化的需求和环境,是持续提升时间管理能力的关键。
from nbdev.showdoc import *from torch import stack, zeros_like as t0, ones_like as t1
from torch.distributions.bernoulli import Bernoulliimg = PILImage(PILImage.create(TEST_IMAGE).resize((600,400)))RandTransform-
class RandTransform(DisplayedTransform):
"A transform that before_call its state at each `__call__`"
do,nm,supports,split_idx = True,None,[],0
def __init__(self,
p:float=1., # 应用变换的概率
nm:str=None,
before_call:callable=None, # 可选的批处理预处理函数
**kwargs
):
store_attr('p')
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.before_call = ifnone(before_call,self.before_call)
def before_call(self,
b,
split_idx:int, # 列车/验证数据集索引
):
"This function can be overridden. Set `self.do` based on `self.p`"
self.do = self.p==1. or random.random() < self.p
def __call__(self,
b,
split_idx:int=None, # 列车/验证数据集索引
**kwargs
):
self.before_call(b, split_idx=split_idx)
return super().__call__(b, split_idx=split_idx, **kwargs) if self.do else b对于所有的 Transform,您可以在初始化时传递 encodes 和 decodes,或者通过子类化并实现它们。您可以对每次 __call__ 调用时被调用的 before_call 方法做同样的操作。请注意,为了确保输入和目标的一致状态,RandTransform 必须在元组级别应用。
默认情况下,before_call 的行为是以概率 p 执行变换(如果是子类化并想要调节该行为,则会检查属性 self.do,如果存在的话,用于决定是否执行变换)。
默认情况下,RandTransform 仅应用于训练集,因此如果您直接调用它而不是通过 Datasets,则必须传递 split_idx=0。通过将变换的属性 split_idx 设置为 None,可以更改这种行为。
RandTransform.before_call<function __main__.RandTransform.before_call(self, b, split_idx: 'int')>show_doc(RandTransform.before_call)RandTransform.before_call
RandTransform.before_call (b, split_idx:int)
This function can be overridden. Set self.do based on self.p
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| b | ||
| split_idx | int | Index of the train/valid dataset |
def _add1(x): return x+1
dumb_tfm = RandTransform(enc=_add1, p=0.5)
start,d1,d2 = 2,False,False
for _ in range(40):
t = dumb_tfm(start, split_idx=0)
if dumb_tfm.do: test_eq(t, start+1); d1=True
else: test_eq(t, start) ; d2=True
assert d1 and d2
dumb_tfm_add1 -- {'p': 0.5}:
encodes: (object,object) -> _add1decodes: 项目转换
def _neg_axis(x, axis):
x[...,axis] = -x[...,axis]
return x
TensorTypes = (TensorImage,TensorMask,TensorPoint,TensorBBox)@patch
def flip_lr(x:Image.Image): return x.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
@patch
def flip_lr(x:TensorImageBase): return x.flip(-1)
@patch
def flip_lr(x:TensorPoint): return TensorPoint(_neg_axis(x.clone(), 0))
@patch
def flip_lr(x:TensorBBox): return TensorBBox(TensorPoint(x.view(-1,2)).flip_lr().view(-1,4))_,axs = subplots(1,2)
show_image(img, ctx=axs[0], title='original')
show_image(img.flip_lr(), ctx=axs[1], title='flipped');/var/folders/fk/s29n0g1x4qnbp5h0xvh8dsnm0000gn/T/ipykernel_5338/3686934465.py:3: DeprecationWarning: FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Transpose.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT instead.
def flip_lr(x:Image.Image): return x.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
def _pnt2tensor(pnts, sz):
t = torch.zeros(*sz)
for p in pnts: t[p[1],p[0]] = 1.
return t
t = _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [2,1]], (3,3))
x = PILImage.create(t)
y = x.flip_lr()
test_eq(tensor(array(y)), _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [0,1]], (3,3)))
pnts = TensorPoint(tensor([[1.,0], [2,1]]) -1)
test_eq(pnts.flip_lr(), tensor([[1.,0], [0,1]]) -1)
bbox = TensorBBox((tensor([[1.,0., 2.,1]]) -1))
test_eq(bbox.flip_lr(), tensor([[1.,0., 0.,1]]) -1)/var/folders/fk/s29n0g1x4qnbp5h0xvh8dsnm0000gn/T/ipykernel_5338/3686934465.py:3: DeprecationWarning: FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Transpose.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT instead.
def flip_lr(x:Image.Image): return x.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)class FlipItem(RandTransform):
"Randomly flip with probability `p`"
def __init__(self, p:float=0.5): super().__init__(p=p)
def encodes(self, x:(Image.Image,*TensorTypes)): return x.flip_lr()调用 @patch 修饰的 flip_lr 行为用于 Image、TensorImage、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
tflip = FlipItem(p=1.)
test_eq(tflip(bbox,split_idx=0), tensor([[1.,0., 0.,1]]) -1)@patch
def dihedral(x:PILImage,
k:int, # 应用二面角变换
):
return x if k==0 else x.transpose(k-1)
@patch
def dihedral(x:TensorImage,
k:int, # 应用二面角变换
):
if k in [1,3,4,7]: x = x.flip(-1)
if k in [2,4,5,7]: x = x.flip(-2)
if k in [3,5,6,7]: x = x.transpose(-1,-2)
return x
@patch
def dihedral(x:TensorPoint,
k:int, # 应用二面角变换
):
if k in [1,3,4,7]: x = _neg_axis(x, 0)
if k in [2,4,5,7]: x = _neg_axis(x, 1)
if k in [3,5,6,7]: x = x.flip(1)
return x
@patch
def dihedral(x:TensorBBox,
k:int, #应用二面角变换
):
pnts = TensorPoint(x.view(-1,2)).dihedral(k).view(-1,2,2)
tl,br = pnts.min(dim=1)[0],pnts.max(dim=1)[0]
return TensorBBox(torch.cat([tl, br], dim=1), img_size=x.img_size)class DihedralItem(RandTransform):
"Randomly flip with probability `p`"
def before_call(self, b, split_idx):
super().before_call(b, split_idx)
self.k = random.randint(0,7)
def encodes(self, x:(Image.Image,*TensorTypes)): return x.dihedral(self.k)调用 @patch 修饰的 PILImage、TensorImage、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox 的二面体变换行为。
默认情况下,应用变换时这 8 种二面体变换(包括无操作)的被选中概率相同。您可以通过传递自定义的 draw 函数来定制此行为。要强制进行特定的翻转,您也可以传递一个介于 0 和 7 之间的整数。
_,axs = subplots(2, 4)
for ax in axs.flatten():
show_image(DihedralItem(p=1.)(img, split_idx=0), ctx=ax)
t = _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [2,1]], (3,3))
x = PILImage.create(t)
for i in range(8):
y = x.dihedral(i)
res = tensor(array(y))
pnts = TensorPoint(tensor([[1.,0.], [2,1]]) -1)
a,b = pnts.dihedral(i), res.nonzero().flip(1).float()-1
assert equals(a,b) or equals(a,b.flip(0))使用裁剪、填充或拉伸进行调整大小
from torchvision.transforms.functional import pad as tvpadmk_class('PadMode', **{o:o.lower() for o in ['Zeros', 'Border', 'Reflection']},
doc="All possible padding mode as attributes to get tab-completion and typo-proofing")_all_ = ['PadMode']show_doc(PadMode, title_level=3)PadMode
PadMode (*args, **kwargs)
All possible padding mode as attributes to get tab-completion and typo-proofing
_pad_modes = {'zeros': 'constant', 'border': 'edge', 'reflection': 'reflect'}
@patch
def _do_crop_pad(x:Image.Image, sz, tl, orig_sz,
pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros, resize_mode=BILINEAR, resize_to=None):
if any(tl.ge(0)) or any(tl.add(sz).le(orig_sz)):
# 图像中至少有一个暗部,因此需要进行裁剪。
c = tl.max(0)
x = x.crop((*c, *tl.add(sz).min(orig_sz)))
if any(tl.lt(0)) or any(tl.add(sz).ge(orig_sz)):
# 至少有一个维度在图像之外,因此需要进行填充。
p = (-tl).max(0)
f = (sz-orig_sz).add(tl).max(0)
x = tvpad(x, (*p, *f), padding_mode=_pad_modes[pad_mode])
if resize_to is not None: x = x.resize(resize_to, resize_mode)
return x
@patch
def _do_crop_pad(x:TensorPoint, sz, tl, orig_sz, pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros, resize_to=None, **kwargs):
#断言 pad_mode 等于 PadMode.Zeros,"Only zero padding is supported for `TensorPoint` and `TensorBBox`"
orig_sz,sz,tl = map(FloatTensor, (orig_sz,sz,tl))
return TensorPoint((x+1)*orig_sz/sz - tl*2/sz - 1, sz=sz if resize_to is None else resize_to)
@patch
def _do_crop_pad(x:TensorBBox, sz, tl, orig_sz, pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros, resize_to=None, **kwargs):
bbox = TensorPoint._do_crop_pad(x.view(-1,2), sz, tl, orig_sz, pad_mode, resize_to).view(-1,4)
return TensorBBox(bbox, img_size=x.img_size)
@patch
def crop_pad(x:TensorBBox|TensorPoint|Image.Image,
sz:int|tuple, # 输入的裁剪/填充尺寸,如果只指定一个值则重复使用
tl:tuple=None, # 裁剪/填充的可选左上角坐标,如果为 `None`,则进行中心裁剪
orig_sz:tuple=None, # 输入的原始大小
pad_mode:PadMode=PadMode.Zeros, # Fastai填充模式
resize_mode=BILINEAR, # Pillow `Image` 调整大小模式
resize_to:tuple=None # 可选的输入后裁剪/填充调整大小
):
if isinstance(sz,int): sz = (sz,sz)
orig_sz = fastuple(_get_sz(x) if orig_sz is None else orig_sz)
sz,tl = fastuple(sz),fastuple(((_get_sz(x)-sz)//2) if tl is None else tl)
return x._do_crop_pad(sz, tl, orig_sz=orig_sz, pad_mode=pad_mode, resize_mode=resize_mode, resize_to=resize_to)def _process_sz(size):
if isinstance(size,int): size=(size,size)
return fastuple(size[1],size[0])
def _get_sz(x):
if isinstance(x, tuple): x = x[0]
if not isinstance(x, Tensor): return fastuple(x.size)
return fastuple(getattr(x, 'img_size', getattr(x, 'sz', (x.shape[-1], x.shape[-2]))))@delegates()
class CropPad(DisplayedTransform):
"Center crop or pad an image to `size`"
order = 0
def __init__(self,
size:int|tuple, # 裁剪或填充的目标尺寸,若指定一个值则重复使用
pad_mode:PadMode=PadMode.Zeros, # 一个 `PadMode`
**kwargs
):
size = _process_sz(size)
store_attr()
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def encodes(self, x:Image.Image|TensorBBox|TensorPoint):
orig_sz = _get_sz(x)
tl = (orig_sz-self.size)//2
return x.crop_pad(self.size, tl, orig_sz=orig_sz, pad_mode=self.pad_mode)调用 @patch 的 crop_pad 行为适用于 Image、TensorImage、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
for ax,sz in zip(axs.flatten(), [300, 500, 700]):
show_image(img.crop_pad(sz), ctx=ax, title=f'Size {sz}');
print(img.crop_pad(sz).shape)(300, 300)
(500, 500)
(700, 700)
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
for ax,mode in zip(axs.flatten(), [PadMode.Zeros, PadMode.Border, PadMode.Reflection]):
show_image(img.crop_pad((600,700), pad_mode=mode), ctx=ax, title=mode);
ta = torch.empty(16,16).uniform_(0,1)
tb = torch.empty(20,20).uniform_(0,1)
x1 = PILImage.create(ta)
x2 = PILImage.create(tb)
crop = CropPad(10)
y1,y2 = crop((x1,x2))
test_eq(y1.size, (10,10))
test_eq(y2.size, (10,10))
test_eq(tensor(array(y1)), ta[3:13,3:13])
test_eq(tensor(array(y2)), tb[5:15,5:15])t = torch.empty(20,16).uniform_(0,1)
x = PILImage.create(t)
crop = CropPad(10)
y = crop(x)
test_eq(y.size, (10,10))
test_eq(tensor(array(y)), t[5:15,3:13])
pts = TensorPoint(torch.tensor([[-1,-1], [-0.5,-0.5], [0.,0.]]), img_size=(16,20))
y,p1 = crop((x,pts))
test_eq(p1, torch.tensor([[-1.6, -2], [-0.8,-1], [0,0]]))#填充测试
t = torch.empty(10,8).uniform_(0,1)
x = PILImage.create(t)
crop = CropPad(12)
y = crop(x)
test_eq(y.size, (12,12))
test_eq(tensor(array(y))[1:11,2:10], t)
pts = TensorPoint(torch.tensor([[-1,-1], [-0.5,-0.5], [0.,0.]]), img_size=(8,10))
y,p1 = crop((x,pts))
test_close(p1, torch.tensor([[-2/3, -5/6], [-1/3,-5/12], [0,0]]))# 裁剪和填充测试
t = torch.empty(10,10).uniform_(0,1)
x = PILImage.create(t)
y1 = x.crop_pad((5, 5), (-2, 2))
y2 = x.crop_pad((5, 5), (8, 2))
y3 = x.crop_pad((5, 5), (-1, -1))
test_eq(y1.shape, (5, 5))
test_eq(y2.shape, (5, 5))
test_eq(y3.shape, (5, 5))
test_eq(tensor(array(y1))[:, 2:], t[2:7, 0:3])
test_eq(tensor(array(y2))[:, :2], t[2:7, 8:])
test_eq(tensor(array(y3))[1:, 1:], t[:4, :4])随机裁剪 -
@delegates()
class RandomCrop(RandTransform):
"Randomly crop an image to `size`"
split_idx,order = None,1
def __init__(self,
size:int|tuple, # 裁剪尺寸,若指定一个值则重复使用
**kwargs
):
size = _process_sz(size)
store_attr()
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def before_call(self,
b,
split_idx:int # 列车/验证数据集索引
):
"Randomly positioning crop if train dataset else center crop"
self.orig_sz = _get_sz(b)
if split_idx: self.tl = (self.orig_sz-self.size)//2
else:
wd = self.orig_sz[0] - self.size[0]
hd = self.orig_sz[1] - self.size[1]
w_rand = (wd, -1) if wd < 0 else (0, wd)
h_rand = (hd, -1) if hd < 0 else (0, hd)
self.tl = fastuple(random.randint(*w_rand), random.randint(*h_rand))
def encodes(self, x:Image.Image|TensorBBox|TensorPoint):
return x.crop_pad(self.size, self.tl, orig_sz=self.orig_sz)show_doc(RandomCrop)RandomCrop
RandomCrop (size:int|tuple, **kwargs)
Randomly crop an image to size
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| size | int | tuple | Size to crop to, duplicated if one value is specified |
class OldRandomCrop(CropPad):
"Randomly crop an image to `size`"
def before_call(self, b, split_idx):
super().before_call(b, split_idx)
w,h = self.orig_sz
if not split_idx: self.tl = (random.randint(0,w-self.cp_size[0]), random.randint(0,h-self.cp_size[1]))_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
f = RandomCrop(200)
for ax in axs: show_image(f(img), ctx=ax);
在验证集上,我们进行中心裁剪。
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
for ax in axs: show_image(f(img, split_idx=1), ctx=ax);
large_sz = 25
t = torch.empty(20, 16, 3).uniform_(0,255).type(torch.uint8)
x = PILImage.create(t)
crop = RandomCrop(large_sz)
y = crop(x, split_idx=0)
test_eq(y.size, (large_sz,large_sz))
test_eq(tensor(y)[:-crop.tl[1], :-crop.tl[0], :].sum(), 0)
small_sz = 10
crop = RandomCrop(small_sz)
y = crop(x, split_idx=0)
test_eq(y.size, (small_sz,small_sz))
test_eq(tensor(array(y)), t[crop.tl[1]:crop.tl[1]+small_sz,crop.tl[0]:crop.tl[0]+small_sz])
crop.as_item=False
pts = TensorPoint(torch.tensor([[-1,-1], [-0.5,-0.5], [0.,0.]]))
