%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2MLPMultivariate
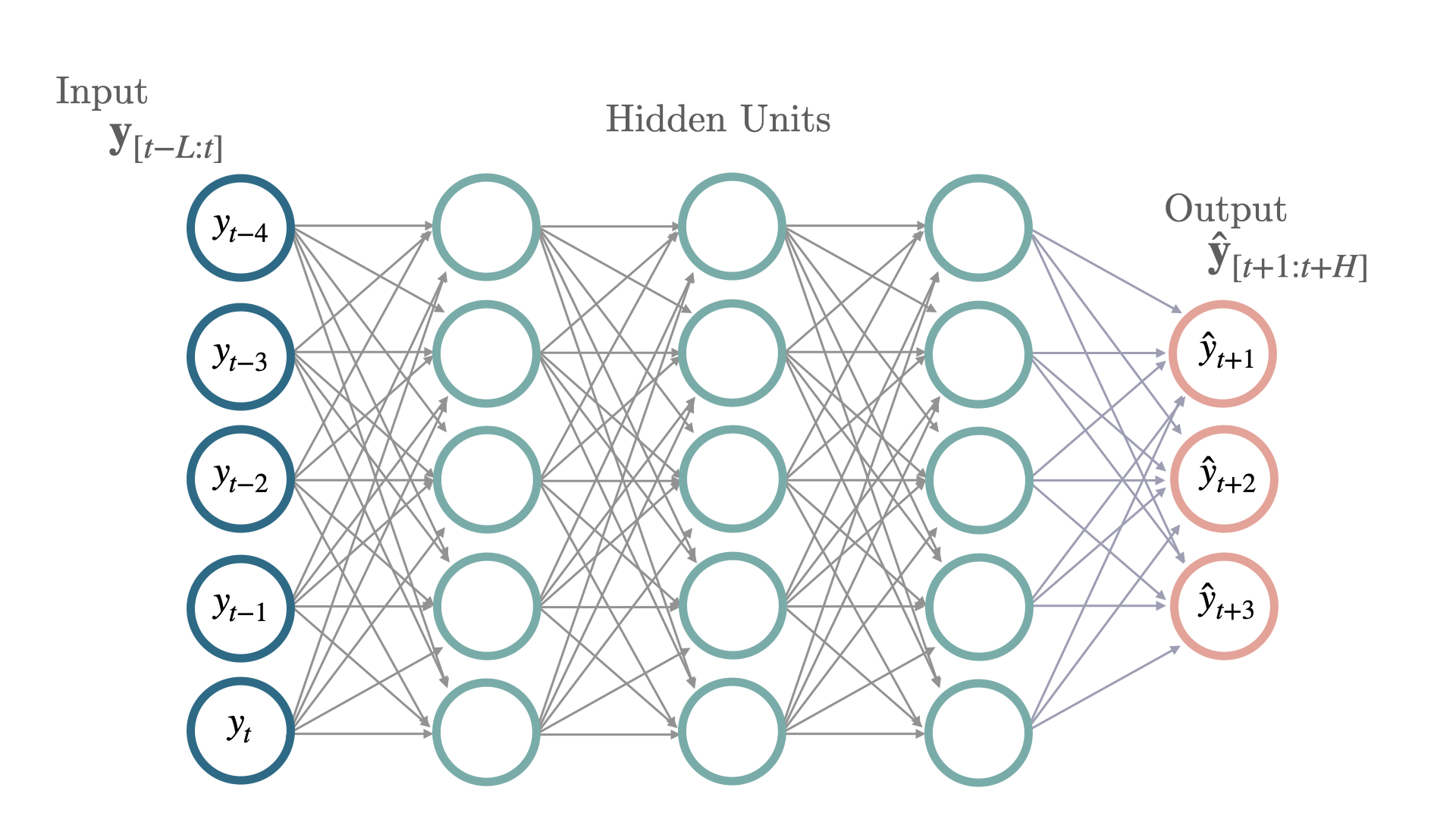
最简单的神经网络架构之一是多层感知器(
MLP),它由堆叠的全连接神经网络组成,通过反向传播进行训练。架构中的每个节点都能够通过其激活函数建模非线性关系。像修正线性单元(ReLU)这样的新型激活函数极大地提高了拟合更深网络的能力,克服了与Sigmoid和TanH激活函数相关的梯度消失问题。在预测任务中,最后一层被更改为遵循自回归问题。该版本是多变量的,表示它将联合预测预测问题的所有时间序列。
参考文献
-Rosenblatt, F. (1958). “感知器:一种用于信息存储和大脑组织的概率模型。”
-Fukushima, K. (1975). “认知层:一种自组织的多层神经网络。”
-Vinod Nair, Geoffrey E. Hinton (2010). “修正线性单元改善限制玻尔兹曼机”
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_docimport torch
import torch.nn as nn
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_multivariate import BaseMultivariateclass MLPMultivariate(BaseMultivariate):
""" MLPMultivariate
Simple Multi Layer Perceptron architecture (MLP) for multivariate forecasting.
This deep neural network has constant units through its layers, each with
ReLU non-linearities, it is trained using ADAM stochastic gradient descent.
The network accepts static, historic and future exogenous data, flattens
the inputs and learns fully connected relationships against the target variables.
