%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2TSMixerx
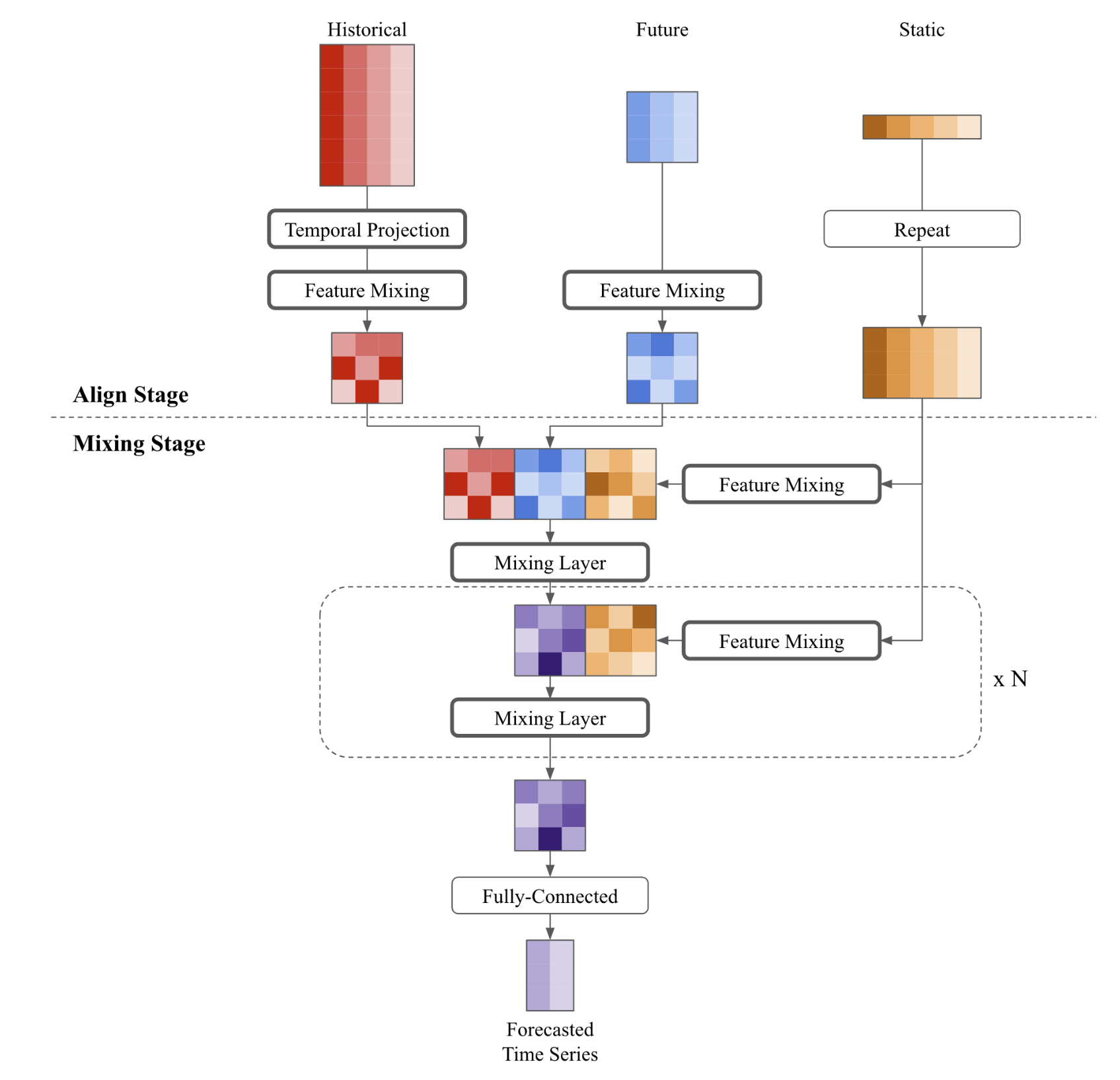
时间序列混合外生模型 (
TSMixerx) 是一种基于多层感知器(MLP)的多变量时间序列预测模型,具有额外外生输入的能力。TSMixerx通过反复结合时间和特征信息,联合学习时间序列的时间和横截面表示,采用堆叠混合层。一个混合层由一个顺序的时间和特征多层感知器(MLP)组成。
参考文献
- Chen, Si-An, Chun-Liang Li, Nate Yoder, Sercan O. Arik, 和 Tomas Pfister (2023). “TSMixer: 一种用于时间序列预测的全MLP架构。”
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_docimport torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_multivariate import BaseMultivariate1. 辅助函数
1.1 混合层
混合层由一个顺序的时间和特征多层感知器(MLP)组成。
class 时间混合(nn.Module):
"""
时间混合
"""
def __init__(self, num_features, h, dropout):
super().__init__()
self.temporal_norm = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape=(h, num_features))
self.temporal_lin = nn.Linear(h, h)
self.temporal_drop = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, input):
x = input.permute(0, 2, 1) # [B, h, C] -> [B, C, h]
x = F.relu(self.temporal_lin(x)) # [B, C, h] -> [B, C, h]
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) # [B, C, h] -> [B, h, C]
x = self.temporal_drop(x) # [B, h, C] -> [B, h, C]
return self.temporal_norm(x + input)
class 特征混合(nn.Module):
"""
特征混合
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, h, dropout, ff_dim):
super().__init__()
self.feature_lin_1 = nn.Linear(in_features=in_features,
out_features=ff_dim)
self.feature_lin_2 = nn.Linear(in_features=ff_dim,
out_features=out_features)
self.feature_drop_1 = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
self.feature_drop_2 = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
self.linear_project_residual = False
if in_features != out_features:
self.project_residual = nn.Linear(in_features = in_features,
out_features = out_features)
self.linear_project_residual = True
self.feature_norm = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape=(h, out_features))
def forward(self, input):
x = F.relu(self.feature_lin_1(input)) # [B, h, C_in] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
x = self.feature_drop_1(x) # [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
x = self.feature_lin_2(x) # [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, C_out]
x = self.feature_drop_2(x) # [B, h, C_out] -> [B, h, C_out]
if self.linear_project_residual:
input = self.project_residual(input) # [B, h, C_in] -> [B, h, C_out]
return self.feature_norm(x + input)
class 混合层(nn.Module):
"""
混合层
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, h, dropout, ff_dim):
super().__init__()