y,p1 = crop((x,pts), split_idx=0)
test_eq(p1, (pts+1) * tensor([1.6,2.]) - tensor(crop.tl).float()/5 - 1)#测试 这是验证集上的中心裁剪
y = crop(x, split_idx=1)
test_eq(y.size, (10,10))
test_eq(tensor(array(y)), t[5:15,3:13])mk_class('ResizeMethod', **{o:o.lower() for o in ['Squish', 'Crop', 'Pad']},
doc="All possible resize method as attributes to get tab-completion and typo-proofing")_all_ = ['ResizeMethod']show_doc(ResizeMethod, title_level=3)ResizeMethod
ResizeMethod (*args, **kwargs)
All possible resize method as attributes to get tab-completion and typo-proofing
test_eq(ResizeMethod.Squish, 'squish')调整大小 -
@delegates()
class Resize(RandTransform):
split_idx,mode,mode_mask,order = None,BILINEAR,NEAREST,1
"Resize image to `size` using `method`"
def __init__(self,
size:int|tuple, # 调整后的尺寸,若指定一个值则重复使用
method:ResizeMethod=ResizeMethod.Crop, # 一个 `ResizeMethod`
pad_mode:PadMode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
resamples=(BILINEAR, NEAREST), # Pillow 的 `Image` 类提供了重采样模式,用于对掩码进行重采样。
**kwargs
):
size = _process_sz(size)
store_attr()
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.mode,self.mode_mask = resamples
def before_call(self,
b,
split_idx:int # 列车/验证数据集索引
):
if self.method==ResizeMethod.Squish: return
self.pcts = (0.5,0.5) if split_idx else (random.random(),random.random())
def encodes(self, x:Image.Image|TensorBBox|TensorPoint):
orig_sz = _get_sz(x)
if self.method==ResizeMethod.Squish:
return x.crop_pad(orig_sz, fastuple(0,0), orig_sz=orig_sz, pad_mode=self.pad_mode,
resize_mode=self.mode_mask if isinstance(x,PILMask) else self.mode, resize_to=self.size)
w,h = orig_sz
op = (operator.lt,operator.gt)[self.method==ResizeMethod.Pad]
m = w/self.size[0] if op(w/self.size[0],h/self.size[1]) else h/self.size[1]
cp_sz = (int(m*self.size[0]),int(m*self.size[1]))
tl = fastuple(int(self.pcts[0]*(w-cp_sz[0])), int(self.pcts[1]*(h-cp_sz[1])))
return x.crop_pad(cp_sz, tl, orig_sz=orig_sz, pad_mode=self.pad_mode,
resize_mode=self.mode_mask if isinstance(x,PILMask) else self.mode, resize_to=self.size)size 可以是一个整数(在这种情况下,图像将被调整为正方形)或者一个元组。根据 method: - 我们将任何矩形挤压到 size - 我们调整大小,使得较短的维度匹配,并使用 pad_mode 进行填充 - 我们调整大小,使得较大的维度匹配并裁剪(在训练集上随机裁剪,在验证集上居中裁剪)
在进行调整大小时,我们对图像使用 resamples[0],对分割掩码使用 resamples[1]。
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
for ax,method in zip(axs.flatten(), [ResizeMethod.Squish, ResizeMethod.Pad, ResizeMethod.Crop]):
rsz = Resize(256, method=method)
show_image(rsz(img, split_idx=0), ctx=ax, title=method);
在验证集上,裁剪总是中心裁剪(在被裁剪的维度上)。
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
for ax,method in zip(axs.flatten(), [ResizeMethod.Squish, ResizeMethod.Pad, ResizeMethod.Crop]):
rsz = Resize(256, method=method)
show_image(rsz(img, split_idx=1), ctx=ax, title=method);
t = torch.empty(20,16).uniform_(0,1)
x = PILImage.create(t)
rsz = Resize(10)
y = rsz(x, split_idx=0)
test_eq(y.size, (10,10))
y = rsz(x, split_idx=1)
test_eq(y.size, (10,10))随机调整大小裁剪 -
@delegates()
class RandomResizedCrop(RandTransform):
"Picks a random scaled crop of an image and resize it to `size`"
split_idx,order = None,1
def __init__(self,
size:int|tuple, # 最终尺寸,若指定一个值则重复。
min_scale:float=0.08, # 作物相对于图像区域的最小比例
ratio=(3/4, 4/3), # 输出宽高比范围
resamples=(BILINEAR, NEAREST), # Pillow `Image` 重采样模式,用于掩码的重采样[1]
val_xtra:float=0.14, # 验证集中边缘裁剪尺寸的比例
max_scale:float=1., # 裁剪的最大比例,相对于图像区域
**kwargs
):
size = _process_sz(size)
store_attr()
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.mode,self.mode_mask = resamples
def before_call(self,
b,
split_idx # 列车/验证数据集索引
):
w,h = self.orig_sz = _get_sz(b)
if split_idx:
xtra = math.ceil(max(*self.size[:2])*self.val_xtra/8)*8
self.final_size = (self.size[0]+xtra, self.size[1]+xtra)
self.tl,self.cp_size = (0,0),self.orig_sz
return
self.final_size = self.size
for attempt in range(10):
area = random.uniform(self.min_scale, self.max_scale) * w * h
ratio = math.exp(random.uniform(math.log(self.ratio[0]), math.log(self.ratio[1])))
nw = int(round(math.sqrt(area * ratio)))
nh = int(round(math.sqrt(area / ratio)))
if nw <= w and nh <= h:
self.cp_size = (nw,nh)
self.tl = random.randint(0,w-nw), random.randint(0,h - nh)
return
if w/h < self.ratio[0]: self.cp_size = (w, int(w/self.ratio[0]))
elif w/h > self.ratio[1]: self.cp_size = (int(h*self.ratio[1]), h)
else: self.cp_size = (w, h)
self.tl = ((w-self.cp_size[0])//2, (h-self.cp_size[1])//2)
def encodes(self, x:Image.Image|TensorBBox|TensorPoint):
res = x.crop_pad(self.cp_size, self.tl, orig_sz=self.orig_sz,
resize_mode=self.mode_mask if isinstance(x,PILMask) else self.mode, resize_to=self.final_size)
if self.final_size != self.size: res = res.crop_pad(self.size) #验证集:最终的中心裁剪
return res作物随机选择一个范围为 (min_scale,max_scale) 的缩放比例和一个范围内的比例,然后使用 resamples[0] 对图像进行调整大小,使用 resamples[1] 对分割掩码进行调整大小。在验证集上,如果图像的比例不在范围内(达到最小值或最大值),则进行中心裁剪,然后调整大小。
crop = RandomResizedCrop(256)
_,axs = plt.subplots(3,3,figsize=(9,9))
for ax in axs.flatten():
cropped = crop(img)
show_image(cropped, ctx=ax);
test_eq(cropped.shape, [256,256])Squish用于验证集,首先去除每一侧的val_xtra比例。
_,axs = subplots(1,3)
for ax in axs.flatten(): show_image(crop(img, split_idx=1), ctx=ax);
通过将max_scale设置为较低的值,可以强制执行小裁剪。
small_crop = RandomResizedCrop(256, min_scale=0.05, max_scale=0.15)
_,axs = plt.subplots(3,3,figsize=(9,9))
for ax in axs.flatten():
cropped = small_crop(img)
show_image(cropped, ctx=ax);
test_eq(cropped.shape, [256,256])RatioResize -
class RatioResize(DisplayedTransform):
'Resizes the biggest dimension of an image to `max_sz` maintaining the aspect ratio'
order = 1
def __init__(self,
max_sz: int, # 调整大小后的图像的最大尺寸
resamples=(BILINEAR, NEAREST), # Pillow `Image` 重采样模式,用于掩码的重采样[1]
**kwargs
):
store_attr()
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def encodes(self, x:Image.Image|TensorBBox|TensorPoint):
w,h = _get_sz(x)
if w >= h: nw,nh = self.max_sz,h*self.max_sz/w
else: nw,nh = w*self.max_sz/h,self.max_sz
return Resize(size=(int(nh),int(nw)), resamples=self.resamples)(x)RatioResize(256)(img)
test_eq(RatioResize(256)(img).size[0], 256)
test_eq(RatioResize(256)(img.dihedral(3)).size[1], 256)GPU上的仿射变换和坐标变换
timg = TensorImage(array(img)).permute(2,0,1).float()/255.
def _batch_ex(bs): return TensorImage(timg[None].expand(bs, *timg.shape).clone())def _init_mat(x):
mat = torch.eye(3, device=x.device).float()
return mat.unsqueeze(0).expand(x.size(0), 3, 3).contiguous()仿射坐标变换 -
使用 coords 中的坐标将 x 中的坐标映射到新的位置,以进行如 flip 等变换。最好使用 TensorImage.affine_coord,因为这将 _grid_sample 和 F.affine_grid 组合在一起,便于使用。使用 F.affine_grid 更容易生成 coords,因为这通常是一个大的 [H,W,2],其中 H 和 W 是图像 x 的高度和宽度。
def _grid_sample(x, coords, mode='bilinear', padding_mode='reflection', align_corners=None):
"Resample pixels in `coords` from `x` by `mode`, with `padding_mode` in ('reflection','border','zeros')."
