%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2NHITS
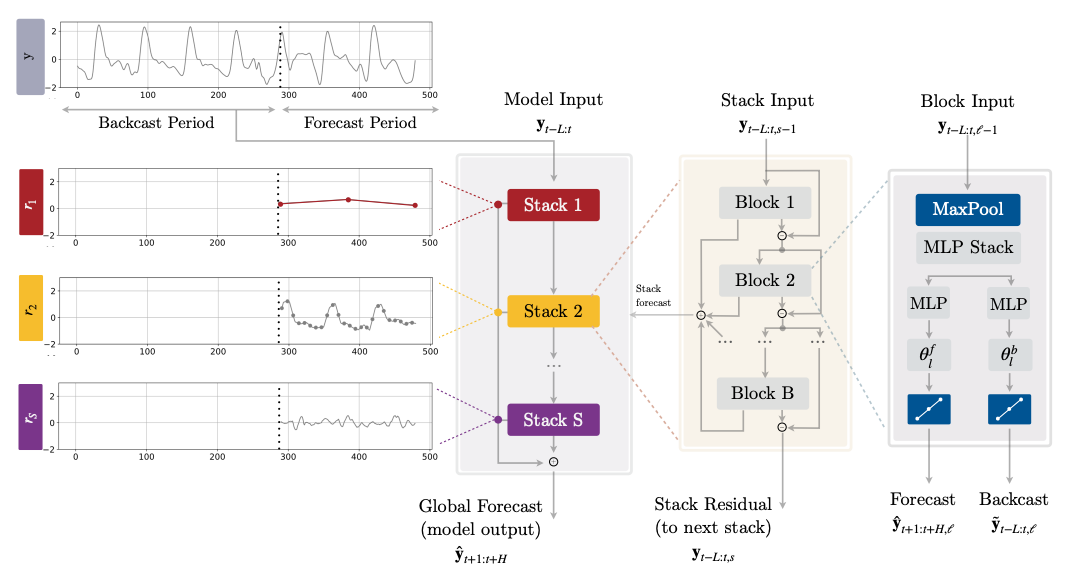
长时间预测的挑战在于预测的波动性和计算复杂性。为了解决这个问题,我们创建了时间序列的神经层次插值(NHITS)。NHITS基于NBEATS并通过层次插值和多速率输入处理来专门化其部分输出,以适应时间序列的不同频率。在长时间预测任务中,NHITS的准确性提高了25%,并在AAAI最佳论文奖Informer上实现了50倍的速度提升。
该模型由多个具有ReLU非线性的MLP组成。各个块通过双重残差堆叠原理连接,使用第l个块的回归输出\(\mathbf{\tilde{y}}_{t-L:t,l}\)和预测输出\(\mathbf{\hat{y}}_{t+1:t+H,l}\)。多速率输入池化、层次插值和回归残差连接共同促进了加法预测在不同信号带中的专门化,减少了内存占用和计算时间,从而改善了体系结构的简约性和准确性。
参考文献
-Boris N. Oreshkin, Dmitri Carpov, Nicolas Chapados, Yoshua Bengio (2019). “N-BEATS: 神经基扩展分析用于可解释的时间序列预测”.
-Cristian Challu, Kin G. Olivares, Boris N. Oreshkin, Federico Garza, Max Mergenthaler-Canseco, Artur Dubrawski (2023). “NHITS: 神经层次插值用于时间序列预测”. 接受于第37届AAAI人工智能会议.
-Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; and Zhang, W. (2020). “Informer: 超越高效变换器的长序列时间序列预测”. 2021年人工智能协会大会(AAAI 2021).
from typing import Tuple, Optional
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_windows import BaseWindowsimport logging
import warnings
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_doc
from neuralforecast.utils import generate_serieslogging.getLogger("pytorch_lightning").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
#plt.rcParams["axes.grid"]=True
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'
#plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (4,2)class _IdentityBasis(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, backcast_size: int, forecast_size: int,
interpolation_mode: str, out_features: int=1):
super().__init__()
assert (interpolation_mode in ['linear','nearest']) or ('cubic' in interpolation_mode)
self.forecast_size = forecast_size
self.backcast_size = backcast_size
self.interpolation_mode = interpolation_mode
self.out_features = out_features
def forward(self, theta: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
backcast = theta[:, :self.backcast_size]
knots = theta[:, self.backcast_size:]
# 在默认维度 dim=-1 := H 上进行插值。
knots = knots.reshape(len(knots), self.out_features, -1)
if self.interpolation_mode in ['nearest', 'linear']:
#结点 = 结点[:,None,:]
forecast = F.interpolate(knots, size=self.forecast_size, mode=self.interpolation_mode)
#预测 = 预测[:,0,:]
elif 'cubic' in self.interpolation_mode:
if self.out_features>1:
raise Exception('Cubic interpolation not available with multiple outputs.')
