import math
import numpy as np
from typing import Optional
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from neuralforecast.common._modules import (
TransEncoderLayer, TransEncoder,
TransDecoderLayer, TransDecoder,
DataEmbedding, AttentionLayer,
)
from neuralforecast.common._base_windows import BaseWindows
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE通知者
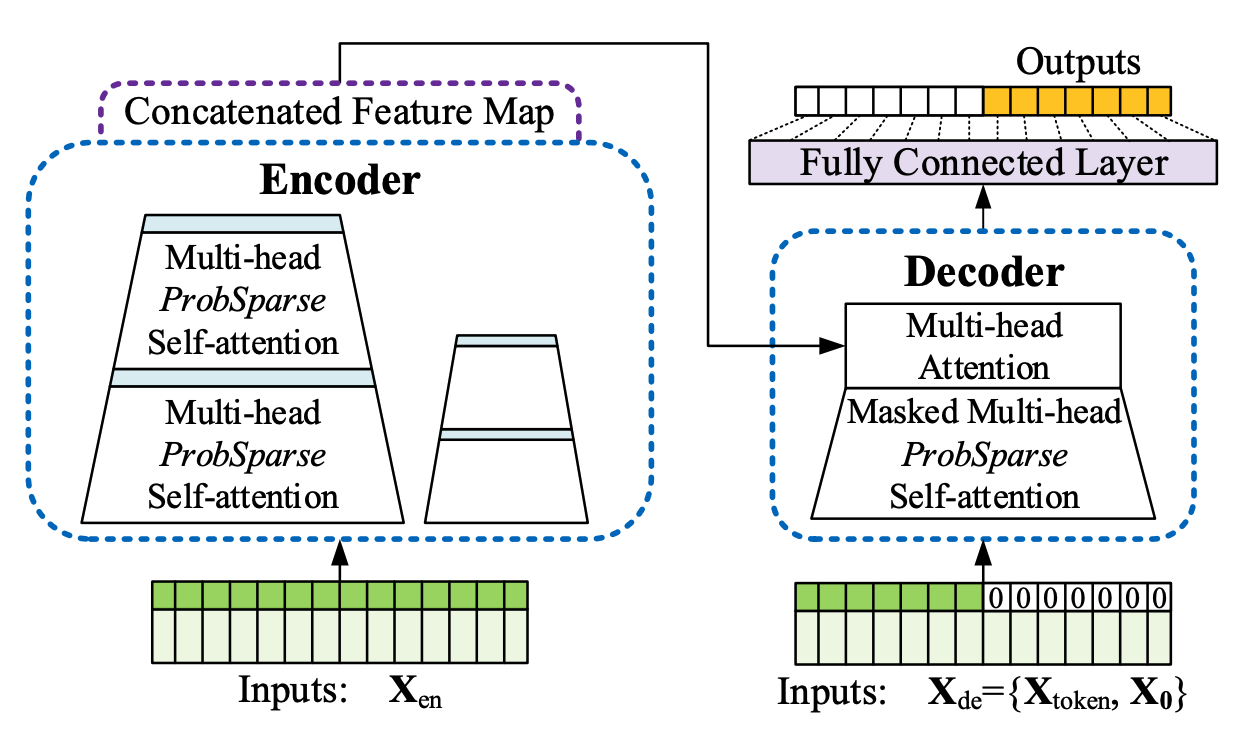
Informer模型解决了传统Transformer在长时间预测中的计算复杂性挑战。
该架构有三个显著特点: - 一个ProbSparse自注意力机制,其时间和内存复杂度为O(Llog(L))。 - 一种自注意力蒸馏过程,优先考虑注意力并高效处理长输入序列。 - 一个MLP多步解码器,在一次前向操作中预测长时间序列,而不是一步步预测。
Informer模型利用三部分的方法定义其嵌入: - 它采用来自卷积网络的编码自回归特征。 - 它使用从谐波函数派生的窗口相对位置嵌入。 - 利用从日历特征获得的绝对位置嵌入。
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_doc1. 辅助函数
class 卷积层(nn.Module):
"""
卷积层
"""
def __init__(self, c_in):
super(卷积层, self).__init__()
self.downConv = nn.Conv1d(in_channels=c_in,
out_channels=c_in,
kernel_size=3,
padding=2,
padding_mode='circular')
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm1d(c_in)
self.activation = nn.ELU()
self.maxPool = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.downConv(x.permute(0, 2, 1))
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.activation(x)
x = self.maxPool(x)
x = x.transpose(1, 2)
return xclass ProbMask():
"""
ProbMask
"""
def __init__(self, B, H, L, index, scores, device="cpu"):
_mask = torch.ones(L, scores.shape[-1], dtype=torch.bool, device=device).triu(1)
_mask_ex = _mask[None, None, :].expand(B, H, L, scores.shape[-1])
indicator = _mask_ex[torch.arange(B)[:, None, None],
torch.arange(H)[None, :, None],
index, :].to(device)
self._mask = indicator.view(scores.shape).to(device)
@property
def mask(self):
return self._mask
class ProbAttention(nn.Module):
"""
ProbAttention
"""
def __init__(self, mask_flag=True, factor=5, scale=None, attention_dropout=0.1, output_attention=False):
super(ProbAttention, self).__init__()
self.factor = factor
self.scale = scale
self.mask_flag = mask_flag
self.output_attention = output_attention
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(attention_dropout)
def _prob_QK(self, Q, K, sample_k, n_top): # n_top: c*ln(L_q)
# Q [B, H, L, D]
B, H, L_K, E = K.shape
_, _, L_Q, _ = Q.shape
# 计算采样后的Q_K
K_expand = K.unsqueeze(-3).expand(B, H, L_Q, L_K, E)
index_sample = torch.randint(L_K, (L_Q, sample_k)) # 实际U = U_部分(因子*ln(L_k))*L_q
K_sample = K_expand[:, :, torch.arange(L_Q).unsqueeze(1), index_sample, :]