# #coords = coords.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous().permute(0, 2, 3, 1) 优化布局以适应grid_sample
if mode=='bilinear': # 获取更平滑向下采样的技巧
mn,mx = coords.min(),coords.max()
# max amount we're affine zooming by (>1 means zooming in)
z = 1/(mx-mn).item()*2
# amount we're resizing by, with 100% extra margin
d = min(x.shape[-2]/coords.shape[-2], x.shape[-1]/coords.shape[-1])/2
# If we're resizing up by >200%, and we're zooming less than that, interpolate first
if d>1 and d>z:
x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=1/d, mode='area', recompute_scale_factor=True)
return F.grid_sample(x, coords, mode=mode, padding_mode=padding_mode, align_corners=align_corners)这是我们开始使用的图像,并将用于以下示例。
img=torch.tensor([[[0,0,0],[1,0,0],[2,0,0]],
[[0,1,0],[1,1,0],[2,1,0]],
[[0,2,0],[1,2,0],[2,2,0]]]).permute(2,0,1)[None]/2.
show_images(img)
在这里我们使用 _grid_sample,但不改变原始图像。注意 grid 中的坐标是如何映射到 img 中的坐标的。
grid=torch.tensor([[[[-1,-1],[0,-1],[1,-1]],
[[-1,0],[0,0],[1,0]],
[[-1,1],[0,1],[1,1.]]]])
img=_grid_sample(img, grid,align_corners=True)
show_images(img)
接下来,我们通过手动编辑网格来进行翻转。
grid=torch.tensor([[[1.,-1],[0,-1],[-1,-1]],
[[1,0],[0,0],[-1,0]],
[[1,1],[0,1],[-1,1]]])
img=_grid_sample(img, grid[None],align_corners=True)
show_images(img)
接下来,我们将图像向上移动一个位置。默认情况下,_grid_sample 使用反射填充。
grid=torch.tensor([[[[-1,0],[0,0],[1,0]],
[[-1,1],[0,1],[1,1]],
[[-1,2],[0,2],[1,2.]]]])
img=_grid_sample(img, grid,align_corners=True)
show_images(img)
affine_coord 使我们能够更轻松地处理图像,因为它允许我们指定远比网格更小的 mat,而网格则要求我们为每个像素指定值。
def affine_grid(
theta:Tensor, # 一批仿射变换矩阵
size:tuple, # 输出尺寸
align_corners:bool=None # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
):
" Generates `TensorFlowField` from a transformation affine matrices `theta`"
return TensorFlowField(F.affine_grid(theta, size, align_corners=align_corners))@patch
def affine_coord(x: TensorImage,
mat:Tensor=None, # 一批仿射变换矩阵
coord_tfm:callable=None, # 可组合坐标变换的部分功能
sz:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `TensorImage`
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 应用于 `TensorImage` 的填充
align_corners=True # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
):
"Apply affine and coordinate transforms to `TensorImage`"
if mat is None and coord_tfm is None and sz is None: return x
size = tuple(x.shape[-2:]) if sz is None else (sz,sz) if isinstance(sz,int) else tuple(sz)
if mat is None: mat = _init_mat(x)[:,:2]
coords = affine_grid(mat, x.shape[:2] + size, align_corners=align_corners)
if coord_tfm is not None: coords = coord_tfm(coords)
return TensorImage(_grid_sample(x, coords, mode=mode, padding_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners))
@patch
def affine_coord(x: TensorMask,
mat:Tensor=None, # 一批仿射变换矩阵
coord_tfm:callable=None, # 可组合坐标变换的部分功能
sz:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode='nearest', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `TensorMask`
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 应用于 `TensorMask` 的填充
align_corners=True # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
):
"Apply affine and coordinate transforms to `TensorMask`"
add_dim = (x.ndim==3)
if add_dim: x = x[:,None]
res = TensorImage.affine_coord(x.float(), mat, coord_tfm, sz, mode, pad_mode, align_corners).long()
if add_dim: res = res[:,0]
return TensorMask(res)
@patch
def affine_coord(x: TensorPoint,
mat:Tensor=None, # 一批仿射变换矩阵
coord_tfm=None, # 可组合坐标变换的部分功能
sz=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode='nearest', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `TensorPoint`
pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros, # 应用于 `TensorPoint` 的填充
align_corners=True # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
):
"Apply affine and coordinate transforms to `TensorPoint`"
#断言 pad_mode 等于 PadMode.Zeros, "Only zero padding is supported for `TensorPoint` and `TensorBBox`"
if sz is None: sz = getattr(x, "img_size", None)
if coord_tfm is not None: x = coord_tfm(x, invert=True)
if mat is not None:
mat = TensorPoint(mat)
x = (x - mat[:,:,2].unsqueeze(1)) @ torch.inverse(mat[:,:,:2].transpose(1,2))
return TensorPoint(x, sz=sz)
@patch
def affine_coord(x: TensorBBox,
mat=None, # 一批仿射变换矩阵
coord_tfm=None, # 可组合坐标变换的部分功能
sz=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode='nearest', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `TensorBBox`
pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros, # 应用于 `TensorBBox` 的填充
align_corners=True # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
):
"Apply affine and coordinate transforms to `TensorBBox`"
if mat is None and coord_tfm is None: return x
if sz is None: sz = getattr(x, "img_size", None)
bs,n = x.shape[:2]
pnts = stack([x[...,:2], stack([x[...,0],x[...,3]],dim=2),
stack([x[...,2],x[...,1]],dim=2), x[...,2:]], dim=2)
pnts = TensorPoint(pnts.view(bs, 4*n, 2), img_size=sz).affine_coord(mat, coord_tfm, sz, mode, pad_mode)
pnts = pnts.view(bs, n, 4, 2)
tl,dr = pnts.min(dim=2)[0],pnts.max(dim=2)[0]
return TensorBBox(torch.cat([tl, dr], dim=2), img_size=sz)def _prepare_mat(x, mat):
h,w = getattr(x, 'img_size', x.shape[-2:])
mat[:,0,1] *= h/w
mat[:,1,0] *= w/h
return mat[:,:2]class AffineCoordTfm(RandTransform):
"Combine and apply affine and coord transforms"
order,split_idx = 30,None
def __init__(self,
aff_fs:callable|MutableSequence=None, # 仿射变换作用于一批数据
coord_fs:callable|MutableSequence=None, # 批量坐标变换功能
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果只指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
mode_mask='nearest', # 遮罩重采样模式
align_corners=None, # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
**kwargs
):
store_attr(but=['aff_fs','coord_fs'])
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.aff_fs,self.coord_fs = L(aff_fs),L(coord_fs)
self.cp_size = None if size is None else (size,size) if isinstance(size, int) else tuple(size)
def before_call(self,
b,
split_idx, # 列车/验证数据集索引
):
while isinstance(b, tuple): b = b[0]
self.split_idx = split_idx
self.do,self.mat = True,self._get_affine_mat(b)
for t in self.coord_fs: t.before_call(b)
def compose(self, tfm):
"Compose `self` with another `AffineCoordTfm` to only do the interpolation step once"
# 待办事项:保持 `name` 与组合同步更新
# 待办:添加选项以仅显示属性的子集,例如,对于 `Flip`
self.aff_fs += tfm.aff_fs
self.coord_fs += tfm.coord_fs
def _get_affine_mat(self, x):
aff_m = _init_mat(x)
if self.split_idx: return _prepare_mat(x, aff_m)
ms = [f(x) for f in self.aff_fs]
ms = [m for m in ms if m is not None]
for m in ms: aff_m = aff_m @ m
return _prepare_mat(x, aff_m)
def _encode(self, x, mode, reverse=False):
coord_func = None if len(self.coord_fs)==0 or self.split_idx else partial(compose_tfms, tfms=self.coord_fs, reverse=reverse)
return x.affine_coord(self.mat, coord_func, sz=self.size, mode=mode, pad_mode=self.pad_mode, align_corners=self.align_corners)
def encodes(self, x:TensorImage): return self._encode(x, self.mode)
def encodes(self, x:TensorMask): return self._encode(x, self.mode_mask)
def encodes(self, x:TensorPoint|TensorBBox): return self._encode(x, self.mode, reverse=True)调用 @patch 的 affine_coord 行为用于 TensorImage、TensorMask、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
在对与 size 相对应的基本网格上执行相应的仿射变换之前,先将 aff_fs 返回的所有矩阵相乘,然后在得到的坐标流上应用所有 coord_fs,最后使用 mode 和 pad_mode 进行插值。
下面是如何在图像上使用 affine_coord 的示例。包括身份变换或原始图像、翻转,以及将图像向左移动。
imgs=_batch_ex(3)
identity=torch.tensor([[1,0,0],[0,1,0.]])
flip=torch.tensor([[-1,0,0],[0,1,0.]])
translation=torch.tensor([[1,0,1.],[0,1,0]])
mats=torch.stack((identity,flip,translation))
show_images(imgs.affine_coord(mats,pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros)) #最容易观察到的零点
现在你可能会问:“这个 mat 是什么?”让我们快速看一下下面的标识。
imgs=_batch_ex(1)
identity=torch.tensor([[1,0,0],[0,1,0.]])
eye=identity[:,0:2]
bi=identity[:,2:3]
eye,bi(tensor([[1., 0.],
[0., 1.]]),
tensor([[0.],
[0.]]))注意张量’eye’是一个单位矩阵。如果我们将其与原始图像中的单个坐标x,y相乘,我们将简单地得到相同的x和y值。在这次乘法后添加bi。例如,让我们将图像翻转,使得左上角位于右上角:
t=torch.tensor([[-1,0,0],[0,1,0.]])
eye=t[:,0:2]
bi=t[:,2:3]
xy=torch.tensor([-1.,-1]) #左上角
torch.sum(xy*eye,dim=1)+bi[0] #现在右上角tensor([ 1., -1.])show_doc(AffineCoordTfm.compose)AffineCoordTfm.compose
AffineCoordTfm.compose (tfm)
Compose self with another AffineCoordTfm to only do the interpolation step once
#测试训练集和验证集上的调整大小操作是否完成
tfm = AffineCoordTfm(size=10)
t = TensorImage(torch.empty(2, 3, 20,16).uniform_(0,1))
for i in [0,1]:
y = tfm(t, split_idx=i)
test_eq(y.shape, [2, 3, 10, 10])随机调整大小裁剪GPU -
class RandomResizedCropGPU(RandTransform):
"Picks a random scaled crop of an image and resize it to `size`"
split_idx,order = None,30
def __init__(self,
size, # 如果指定了一个值,则最终尺寸将重复。
min_scale=0.08, # 作物相对于图像区域的最小比例
ratio=(3/4, 4/3), # 输出宽高比范围
mode='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
valid_scale=1., # 验证集作物相对于图像区域的缩放比例
max_scale=1., # 裁剪的最大比例,相对于图像区域
mode_mask='nearest', # `TensorMask` 的插值模式
**kwargs
):
if isinstance(size, int): size = (size,size)
store_attr()
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def before_call(self, b, split_idx):
self.do = True
h,w = fastuple((b[0] if isinstance(b, tuple) else b).shape[-2:])
for attempt in range(10):
if split_idx: break
area = random.uniform(self.min_scale,self.max_scale) * w * h
ratio = math.exp(random.uniform(math.log(self.ratio[0]), math.log(self.ratio[1])))
nw = int(round(math.sqrt(area * ratio)))
nh = int(round(math.sqrt(area / ratio)))
if nw <= w and nh <= h:
self.cp_size = (nh,nw)
self.tl = random.randint(0,h - nh),random.randint(0,w-nw)
return
if w/h < self.ratio[0]: self.cp_size = (int(w/self.ratio[0]), w)
elif w/h > self.ratio[1]: self.cp_size = (h, int(h*self.ratio[1]))
else: self.cp_size = (h, w)
if split_idx: self.cp_size = (int(self.cp_size[0]*self.valid_scale), int(self.cp_size[1]*self.valid_scale))
self.tl = ((h-self.cp_size[0])//2,(w-self.cp_size[1])//2)
def _encode(self, x, mode):
x = x[...,self.tl[0]:self.tl[0]+self.cp_size[0], self.tl[1]:self.tl[1]+self.cp_size[1]]
return x.affine_coord(sz=self.size, mode=mode)
def encodes(self, x:TensorImage|TensorPoint|TensorBBox): return self._encode(x, self.mode)
def encodes(self, x:TensorMask): return self._encode(x, self.mode_mask)t = _batch_ex(8)
rrc = RandomResizedCropGPU(224, p=1.)