batch_size = len(backcast)
knots = knots[:,None,:,:]
forecast = torch.zeros((len(knots), self.forecast_size), device=knots.device)
n_batches = int(np.ceil(len(knots)/batch_size))
for i in range(n_batches):
forecast_i = F.interpolate(knots[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size],
size=self.forecast_size, mode='bicubic')
forecast[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size] += forecast_i[:,0,0,:] # [B,None,H,H] -> [B,H]
forecast = forecast[:,None,:] # [B,H] -> [B,无,H]
# [B,Q,H] -> [B,H,Q]
forecast = forecast.permute(0, 2, 1)
return backcast, forecastACTIVATIONS = ['ReLU',
'Softplus',
'Tanh',
'SELU',
'LeakyReLU',
'PReLU',
'Sigmoid']
POOLING = ['MaxPool1d',
'AvgPool1d']
class NHITSBlock(nn.Module):
"""
NHITS模块,其参数为基函数。
"""
def __init__(self,
input_size: int,
h: int,
n_theta: int,
mlp_units: list,
basis: nn.Module,
futr_input_size: int,
hist_input_size: int,
stat_input_size: int,
n_pool_kernel_size: int,
pooling_mode: str,
dropout_prob: float,
activation: str):
super().__init__()
pooled_hist_size = int(np.ceil(input_size/n_pool_kernel_size))
pooled_futr_size = int(np.ceil((input_size+h)/n_pool_kernel_size))
input_size = pooled_hist_size + \
hist_input_size * pooled_hist_size + \
futr_input_size * pooled_futr_size + stat_input_size
self.dropout_prob = dropout_prob
self.futr_input_size = futr_input_size
self.hist_input_size = hist_input_size
self.stat_input_size = stat_input_size
assert activation in ACTIVATIONS, f'{activation} is not in {ACTIVATIONS}'
assert pooling_mode in POOLING, f'{pooling_mode} is not in {POOLING}'
activ = getattr(nn, activation)()
self.pooling_layer = getattr(nn, pooling_mode)(kernel_size=n_pool_kernel_size,
stride=n_pool_kernel_size, ceil_mode=True)
# 块状多层感知器
hidden_layers = [nn.Linear(in_features=input_size,
out_features=mlp_units[0][0])]
for layer in mlp_units:
hidden_layers.append(nn.Linear(in_features=layer[0],
out_features=layer[1]))
hidden_layers.append(activ)
if self.dropout_prob>0:
#raise NotImplementedError('dropout')
hidden_layers.append(nn.Dropout(p=self.dropout_prob))
output_layer = [nn.Linear(in_features=mlp_units[-1][1], out_features=n_theta)]
layers = hidden_layers + output_layer
self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.basis = basis
def forward(self, insample_y: torch.Tensor, futr_exog: torch.Tensor,
hist_exog: torch.Tensor, stat_exog: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
# 汇集
# Pool1d 需要 3D 输入,格式为 (B, C, L),正在添加 C 维度。
insample_y = insample_y.unsqueeze(1)
insample_y = self.pooling_layer(insample_y)
insample_y = insample_y.squeeze(1)
# 将 MLP 输入展平 [B, L+H, C] -> [B, (L+H)*C]
# 连接 [ Y_t, | X_{t-L},..., X_{t} | F_{t-L},..., F_{t+H} | S ]
batch_size = len(insample_y)
if self.hist_input_size > 0:
hist_exog = hist_exog.permute(0,2,1) # [B, L, C] -> [B, C, L]
hist_exog = self.pooling_layer(hist_exog)
hist_exog = hist_exog.permute(0,2,1) # [B, C, L] -> [B, L, C]
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, hist_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
if self.futr_input_size > 0:
futr_exog = futr_exog.permute(0,2,1) # [B, L, C] -> [B, C, L]
futr_exog = self.pooling_layer(futr_exog)
futr_exog = futr_exog.permute(0,2,1) # [B, C, L] -> [B, L, C]
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, futr_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
if self.stat_input_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, stat_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
# 计算局部投影权重和投影
theta = self.layers(insample_y)
backcast, forecast = self.basis(theta)
return backcast, forecastclass NHITS(BaseWindows):
""" NHITS
The Neural Hierarchical Interpolation for Time Series (NHITS), is an MLP-based deep
neural architecture with backward and forward residual links. NHITS tackles volatility and
memory complexity challenges, by locally specializing its sequential predictions into
the signals frequencies with hierarchical interpolation and pooling.
