%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2MLP
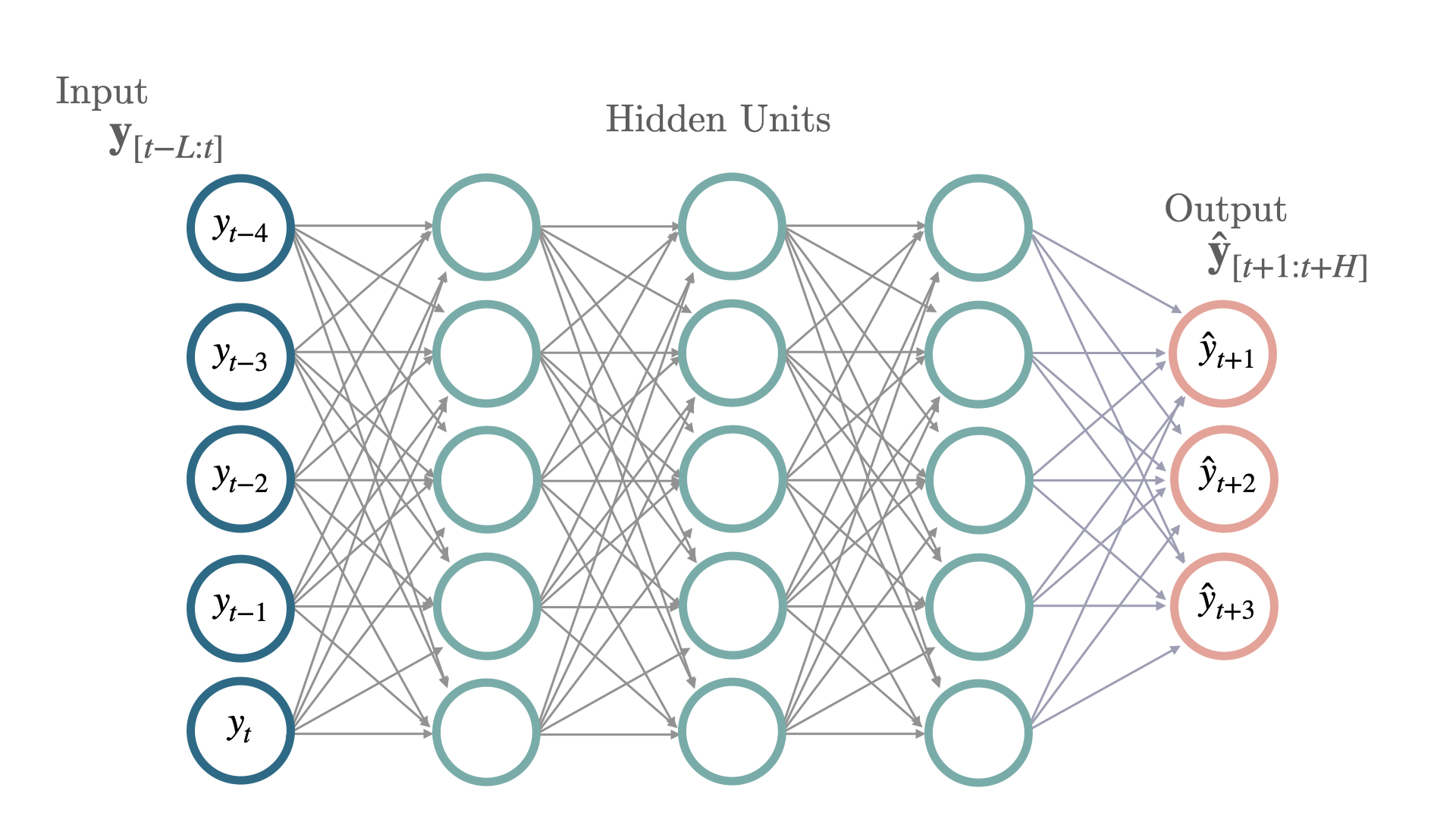
最简单的神经架构之一是多层感知器(
MLP),由堆叠的全连接神经网络组成,采用反向传播进行训练。架构中的每个节点都能够通过其激活函数建模非线性关系。新的激活函数如修正线性单元(ReLU)大大提高了拟合更深层网络的能力,克服了与Sigmoid和TanH激活相关的梯度消失问题。对于预测任务,最后一层被更改为自回归问题。
参考文献
-Rosenblatt, F. (1958). “感知器:一种用于信息存储和组织的概率模型。”
-Fukushima, K. (1975). “Cognitron:一种自组织的多层神经网络。”
-Vinod Nair, Geoffrey E. Hinton (2010). “修正线性单元改善限制玻尔兹曼机”
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_docfrom typing import Optional
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_windows import BaseWindowsclass MLP(BaseWindows):
""" MLP
Simple Multi Layer Perceptron architecture (MLP).
This deep neural network has constant units through its layers, each with
ReLU non-linearities, it is trained using ADAM stochastic gradient descent.