y = rrc(t)
_,axs = plt.subplots(2,4, figsize=(12,6))
for ax in axs.flatten():
show_image(y[i], ctx=ax)
t = _batch_ex(2)
rrc = RandomResizedCropGPU(224, p=1., min_scale=0.05, max_scale=0.1)
y = rrc(t)
_,axs = plt.subplots(2,4, figsize=(12,6))
for ax in axs.flatten():
show_image(y[i], ctx=ax)
RandomResizedCropGPU 在批处理中的所有图像使用相同的区域。
GPU 辅助工具
本节包含用于在GPU上处理增强的辅助工具,这些工具在整个代码中使用。
def mask_tensor(
x:Tensor, # 输入 `Tensor`
p=0.5, # 不戴口罩的概率
neutral=0., # 掩码值
batch=False # 在整个批次上应用相同的掩码
):
"Mask elements of `x` with `neutral` with probability `1-p`"
if p==1.: return x
if batch: return x if random.random() < p else x.new_zeros(*x.size()) + neutral
if neutral != 0: x.add_(-neutral)
# 额外投射以浮点数和长整型防止在mps加速器上崩溃(问题 #3911)
mask = x.new_empty(*x.size()).float().bernoulli_(p).long()
x.mul_(mask)
return x.add_(neutral) if neutral != 0 else x让我们来看看mask_tensor可能如何使用的一些示例,我们使用clone()是因为这个操作会覆盖输入。对于这个示例,我们尝试使用度数来旋转图像。
with no_random():
x=torch.tensor([60,-30,90,-210,270,-180,120,-240,150])
print('p=0.5: ',mask_tensor(x.clone()))
print('p=1.0: ',mask_tensor(x.clone(),p=1.))
print('p=0.0: ',mask_tensor(x.clone(),p=0.))p=0.5: tensor([ 60, -30, 90, -210, 0, -180, 0, 0, 150])
p=1.0: tensor([ 60, -30, 90, -210, 270, -180, 120, -240, 150])
p=0.0: tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])注意到 p 控制一个值被替换为 0 的可能性,或者保持不变,因为 0 度旋转就只是原始图像。batch 作用于整个批次,而不是批次中的单个元素。现在让我们考虑一个不同的例子,即处理亮度。注意:亮度为 0 时是完全黑色的图像。
x=torch.tensor([0.6,0.4,0.3,0.7,0.4])
print('p=0.: ',mask_tensor(x.clone(),p=0))
print('p=0.,neutral=0.5: ',mask_tensor(x.clone(),p=0,neutral=0.5))p=0.: tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
p=0.,neutral=0.5: tensor([0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000])在这里,如果我们有一幅完全黑色的图像,那将是非常糟糕的,因为这不是一幅未改变的图像。相反,我们将 neutral 设置为 0.5,这个值是未改变图像的亮度值。
_draw_mask用于支持许多后续变换的API,以创建mask_tensor。(p, neutral, batch)将传递给mask_tensor。def_draw是默认的绘制函数,当未提供自定义用户设置时将执行此函数。draw是用户定义的行为,可以是一个函数、浮点数列表或单个浮点数。draw和def_draw必须返回一个张量。
def _draw_mask(x, def_draw, draw=None, p=0.5, neutral=0., batch=False):
"Creates mask_tensor based on `x` with `neutral` with probability `1-p`. "
if draw is None: draw=def_draw
if callable(draw): res=draw(x)
elif is_listy(draw):
assert len(draw)>=x.size(0)
res = tensor(draw[:x.size(0)], dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
else: res = x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + draw
return TensorBase(mask_tensor(res, p=p, neutral=neutral, batch=batch))在这里,我们使用从1到8的随机整数作为我们的def_draw,这个例子与Dihedral非常相似。
x = torch.zeros(10,2,3)
def def_draw(x):
x=torch.randint(1,8, (x.size(0),))
return x
with no_random(): print(torch.randint(1,8, (x.size(0),)))
with no_random(): print(_draw_mask(x, def_draw))tensor([2, 3, 5, 6, 5, 4, 6, 6, 1, 1])
TensorBase([2, 0, 0, 6, 5, 4, 6, 0, 0, 1])接下来,有三种方式来定义 draw,作为常量、作为列表,以及作为函数。所有这些都覆盖了 def_draw,因此它对最终结果没有影响。
with no_random():
print('const: ',_draw_mask(x, def_draw, draw=1))
print('list : ', _draw_mask(x, def_draw, draw=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]))
print('list : ',_draw_mask(x[0:2], def_draw, draw=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]))
print('funct: ',_draw_mask(x, def_draw, draw=lambda x: torch.arange(1,x.size(0)+1)))
try:
_draw_mask(x, def_draw, draw=[1,2])
except AssertionError as e:
print(type(e),'\n',e)const: TensorBase([1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 0., 0., 1., 1.])
list : TensorBase([ 1., 2., 0., 0., 5., 0., 7., 0., 0., 10.])
list : TensorBase([1., 0.])
funct: TensorBase([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
<class 'AssertionError'>
注意,当使用列表时,它的大小可以大于批量大小,但不能小于批量大小。否则,将没有足够的增强来处理批次中的元素。
x = torch.zeros(5,2,3)
def_draw = lambda x: torch.randint(0,8, (x.size(0),))
t = _draw_mask(x, def_draw)
assert (0. <= t).all() and (t <= 7).all()
t = _draw_mask(x, def_draw, 1)
assert (0. <= t).all() and (t <= 1).all()
test_eq(_draw_mask(x, def_draw, 1, p=1), tensor([1.,1,1,1,1]))
test_eq(_draw_mask(x, def_draw, [0,1,2,3,4], p=1), tensor([0.,1,2,3,4]))
test_eq(_draw_mask(x[0:3], def_draw, [0,1,2,3,4], p=1), tensor([0.,1,2]))
for i in range(5):
t = _draw_mask(x, def_draw, 1,batch=True)
assert (t==torch.zeros(5)).all() or (t==torch.ones(5)).all()翻转/二面角 GPU 辅助函数
affine_mat 用于将长度为6的向量转换为形状为 [bs,3,3] 的张量。这使我们能够组合仿射变换。
def affine_mat(*ms):
"Restructure length-6 vector `ms` into an affine matrix with 0,0,1 in the last line"
return stack([stack([ms[0], ms[1], ms[2]], dim=1),
stack([ms[3], ms[4], ms[5]], dim=1),
stack([t0(ms[0]), t0(ms[0]), t1(ms[0])], dim=1)], dim=1)这是使用 affine_mat 翻转图像的示例。
flips=torch.tensor([-1,1,-1])
ones=t1(flips)
zeroes=t0(flips)
affines=affine_mat(flips,zeroes,zeroes,zeroes,ones,zeroes)
print(affines)tensor([[[-1, 0, 0],
[ 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1]],
[[ 1, 0, 0],
[ 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1]],
[[-1, 0, 0],
[ 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1]]])这是为了让我们能够合并多个仿射变换,而不必对整个图像进行数学计算。我们需要这些矩阵的尺寸相同,以便能够进行矩阵乘法来合并仿射变换。虽然通常是在整个批处理上进行的,但这是对单个图像进行多个翻转变换的样子。由于我们翻转了两次,因此最终得到的仿射矩阵将简单地返回我们的原始图像。
如果您想了解更多关于此如何工作的内容,请参见 affine_coord。
x = torch.eye(3,dtype=torch.int64)
for affine in affines:
x @= affine
print(x)tensor([[-1, 0, 0],
[ 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1]])
tensor([[-1, 0, 0],
[ 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1]])
tensor([[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]])flip_mat 将生成一个 [bs,3,3] 的张量,表示我们对一个批次的翻转操作,其概率为 p。draw 可以用来定义一个函数、常量或列表,指定使用哪些翻转操作。如果 draw 是一个列表,则长度必须大于或等于批次大小。对于 draw,0 表示原始图像,1 表示翻转后的图像。batch 表示整个批次将被翻转或不翻转。
def flip_mat(
x:Tensor, # 输入张量
p=0.5, # 应用变换的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义翻转而非随机
batch:bool=False # 对整个批次应用相同的翻转
):
"Return a random flip matrix"
def _def_draw(x): return x.new_ones(x.size(0))
mask = x.new_ones(x.size(0)) - 2*_draw_mask(x, _def_draw, draw=draw, p=p, batch=batch)
return affine_mat(mask, t0(mask), t0(mask),
t0(mask), t1(mask), t0(mask))以下是一些如何使用draw作为常量、列表和函数的示例。
with no_random():
x=torch.randn(2,4,3)
print('const: ',flip_mat(x, draw=1))
print('list : ', flip_mat(x, draw=[1, 0]))
print('list : ',flip_mat(x[0:2], draw=[1, 0, 1, 0, 1]))
print('funct: ',flip_mat(x, draw=lambda x: torch.ones(x.size(0))))
test_fail(lambda: flip_mat(x, draw=[1]))const: TensorBase([[[-1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]],
[[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]]])
list : TensorBase([[[-1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]],
[[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]]])
list : TensorBase([[[-1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]],
[[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]]])
funct: TensorBase([[[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]],
[[-1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]]])x = flip_mat(torch.randn(100,4,3))
test_eq(set(x[:,0,0].numpy()), {-1,1}) #可能失败,失败概率为2*2**(-100)(仅选择1或-1)def _get_default(x, mode=None, pad_mode=None):
if mode is None: mode='bilinear' if isinstance(x, TensorMask) else 'bilinear'
if pad_mode is None: pad_mode=PadMode.Zeros if isinstance(x, (TensorPoint, TensorBBox)) else PadMode.Reflection
x0 = x[0] if isinstance(x, tuple) else x
return x0,mode,pad_mode翻转 -
水平翻转图像、掩膜、点和边界框。p 是应用翻转的概率。draw 可用于定义自定义翻转行为。
@patch
def flip_batch(x: TensorImage|TensorMask|TensorPoint|TensorBBox,
p=0.5, # 翻转应用的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义翻转而非随机
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode=None, # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `x`
pad_mode=None, # 应用于 `x` 的填充
align_corners=True, # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
batch=False # 对整个批次应用相同的翻转
):
x0,mode,pad_mode = _get_default(x, mode, pad_mode)
mat=flip_mat(x0, p=p, draw=draw, batch=batch)
return x.affine_coord(mat=mat[:,:2], sz=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)t = _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [2,1]], (3,3))
y = TensorImage(t[None,None]).flip_batch(p=1.)
test_eq(y, _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [0,1]], (3,3))[None,None])
pnts = TensorPoint((tensor([[1.,0.], [2,1]]) -1)[None])
test_eq(pnts.flip_batch(p=1.), tensor([[[1.,0.], [0,1]]]) -1)
bbox = TensorBBox(((tensor([[1.,0., 2.,1]]) -1)[None]))
test_eq(bbox.flip_batch(p=1.), tensor([[[0.,0., 1.,1.]]]) -1)class Flip(AffineCoordTfm):
"Randomly flip a batch of images with a probability `p`"
def __init__(self,
p=0.5, # 翻转应用的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义翻转而非随机
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
align_corners=True, # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
batch=False # 对整个批次应用相同的翻转
):
aff_fs = partial(flip_mat, p=p, draw=draw, batch=batch)
super().__init__(aff_fs, size=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners, p=p)调用 @patch 的 flip_batch 行为用于 TensorImage、TensorMask、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
以下是使用 flip 的一些示例。请注意,常量 draw=1 实际上与默认设置相同。同时请注意,通过将 p=1. 并定义自定义 draw,我们可以在第三个示例中获得更细致的控制。
with no_random(32):
imgs = _batch_ex(5)
deflt = Flip()
const = Flip(p=1.,draw=1) #与默认相同
listy = Flip(p=1.,draw=[1,0,1,0,1]) #完全手动操作!!!
funct = Flip(draw=lambda x: torch.ones(x.size(0))) #与默认相同
show_images( deflt(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Flip')
show_images( const(imgs) ,suptitle='Constant Flip',titles=[f'Flipped' for i in['','','','','']]) #同上
show_images( listy(imgs) ,suptitle='Listy Flip',titles=[f'{i}Flipped' for i in ['','Not ','','Not ','']])
show_images( funct(imgs) ,suptitle='Flip By Function') #与默认相同



flip = Flip(p=1.)