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, Forecast horizon. <br>
`input_size`: int, autorregresive inputs size, y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> y_[t-2:t]=[1,2].<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`exclude_insample_y`: bool=False, the model skips the autoregressive features y[t-input_size:t] if True.<br>
`activation`: str, activation from ['ReLU', 'Softplus', 'Tanh', 'SELU', 'LeakyReLU', 'PReLU', 'Sigmoid'].<br>
`stack_types`: List[str], stacks list in the form N * ['identity'], to be deprecated in favor of `n_stacks`. Note that len(stack_types)=len(n_freq_downsample)=len(n_pool_kernel_size).<br>
`n_blocks`: List[int], Number of blocks for each stack. Note that len(n_blocks) = len(stack_types).<br>
`mlp_units`: List[List[int]], Structure of hidden layers for each stack type. Each internal list should contain the number of units of each hidden layer. Note that len(n_hidden) = len(stack_types).<br>
`n_freq_downsample`: List[int], list with the stack's coefficients (inverse expressivity ratios). Note that len(stack_types)=len(n_freq_downsample)=len(n_pool_kernel_size).<br>
`interpolation_mode`: str='linear', interpolation basis from ['linear', 'nearest', 'cubic'].<br>
`n_pool_kernel_size`: List[int], list with the size of the windows to take a max/avg over. Note that len(stack_types)=len(n_freq_downsample)=len(n_pool_kernel_size).<br>
`pooling_mode`: str, input pooling module from ['MaxPool1d', 'AvgPool1d'].<br>
`dropout_prob_theta`: float, Float between (0, 1). Dropout for NHITS basis.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`valid_batch_size`: int=None, number of different series in each validation and test batch, if None uses batch_size.<br>
`windows_batch_size`: int=1024, number of windows to sample in each training batch, default uses all.<br>
`inference_windows_batch_size`: int=-1, number of windows to sample in each inference batch, -1 uses all.<br>
`start_padding_enabled`: bool=False, if True, the model will pad the time series with zeros at the beginning, by input size.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
**References:**<br>
-[Cristian Challu, Kin G. Olivares, Boris N. Oreshkin, Federico Garza,
Max Mergenthaler-Canseco, Artur Dubrawski (2023). "NHITS: Neural Hierarchical Interpolation for Time Series Forecasting".
Accepted at the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12886)
"""
# 类属性
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'windows'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = True
EXOGENOUS_STAT = True
def __init__(self,
h,
input_size,
futr_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
stat_exog_list = None,
exclude_insample_y = False,
stack_types: list = ['identity', 'identity', 'identity'],
n_blocks: list = [1, 1, 1],
mlp_units: list = 3 * [[512, 512]],
n_pool_kernel_size: list = [2, 2, 1],
n_freq_downsample: list = [4, 2, 1],
pooling_mode: str = 'MaxPool1d',
interpolation_mode: str = 'linear',
dropout_prob_theta = 0.,
activation = 'ReLU',
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = 3,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
valid_batch_size: Optional[int] = None,
windows_batch_size: int = 1024,
inference_windows_batch_size: int = -1,
start_padding_enabled = False,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader = 0,
drop_last_loader = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
# 继承BaseWindows类
super(NHITS, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
exclude_insample_y = exclude_insample_y,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
windows_batch_size=windows_batch_size,
valid_batch_size=valid_batch_size,
inference_windows_batch_size=inference_windows_batch_size,
start_padding_enabled=start_padding_enabled,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# 建筑
blocks = self.create_stack(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
stack_types=stack_types,
futr_input_size=self.futr_exog_size,
hist_input_size=self.hist_exog_size,
stat_input_size=self.stat_exog_size,
n_blocks=n_blocks,
mlp_units=mlp_units,
n_pool_kernel_size=n_pool_kernel_size,
n_freq_downsample=n_freq_downsample,
pooling_mode=pooling_mode,
interpolation_mode=interpolation_mode,
dropout_prob_theta=dropout_prob_theta,
activation=activation)
self.blocks = torch.nn.ModuleList(blocks)
def create_stack(self,
h,
input_size,
stack_types,
n_blocks,
mlp_units,
n_pool_kernel_size,
n_freq_downsample,
pooling_mode,
interpolation_mode,
dropout_prob_theta,
activation,
futr_input_size, hist_input_size, stat_input_size):
block_list = []
for i in range(len(stack_types)):
for block_id in range(n_blocks[i]):
assert stack_types[i] == 'identity', f'Block type {stack_types[i]} not found!'
