%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2NBEATSx
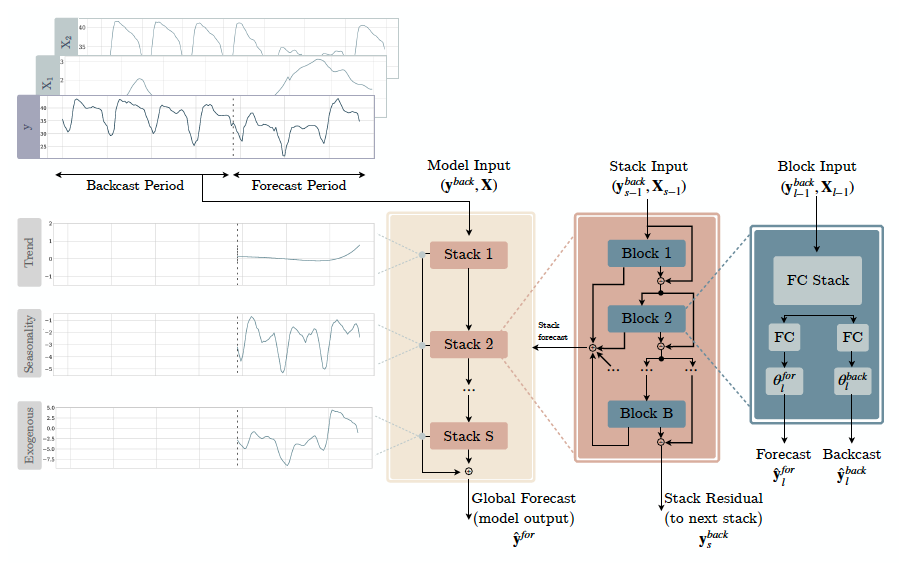
神经基扩展分析(NBEATS)是一种基于MLP的深度神经架构,具有前向和后向残差链接。该网络有两种变体:(1)在其可解释配置中,NBEATS将信号顺序投影到多项式和谐基础上,以学习趋势和季节性成分;(2)在其通用配置中,它将多项式和谐基础替换为恒等基础并增加网络的深度。带外生变量的神经基扩展分析(NBEATSx)结合了在预测时可用的外生时间变量的投影。
该方法在M3、M4和旅游竞赛数据集上表现出色,准确性提高了3%,超过了ESRNN M4竞赛的获胜者。在电力价格预测任务中,NBEATSx模型的准确性分别比ESRNN和NBEATS提高了20%和5%,比任务专用架构提高了5%。
参考文献
-Boris N. Oreshkin, Dmitri Carpov, Nicolas Chapados, Yoshua Bengio (2019). “N-BEATS: 神经基扩展分析用于可解释时间序列预测”.
-Kin G. Olivares, Cristian Challu, Grzegorz Marcjasz, Rafał Weron, Artur Dubrawski (2021). “带外生变量的神经基扩展分析:使用NBEATSx预测电力价格”.