t = _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [2,1]], (3,3))
y = flip(TensorImage(t[None,None]), split_idx=0)
test_eq(y, _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [0,1]], (3,3))[None,None])
pnts = TensorPoint((tensor([[1.,0.], [2,1]]) -1)[None])
test_eq(flip(pnts, split_idx=0), tensor([[[1.,0.], [0,1]]]) -1)
bbox = TensorBBox(((tensor([[1.,0., 2.,1]]) -1)[None]))
test_eq(flip(bbox, split_idx=0), tensor([[[0.,0., 1.,1.]]]) -1)class DeterministicDraw():
def __init__(self, vals): self.vals,self.count = vals,-1
def __call__(self, x):
self.count += 1
return x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + self.vals[self.count%len(self.vals)]t = _batch_ex(8)
draw = DeterministicDraw(list(range(8)))
for i in range(15): test_eq(draw(t), torch.zeros(8)+(i%8))class DeterministicFlip(Flip):
"Flip the batch every other call"
def __init__(self,
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
align_corners=True, # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
**kwargs
):
super().__init__(p=1., draw=DeterministicDraw([0,1]), mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners, **kwargs)接下来,我们将循环遍历示例图像的多个批次。DeterministicFlip 首先不翻转图像,然后在下一个批次中将翻转图像。
b = _batch_ex(2)
dih = DeterministicFlip()
for i,flipped in enumerate(['Not Flipped','Flipped']*2):
show_images(dih(b),suptitle=f'Batch {i}',titles=[flipped]*2)


二面角 -
由于我们正在处理正方形和长方形,我们可以将二面翻转视为沿水平方向、垂直方向和对角线及其组合的翻转。不过请记住,长方形在对角线方向上并不是对称的,因此这将有效地裁剪部分长方形。
def dihedral_mat(
x:Tensor, # 输入 `张量`
p:float=0.5, # 保持不变的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义二面角而非随机
batch:bool=False # 对整个批次应用相同的二面角
):
"Return a random dihedral matrix"
def _def_draw(x): return torch.randint(0,8, (x.size(0),), device=x.device)
def _def_draw_b(x): return random.randint(0,7) + x.new_zeros((x.size(0),)).long()
idx = _draw_mask(x, _def_draw_b if batch else _def_draw, draw=draw, p=p, batch=batch).long()
xs = tensor([1,-1,1,-1,-1,1,1,-1], device=x.device).gather(0, idx)
ys = tensor([1,1,-1,1,-1,-1,1,-1], device=x.device).gather(0, idx)
m0 = tensor([1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0], device=x.device).gather(0, idx)
m1 = tensor([0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1], device=x.device).gather(0, idx)
return affine_mat(xs*m0, xs*m1, t0(xs),
ys*m1, ys*m0, t0(xs)).float()@patch
def dihedral_batch(x: TensorImage|TensorMask|TensorPoint|TensorBBox,
p=0.5, # 应用双翼机概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义二面角而非随机
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `x`
pad_mode=None, # 应用于 `x` 的填充
batch=False, # 对整个批次应用相同的二面角
align_corners=True # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
):
x0,mode,pad_mode = _get_default(x, mode, pad_mode)
mat = _prepare_mat(x, dihedral_mat(x0, p=p, draw=draw, batch=batch))
return x.affine_coord(mat=mat, sz=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)class Dihedral(AffineCoordTfm):
"Apply a random dihedral transformation to a batch of images with a probability `p`"
def __init__(self,
p=0.5, # 应用双翼面布局的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义二面角而非随机
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
batch=False, # 对整个批次应用相同的二面角
align_corners=True # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
):
f = partial(dihedral_mat, p=p, draw=draw, batch=batch)
super().__init__(aff_fs=f, size=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)调用 @patch 修饰的 dihedral_batch 行为,用于 TensorImage、TensorMask、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
draw 可以被指定用于自定义在应用变换时选择哪个翻转(默认是介于 0 和 7 之间的随机数)。它可以是一个介于 0 和 7 之间的整数,一个这样的整数列表(该列表的长度应等于或大于批量的大小),或者一个返回介于 0 和 7 之间的长整型张量的可调用对象。
with no_random():
imgs = _batch_ex(5)
deflt = Dihedral()
const = Dihedral(p=1.,draw=1) #与flip_batch相同
listy = Dihedral(p=1.,draw=[0,1,2,3,4]) #完全手动操作!!!
funct = Dihedral(draw=lambda x: torch.randint(0,8,(x.size(0),))) #与默认相同
show_images( deflt(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Flips',titles=[i for i in range(imgs.size(0))])
show_images( const(imgs) ,suptitle='Constant Horizontal Flip',titles=[f'Flip 1' for i in [0,1,1,1,1]])
show_images( listy(imgs) ,suptitle='Manual Listy Flips',titles=[f'Flip {i}' for i in [0,1,2,3,4]]) #手动指定,非随机!
show_images( funct(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Functional Flips',titles=[i for i in range(imgs.size(0))]) #与默认相同



#测试图像和点的行为是否一致
t = _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [2,1], [2,2]], (3,3))[None,None].expand(8,1,3,3)
dih = Dihedral(p=1., draw=list(range(8)))
dih.as_item=False
pnts = tensor([[[1.,0.], [2,1], [2,2]]]) -1
y,z = dih((TensorImage(t),TensorPoint(pnts.expand(8,3,2))), split_idx=0)
res = y.nonzero()
for i in range(8):
vals = {(t[0] + t[1]*3).item() for t in res[i*3:(i+1)*3][:,2:].flip(1)}
vals1 = {(t[0] + t[1]*3).item() for t in z[i]+1}
test_eq(vals, vals1)
#测试顺序与二面角项相同
tt = _pnt2tensor([[1,0], [2,1], [2,2]], (3,3))
x = PILImage.create(tt)
for i in range(8):
y1 = x.dihedral(i)
test_eq(y[i,0], tensor(array(y1)))class DeterministicDihedral(Dihedral):
def __init__(self,
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
align_corners=None # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
):
"Flip the batch every other call"
super().__init__(p=1., draw=DeterministicDraw(list(range(8))), pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)DeterministicDihedral 确保第一次调用不会被翻转,然后后续调用将按照确定性顺序翻转。在进行完所有 7 种可能的二面翻转后,模式将重置为未翻转版本。如果我们在批量大小为 1 的情况下进行此操作,它看起来会是这样的:
t = _batch_ex(10)
dih = DeterministicDihedral()
_,axs = plt.subplots(2,5, figsize=(14,6))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()):
y = dih(t)
show_image(y[0], ctx=ax, title=f'Batch {i}')
旋转 -
def rotate_mat(
x:Tensor, # 输入 `张量`
max_deg:int=10, # 最大旋转角度
p:float=0.5, # 应用旋转的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 习俗传承而非随机
batch:bool=False # 对整个批次应用相同的旋转
):
"Return a random rotation matrix with `max_deg` and `p`"
def _def_draw(x): return x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(-max_deg, max_deg)
def _def_draw_b(x): return x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(-max_deg, max_deg)
thetas = _draw_mask(x, _def_draw_b if batch else _def_draw, draw=draw, p=p, batch=batch) * math.pi/180
return affine_mat(thetas.cos(), thetas.sin(), t0(thetas),
-thetas.sin(), thetas.cos(), t0(thetas))@patch
@delegates(rotate_mat)
def rotate(x: TensorImage|TensorMask|TensorPoint|TensorBBox,
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出大小将重复。
mode:str=None, # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `x`
pad_mode=None, # 应用于 `x` 的填充
align_corners:bool=True, # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
**kwargs
):
x0,mode,pad_mode = _get_default(x, mode, pad_mode)
mat = _prepare_mat(x, rotate_mat(x0, **kwargs))
return x.affine_coord(mat=mat, sz=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)class Rotate(AffineCoordTfm):
"Apply a random rotation of at most `max_deg` with probability `p` to a batch of images"
def __init__(self,
max_deg:int=10, # 最大旋转度
p:float=0.5, # 应用旋转的概率
draw:int|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 自定义轮换而非随机
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
align_corners:bool=True, # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
batch:bool=False # 对整个批次应用相同的旋转
):
aff_fs = partial(rotate_mat, max_deg=max_deg, p=p, draw=draw, batch=batch)
super().__init__(aff_fs=aff_fs, size=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)调用 @patch 装饰的 rotate 行为用于 TensorImage、TensorMask、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
draw可以指定,如果你想自定义在应用变换时选择哪个角度(默认是在-max_deg和max_deg之间的随机浮点数)。它可以是一个浮点数,一个浮点数列表(列表的长度应该等于或大于批次的大小),或一个返回浮点张量的可调用对象。
默认情况下,旋转只能旋转10度,这使得变化不容易被看出。这通常与flip或dihedral结合使用,后者默认情况下会产生更大的变化。例如,旋转180度与垂直翻转是相同的。
with no_random():
thetas = [-30,-15,0,15,30]
imgs = _batch_ex(5)
deflt = Rotate()
const = Rotate(p=1.,draw=180) #与垂直翻转相同
listy = Rotate(p=1.,draw=[-30,-15,0,15,30]) #完全手动操作!!!
funct = Rotate(draw=lambda x: x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(-10, 10)) #与默认相同
show_images( deflt(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Rotate, notice the small rotation',titles=[i for i in range(imgs.size(0))])
show_images( const(imgs) ,suptitle='Constant 180 Rotate',titles=[f'180 Degrees' for i in range(imgs.size(0))])
#手动指定,非随机!