# 混合层由时间混合器和特征混合器组成。
self.temporal_mixer = 时间混合(num_features=in_features,
h=h,
dropout=dropout)
self.feature_mixer = 特征混合(in_features=in_features,
out_features=out_features,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
def forward(self, input):
x = self.temporal_mixer(input) # [B, h, C_in] -> [B, h, C_in]
x = self.feature_mixer(x) # [B, h, C_in] -> [B, h, C_out]
return x
class 混合层与静态外生变量(nn.Module):
"""
混合层与静态外生变量
"""
def __init__(self, h, dropout, ff_dim, stat_input_size):
super().__init__()
# 静态外生变量的特征混合器
self.feature_mixer_stat = 特征混合(in_features=stat_input_size,
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
# 混合层由时间混合器和特征混合器组成。
self.temporal_mixer = 时间混合(num_features=2 * ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout)
self.feature_mixer = 特征混合(in_features=2 * ff_dim,
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
def forward(self, inputs):
input, stat_exog = inputs
x_stat = self.feature_mixer_stat(stat_exog) # [B, h, S] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
x = torch.cat((input, x_stat), dim=2) # [B, h, ff_dim] + [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, 2 * ff_dim]
x = self.temporal_mixer(x) # [B, h, 2 * ff_dim] -> [B, h, 2 * ff_dim]
x = self.feature_mixer(x) # [B, h, 2 * ff_dim] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
return (x, stat_exog)1.2 可逆实例归一化
一种可逆的实例归一化层,基于这个参考实现。
class ReversibleInstanceNorm1d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_series, eps=1e-5):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones((1, 1, 1, n_series)))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, 1, 1, n_series)))
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
# 批量统计
self.batch_mean = torch.mean(x, axis=2, keepdim=True).detach()
self.batch_std = torch.sqrt(torch.var(x, axis=2, keepdim=True, unbiased=False) + self.eps).detach()
# 实例归一化
x = x - self.batch_mean
x = x / self.batch_std
x = x * self.weight
x = x + self.bias
return x
def reverse(self, x):
# 逆转正常化
x = x - self.bias
x = x / self.weight
x = x * self.batch_std
x = x + self.batch_mean
return x2. 模型
class TSMixerx(BaseMultivariate):
""" TSMixerx
Time-Series Mixer exogenous (`TSMixerx`) is a MLP-based multivariate time-series forecasting model, with capability for additional exogenous inputs. `TSMixerx` jointly learns temporal and cross-sectional representations of the time-series by repeatedly combining time- and feature information using stacked mixing layers. A mixing layer consists of a sequential time- and feature Multi Layer Perceptron (`MLP`).