import logging
import warnings
from fastcore.test import test_eq, test_fail
from nbdev.showdoc import show_doc
from neuralforecast.utils import generate_seriesfrom typing import Tuple, Optional
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_windows import BaseWindows在当今快节奏的世界中,时间管理已成为一项至关重要的技能。无论是在职场还是个人生活中,有效地管理时间可以显著提高生产力,减少压力,并最终提升整体生活质量。时间管理不仅仅是简单地安排任务,它还涉及优先级排序、设定现实目标以及持续的自我反思和调整。通过采用诸如番茄工作法、艾森豪威尔矩阵等策略,个人可以更好地组织他们的日常活动,确保重要任务得到优先处理,而不会被琐事所淹没。此外,利用技术工具如日历应用、任务管理软件和时间跟踪器,可以进一步优化时间管理实践,使其更加高效和有条理。总之,掌握时间管理技巧不仅能帮助我们更好地应对日常挑战,还能为实现长期目标奠定坚实基础。
logging.getLogger("pytorch_lightning").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")class IdentityBasis(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, backcast_size: int, forecast_size: int, out_features: int = 1):
super().__init__()
self.out_features = out_features
self.forecast_size = forecast_size
self.backcast_size = backcast_size
def forward(self, theta: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
backcast = theta[:, : self.backcast_size]
forecast = theta[:, self.backcast_size :]
forecast = forecast.reshape(len(forecast), -1, self.out_features)
return backcast, forecast
class TrendBasis(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
degree_of_polynomial: int,
backcast_size: int,
forecast_size: int,
out_features: int = 1,
):
super().__init__()
self.out_features = out_features
polynomial_size = degree_of_polynomial + 1
self.backcast_basis = nn.Parameter(
torch.tensor(
np.concatenate(
[
np.power(
np.arange(backcast_size, dtype=float) / backcast_size, i
)[None, :]
for i in range(polynomial_size)
]
),
dtype=torch.float32,
),
requires_grad=False,
)
self.forecast_basis = nn.Parameter(
torch.tensor(
np.concatenate(
[
np.power(
np.arange(forecast_size, dtype=float) / forecast_size, i
)[None, :]
for i in range(polynomial_size)
]
),
dtype=torch.float32,
),
requires_grad=False,
)
def forward(self, theta: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
polynomial_size = self.forecast_basis.shape[0] # [多项式规模, L+H]
backcast_theta = theta[:, :polynomial_size]
forecast_theta = theta[:, polynomial_size:]
forecast_theta = forecast_theta.reshape(
len(forecast_theta), polynomial_size, -1
)
backcast = torch.einsum("bp,pt->bt", backcast_theta, self.backcast_basis)
forecast = torch.einsum("bpq,pt->btq", forecast_theta, self.forecast_basis)
return backcast, forecast
class ExogenousBasis(nn.Module):
# 参考链接:https://github.com/cchallu/nbeatsx
def __init__(self, forecast_size: int):
super().__init__()
self.forecast_size = forecast_size
def forward(self, theta: torch.Tensor, futr_exog: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
backcast_basis = futr_exog[:, :-self.forecast_size, :].permute(0, 2, 1)
forecast_basis = futr_exog[:, -self.forecast_size:, :].permute(0, 2, 1)
cut_point = forecast_basis.shape[1]
backcast_theta=theta[:, cut_point:]
forecast_theta=theta[:, :cut_point].reshape(
len(theta), cut_point, -1
)
backcast = torch.einsum('bp,bpt->bt', backcast_theta, backcast_basis)
forecast = torch.einsum('bpq,bpt->btq', forecast_theta, forecast_basis)
return backcast, forecast
class SeasonalityBasis(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
harmonics: int,
backcast_size: int,
forecast_size: int,
out_features: int = 1,
):
super().__init__()
self.out_features = out_features
frequency = np.append(
np.zeros(1, dtype=float),
np.arange(harmonics, harmonics / 2 * forecast_size, dtype=float)
/ harmonics,
)[None, :]
backcast_grid = (
-2
* np.pi
* (np.arange(backcast_size, dtype=float)[:, None] / forecast_size)
* frequency
)
forecast_grid = (
2
* np.pi
* (np.arange(forecast_size, dtype=float)[:, None] / forecast_size)
* frequency
)
backcast_cos_template = torch.tensor(
np.transpose(np.cos(backcast_grid)), dtype=torch.float32
)
backcast_sin_template = torch.tensor(
np.transpose(np.sin(backcast_grid)), dtype=torch.float32
)
backcast_template = torch.cat(
[backcast_cos_template, backcast_sin_template], dim=0
)
forecast_cos_template = torch.tensor(