The network accepts static, historic and future exogenous data, flattens
the inputs and learns fully connected relationships against the target variable.
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, forecast horizon.<br>
`input_size`: int, considered autorregresive inputs (lags), y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> lags=[1,2].<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`exclude_insample_y`: bool=False, the model skips the autoregressive features y[t-input_size:t] if True.<br>
`n_layers`: int, number of layers for the MLP.<br>
`hidden_size`: int, number of units for each layer of the MLP.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`valid_batch_size`: int=None, number of different series in each validation and test batch, if None uses batch_size.<br>
`windows_batch_size`: int=1024, number of windows to sample in each training batch, default uses all.<br>
`inference_windows_batch_size`: int=-1, number of windows to sample in each inference batch, -1 uses all.<br>
`start_padding_enabled`: bool=False, if True, the model will pad the time series with zeros at the beginning, by input size.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int=1, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'windows'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = True
EXOGENOUS_STAT = True
def __init__(self,
h,
input_size,
futr_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
stat_exog_list = None,
exclude_insample_y = False,
num_layers = 2,
hidden_size = 1024,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
valid_batch_size: Optional[int] = None,
windows_batch_size = 1024,
inference_windows_batch_size = -1,
start_padding_enabled = False,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
# 继承BaseWindows类
super(MLP, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
exclude_insample_y = exclude_insample_y,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
valid_batch_size=valid_batch_size,
windows_batch_size=windows_batch_size,
inference_windows_batch_size=inference_windows_batch_size,
start_padding_enabled=start_padding_enabled,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# 建筑
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
input_size_first_layer = input_size + self.hist_exog_size * input_size + \
self.futr_exog_size*(input_size + h) + self.stat_exog_size
# 多层感知器
layers = [nn.Linear(in_features=input_size_first_layer, out_features=hidden_size)]
for i in range(num_layers - 1):
layers += [nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_size, out_features=hidden_size)]
self.mlp = nn.ModuleList(layers)
# 具有损耗相关尺寸的适配器
self.out = nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_size,
out_features=h * self.loss.outputsize_multiplier)
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# 解析Windows批处理文件
insample_y = windows_batch['insample_y']
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog']
hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog']
stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog']
# 展平 MLP 输入 [B, L+H, C] -> [B, (L+H)*C]
# 连接 [ Y_t, | X_{t-L},..., X_{t} | F_{t-L},..., F_{t+H} | S ]
batch_size = len(insample_y)
if self.hist_exog_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, hist_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, futr_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, stat_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
y_pred = insample_y.clone()
for layer in self.mlp:
y_pred = torch.relu(layer(y_pred))
y_pred = self.out(y_pred)
y_pred = y_pred.reshape(batch_size, self.h,
self.loss.outputsize_multiplier)
y_pred = self.loss.domain_map(y_pred)
return y_predshow_doc(MLP)show_doc(MLP.fit, name='MLP.fit')show_doc(MLP.predict, name='MLP.predict')import logging
import warnings
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersDF as Y_df
from neuralforecast.tsdataset import TimeSeriesDataset# 测试性能拟合/预测方法
logging.getLogger("pytorch_lightning").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
Y_train_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds<='1959-12-31'] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds>'1959-12-31'] # 12项测试
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_train_df)
model = MLP(h=12, input_size=24, max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset)
y_hat = model.predict(dataset=dataset)
Y_test_df['MLP'] = y_hat
#测试我们恢复了相同的预测
y_hat2 = model.predict(dataset=dataset)
test_eq(y_hat, y_hat2)
pd.concat([Y_train_df, Y_test_df]).drop('unique_id', axis=1).set_index('ds').plot()# 用test_size测试无泄漏
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = MLP(h=12, input_size=24, max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, test_size=12)
y_hat_test = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(
y_hat,
y_hat_test,
decimal=4
)
# 测试我们恢复相同的预测
y_hat_test2 = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
test_eq(y_hat_test, y_hat_test2)# 测试验证步骤
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_train_df)
model = MLP(h=12, input_size=24, step_size=1,
hidden_size=1024, num_layers=2,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, val_size=12)
y_hat_w_val = model.predict(dataset=dataset)
Y_test_df['MLP'] = y_hat_w_val
pd.concat([Y_train_df, Y_test_df]).drop('unique_id', axis=1).set_index('ds').plot()# 使用test_size和val_size进行无泄漏测试
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = MLP(h=12, input_size=24, step_size=1,
hidden_size=1024, num_layers=2,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, val_size=12, test_size=12)
y_hat_test_w_val = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(y_hat_test_w_val,
y_hat_w_val, decimal=4)使用示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import MLP
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import DistributionLoss
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = MLP(h=12, input_size=24,
loss=DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal', level=[80, 90]),
scaler_type='robust',
learning_rate=1e-3,
max_steps=200,
val_check_steps=10,
early_stop_patience_steps=2)
fcst = NeuralForecast(
models=[model],
freq='M'
)
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['MLP-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['MLP-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['MLP-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.plot()Give us a ⭐ on Github