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, forecast horizon.<br>
`input_size`: int, considered autorregresive inputs (lags), y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> lags=[1,2].<br>
`n_series`: int, number of time-series.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`n_block`: int=2, number of mixing layers in the model.<br>
`ff_dim`: int=64, number of units for the second feed-forward layer in the feature MLP.<br>
`dropout`: float=0.0, dropout rate between (0, 1) .<br>
`revin`: bool=True, if True uses Reverse Instance Normalization on `insample_y` and applies it to the outputs.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int=1, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
**References:**<br>
- [Chen, Si-An, Chun-Liang Li, Nate Yoder, Sercan O. Arik, and Tomas Pfister (2023). "TSMixer: An All-MLP Architecture for Time Series Forecasting."](http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.06053)
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'multivariate'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = True
EXOGENOUS_STAT = True
def __init__(self,
h,
input_size,
n_series,
futr_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
stat_exog_list = None,
n_block = 2,
ff_dim = 64,
dropout = 0.0,
revin = True,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
# Inherit BaseMultvariate class
super(TSMixerx, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
n_series=n_series,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
random_seed=random_seed,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# Reversible InstanceNormalization layer
self.revin = revin
if self.revin:
self.norm = ReversibleInstanceNorm1d(n_series = n_series)
# Forecast horizon
self.h = h
# Temporal projection and feature mixing of historical variables
self.temporal_projection = nn.Linear(in_features=input_size,
out_features=h)
self.feature_mixer_hist = FeatureMixing(in_features=n_series * (1 + self.hist_exog_size + self.futr_exog_size),
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
first_mixing_ff_dim_multiplier = 1
# Feature mixing of future variables
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
self.feature_mixer_futr = FeatureMixing(in_features = n_series * self.futr_exog_size,
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
first_mixing_ff_dim_multiplier += 1
# Feature mixing of static variables
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
self.feature_mixer_stat = FeatureMixing(in_features=self.stat_exog_size * n_series,
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
first_mixing_ff_dim_multiplier += 1
# 第一混合层
self.first_mixing = MixingLayer(in_features = first_mixing_ff_dim_multiplier * ff_dim,
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
# Mixing layer block
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
mixing_layers = [MixingLayerWithStaticExogenous(
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim,
stat_input_size=self.stat_exog_size * n_series)
for _ in range(n_block)]
else:
mixing_layers = [MixingLayer(in_features=ff_dim,
out_features=ff_dim,
h=h,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
for _ in range(n_block)]
self.mixing_block = nn.Sequential(*mixing_layers)
# Linear output with Loss dependent dimensions
self.out = nn.Linear(in_features=ff_dim,
out_features=self.loss.outputsize_multiplier * n_series)
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# Parse batch
x = windows_batch['insample_y'] # [batch_size (B), input_size (L), n_series (N)]
hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog'] # [B, hist_exog_size (X), L, N]
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog'] # [B, futr_exog_size (F), L + h, N]
stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog'] # [N, stat_exog_size (S)]
batch_size, input_size = x.shape[:2]
# 为x添加通道维度
x = x.unsqueeze(1) # [B, L, N] -> [B, 1, L, N]
# 将revin应用于x
if self.revin:
x = self.norm(x) # [批次, 1, 长度, 嵌入维度] -> [批次, 1, 长度, 嵌入维度]
# 将 x 与历史外生变量连接
if self.hist_exog_size > 0:
x = torch.cat((x, hist_exog), dim=1) # [B, 1, L, N] + [B, X, L, N] -> [B, 1 + X, L, N]
# 将x与输入序列的未来外生变量连接起来
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
futr_exog_hist = futr_exog[:, :, :input_size] # [B, F, L + h, N] -> [B, F, L, N]
x = torch.cat((x, futr_exog_hist), dim=1) # [B, 1 + X, L, N] + [B, F, L, N] -> [B, 1 + X + F, L, N]
# x的时间投影与特征混合
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2) # [B, 1 + X + F, L, N] -> [B, 1 + X + F, N, L]
x = self.temporal_projection(x) # [B, 1 + X + F, N, L] -> [B, 1 + X + F, N, h]
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # [B, 1 + X + F, N, h] -> [B, h, 1 + X + F, N]
x = x.reshape(batch_size, self.h, -1) # [B, h, 1 + X + F, N] -> [B, h, (1 + X + F) * N]
x = self.feature_mixer_hist(x) # [B, h, (1 + X + F) * N] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
# 将x与输出范围的未来外生变量连接起来
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
x_futr = futr_exog[:, :, input_size:] # [B, F, L + h, N] -> [B, F, h, N]
x_futr = x_futr.permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # [B, F, h, N] -> [B, h, F, N]
x_futr = x_futr.reshape(batch_size,
self.h, -1) # [B, h, N, F] -> [B, h, N * F]
x_futr = self.feature_mixer_futr(x_futr) # [B, h, N * F] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