np.transpose(np.cos(forecast_grid)), dtype=torch.float32
)
forecast_sin_template = torch.tensor(
np.transpose(np.sin(forecast_grid)), dtype=torch.float32
)
forecast_template = torch.cat(
[forecast_cos_template, forecast_sin_template], dim=0
)
self.backcast_basis = nn.Parameter(backcast_template, requires_grad=False)
self.forecast_basis = nn.Parameter(forecast_template, requires_grad=False)
def forward(self, theta: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
harmonic_size = self.forecast_basis.shape[0] # [谐波大小,L+H]
backcast_theta = theta[:, :harmonic_size]
forecast_theta = theta[:, harmonic_size:]
forecast_theta = forecast_theta.reshape(len(forecast_theta), harmonic_size, -1)
backcast = torch.einsum("bp,pt->bt", backcast_theta, self.backcast_basis)
forecast = torch.einsum("bpq,pt->btq", forecast_theta, self.forecast_basis)
return backcast, forecastACTIVATIONS = ["ReLU", "Softplus", "Tanh", "SELU", "LeakyReLU", "PReLU", "Sigmoid"]
class NBEATSBlock(nn.Module):
"""
N-BEATS 模块,接受一个基函数作为参数。
"""
def __init__(
self,
input_size: int,
h: int,
futr_input_size: int,
hist_input_size: int,
stat_input_size: int,
n_theta: int,
mlp_units: list,
basis: nn.Module,
dropout_prob: float,
activation: str,
):
""" """
super().__init__()
self.dropout_prob = dropout_prob
self.futr_input_size = futr_input_size
self.hist_input_size = hist_input_size
self.stat_input_size = stat_input_size
assert activation in ACTIVATIONS, f"{activation} is not in {ACTIVATIONS}"
activ = getattr(nn, activation)()
# 块的输入向量是
# y_滞后项(输入大小)+ 历史外生变量(历史输入大小*输入大小)+
# 未来外生变量(futr_input_size*input_size)+ 静态外生变量(stat_input_size)
# [ Y_[t-L:t], X_[t-L:t], F_[t-L:t+H], S ]
input_size = (
input_size
+ hist_input_size * input_size
+ futr_input_size * (input_size + h)
+ stat_input_size
)
hidden_layers = [
nn.Linear(in_features=input_size, out_features=mlp_units[0][0])
]
for layer in mlp_units:
hidden_layers.append(nn.Linear(in_features=layer[0], out_features=layer[1]))
hidden_layers.append(activ)
if self.dropout_prob > 0:
hidden_layers.append(nn.Dropout(p=self.dropout_prob))
output_layer = [nn.Linear(in_features=mlp_units[-1][1], out_features=n_theta)]
layers = hidden_layers + output_layer
self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.basis = basis
def forward(
self,
insample_y: torch.Tensor,
futr_exog: torch.Tensor,
hist_exog: torch.Tensor,
stat_exog: torch.Tensor,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
# 将 MLP 输入展平 [B, L+H, C] -> [B, (L+H)*C]
# 连接 [ Y_t, | X_{t-L},..., X_{t} | F_{t-L},..., F_{t+H} | S ]
batch_size = len(insample_y)
if self.hist_input_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(
(insample_y, hist_exog.reshape(batch_size, -1)), dim=1
)
if self.futr_input_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(
(insample_y, futr_exog.reshape(batch_size, -1)), dim=1
)
if self.stat_input_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(
(insample_y, stat_exog.reshape(batch_size, -1)), dim=1
)
# 计算局部投影权重和投影
theta = self.layers(insample_y)
if isinstance(self.basis, ExogenousBasis):
if self.futr_input_size > 0 and self.stat_input_size > 0:
futr_exog = torch.cat(
(
futr_exog,
stat_exog.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, futr_exog.shape[1], -1)
),
dim=2
)
elif self.futr_input_size >0:
futr_exog = futr_exog
elif self.stat_input_size >0:
futr_exog = stat_exog
else:
raise(ValueError("No stats or future exogenous. ExogenousBlock not supported."))
backcast, forecast = self.basis(theta, futr_exog)
return backcast, forecast
else:
backcast, forecast = self.basis(theta)
return backcast, forecastclass NBEATSx(BaseWindows):
"""NBEATSx
The Neural Basis Expansion Analysis with Exogenous variables (NBEATSx) is a simple
and effective deep learning architecture. It is built with a deep stack of MLPs with
doubly residual connections. The NBEATSx architecture includes additional exogenous
blocks, extending NBEATS capabilities and interpretability. With its interpretable
version, NBEATSx decomposes its predictions on seasonality, trend, and exogenous effects.
