注意
Go to the end 下载完整示例代码。
Delaunay三角剖分
这个例子演示了如何计算输入图的Delaunay三角剖分。我们首先使用随机的numpy数组生成一个2D网格上的点集,并生成一个具有这些顶点坐标但没有边的图。
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial import Delaunay
import igraph as ig
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
我们首先在二维单位立方体中生成一个随机图,固定随机种子以确保可重复性。
np.random.seed(0)
x, y = np.random.rand(2, 30)
g = ig.Graph(30)
g.vs['x'] = x
g.vs['y'] = y
因为我们已经设置了x和y顶点属性,我们可以使用
igraph.Graph.layout_auto()将它们包装成一个igraph.Layout
对象。
layout = g.layout_auto()
现在我们可以使用scipy的scipy.spatial.Delaunay类来计算Delaunay三角剖分:
给定三角剖分,我们可以将边添加到原始图中:
因为相邻的三角形共享一条边,所以图中现在包含了一些重复的边。简化图以去除这些多重边,每条边只保留一次,这是非常有用的:
g.simplify()
<igraph.Graph object at 0x7fa6d8c6cf50>
最后,绘制图形可以很好地了解三角剖分的样子:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ig.plot(
g,
layout=layout,
target=ax,
vertex_size=4,
vertex_color="lightblue",
edge_width=0.8
)
plt.show()

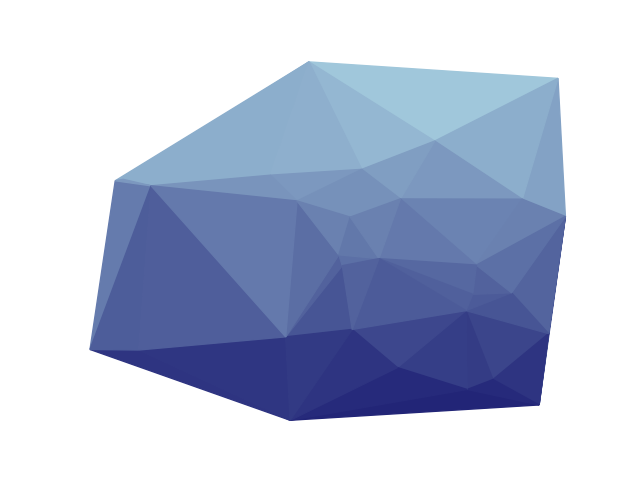
替代绘图风格
我们可以使用 matplotlib 来绘制三角形的面而不是边。首先,我们为三角形的面创建一个色调渐变:
palette = ig.GradientPalette("midnightblue", "lightblue", 100)
然后我们可以使用
matplotlib.patches.Polygon 来“绘制”三角形,并使用
igraph.plot() 来绘制图形:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for tri in delaunay.simplices:
# get the points of the triangle
tri_points = [delaunay.points[tri[i]] for i in range(3)]
# calculate the vertical center of the triangle
center = (tri_points[0][1] + tri_points[1][1] + tri_points[2][1]) / 3
# draw triangle onto axes
poly = plt.Polygon(tri_points, color=palette.get(int(center * 100)))
ax.add_patch(poly)
ig.plot(
g,
layout=layout,
target=ax,
vertex_size=0,
edge_width=0.2,
edge_color="white",
)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1))
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间: (0 分钟 1.766 秒)