Q_K_sample = torch.matmul(Q.unsqueeze(-2), K_sample.transpose(-2, -1)).squeeze()
# 找到具有稀疏性度量的Top_k查询
M = Q_K_sample.max(-1)[0] - torch.div(Q_K_sample.sum(-1), L_K)
M_top = M.topk(n_top, sorted=False)[1]
# 使用简化的Q来计算Q_K
Q_reduce = Q[torch.arange(B)[:, None, None],
torch.arange(H)[None, :, None],
M_top, :] # 因子*ln(L_q)
Q_K = torch.matmul(Q_reduce, K.transpose(-2, -1)) # 因子*ln(L_q)*L_k
return Q_K, M_top
def _get_initial_context(self, V, L_Q):
B, H, L_V, D = V.shape
if not self.mask_flag:
# V_sum = V.在倒数第二维度上求和()
V_sum = V.mean(dim=-2)
contex = V_sum.unsqueeze(-2).expand(B, H, L_Q, V_sum.shape[-1]).clone()
else: # 戴口罩
assert (L_Q == L_V) # 要求L_Q == L_V,即仅限于自注意力机制。
contex = V.cumsum(dim=-2)
return contex
def _update_context(self, context_in, V, scores, index, L_Q, attn_mask):
B, H, L_V, D = V.shape
if self.mask_flag:
attn_mask = ProbMask(B, H, L_Q, index, scores, device=V.device)
scores.masked_fill_(attn_mask.mask, -np.inf)
attn = torch.softmax(scores, dim=-1) # nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(scores)
context_in[torch.arange(B)[:, None, None],
torch.arange(H)[None, :, None],
index, :] = torch.matmul(attn, V).type_as(context_in)
if self.output_attention:
attns = (torch.ones([B, H, L_V, L_V], device=attn.device) / L_V).type_as(attn)
attns[torch.arange(B)[:, None, None], torch.arange(H)[None, :, None], index, :] = attn
return (context_in, attns)
else:
return (context_in, None)
def forward(self, queries, keys, values, attn_mask):
B, L_Q, H, D = queries.shape
_, L_K, _, _ = keys.shape
queries = queries.transpose(2, 1)
keys = keys.transpose(2, 1)
values = values.transpose(2, 1)
U_part = self.factor * np.ceil(np.log(L_K)).astype('int').item() # c*ln(L_k)
u = self.factor * np.ceil(np.log(L_Q)).astype('int').item() # c*ln(L_q)
U_part = U_part if U_part < L_K else L_K
u = u if u < L_Q else L_Q
scores_top, index = self._prob_QK(queries, keys, sample_k=U_part, n_top=u)
# 添加比例因子
scale = self.scale or 1. / math.sqrt(D)
if scale is not None:
scores_top = scores_top * scale
# 获取上下文
context = self._get_initial_context(values, L_Q)
# 使用选定的top_k查询更新上下文
context, attn = self._update_context(context, values, scores_top, index, L_Q, attn_mask)
return context.contiguous(), attn2. 信息员
class Informer(BaseWindows):
""" Informer
The Informer model tackles the vanilla Transformer computational complexity challenges for long-horizon forecasting.