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, Forecast horizon. <br>
`input_size`: int, autorregresive inputs size, y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> y_[t-2:t]=[1,2].<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`exclude_insample_y`: bool=False, the model skips the autoregressive features y[t-input_size:t] if True.<br>
`n_harmonics`: int, Number of harmonic oscillations in the SeasonalityBasis [cos(i * t/n_harmonics), sin(i * t/n_harmonics)]. Note that it will only be used if 'seasonality' is in `stack_types`.<br>
`n_polynomials`: int, Number of polynomial terms for TrendBasis [1,t,...,t^n_poly]. Note that it will only be used if 'trend' is in `stack_types`.<br>
`stack_types`: List[str], List of stack types. Subset from ['seasonality', 'trend', 'identity'].<br>
`n_blocks`: List[int], Number of blocks for each stack. Note that len(n_blocks) = len(stack_types).<br>
`mlp_units`: List[List[int]], Structure of hidden layers for each stack type. Each internal list should contain the number of units of each hidden layer. Note that len(n_hidden) = len(stack_types).<br>
`dropout_prob_theta`: float, Float between (0, 1). Dropout for N-BEATS basis.<br>
`activation`: str, activation from ['ReLU', 'Softplus', 'Tanh', 'SELU', 'LeakyReLU', 'PReLU', 'Sigmoid'].<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=3, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`valid_batch_size`: int=None, number of different series in each validation and test batch, if None uses batch_size.<br>
`windows_batch_size`: int=1024, number of windows to sample in each training batch, default uses all.<br>
`inference_windows_batch_size`: int=-1, number of windows to sample in each inference batch, -1 uses all.<br>
`start_padding_enabled`: bool=False, if True, the model will pad the time series with zeros at the beginning, by input size.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int, random seed initialization for replicability.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
**References:**<br>
-[Kin G. Olivares, Cristian Challu, Grzegorz Marcjasz, Rafał Weron, Artur Dubrawski (2021).
"Neural basis expansion analysis with exogenous variables: Forecasting electricity prices with NBEATSx".](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.05522)
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = "windows"
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = True
EXOGENOUS_STAT = True
def __init__(
self,
h,
input_size,
futr_exog_list=None,
hist_exog_list=None,
stat_exog_list=None,
exclude_insample_y=False,
n_harmonics=2,
n_polynomials=2,
stack_types: list = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality"],
n_blocks: list = [1, 1, 1],
mlp_units: list = 3 * [[512, 512]],
dropout_prob_theta=0.0,
activation="ReLU",
shared_weights=False,
loss=MAE(),
valid_loss=None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = 3,
early_stop_patience_steps: int = -1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size=32,
valid_batch_size: Optional[int] = None,
windows_batch_size: int = 1024,
inference_windows_batch_size: int = -1,
start_padding_enabled: bool = False,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = "identity",
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs,
):
# Protect horizon collapsed seasonality and trend NBEATSx-i basis
if h == 1 and (("seasonality" in stack_types) or ("trend" in stack_types)):
raise Exception(
"Horizon `h=1` incompatible with `seasonality` or `trend` in stacks"
)
# Inherit BaseWindows class
super(NBEATSx, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size = input_size,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
exclude_insample_y=exclude_insample_y,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
valid_batch_size=valid_batch_size,
windows_batch_size = windows_batch_size,
inference_windows_batch_size=inference_windows_batch_size,
start_padding_enabled=start_padding_enabled,
