from typing import Optional
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.fft
from neuralforecast.common._modules import DataEmbedding
from neuralforecast.common._base_windows import BaseWindows
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAETimesNet
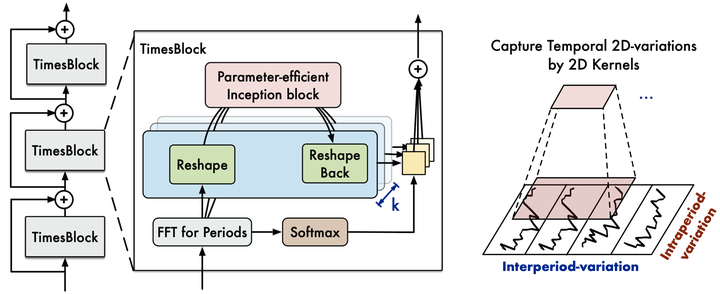
TimesNet单变量模型解决了对多个时段和跨时段时间变化建模的挑战。
该架构具有以下独特特征: - 一个嵌入层,将输入序列映射到潜在空间。 - 基于FFT找到的周期,将一维时间序列转换为二维张量。 - 一个卷积Inception模块,捕捉不同尺度和周期之间的时间变化。
参考文献
- Haixu Wu和Tengge Hu和Yong Liu和Hang Zhou和Jianmin Wang和Mingsheng Long. TimesNet:用于一般时间序列分析的时间二维变化建模 - 基于https://github.com/thuml/Time-Series-Library中的实现(许可: https://github.com/thuml/Time-Series-Library/blob/main/LICENSE)
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_doc1. 辅助函数
class Inception_Block_V1(nn.Module):
"""
Inception_Block_V1
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_kernels=6, init_weight=True):
super(Inception_Block_V1, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.num_kernels = num_kernels
kernels = []
for i in range(self.num_kernels):
kernels.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2 * i + 1, padding=i))
self.kernels = nn.ModuleList(kernels)
if init_weight:
self._initialize_weights()
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
res_list = []
for i in range(self.num_kernels):
res_list.append(self.kernels[i](x))
res = torch.stack(res_list, dim=-1).mean(-1)
return resdef FFT_for_Period(x, k=2):
# [B, T, C]
xf = torch.fft.rfft(x, dim=1)
# 通过振幅寻找周期
frequency_list = abs(xf).mean(0).mean(-1)
frequency_list[0] = 0
_, top_list = torch.topk(frequency_list, k)
top_list = top_list.detach().cpu().numpy()
period = x.shape[1] // top_list
return period, abs(xf).mean(-1)[:, top_list]
class 时间区块(nn.Module):
"""
时间区块
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, h, k, hidden_size, conv_hidden_size, num_kernels):
super(时间区块, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.h = h
self.k = k
# 参数高效设计
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
Inception_Block_V1(hidden_size, conv_hidden_size,
num_kernels=num_kernels),
nn.GELU(),
Inception_Block_V1(conv_hidden_size, hidden_size,
num_kernels=num_kernels)
)
def forward(self, x):
B, T, N = x.size()
period_list, period_weight = FFT_for_Period(x, self.k)
res = []
for i in range(self.k):
period = period_list[i]
# 填充
if (self.input_size + self.h) % period != 0:
length = (
((self.input_size + self.h) // period) + 1) * period
padding = torch.zeros([x.shape[0], (length - (self.input_size + self.h)), x.shape[2]], device=x.device)
out = torch.cat([x, padding], dim=1)
else:
length = (self.input_size + self.h)
out = x
# 重塑
out = out.reshape(B, length // period, period,
N).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
# 2D卷积:从1D变体到2D变体
out = self.conv(out)
# 重塑回原状
out = out.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(B, -1, N)
res.append(out[:, :(self.input_size + self.h), :])
res = torch.stack(res, dim=-1)
# 自适应聚合
period_weight = F.softmax(period_weight, dim=1)
period_weight = period_weight.unsqueeze(
1).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, T, N, 1)
res = torch.sum(res * period_weight, -1)
# 残差连接
res = res + x
return res2. TimesNet
class TimesNet(BaseWindows):
""" TimesNet
The TimesNet univariate model tackles the challenge of modeling multiple intraperiod and interperiod temporal variations.