n_theta = (input_size + self.loss.outputsize_multiplier*max(h//n_freq_downsample[i], 1) )
basis = _IdentityBasis(backcast_size=input_size, forecast_size=h,
out_features=self.loss.outputsize_multiplier,
interpolation_mode=interpolation_mode)
nbeats_block = NHITSBlock(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
futr_input_size=futr_input_size,
hist_input_size=hist_input_size,
stat_input_size=stat_input_size,
n_theta=n_theta,
mlp_units=mlp_units,
n_pool_kernel_size=n_pool_kernel_size[i],
pooling_mode=pooling_mode,
basis=basis,
dropout_prob=dropout_prob_theta,
activation=activation)
# 选择评估类型并将其应用于块的所有层
block_list.append(nbeats_block)
return block_list
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# 解析Windows批处理文件
insample_y = windows_batch['insample_y']
insample_mask = windows_batch['insample_mask']
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog']
hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog']
stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog']
# 样本内
residuals = insample_y.flip(dims=(-1,)) #回溯初始化
insample_mask = insample_mask.flip(dims=(-1,))
forecast = insample_y[:, -1:, None] # 与Naive1同层
block_forecasts = [ forecast.repeat(1, self.h, 1) ]
for i, block in enumerate(self.blocks):
backcast, block_forecast = block(insample_y=residuals, futr_exog=futr_exog,
hist_exog=hist_exog, stat_exog=stat_exog)
residuals = (residuals - backcast) * insample_mask
forecast = forecast + block_forecast
if self.decompose_forecast:
block_forecasts.append(block_forecast)
# 调整输出领域
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(forecast)
if self.decompose_forecast:
# (批次大小, 块数, 头数, 输出维度)
block_forecasts = torch.stack(block_forecasts)
block_forecasts = block_forecasts.permute(1,0,2,3)
block_forecasts = block_forecasts.squeeze(-1) # 单变量输出
return block_forecasts
else:
return forecastshow_doc(NHITS)show_doc(NHITS.fit, name='NHITS.fit')show_doc(NHITS.predict, name='NHITS.predict')import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersDF as Y_df
from neuralforecast.tsdataset import TimeSeriesDatasetY_train_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds<Y_df['ds'].values[-24]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = Y_df[Y_df.ds>=Y_df['ds'].values[-24]] # 12项测试
dataset, *_ = TimeSeriesDataset.from_df(df = Y_train_df)
model = NHITS(h=24,
input_size=24*2,
max_steps=1,
windows_batch_size=None,
n_freq_downsample=[12,4,1],
pooling_mode='MaxPool1d')
model.fit(dataset=dataset)
y_hat = model.predict(dataset=dataset)
Y_test_df['NHITS'] = y_hat
pd.concat([Y_train_df, Y_test_df]).drop('unique_id', axis=1).set_index('ds').plot()# 定性分解评价
y_hat = model.decompose(dataset=dataset)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(5, 1, figsize=(10, 15))
ax[0].plot(Y_test_df['y'].values, label='True', color="#9C9DB2", linewidth=4)
ax[0].plot(y_hat.sum(axis=1).flatten(), label='Forecast', color="#7B3841")
ax[0].legend(prop={'size': 20})
for label in (ax[0].get_xticklabels() + ax[0].get_yticklabels()):
label.set_fontsize(18)
ax[0].set_ylabel('y', fontsize=20)
ax[1].plot(y_hat[0,0], label='level', color="#7B3841")
ax[1].set_ylabel('Level', fontsize=20)
ax[2].plot(y_hat[0,1], label='stack1', color="#7B3841")
ax[2].set_ylabel('Stack 1', fontsize=20)
ax[3].plot(y_hat[0,2], label='stack2', color="#D9AE9E")
ax[3].set_ylabel('Stack 2', fontsize=20)
ax[4].plot(y_hat[0,3], label='stack3', color="#D9AE9E")
ax[4].set_ylabel('Stack 3', fontsize=20)
ax[4].set_xlabel('Prediction \u03C4 \u2208 {t+1,..., t+H}', fontsize=20)使用示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import NHITS
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import DistributionLoss
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = NHITS(h=12,
input_size=24,
loss=DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT', level=[80, 90], return_params=True),
stat_exog_list=['airline1'],
futr_exog_list=['trend'],
n_freq_downsample=[2, 1, 1],
scaler_type='robust',
max_steps=200,
early_stop_patience_steps=2,
inference_windows_batch_size=1,
val_check_steps=10,
learning_rate=1e-3)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
# 绘制分位数预测图
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['NHITS-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['NHITS-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['NHITS-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.plot()Give us a ⭐ on Github