step_size = step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# Architecture
blocks = self.create_stack(
h=h,
input_size=input_size,
futr_input_size=self.futr_exog_size,
hist_input_size=self.hist_exog_size,
stat_input_size=self.stat_exog_size,
stack_types=stack_types,
n_blocks=n_blocks,
mlp_units=mlp_units,
dropout_prob_theta=dropout_prob_theta,
activation=activation,
shared_weights=shared_weights,
n_polynomials=n_polynomials,
n_harmonics=n_harmonics,
)
self.blocks = torch.nn.ModuleList(blocks)
# Adapter with Loss dependent dimensions
if self.loss.outputsize_multiplier > 1:
self.out = nn.Linear(
in_features=h, out_features=h * self.loss.outputsize_multiplier
)
def create_stack(
self,
h,
input_size,
stack_types,
n_blocks,
mlp_units,
dropout_prob_theta,
activation,
shared_weights,
n_polynomials,
n_harmonics,
futr_input_size,
hist_input_size,
stat_input_size,
):
block_list = []
for i in range(len(stack_types)):
for block_id in range(n_blocks[i]):
# Shared weights
if shared_weights and block_id > 0:
nbeats_block = block_list[-1]
else:
if stack_types[i] == "seasonality":
n_theta = (
2
* (self.loss.outputsize_multiplier + 1)
* int(np.ceil(n_harmonics / 2 * h) - (n_harmonics - 1))
)
basis = SeasonalityBasis(
harmonics=n_harmonics,
backcast_size=input_size,
forecast_size=h,
out_features=self.loss.outputsize_multiplier,
)
elif stack_types[i] == "trend":
n_theta = (self.loss.outputsize_multiplier + 1) * (
n_polynomials + 1
)
basis = TrendBasis(
degree_of_polynomial=n_polynomials,
backcast_size=input_size,
forecast_size=h,
out_features=self.loss.outputsize_multiplier,
)
elif stack_types[i] == "identity":
n_theta = input_size + self.loss.outputsize_multiplier * h
basis = IdentityBasis(
backcast_size=input_size,
forecast_size=h,
out_features=self.loss.outputsize_multiplier,
)
elif stack_types[i] == "exogenous":
if futr_input_size + stat_input_size > 0:
n_theta = 2*(
futr_input_size + stat_input_size
)
basis = ExogenousBasis(forecast_size=h)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Block type {stack_types[i]} not found!")
nbeats_block = NBEATSBlock(
input_size=input_size,
h=h,
futr_input_size=futr_input_size,
hist_input_size=hist_input_size,
stat_input_size=stat_input_size,
n_theta=n_theta,
mlp_units=mlp_units,
basis=basis,
dropout_prob=dropout_prob_theta,
activation=activation,
)
# Select type of evaluation and apply it to all layers of block
block_list.append(nbeats_block)
return block_list
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# Parse windows_batch
insample_y = windows_batch["insample_y"]
insample_mask = windows_batch["insample_mask"]
futr_exog = windows_batch["futr_exog"]
hist_exog = windows_batch["hist_exog"]
stat_exog = windows_batch["stat_exog"]
# NBEATSx' forward
residuals = insample_y.flip(dims=(-1,)) # 回溯初始化
insample_mask = insample_mask.flip(dims=(-1,))
forecast = insample_y[:, -1:, None] # 与Naive1同等级
block_forecasts = [forecast.repeat(1, self.h, 1)]
for i, block in enumerate(self.blocks):
backcast, block_forecast = block(
insample_y=residuals,
futr_exog=futr_exog,
hist_exog=hist_exog,
stat_exog=stat_exog,
)
residuals = (residuals - backcast) * insample_mask
forecast = forecast + block_forecast
if self.decompose_forecast:
block_forecasts.append(block_forecast)
# 调整输出领域
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(forecast)
if self.decompose_forecast:
# (批次大小, 块数, 隐藏层维度)
block_forecasts = torch.stack(block_forecasts)
block_forecasts = block_forecasts.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)
block_forecasts = block_forecasts.squeeze(-1) # 单变量输出
return block_forecasts
else:
return forecastshow_doc(NBEATSx)show_doc(NBEATSx.fit, name='NBEATSx.fit')show_doc(NBEATSx.predict, name='NBEATSx.predict')import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MQLoss
from neuralforecast.tsdataset import TimeSeriesDataset
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersDF as Y_df