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, forecast horizon.<br>
`input_size`: int, considered autorregresive inputs (lags), y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> lags=[1,2].<br>
`n_series`: int, number of time-series.<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`n_layers`: int, number of layers for the MLP.<br>
`hidden_size`: int, number of units for each layer of the MLP.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int=1, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'multivariate'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = True
EXOGENOUS_STAT = True
def __init__(self,
h,
input_size,
n_series,
futr_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
stat_exog_list = None,
num_layers = 2,
hidden_size = 1024,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
# 继承BaseMultivariate类
super(MLPMultivariate, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
n_series=n_series,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# 建筑
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
input_size_first_layer = n_series * (input_size + self.hist_exog_size * input_size + \
self.futr_exog_size*(input_size + h) + self.stat_exog_size)
# 多层感知器
layers = [nn.Linear(in_features=input_size_first_layer, out_features=hidden_size)]
for i in range(num_layers - 1):
layers += [nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_size, out_features=hidden_size)]
self.mlp = nn.ModuleList(layers)
# 具有损耗相关尺寸的适配器
self.out = nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_size,
out_features=h * self.loss.outputsize_multiplier * n_series)
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# 解析Windows批处理文件
x = windows_batch['insample_y'] # [批量大小 (B), 输入长度 (L), 序列数量 (N)]
hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog'] # [B, hist_exog_size (X), L, N]
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog'] # [B, 未来外生变量大小 (F), L + h, N]
stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog'] # [N, stat_exog_size (S)]
# 将 MLP 输入展平 [B, C, L+H, N] -> [B, C * (L+H) * N]
# 连接 [ Y^1_t, ..., Y^N_t | X^1_{t-L},..., X^1_{t}, ..., X^N_{t} | F^1_{t-L},..., F^1_{t+H}, ...., F^N_{t+H} | S^1, ..., S^N ]
batch_size = x.shape[0]
x = x.reshape(batch_size, -1)
if self.hist_exog_size > 0:
x = torch.cat(( x, hist_exog.reshape(batch_size, -1) ), dim=1)
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
x = torch.cat(( x, futr_exog.reshape(batch_size, -1) ), dim=1)
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
x = torch.cat(( x, stat_exog.reshape(batch_size, -1) ), dim=1)
for layer in self.mlp:
x = torch.relu(layer(x))
x = self.out(x)
x = x.reshape(batch_size, self.h, -1)
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(x)
# domain_map 可能在 n_series == 1 的情况下压缩了最后一个维度。
# 请注意,在元组损失的情况下,此方法会失效,因为Multivariate目前尚不支持元组损失。
if forecast.ndim == 2:
return forecast.unsqueeze(-1)
else:
return forecastshow_doc(MLPMultivariate)show_doc(MLPMultivariate.fit, name='MLPMultivariate.fit')show_doc(MLPMultivariate.predict, name='MLPMultivariate.predict')import logging
import warnings
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE, MSE, RMSE, MAPE, SMAPE, MASE, relMSE, QuantileLoss, MQLoss, DistributionLoss,PMM, GMM, NBMM, HuberLoss, TukeyLoss, HuberQLoss, HuberMQLoss# 测试损失
logging.getLogger("pytorch_lightning").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
AirPassengersStatic_single = AirPassengersStatic[AirPassengersStatic["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
Y_train_df_single = Y_train_df[Y_train_df["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
Y_test_df_single = Y_test_df[Y_test_df["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
losses = [MAE(), MSE(), RMSE(), MAPE(), SMAPE(), MASE(seasonality=12), relMSE(y_train=Y_train_df), QuantileLoss(q=0.5), MQLoss(), DistributionLoss(distribution='Bernoulli'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Poisson'), DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT'), DistributionLoss(distribution='NegativeBinomial'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Tweedie'), PMM(), GMM(), NBMM(), HuberLoss(), TukeyLoss(), HuberQLoss(q=0.5), HuberMQLoss()]
valid_losses = [MAE(), MSE(), RMSE(), MAPE(), SMAPE(), MASE(seasonality=12), relMSE(y_train=Y_train_df), QuantileLoss(q=0.5), MQLoss(), DistributionLoss(distribution='Bernoulli'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Poisson'), DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT'), DistributionLoss(distribution='NegativeBinomial'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Tweedie'), PMM(), GMM(), NBMM(), HuberLoss(), TukeyLoss(), HuberQLoss(q=0.5), HuberMQLoss()]
for loss, valid_loss in zip(losses, valid_losses):
try:
model = MLPMultivariate(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=2,
loss = loss,
valid_loss = valid_loss,
scaler_type='robust',
learning_rate=1e-3,
max_steps=2,
val_check_steps=10,
early_stop_patience_steps=2,
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
except Exception as e:
assert str(e) == f"{loss} is not supported in a Multivariate model."
# 测试 n_系列 = 1
model = MLPMultivariate(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=1,
loss = MAE(),
scaler_type='robust',
learning_rate=1e-3,
max_steps=2,
val_check_steps=10,
early_stop_patience_steps=2,
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df_single, static_df=AirPassengersStatic_single, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df_single) 使用示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import MLPMultivariate
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = MLPMultivariate(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=2,
loss = MAE(),
scaler_type='robust',
learning_rate=1e-3,
max_steps=200,
val_check_steps=10,
early_stop_patience_steps=2)
fcst = NeuralForecast(
models=[model],
freq='M'
)
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['MLPMultivariate'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.plot()Give us a ⭐ on Github