Parameters
----------
h : int
Forecast horizon.
input_size : int
Length of input window (lags).
futr_exog_list : list of str, optional (default=None)
Future exogenous columns.
hist_exog_list : list of str, optional (default=None)
Historic exogenous columns.
stat_exog_list : list of str, optional (default=None)
Static exogenous columns.
exclude_insample_y : bool (default=False)
The model skips the autoregressive features y[t-input_size:t] if True
hidden_size : int (default=64)
Size of embedding for embedding and encoders.
dropout : float between [0, 1) (default=0.1)
Dropout for embeddings.
conv_hidden_size: int (default=64)
Channels of the Inception block.
top_k: int (default=5)
Number of periods.
num_kernels: int (default=6)
Number of kernels for the Inception block.
encoder_layers : int, (default=2)
Number of encoder layers.
loss: PyTorch module (default=MAE())
Instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).
valid_loss: PyTorch module (default=None, uses loss)
Instantiated validation loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).
max_steps: int (default=1000)
Maximum number of training steps.
learning_rate : float (default=1e-4)
Learning rate.
num_lr_decays`: int (default=-1)
Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps. If -1, no learning rate decay is performed.
early_stop_patience_steps : int (default=-1)
Number of validation iterations before early stopping. If -1, no early stopping is performed.
val_check_steps : int (default=100)
Number of training steps between every validation loss check.
batch_size : int (default=32)
Number of different series in each batch.
valid_batch_size : int (default=None)
Number of different series in each validation and test batch, if None uses batch_size.
windows_batch_size : int (default=64)
Number of windows to sample in each training batch.
inference_windows_batch_size : int (default=256)
Number of windows to sample in each inference batch.
start_padding_enabled : bool (default=False)
If True, the model will pad the time series with zeros at the beginning by input size.
scaler_type : str (default='standard')
Type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
random_seed : int (default=1)
Random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.
num_workers_loader : int (default=0)
Workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.
drop_last_loader : bool (default=False)
If True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional (default=None)
User specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional (defualt=None)
List of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
**trainer_kwargs
Keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer)
References
----------
Haixu Wu and Tengge Hu and Yong Liu and Hang Zhou and Jianmin Wang and Mingsheng Long. TimesNet: Temporal 2D-Variation Modeling for General Time Series Analysis. https://openreview.net/pdf?id=ju_Uqw384Oq
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'windows'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = False
EXOGENOUS_STAT = False
def __init__(self,
h: int,
input_size: int,
stat_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
futr_exog_list = None,
exclude_insample_y = False,
hidden_size: int = 64,
dropout: float = 0.1,
conv_hidden_size: int = 64,
top_k: int = 5,
num_kernels: int = 6,
encoder_layers: int = 2,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-4,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
valid_batch_size: Optional[int] = None,
windows_batch_size = 64,
inference_windows_batch_size = 256,
start_padding_enabled = False,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'standard',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
super(TimesNet, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
futr_exog_list = futr_exog_list,
exclude_insample_y = exclude_insample_y,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
windows_batch_size=windows_batch_size,
valid_batch_size=valid_batch_size,
inference_windows_batch_size=inference_windows_batch_size,
start_padding_enabled = start_padding_enabled,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# Architecture
self.c_out = self.loss.outputsize_multiplier
self.enc_in = 1
self.dec_in = 1
self.model = nn.ModuleList([TimesBlock(input_size=input_size,
h=h,
k=top_k,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
conv_hidden_size=conv_hidden_size,
num_kernels=num_kernels)
for _ in range(encoder_layers)])
self.enc_embedding = DataEmbedding(c_in=self.enc_in,
exog_input_size=self.futr_exog_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
pos_embedding=True, # Original implementation uses true
dropout=dropout)
self.encoder_layers = encoder_layers
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.predict_linear = nn.Linear(self.input_size, self.h + self.input_size)
self.projection = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.c_out, bias=True)
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# Parse windows_batch
insample_y = windows_batch['insample_y']
#insample_mask = windows_batch['insample_mask']
#hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog']
#stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog']
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog']
# 解析输入
insample_y = insample_y.unsqueeze(-1) # [Ws,L,1]
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
x_mark_enc = futr_exog[:,:self.input_size,:]
else:
x_mark_enc = None
# 嵌入
enc_out = self.enc_embedding(insample_y, x_mark_enc)
enc_out = self.predict_linear(enc_out.permute(0, 2, 1)).permute(0, 2, 1) # 对齐时间维度
# TimesNet
for i in range(self.encoder_layers):
enc_out = self.layer_norm(self.model[i](enc_out))
# 项目回顾
dec_out = self.projection(enc_out)
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(dec_out[:, -self.h:])
return forecastshow_doc(TimesNet)show_doc(TimesNet.fit, name='TimesNet.fit')show_doc(TimesNet.predict, name='TimesNet.predict')使用示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import DistributionLoss
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic, augment_calendar_df
AirPassengersPanel, calendar_cols = augment_calendar_df(df=AirPassengersPanel, freq='M')
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = TimesNet(h=12,
input_size=24,
hidden_size = 16,
conv_hidden_size = 32,
loss=DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal', level=[80, 90]),
futr_exog_list=calendar_cols,
scaler_type='standard',
learning_rate=1e-3,
max_steps=5,
val_check_steps=50,
early_stop_patience_steps=2)
nf = NeuralForecast(
models=[model],
freq='M'
)
nf.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = nf.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
if model.loss.is_distribution_output:
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['TimesNet-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['TimesNet-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['TimesNet-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.plot()
else:
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['TimesNet'], c='blue', label='Forecast')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()Give us a ⭐ on Github