show_images( listy(imgs) ,suptitle='Manual List Rotate',titles=[f'{i} Degrees' for i in [-30,-15,0,15,30]])
#与默认相同
show_images( funct(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Functional Rotate',titles=[i for i in range(imgs.size(0))])



放大 -
def zoom_mat(
x:Tensor, # 输入 `张量`
min_zoom:float=1., # 最小缩放
max_zoom:float=1.1, # 最大变焦
p:float=0.5, # 应用缩放的概率
draw:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户自定义缩放比例
draw_x:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户定义的缩放中心点x坐标
draw_y:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户定义的缩放中心点在y轴上的位置
batch:bool=False # 对整个批次应用相同的缩放比例
):
"Return a random zoom matrix with `max_zoom` and `p`"
def _def_draw(x): return x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(min_zoom, max_zoom)
def _def_draw_b(x): return x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(min_zoom, max_zoom)
def _def_draw_ctr(x): return x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(0,1)
def _def_draw_ctr_b(x): return x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(0,1)
assert(min_zoom<=max_zoom)
s = 1/_draw_mask(x, _def_draw_b if batch else _def_draw, draw=draw, p=p, neutral=1., batch=batch)
def_draw_c = _def_draw_ctr_b if batch else _def_draw_ctr
col_pct = _draw_mask(x, def_draw_c, draw=draw_x, p=1., batch=batch)
row_pct = _draw_mask(x, def_draw_c, draw=draw_y, p=1., batch=batch)
col_c = (1-s) * (2*col_pct - 1)
row_c = (1-s) * (2*row_pct - 1)
return affine_mat(s, t0(s), col_c,
t0(s), s, row_c)@patch
@delegates(zoom_mat)
def zoom(x: TensorImage|TensorMask|TensorPoint|TensorBBox,
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `x`
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 应用于 `x` 的填充
align_corners:bool=True, # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
**kwargs
):
x0,mode,pad_mode = _get_default(x, mode, pad_mode)
return x.affine_coord(mat=zoom_mat(x0, **kwargs)[:,:2], sz=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)class Zoom(AffineCoordTfm):
"Apply a random zoom of at most `max_zoom` with probability `p` to a batch of images"
def __init__(self,
min_zoom:float=1., # 最小缩放
max_zoom:float=1.1, # 最大变焦
p:float=0.5, # 应用缩放的概率
draw:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户自定义缩放比例
draw_x:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户定义的缩放中心点 x 坐标
draw_y:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户定义的缩放中心点在y轴上的位置
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
batch=False, # 对整个批次应用相同的缩放比例
align_corners=True # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
):
aff_fs = partial(zoom_mat, min_zoom=min_zoom, max_zoom=max_zoom, p=p, draw=draw, draw_x=draw_x, draw_y=draw_y, batch=batch)
super().__init__(aff_fs, size=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)调用 @patch 的 zoom 行为用于 TensorImage、TensorMask、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox。
draw、draw_x 和 draw_y 可以被指定,如果你想自定义在应用变换时选择哪个比例和中心(默认情况下,draw 为 1 到 max_zoom 之间的随机浮点数,draw_x 和 draw_y 在 0 到 1 之间)。每个参数可以是一个浮点数,一个浮点数列表(此时列表长度应等于或大于批次大小),或者是一个返回浮点张量的可调用对象。
draw_x 和 draw_y 被期望为中心的位置百分比,0 表示最左/最上,1 表示最右/最下。
注意:默认情况下,缩放较小。
with no_random():
scales = [0.8, 1., 1.1, 1.25, 1.5]
imgs = _batch_ex(5)
deflt = Zoom()
const = Zoom(p=1., draw=1.5) #'Constant scale and different random centers'
listy = Zoom(p=1.,draw=scales,draw_x=0.5, draw_y=0.5) #完全手动秤,恒定中心
funct = Zoom(draw=lambda x: x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(1., 1.1)) #与默认相同
show_images( deflt(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Zoom, note the small zooming', titles=[i for i in range(imgs.size(0))])
show_images( const(imgs) ,suptitle='Constant Scale, Valiable Position', titles=[f'Scale 1.5x' for i in range(imgs.size(0))])
show_images( listy(imgs) ,suptitle='Manual Listy Scale, Centered', titles=[f'Scale {i}x' for i in scales])
show_images( funct(imgs) ,suptitle='Default Functional Zoom', titles=[i for i in range(imgs.size(0))]) #与默认相同



变形
def solve(A,B):
return torch.linalg.solve(A,B)def find_coeffs(
p1:Tensor, # 原始点
p2:Tensor, # 目标点
):
"Find coefficients for warp tfm from `p1` to `p2`"
m = []
p = p1[:,0,0]
#我们需要求解的方程。
for i in range(p1.shape[1]):
m.append(stack([p2[:,i,0], p2[:,i,1], t1(p), t0(p), t0(p), t0(p), -p1[:,i,0]*p2[:,i,0], -p1[:,i,0]*p2[:,i,1]]))
m.append(stack([t0(p), t0(p), t0(p), p2[:,i,0], p2[:,i,1], t1(p), -p1[:,i,1]*p2[:,i,0], -p1[:,i,1]*p2[:,i,1]]))
#我们寻求的8个标量是AX = B的解
A = stack(m).permute(2, 0, 1)
B = p1.view(p1.shape[0], 8, 1)
return solve(A,B)def apply_perspective(
coords:Tensor, # 原始坐标
coeffs:Tensor # 扭曲变换矩阵
):
"Apply perspective tranform on `coords` with `coeffs`"
sz = coords.shape
coords = coords.view(sz[0], -1, 2)
coeffs = torch.cat([coeffs, t1(coeffs[:,:1])], dim=1).view(coeffs.shape[0], 3,3)
coords1 = coords @ coeffs[...,:2].transpose(1,2) + coeffs[...,2].unsqueeze(1)
if (coords1[...,2]==0.).any(): return coords[...,:2].view(*sz)
coords = coords1/coords1[...,2].unsqueeze(-1)
return coords[...,:2].view(*sz)class _WarpCoord():
def __init__(self, magnitude=0.2, p=0.5, draw_x=None, draw_y=None, batch=False):
store_attr()
self.coeffs = None
def _def_draw(self, x):
if not self.batch: return x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(-self.magnitude, self.magnitude)
return x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(-self.magnitude, self.magnitude)
def before_call(self, x):
x_t = _draw_mask(x, self._def_draw, self.draw_x, p=self.p, batch=self.batch)
y_t = _draw_mask(x, self._def_draw, self.draw_y, p=self.p, batch=self.batch)
orig_pts = torch.tensor([[-1,-1], [-1,1], [1,-1], [1,1]], dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
self.orig_pts = orig_pts.unsqueeze(0).expand(x.size(0),4,2)
targ_pts = stack([stack([-1-y_t, -1-x_t]), stack([-1+y_t, 1+x_t]),
stack([ 1+y_t, -1+x_t]), stack([ 1-y_t, 1-x_t])])
self.targ_pts = targ_pts.permute(2,0,1)
def __call__(self, x, invert=False):
coeffs = find_coeffs(self.targ_pts, self.orig_pts) if invert else find_coeffs(self.orig_pts, self.targ_pts)
return apply_perspective(x, coeffs)@patch
@delegates(_WarpCoord.__init__)
def warp(x:TensorImage|TensorMask|TensorPoint|TensorBBox,
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 插值方法应用于 `x`
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 应用于 `x` 的填充
align_corners:bool=True, # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
**kwargs
):
x0,mode,pad_mode = _get_default(x, mode, pad_mode)
coord_tfm = _WarpCoord(**kwargs)
coord_tfm.before_call(x0)
return x.affine_coord(coord_tfm=coord_tfm, sz=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners)x1 = tensor([[1.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]])
x2 = tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,1.]])
x3 = tensor([[1.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,0.]])
x4 = tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,1.]])
y = TensorImage(stack([x1,x2,x3,x4])[:,None])
y = y.warp(p=1., draw_x=[0.,0,-0.5,0.5], draw_y=[-0.5,0.5,0.,0.])
test_eq(y[0,0], tensor([[0.,1.,0.,1.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]]))
test_eq(y[1,0], tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,1.,0.,1.,0.]]))
test_eq(y[2,0], tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]]))
test_eq(y[3,0], tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]]))x = torch.tensor([[[-1.,-1], [1,-1]], [[-1,1],[1,1]], [[-1,-1], [-1,1]], [[1,-1], [1,1]]])
y = TensorPoint(x).warp(p=1., draw_x=[0.,0,-0.5,0.5], draw_y=[-0.5,0.5,0.,0.])
test_eq(y, torch.tensor([[[-0.5,-1], [0.5,-1]], [[-0.5,1],[0.5,1]], [[-1,-0.5], [-1,0.5]], [[1,-0.5], [1,0.5]]]))class Warp(AffineCoordTfm):
"Apply perspective warping with `magnitude` and `p` on a batch of matrices"
def __init__(self,
magnitude:float=0.2, # 默认的扭曲幅度
p:float=0.5, # 应用翘曲的概率
draw_x:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户定义的x方向扭曲幅度
draw_y:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 用户定义的y方向扭曲幅度
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
batch:bool=False, # 在整个批次中应用相同的经纱
align_corners:bool=True # PyTorch 中的 `F.grid_sample` 函数,其 `align_corners` 参数
):
store_attr()
coord_fs = _WarpCoord(magnitude=magnitude, p=p, draw_x=draw_x, draw_y=draw_y, batch=batch)
super().__init__(coord_fs=coord_fs, size=size, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, align_corners=align_corners )调用 @patch 的 warp 行为适用于 TensorImage、TensorMask、TensorPoint 和 TensorBBox
draw_x 和 draw_y 可以指定,如果您想自定义在应用变换时所选择的幅度(默认是在 -magnitude 和 magnitude 之间的随机浮点数)。每个值可以是一个浮点数、一个浮点数列表(该列表的长度应等于或大于批次的大小),或是一个返回浮点张量的可调用对象。
scales = [-0.4, -0.2, 0., 0.2, 0.4]
imgs=_batch_ex(5)
vert_warp = Warp(p=1., draw_y=scales, draw_x=0.)
horz_warp = Warp(p=1., draw_x=scales, draw_y=0.)
show_images( vert_warp(imgs) ,suptitle='Vertical warping', titles=[f'magnitude {i}' for i in scales])
show_images( horz_warp(imgs) ,suptitle='Horizontal warping', titles=[f'magnitude {i}' for i in scales])

x1 = tensor([[1.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]])
x2 = tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,1.]])
x3 = tensor([[1.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,0.]])
x4 = tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,1.]])
warp = Warp(p=1., draw_x=[0.,0,-0.5,0.5], draw_y=[-0.5,0.5,0.,0.])
y = warp(TensorImage(stack([x1,x2,x3,x4])[:,None]), split_idx=0)
test_eq(y[0,0], tensor([[0.,1.,0.,1.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]]))
test_eq(y[1,0], tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,1.,0.,1.,0.]]))
test_eq(y[2,0], tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [1.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]]))
test_eq(y[3,0], tensor([[0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,1.], [0.,0.,0.,0.,0.]]))x = torch.tensor([[[-1.,-1], [1,-1]], [[-1,1],[1,1]], [[-1,-1], [-1,1]], [[1,-1], [1,1]]])
y = warp(TensorPoint(x), split_idx=0)
test_eq(y, torch.tensor([[[-0.5,-1], [0.5,-1]], [[-0.5,1],[0.5,1]], [[-1,-0.5], [-1,0.5]], [[1,-0.5], [1,0.5]]]))照明变换
光照变换是影响图像中光线表现的转换。这些变换不像之前的变换那样改变物体的位置,而是模拟光线在场景中的变化。 simclr 论文 对这些变换与其他变换进行了评估,以用于自监督图像分类的应用场景,值得注意的是,他们使用“颜色”和“颜色扭曲”来指代这些变换的组合。
@patch
def lighting(x: TensorImage, func): return torch.sigmoid(func(logit(x)))class SubTensorImage(TensorImage):
pass
t=SubTensorImage(1)
assert isinstance(t.lighting(noop), SubTensorImage)大多数灯光转换在“logit 空间”中效果更好,因为我们不想通过超出最大或最小亮度来使图像过曝。对 logit 进行 sigmoid 变换可以让我们回到“线性空间”。
x=TensorImage(torch.tensor([.01* i for i in range(0,101)]))
f_lin= lambda x:(2*(x-0.5)+0.5).clamp(0,1) #蓝线
f_log= lambda x:2*x #红线
plt.plot(x,f_lin(x),'b',x,x.lighting(f_log),'r');
上面的图显示了在线性空间和对数空间中进行对比变换的结果。注意到蓝色线性图必须被限制,我们失去了0.0与0.2相比的大小信息。而在红色图中,值呈曲线形状,因此我们保留了这种相对信息。
首先,我们创建一个通用的 SpaceTfm。这使我们可以将多个变换组合在一起,从而我们只需在进行多个变换之前转换一次到某个空间。space_fn 必须从 rgb 转换到某个空间,应用一个函数,然后再转换回 rgb。fs 应该是类似列表的,包含将被组合在一起的函数。
class SpaceTfm(RandTransform):
"Apply `fs` to the logits"
order = 40
def __init__(self,
fs:callable|MutableSequence, # 应用于空间的变换函数
space_fn:callable, # 将RGB转换为某个空间,应用`fs`后再转换回RGB的函数
**kwargs
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.space_fn=space_fn
self.fs=L(fs)
def before_call(self,
b,
split_idx:int, # 列车/验证数据集索引
):
self.do = True
while isinstance(b, tuple): b = b[0]
for t in self.fs: t.before_call(b)
def compose(self,
tfm:callable # 组合变换函数
):
"Compose `self` with another `LightingTransform`"
self.fs += tfm.fs
def encodes(self,x:TensorImage): return self.space_fn(x,partial(compose_tfms, tfms=self.fs))LightingTfm 是一个 SpaceTfm,它使用 TensorImage.lighting 转换到对数空间。使用此方法可以在图像变得非常暗或非常亮时限制细节的丢失。
class LightingTfm(SpaceTfm):
"Apply `fs` to the logits"
order = 40
def __init__(self,
fs:callable|MutableSequence, # 在logit空间中应用的转换函数,
**kwargs
):
super().__init__(fs, TensorImage.lighting, **kwargs)亮度是指场景中的光线量。它可以是零,即图像完全黑色,或者是完全白色的值。这在你预计数据集中有过曝或欠曝图像时可能特别有用。
class _BrightnessLogit():
def __init__(self, max_lighting=0.2, p=0.75, draw=None, batch=False): store_attr()
def _def_draw(self, x):
if not self.batch: return x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(0.5*(1-self.max_lighting), 0.5*(1+self.max_lighting))
return x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(0.5*(1-self.max_lighting), 0.5*(1+self.max_lighting))
def before_call(self, x):
self.change = _draw_mask(x, self._def_draw, draw=self.draw, p=self.p, neutral=0.5, batch=self.batch)
def __call__(self, x): return x.add_(logit(self.change[:,None,None,None]))@patch
@delegates(_BrightnessLogit.__init__)
def brightness(x: TensorImage, **kwargs):
func = _BrightnessLogit(**kwargs)
func.before_call(x)
return x.lighting(func)class Brightness(LightingTfm):
def __init__(self,
max_lighting:float=0.2, # 最大亮度变化幅度
p:float=0.75, # 应用变换的概率
draw:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 批量转换的用户定义行为
batch=False # 将整个批次的亮度调整为相同
):
"Apply change in brightness of `max_lighting` to batch of images with probability `p`."