The architecture has three distinctive features:
1) A ProbSparse self-attention mechanism with an O time and memory complexity Llog(L).
2) A self-attention distilling process that prioritizes attention and efficiently handles long input sequences.
3) An MLP multi-step decoder that predicts long time-series sequences in a single forward operation rather than step-by-step.
The Informer model utilizes a three-component approach to define its embedding:
1) It employs encoded autoregressive features obtained from a convolution network.
2) It uses window-relative positional embeddings derived from harmonic functions.
3) Absolute positional embeddings obtained from calendar features are utilized.
*Parameters:*<br>
`h`: int, forecast horizon.<br>
`input_size`: int, maximum sequence length for truncated train backpropagation. Default -1 uses all history.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`exclude_insample_y`: bool=False, the model skips the autoregressive features y[t-input_size:t] if True.<br>
`decoder_input_size_multiplier`: float = 0.5, .<br>
`hidden_size`: int=128, units of embeddings and encoders.<br>
`n_head`: int=4, controls number of multi-head's attention.<br>
`dropout`: float (0, 1), dropout throughout Informer architecture.<br>
`factor`: int=3, Probsparse attention factor.<br>
`conv_hidden_size`: int=32, channels of the convolutional encoder.<br>
`activation`: str=`GELU`, activation from ['ReLU', 'Softplus', 'Tanh', 'SELU', 'LeakyReLU', 'PReLU', 'Sigmoid', 'GELU'].<br>
`encoder_layers`: int=2, number of layers for the TCN encoder.<br>
`decoder_layers`: int=1, number of layers for the MLP decoder.<br>
`distil`: bool = True, wether the Informer decoder uses bottlenecks.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`valid_batch_size`: int=None, number of different series in each validation and test batch, if None uses batch_size.<br>
`windows_batch_size`: int=1024, number of windows to sample in each training batch, default uses all.<br>
`inference_windows_batch_size`: int=1024, number of windows to sample in each inference batch.<br>
`start_padding_enabled`: bool=False, if True, the model will pad the time series with zeros at the beginning, by input size.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='robust', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int=1, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
*References*<br>
- [Haoyi Zhou, Shanghang Zhang, Jieqi Peng, Shuai Zhang, Jianxin Li, Hui Xiong, Wancai Zhang. "Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.07436)<br>
"""
# 类属性
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'windows'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = False
EXOGENOUS_STAT = False
def __init__(self,
h: int,
input_size: int,
stat_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
futr_exog_list = None,
exclude_insample_y = False,
decoder_input_size_multiplier: float = 0.5,
hidden_size: int = 128,
dropout: float = 0.05,
factor: int = 3,
n_head: int = 4,
conv_hidden_size: int = 32,
activation: str = 'gelu',
encoder_layers: int = 2,
decoder_layers: int = 1,
distil: bool = True,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 5000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-4,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
valid_batch_size: Optional[int] = None,
windows_batch_size = 1024,
inference_windows_batch_size = 1024,
start_padding_enabled = False,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
super(Informer, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
futr_exog_list = futr_exog_list,
exclude_insample_y = exclude_insample_y,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
valid_batch_size=valid_batch_size,
windows_batch_size=windows_batch_size,
inference_windows_batch_size = inference_windows_batch_size,
start_padding_enabled=start_padding_enabled,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# 建筑学
self.label_len = int(np.ceil(input_size * decoder_input_size_multiplier))