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersStatic as Y_static# 月
Y_df['month'] = Y_df['ds'].dt.month
Y_df['year'] = Y_df['ds'].dt.year
Y_train_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds<Y_df['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds>=Y_df['ds'].values[-12]] # 12项测试
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(df = Y_train_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12,
input_size=24,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
windows_batch_size=None,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset)
dataset2 = dataset.update_dataset(dataset, Y_test_df)
model.set_test_size(12)
y_hat = model.predict(dataset=dataset2)
Y_test_df['NBEATSx'] = y_hat
pd.concat([Y_train_df, Y_test_df]).drop(['unique_id','month'], axis=1).set_index('ds').plot()#测试我们恢复了相同的预测
y_hat2 = model.predict(dataset=dataset2)
test_eq(y_hat, y_hat2)#测试无泄漏,测试规模为test_size
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12,
input_size=24,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
windows_batch_size=None,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, test_size=12)
y_hat_test = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(y_hat, y_hat_test, decimal=4)
#测试我们恢复了相同的预测
y_hat_test2 = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
test_eq(y_hat_test, y_hat_test2)#测试无泄漏,测试规模为test_size
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12,
input_size=24,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
windows_batch_size=None,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, test_size=12)
y_hat_test = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(y_hat, y_hat_test, decimal=4)
#测试我们恢复相同的预测
y_hat_test2 = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
test_eq(y_hat_test, y_hat_test2)# 测试季节性/趋势基础保护
test_fail(NBEATSx.__init__,
contains='Horizon `h=1` incompatible with `seasonality` or `trend` in stacks',
kwargs=dict(self=BaseWindows, h=1, input_size=4))# 测试推理_Windows_批处理大小
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12,
input_size=24,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
windows_batch_size=None,
inference_windows_batch_size=1,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, test_size=12)
y_hat_test = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
#测试 我们使用不同的inference_windows_batch_size恢复相同的预测
model.inference_windows_batch_size=-1
y_hat_test2 = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
test_eq(y_hat_test, y_hat_test2)# 检查验证检查步骤保护,使其小于最大步骤数。
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12,
input_size=24,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
windows_batch_size=None,
early_stop_patience_steps=1,
max_steps=1,
val_check_steps=5
)
model.fit(dataset=dataset, test_size=12, val_size=12)
test_eq(model.trainer_kwargs['val_check_interval'], 1)# 使用外生基进行测试,包括静态和未来外生变量
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(df = Y_train_df, static_df=Y_static)
model = NBEATSx(h=12,
input_size=24,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
stat_exog_list=['airline1', 'airline2'],
windows_batch_size=None,
max_steps=1)
model.fit(dataset=dataset)
dataset2 = dataset.update_dataset(dataset, Y_test_df)
model.set_test_size(12)
y_hat = model.predict(dataset=dataset2)
assert(len(y_hat)==12)Y_train_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds<Y_df['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds>=Y_df['ds'].values[-12]] # 12项测试
# 适合的MQ-MLP
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_train_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12, input_size=24, max_steps=1,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'],
loss=MQLoss(level=[80, 90]))
model.fit(dataset=dataset, val_size=12)
# 解析分位数预测
dataset2 = dataset.update_dataset(dataset, Y_test_df)
model.set_test_size(12)
y_hat = model.predict(dataset=dataset2)
Y_hat_df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(data=y_hat,