store_attr()
super().__init__(_BrightnessLogit(max_lighting, p, draw, batch))调用 @patch 的 Brightness 行为用于 TensorImage
draw 可以指定,如果您想自定义在应用变换时选择的幅度(默认值是介于 -0.5*(1-max_lighting) 和 0.5*(1+max_lighting) 之间的随机浮点数)。每个值可以是一个浮点数,一个浮点数列表(此时列表长度应大于或等于批处理的大小),或者一个返回浮点张量的可调用对象。
scales = [0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9]
y = _batch_ex(5).brightness(draw=scales, p=1.)
fig,axs = plt.subplots(1,5, figsize=(15,3))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()):
show_image(y[i], ctx=ax, title=f'scale {scales[i]}')
x = torch.randn(5, 3, 4, 4)
bright = Brightness(draw=scales, p=1.)
print('***', bright.space_fn)
y = bright(TensorImage(x), split_idx=0)
y1 = torch.sigmoid(logit(x) + logit(tensor(scales))[:,None,None,None])
test_close(y, y1)
test_eq(bright(TensorMask(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(bright(TensorPoint(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(bright(TensorBBox(x), split_idx=0), x)*** <function TensorImage.lighting at 0x14bfc0d30>对比度将像素推向最大值或最小值。对比度的最小值是一个纯灰色图像。举个例子,拍摄一个在黑暗房间中明亮光源的照片。你的眼睛应该能够看到房间中的一些细节,但拍摄出来的照片应该具有更高的对比度,背景中的所有细节都因为黑暗而缺失。这是这个变换可以帮助模拟的一个例子。
class _ContrastLogit():
def __init__(self, max_lighting=0.2, p=0.75, draw=None, batch=False): store_attr()
def _def_draw(self, x):
if not self.batch: res = x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(math.log(1-self.max_lighting), -math.log(1-self.max_lighting))
else: res = x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(math.log(1-self.max_lighting), -math.log(1-self.max_lighting))
return torch.exp(res)
def before_call(self, x):
self.change = _draw_mask(x, self._def_draw, draw=self.draw, p=self.p, neutral=1., batch=self.batch)
def __call__(self, x): return x.mul_(self.change[:,None,None,None])@patch
@delegates(_ContrastLogit.__init__)
def contrast(x: TensorImage, **kwargs):
func = _ContrastLogit(**kwargs)
func.before_call(x)
return x.lighting(func)class Contrast(LightingTfm):
"Apply change in contrast of `max_lighting` to batch of images with probability `p`."
def __init__(self,
max_lighting=0.2, # 对比度变化的最大范围
p=0.75, # 应用变换的概率
draw:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 批量转换的用户定义行为
batch=False
):
store_attr()
super().__init__(_ContrastLogit(max_lighting, p, draw, batch))调用 @patch 的 TensorImage 的 contrast 行为
draw 可以被指定用来定制在应用变换时选择的幅度(默认为在 (1-max_lighting) 和 1/(1-max_lighting) 之间随机取的浮点数)。每个值可以是一个浮点数,一个浮点数列表(此时列表长度应大于或等于批次大小),或者是一个返回浮点张量的可调用对象。
scales = [0.65, 0.8, 1., 1.25, 1.55]
y = _batch_ex(5).contrast(p=1., draw=scales)
fig,axs = plt.subplots(1,5, figsize=(15,3))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(y[i], ctx=ax, title=f'scale {scales[i]}')
x = torch.randn(5, 3, 4, 4)
cont = Contrast(p=1., draw=scales)
y = cont(TensorImage(x), split_idx=0)
y1 = torch.sigmoid(logit(x) * tensor(scales)[:,None,None,None])
test_close(y, y1)
test_eq(cont(TensorMask(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(cont(TensorPoint(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(cont(TensorBBox(x), split_idx=0), x)def grayscale(x):
"Tensor to grayscale tensor. Uses the ITU-R 601-2 luma transform. "
return (x*torch.tensor([0.2989,0.5870,0.1140],device=x.device)[...,None,None]).sum(1)[:,None]以上只是将图像转换为灰度的一种方法。我们选择这种方法是因为它速度较快。请注意,每个通道的权重之和为1。
f'{sum([0.2989,0.5870,0.1140]):.3f}''1.000'class _SaturationLogit():
def __init__(self, max_lighting=0.2, p=0.75, draw=None, batch=False): store_attr()
def _def_draw(self, x):
if not self.batch: res = x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(math.log(1-self.max_lighting), -math.log(1-self.max_lighting))
else: res = x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(math.log(1-self.max_lighting), -math.log(1-self.max_lighting))
return torch.exp(res)
def before_call(self, x):
self.change = _draw_mask(x, self._def_draw, draw=self.draw, p=self.p, neutral=1., batch=self.batch)
def __call__(self, x):
#在原位插值灰度图像和原始图像
gs = grayscale(x)
gs.mul_(1-self.change[:,None,None,None])
x.mul_(self.change[:,None,None,None])
return x.add_(gs)@patch
@delegates(_SaturationLogit.__init__)
def saturation(x: TensorImage, **kwargs):
func = _SaturationLogit(**kwargs)
func.before_call(x)
return x.lighting(func)class Saturation(LightingTfm):
"Apply change in saturation of `max_lighting` to batch of images with probability `p`."
# 参考:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torchvision/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.functional.adjust_saturation
def __init__(self,
max_lighting:float=0.2, # 最大亮度变化幅度
p:float=0.75, # 应用变换的概率
draw:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 批量转换的用户定义行为
batch:bool=False # 对整个批次应用相同的饱和度
):
store_attr()
super().__init__(_SaturationLogit(max_lighting, p, draw, batch))调用 @patch 的 saturation 行为用于 TensorImage
scales = [0., 0.5, 1., 1.5, 2.0]
y = _batch_ex(5).saturation(p=1., draw=scales)
fig,axs = plt.subplots(1,5, figsize=(15,3))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(y[i], ctx=ax, title=f'scale {scales[i]}')
饱和度控制图像中色彩的数量,但不影响图像的亮度或黑暗程度。它对中性色(如白色、灰色和黑色)没有影响。在零饱和度时,实际上会得到一幅灰度图像。将饱和度推高到超过1时,会使更多中性色呈现出任何潜在的色彩。
x = torch.randn(5, 3, 4, 4)
sat = Saturation(p=1., draw=scales)
y = sat(TensorImage(x), split_idx=0)
y1 = logit(x) * tensor(scales)[:,None,None,None]
y1 += grayscale(logit(x)) * (1-tensor(scales)[:,None,None,None])
y1 = torch.sigmoid(y1)
test_close(y, y1)
test_eq(sat(TensorMask(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(sat(TensorPoint(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(sat(TensorBBox(x), split_idx=0), x)rgb2hsv 和 hsv2rgb 是用于在 hsv 空间之间转换的工具。Hsv 空间代表色相、饱和度和明度空间。这使我们能够更容易地执行某些变换。
torch.max(tensor([1]).as_subclass(TensorBase), dim=0)torch.return_types.max(
values=TensorBase(1),
indices=TensorBase(0))def rgb2hsv(
img:Tensor # 一批RGB图像的张量
):
"Converts a RGB image to an HSV image. Note: Will not work on logit space images."
r, g, b = img.unbind(1)
# 由于 https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/47069 的问题,临时注释掉了。
# maxc = torch.max(img, dim=1).values
# minc = torch.min(img, dim=1).values
maxc = torch.max(img, dim=1)[0]
minc = torch.min(img, dim=1)[0]
eqc = maxc == minc
cr = maxc - minc
s = cr / torch.where(eqc, maxc.new_ones(()), maxc)
cr_divisor = torch.where(eqc, maxc.new_ones(()), cr)
rc = (maxc - r) / cr_divisor
gc = (maxc - g) / cr_divisor
bc = (maxc - b) / cr_divisor
hr = (maxc == r) * (bc - gc)
hg = ((maxc == g) & (maxc != r)) * (2.0 + rc - bc)
hb = ((maxc != g) & (maxc != r)) * (4.0 + gc - rc)
h = (hr + hg + hb)
h = torch.fmod((h / 6.0 + 1.0), 1.0)
return torch.stack((h, s, maxc),dim=1)def hsv2rgb(
img:Tensor, # 一批图像 `Tensor 以 HSV 格式表示`
):
"Converts a HSV image to an RGB image."
h, s, v = img.unbind(1)
i = torch.floor(h * 6.0)
f = (h * 6.0) - i
i = i.to(dtype=torch.int32)
p = torch.clamp((v * (1.0 - s)), 0.0, 1.0)
q = torch.clamp((v * (1.0 - s * f)), 0.0, 1.0)
t = torch.clamp((v * (1.0 - s * (1.0 - f))), 0.0, 1.0)
i = i % 6
mask = i[:,None] == torch.arange(6,device=i.device)[:, None, None][None]
a1 = torch.stack((v, q, p, p, t, v),dim=1)
a2 = torch.stack((t, v, v, q, p, p),dim=1)
a3 = torch.stack((p, p, t, v, v, q),dim=1)
a4 = torch.stack((a1, a2, a3),dim=1)
return torch.einsum("nijk, nxijk -> nxjk", mask.to(dtype=img.dtype), a4)与在logit空间中进行的lighting非常相似,hsv变换是在hsv空间中进行的。我们可以组合在hsv空间中进行的任何变换。
@patch
def hsv(x: TensorImage, func): return TensorImage(hsv2rgb(func(rgb2hsv(x))))class HSVTfm(SpaceTfm):
"Apply `fs` to the images in HSV space"
def __init__(self, fs, **kwargs):
super().__init__(fs, TensorImage.hsv, **kwargs)调用 @patch 装饰的 TensorImage 的 hsv 行为
fig,axs=plt.subplots(figsize=(20, 4),ncols=5)
axs[0].set_ylabel('Hue')
for ax in axs:
ax.set_xlabel('Saturation')
ax.set_yticklabels([])
ax.set_xticklabels([])
hsvs=torch.stack([torch.arange(0,2.1,0.01)[:,None].repeat(1,210),
torch.arange(0,1.05,0.005)[None].repeat(210,1),
torch.ones([210,210])])[None]
for ax,i in zip(axs,range(0,5)):
if i>0: hsvs[:,2].mul_(0.80)
ax.set_title('V='+'%.1f' %0.8**i)
ax.imshow(hsv2rgb(hsvs)[0].permute(1,2,0))
对于色相变换,我们使用HSV空间而不是对数空间。HSV代表色相、饱和度和明度。HSV空间中的色相仅在彩虹的颜色之间循环。注意没有最大值,因为颜色会重复。
上面是一些在不同明度(V)下的色相(H)和饱和度(S)的示例。需要注意的是,HSV空间中的一个特性是,当饱和度最低时,V控制你获得的颜色。
class _Hue():
def __init__(self, max_hue=0.1, p=0.75, draw=None, batch=False): store_attr()
def _def_draw(self, x):
if not self.batch: res = x.new_empty(x.size(0)).uniform_(math.log(1-self.max_hue), -math.log(1-self.max_hue))
else: res = x.new_zeros(x.size(0)) + random.uniform(math.log(1-self.max_hue), -math.log(1-self.max_hue))
return torch.exp(res)
def before_call(self, x):
self.change = _draw_mask(x, self._def_draw, draw=self.draw, p=self.p, neutral=0., batch=self.batch)
def __call__(self, x):
h,s,v = x.unbind(1)
h += self.change[:,None,None]
h = h % 1.0
return x.set_(torch.stack((h, s, v),dim=1))@patch
@delegates(_Hue.__init__)
def hue(x: TensorImage, **kwargs):
func = _Hue(**kwargs)
func.before_call(x)
return TensorImage(x.hsv(func))class Hue(HSVTfm):
"Apply change in hue of `max_hue` to batch of images with probability `p`."