if (self.label_len >= input_size) or (self.label_len <= 0):
raise Exception(f'Check decoder_input_size_multiplier={decoder_input_size_multiplier}, range (0,1)')
if activation not in ['relu', 'gelu']:
raise Exception(f'Check activation={activation}')
self.c_out = self.loss.outputsize_multiplier
self.output_attention = False
self.enc_in = 1
self.dec_in = 1
# 嵌入
self.enc_embedding = DataEmbedding(c_in=self.enc_in,
exog_input_size=self.futr_exog_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
pos_embedding=True,
dropout=dropout)
self.dec_embedding = DataEmbedding(self.dec_in,
exog_input_size=self.futr_exog_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
pos_embedding=True,
dropout=dropout)
# 编码器
self.encoder = TransEncoder(
[
TransEncoderLayer(
AttentionLayer(
ProbAttention(False, factor,
attention_dropout=dropout,
output_attention=self.output_attention),
hidden_size, n_head),
hidden_size,
conv_hidden_size,
dropout=dropout,
activation=activation
) for l in range(encoder_layers)
],
[
ConvLayer(
hidden_size
) for l in range(encoder_layers - 1)
] if distil else None,
norm_layer=torch.nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
)
# 解码器
self.decoder = TransDecoder(
[
TransDecoderLayer(
AttentionLayer(
ProbAttention(True, factor, attention_dropout=dropout, output_attention=False),
hidden_size, n_head),
AttentionLayer(
ProbAttention(False, factor, attention_dropout=dropout, output_attention=False),
hidden_size, n_head),
hidden_size,
conv_hidden_size,
dropout=dropout,
activation=activation,
)
for l in range(decoder_layers)
],
norm_layer=torch.nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size),
projection=nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.c_out, bias=True)
)
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# 解析Windows批处理文件
insample_y = windows_batch['insample_y']
#insample_mask = windows_batch['insample_mask']
#hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog']
#stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog']
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog']
insample_y = insample_y.unsqueeze(-1) # [Ws,L,1]
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
x_mark_enc = futr_exog[:,:self.input_size,:]
x_mark_dec = futr_exog[:,-(self.label_len+self.h):,:]
else:
x_mark_enc = None
x_mark_dec = None
x_dec = torch.zeros(size=(len(insample_y),self.h,1), device=insample_y.device)
x_dec = torch.cat([insample_y[:,-self.label_len:,:], x_dec], dim=1)
enc_out = self.enc_embedding(insample_y, x_mark_enc)
enc_out, _ = self.encoder(enc_out, attn_mask=None) # 注意力可视化
dec_out = self.dec_embedding(x_dec, x_mark_dec)
dec_out = self.decoder(dec_out, enc_out, x_mask=None,
cross_mask=None)
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(dec_out[:, -self.h:])
return forecastshow_doc(Informer)show_doc(Informer.fit, name='Informer.fit')show_doc(Informer.predict, name='Informer.predict')使用示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import Informer
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic, augment_calendar_df
AirPassengersPanel, calendar_cols = augment_calendar_df(df=AirPassengersPanel, freq='M')
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = Informer(h=12,
input_size=24,
hidden_size = 16,
conv_hidden_size = 32,
n_head = 2,
loss=MAE(),
futr_exog_list=calendar_cols,
scaler_type='robust',
learning_rate=1e-3,
max_steps=5,
val_check_steps=50,
early_stop_patience_steps=2)
nf = NeuralForecast(
models=[model],
freq='M'
)
nf.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = nf.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
if model.loss.is_distribution_output:
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['Informer-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['Informer-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['Informer-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.plot()
else:
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['Informer'], c='blue', label='Forecast')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()Give us a ⭐ on Github