columns=['NBEATS'+q for q in model.loss.output_names],
index=Y_test_df.index)
# 绘制分位数预测
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df]).drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['NBEATS-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['NBEATS-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['NBEATS-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.plot()# 测试验证步骤
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_train_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12, input_size=24,
windows_batch_size=None, max_steps=1,
scaler_type='robust',
stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],
n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],
futr_exog_list=['month','year'])
model.fit(dataset=dataset, val_size=12)
dataset2 = dataset.update_dataset(dataset, Y_test_df)
model.set_test_size(12)
y_hat_w_val = model.predict(dataset=dataset2)
Y_test_df['N-BEATS'] = y_hat_w_val
pd.concat([Y_train_df, Y_test_df]).drop('unique_id', axis=1).set_index('ds').plot()
plt.grid()# 使用test_size和val_size进行无泄漏测试
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_train_df)
model = NBEATSx(h=12, input_size=24, windows_batch_size=None, max_steps=1,
scaler_type='robust',stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],n_blocks = [1,1,1,1],futr_exog_list=['month','year'])
model.fit(dataset=dataset, val_size=12)
dataset2 = dataset.update_dataset(dataset, Y_test_df)
model.set_test_size(12)
y_hat_w_val = model.predict(dataset=dataset2)
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(Y_df)
model = NBEATSx(input_size=24, h=12, windows_batch_size=None, max_steps=1,
scaler_type='robust',stack_types = ["identity", "trend", "seasonality", "exogenous"],n_blocks = [1,1,1,1], futr_exog_list=['month','year'])
model.fit(dataset=dataset, val_size=12, test_size=12)
y_hat_test_w_val = model.predict(dataset=dataset, step_size=1)
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(y_hat_test_w_val, y_hat_w_val, decimal=4)# 定性分解评价
y_hat = model.decompose(dataset=dataset)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 1, figsize=(10, 15))
ax[0].plot(Y_test_df['y'].values, label='True', color="#9C9DB2", linewidth=4)
ax[0].plot(y_hat.sum(axis=1).flatten(), label='Forecast', color="#7B3841")
ax[0].grid()
ax[0].legend(prop={'size': 20})
for label in (ax[0].get_xticklabels() + ax[0].get_yticklabels()):
label.set_fontsize(18)
ax[0].set_ylabel('y', fontsize=20)
ax[1].plot(y_hat[0,0], label='level', color="#7B3841")
ax[1].grid()
ax[1].set_ylabel('Level', fontsize=20)
ax[2].plot(y_hat[0,1], label='stack1', color="#7B3841")
ax[2].grid()
ax[2].set_ylabel('Identity', fontsize=20)
ax[3].plot(y_hat[0,2], label='stack2', color="#D9AE9E")
ax[3].grid()
ax[3].set_ylabel('Trend', fontsize=20)
ax[4].plot(y_hat[0,3], label='stack3', color="#D9AE9E")
ax[4].grid()
ax[4].set_ylabel('Seasonality', fontsize=20)
ax[5].plot(y_hat[0,4], label='stack4', color="#D9AE9E")
ax[5].grid()
ax[5].set_ylabel('Exogenous', fontsize=20)
ax[5].set_xlabel('Prediction \u03C4 \u2208 {t+1,..., t+H}', fontsize=20)使用示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import NBEATSx
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MQLoss
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = NBEATSx(h=12, input_size=24,
loss=MQLoss(level=[80, 90]),
scaler_type='robust',
dropout_prob_theta=0.5,
stat_exog_list=['airline1'],
futr_exog_list=['trend'],
max_steps=200,
val_check_steps=10,
early_stop_patience_steps=2)
nf = NeuralForecast(
models=[model],
freq='M'
)
nf.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
Y_hat_df = nf.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
# 绘制分位数预测图
Y_hat_df = Y_hat_df.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['NBEATSx-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['NBEATSx-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['NBEATSx-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.plot()Give us a ⭐ on Github