# 参考:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torchvision/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.functional.adjust_hue
def __init__(self,
max_hue:float=0.1, # 最大色相变化幅度
p:float=0.75, # 应用变换的概率
draw:float|MutableSequence|callable=None, # 批量转换的用户定义行为
batch=False # 将相同的色调应用于整个批次
):
super().__init__(_Hue(max_hue, p, draw, batch))调用 @patch 的 hue 行为用于 TensorImage
scales = [0.5, 0.75, 1., 1.5, 1.75]
y = _batch_ex(len(scales)).hue(p=1., draw=scales)
fig,axs = plt.subplots(1,len(scales), figsize=(15,3))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(y[i], ctx=ax, title=f'scale {scales[i]}')
test_close(y[0:2], y[3:5])
test_close(y[2],_batch_ex(1))
x = torch.randn(5, 3, 4, 4)
hue = Hue(p=1., draw=scales)
test_close(hue(TensorImage(x), split_idx=0),TensorImage(x).hue(p=1.,draw=scales))
test_eq(hue(TensorMask(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(hue(TensorPoint(x), split_idx=0), x)
test_eq(hue(TensorBBox(x), split_idx=0), x)随机擦除
随机擦除数据增强。这个由罗斯·怀特曼设计的变体,可以在对图像张量进行归一化后,应用于一个批次或单个图像。
def cutout_gaussian(
x:Tensor, # 输入图像
areas:list # 需要裁剪的区域列表。顺序为:rl, rh, cl, ch
):
"Replace all `areas` in `x` with N(0,1) noise"
chan,img_h,img_w = x.shape[-3:]
for rl,rh,cl,ch in areas: x[..., rl:rh, cl:ch].normal_()
return x由于这应该在归一化之后应用,我们将定义一个助手函数在归一化内部应用一个函数。
def norm_apply_denorm(
x:Tensor, # 输入图像
f:callable, # 应用功能
nrm:callable # 归一化变换
):
"Normalize `x` with `nrm`, then apply `f`, then denormalize"
y = f(nrm(x.clone()))
return nrm.decode(y).clamp(0,1)nrm = Normalize.from_stats(*imagenet_stats, cuda=False)f = partial(cutout_gaussian, areas=[(100,200,100,200),(200,300,200,300)])
show_image(norm_apply_denorm(timg, f, nrm)[0]);
def _slice(area, sz):
bound = int(round(math.sqrt(area)))
loc = random.randint(0, max(sz-bound, 0))
return loc,loc+boundclass RandomErasing(RandTransform):
"Randomly selects a rectangle region in an image and randomizes its pixels."
order = 100 # 归一化后
def __init__(self,
p:float=0.5, # 应用随机擦除的概率
sl:float=0., # 最小擦除区域比例
sh:float=0.3, # 最大擦除区域比例
min_aspect:float=0.3, # 擦除区域的最小纵横比
max_count:int=1 # 每张图像的最大擦除块数,每个框的面积按数量缩放
):
store_attr()
super().__init__(p=p)
self.log_ratio = (math.log(min_aspect), math.log(1/min_aspect))
def _bounds(self, area, img_h, img_w):
r_area = random.uniform(self.sl,self.sh) * area
aspect = math.exp(random.uniform(*self.log_ratio))
return _slice(r_area*aspect, img_h) + _slice(r_area/aspect, img_w)
def encodes(self,x:TensorImage):
count = random.randint(1, self.max_count)
_,img_h,img_w = x.shape[-3:]
area = img_h*img_w/count
areas = [self._bounds(area, img_h, img_w) for _ in range(count)]
return cutout_gaussian(x, areas)tfm = RandomErasing(p=1., max_count=6)
_,axs = subplots(2,3, figsize=(12,6))
f = partial(tfm, split_idx=0)
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(norm_apply_denorm(timg, f, nrm)[0], ctx=ax)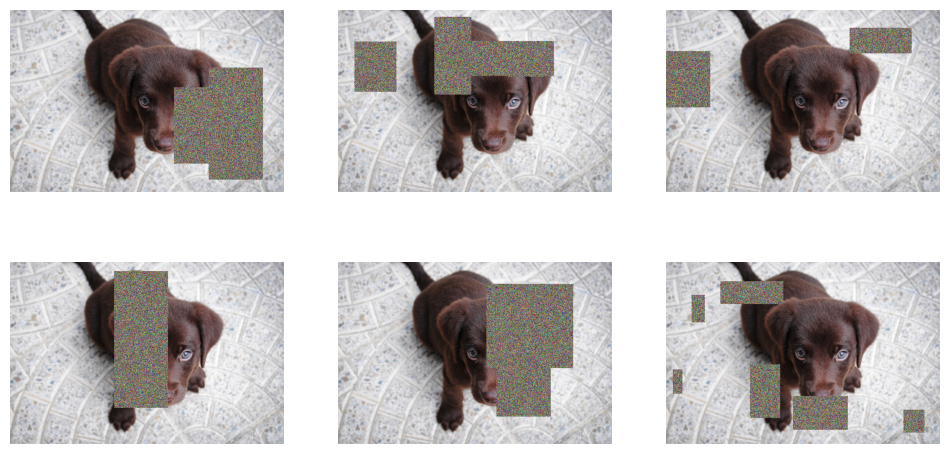
tfm = RandomErasing(p=1., max_count=6)
_,axs = subplots(2,3, figsize=(12,6))
f = partial(tfm, split_idx=0)
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(norm_apply_denorm(timg, f, nrm)[0], ctx=ax)
tfm = RandomErasing(p=1., max_count=6)
_,axs = subplots(2,3, figsize=(12,6))
f = partial(tfm, split_idx=1)
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(norm_apply_denorm(timg, f, nrm)[0], ctx=ax)
一起完成
def _compose_same_tfms(tfms):
tfms = L(tfms)
if len(tfms) == 0: return None
res = tfms[0]
for tfm in tfms[1:]: res.compose(tfm)
return resdef setup_aug_tfms(tfms):
"Go through `tfms` and combines together affine/coord or lighting transforms"
aff_tfms = [tfm for tfm in tfms if isinstance(tfm, AffineCoordTfm)]
lig_tfms = [tfm for tfm in tfms if isinstance(tfm, LightingTfm)]
others = [tfm for tfm in tfms if tfm not in aff_tfms+lig_tfms]
lig_tfm = _compose_same_tfms(lig_tfms)
aff_tfm = _compose_same_tfms(aff_tfms)
res = [aff_tfm] if aff_tfm is not None else []
if lig_tfm is not None: res.append(lig_tfm)
return res + others#仅限仿射
tfms = [Rotate(draw=10., p=1), Zoom(draw=1.1, draw_x=0.5, draw_y=0.5, p=1.)]
comp = setup_aug_tfms([Rotate(draw=10., p=1), Zoom(draw=1.1, draw_x=0.5, draw_y=0.5, p=1.)])
test_eq(len(comp), 1)
x = torch.randn(4,3,5,5)
test_close(comp[0]._get_affine_mat(x)[...,:2],tfms[0]._get_affine_mat(x)[...,:2] @ tfms[1]._get_affine_mat(x)[...,:2])
#We can't test that the ouput of comp or the composition of tfms on x is the same cause it's not (1 interpol vs 2 sp)#仿射变换 + 光照效果
tfms = [Rotate(), Zoom(), Warp(), Brightness(), Flip(), Contrast()]
comp = setup_aug_tfms(tfms)aff_tfm,lig_tfm = comp
test_eq(len(aff_tfm.aff_fs+aff_tfm.coord_fs+comp[1].fs), 6)
test_eq(len(aff_tfm.aff_fs), 3)
test_eq(len(aff_tfm.coord_fs), 1)
test_eq(len(lig_tfm.fs), 2)def aug_transforms(
mult:float=1.0, # 应用于 `max_rotate`、`max_lighting` 和 `max_warp` 的乘法
do_flip:bool=True, # 随机翻转
flip_vert:bool=False, # 垂直翻转
max_rotate:float=10., # 最大旋转角度
min_zoom:float=1., # 最小缩放
max_zoom:float=1.1, # 最大变焦
max_lighting:float=0.2, # 最大亮度变化幅度
max_warp:float=0.2, # 每单位变化的最大翘曲值
p_affine:float=0.75, # 应用仿射变换的概率
p_lighting:float=0.75, # 改变亮度和对比度的概率
xtra_tfms:list=None, # 自定义转换
size:int|tuple=None, # 如果指定一个值,则输出尺寸将重复。
mode:str='bilinear', # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 插值
pad_mode=PadMode.Reflection, # 一个 `PadMode`
align_corners=True, # PyTorch `F.grid_sample` 对齐角点
batch=False, # 对整个批次应用相同的变换
min_scale=1. # 裁剪的最小比例,相对于图像区域
):
"Utility func to easily create a list of flip, rotate, zoom, warp, lighting transforms."
res,tkw = [],dict(size=size if min_scale==1. else None, mode=mode, pad_mode=pad_mode, batch=batch, align_corners=align_corners)
max_rotate,max_lighting,max_warp = array([max_rotate,max_lighting,max_warp])*mult
if do_flip: res.append(Dihedral(p=0.5, **tkw) if flip_vert else Flip(p=0.5, **tkw))
if max_warp: res.append(Warp(magnitude=max_warp, p=p_affine, **tkw))
if max_rotate: res.append(Rotate(max_deg=max_rotate, p=p_affine, **tkw))
if min_zoom<1 or max_zoom>1: res.append(Zoom(min_zoom=min_zoom, max_zoom=max_zoom, p=p_affine, **tkw))
if max_lighting:
res.append(Brightness(max_lighting=max_lighting, p=p_lighting, batch=batch))
res.append(Contrast(max_lighting=max_lighting, p=p_lighting, batch=batch))
if min_scale!=1.: xtra_tfms = RandomResizedCropGPU(size, min_scale=min_scale, ratio=(1,1)) + L(xtra_tfms)
return setup_aug_tfms(res + L(xtra_tfms))当 do_flip=True 时,会添加随机翻转(或如果 flip_vert=True 则为对称翻转),概率为 p=0.5。通过 p_affine 进行最大旋转角度为 max_rotate 的随机旋转,大小在 min_zoom 和 max_zoom 之间的随机缩放,以及最大扭曲为 max_warp 的透视变换。通过 p_lighting 我们进行最大亮度变化和对比度变化为 max_lighting。可以添加自定义的 xtra_tfms。size、mode 和 pad_mode 将用于插值。max_rotate,max_lighting,max_warp 将乘以 mult,以便您可以更轻松地通过单个参数增加或减少增强效果。
tfms = aug_transforms(pad_mode='zeros', mult=2, min_scale=0.5)
y = _batch_ex(9)
for t in tfms: y = t(y, split_idx=0)
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(12,3))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(y[i], ctx=ax)
tfms = aug_transforms(pad_mode='zeros', mult=2, batch=True)
y = _batch_ex(9)
for t in tfms: y = t(y, split_idx=0)
_,axs = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(12,3))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()): show_image(y[i], ctx=ax)
集成测试
分割
camvid = untar_data(URLs.CAMVID_TINY)
fns = get_image_files(camvid/'images')
cam_fn = fns[0]
mask_fn = camvid/'labels'/f'{cam_fn.stem}_P{cam_fn.suffix}'
def _cam_lbl(fn): return mask_fncam_dsrc = Datasets([cam_fn]*10, [PILImage.create, [_cam_lbl, PILMask.create]])
cam_tdl = TfmdDL(cam_dsrc.train, after_item=ToTensor(),
after_batch=[IntToFloatTensor(), *aug_transforms()], bs=9)
cam_tdl.show_batch(max_n=9, vmin=1, vmax=30)
点目标
mnist = untar_data(URLs.MNIST_TINY)
mnist_fn = 'images/mnist3.png'
pnts = np.array([[0,0], [0,35], [28,0], [28,35], [9, 17]])
def _pnt_lbl(fn)->None: return TensorPoint.create(pnts)pnt_dsrc = Datasets([mnist_fn]*10, [[PILImage.create, Resize((35,28))], _pnt_lbl])
pnt_tdl = TfmdDL(pnt_dsrc.train, after_item=[PointScaler(), ToTensor()],
after_batch=[IntToFloatTensor(), *aug_transforms(max_warp=0)], bs=9)
pnt_tdl.show_batch(max_n=9)
边界框
coco = untar_data(URLs.COCO_TINY)
images, lbl_bbox = get_annotations(coco/'train.json')
idx=2
coco_fn,bbox = coco/'train'/images[idx],lbl_bbox[idx]
def _coco_bb(x): return TensorBBox.create(bbox[0])
def _coco_lbl(x): return bbox[1]coco_dsrc = Datasets([coco_fn]*10, [PILImage.create, [_coco_bb], [_coco_lbl, MultiCategorize(add_na=True)]], n_inp=1)
coco_tdl = TfmdDL(coco_dsrc, bs=9, after_item=[BBoxLabeler(), PointScaler(), ToTensor(), Resize(256)],
after_batch=[IntToFloatTensor(), *aug_transforms()])
coco_tdl.show_batch(max_n=9)
导出 -
from nbdev import nbdev_export
nbdev_export()