x = torch.cat((x, x_futr), dim=2) # [B, h, ff_dim] + [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, 2 * ff_dim]
# 将 x 与静态外生变量连接起来
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
stat_exog = stat_exog.reshape(-1) # [N, S] -> [N * S]
stat_exog = stat_exog.unsqueeze(0)\
.unsqueeze(1)\
.repeat(batch_size,
self.h,
1) # [N * S] -> [B, h, N * S]
x_stat = self.feature_mixer_stat(stat_exog) # [B, h, N * S] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
x = torch.cat((x, x_stat), dim=2) # [B, h, 2 * ff_dim] + [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, 3 * ff_dim]
# 第一混合层
x = self.first_mixing(x) # [B, h, 3 * ff_dim] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
# N个混合层块
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
x, _ = self.mixing_block((x, stat_exog)) # [B, h, ff_dim], [B, h, N * S] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
else:
x = self.mixing_block(x) # [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, ff_dim]
# 全连接输出层
x = self.out(x) # [B, h, ff_dim] -> [B, h, N * n_outputs]
# 输出端的反向实例归一化
if self.revin:
x = x.reshape(batch_size,
self.h,
self.loss.outputsize_multiplier,
-1) # [B, h, N * n_outputs] -> [B, h, n_outputs, N]
x = self.norm.reverse(x)
x = x.reshape(batch_size, self.h, -1) # [B, h, n_outputs, N] -> [B, h, n_outputs * N]
# 映射到损失域
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(x)
# 在 n_series == 1 的情况下,domain_map 可能已经压缩了最后一个维度。
# 请注意,在元组损失的情况下,此方法会失败,但多元损失尚不支持元组损失。
if forecast.ndim == 2:
return forecast.unsqueeze(-1)
else:
return forecastshow_doc(TSMixerx)show_doc(TSMixerx.fit, name='TSMixerx.fit')show_doc(TSMixerx.predict, name='TSMixerx.predict')import logging
import warnings
import pandas as pd
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic, generate_series
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE, MSE, RMSE, MAPE, SMAPE, MASE, relMSE, QuantileLoss, MQLoss, DistributionLoss,PMM, GMM, NBMM, HuberLoss, TukeyLoss, HuberQLoss, HuberMQLoss
# 测试损失
logging.getLogger("pytorch_lightning").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
AirPassengersStatic_single = AirPassengersStatic[AirPassengersStatic["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
Y_train_df_single = Y_train_df[Y_train_df["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
Y_test_df_single = Y_test_df[Y_test_df["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
losses = [MAE(), MSE(), RMSE(), MAPE(), SMAPE(), MASE(seasonality=12), relMSE(y_train=Y_train_df), QuantileLoss(q=0.5), MQLoss(), DistributionLoss(distribution='Bernoulli'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Poisson'), DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT'), DistributionLoss(distribution='NegativeBinomial'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Tweedie'), PMM(), GMM(), NBMM(), HuberLoss(), TukeyLoss(), HuberQLoss(q=0.5), HuberMQLoss()]
valid_losses = [MAE(), MSE(), RMSE(), MAPE(), SMAPE(), MASE(seasonality=12), relMSE(y_train=Y_train_df), QuantileLoss(q=0.5), MQLoss(), DistributionLoss(distribution='Bernoulli'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Poisson'), DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT'), DistributionLoss(distribution='NegativeBinomial'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Tweedie'), PMM(), GMM(), NBMM(), HuberLoss(), TukeyLoss(), HuberQLoss(q=0.5), HuberMQLoss()]
for loss, valid_loss in zip(losses, valid_losses):
try:
model = TSMixerx(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=2,
stat_exog_list=['airline1'],
futr_exog_list=['trend'],
n_block=4,
ff_dim=4,
revin=True,
scaler_type='standard',
max_steps=2,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
batch_size=32
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
except Exception as e:
assert str(e) == f"{loss} is not supported in a Multivariate model."
# 测试 n_系列 = 1
model = TSMixerx(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=1,
stat_exog_list=['airline1'],
futr_exog_list=['trend'],
n_block=4,
ff_dim=4,
revin=True,
scaler_type='standard',
max_steps=2,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=MAE(),
valid_loss=MAE(),
batch_size=32
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df_single, static_df=AirPassengersStatic_single, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df_single)
# 测试 n_系列 > 1024
# 查看问题:https://github.com/Nixtla/neuralforecast/issues/948
n_series = 1111
Y_df, S_df = generate_series(n_series=n_series, n_temporal_features=2, n_static_features=2)
model = TSMixerx(
h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=n_series,
stat_exog_list=['static_0', 'static_1'],
hist_exog_list=["temporal_0", "temporal_1"],
n_block=4,
ff_dim=3,
revin=True,
scaler_type="standard",
max_steps=5,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=MAE(),
valid_loss=MAE(),
batch_size=32,
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq="D")
fcst.fit(df=Y_df, static_df=S_df, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict()3. 使用示例
训练模型并使用 predict 方法预测未来值。
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import TSMixerx
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = TSMixerx(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=2,
stat_exog_list=['airline1'],
futr_exog_list=['trend'],
n_block=4,
ff_dim=4,
revin=True,
scaler_type='standard',
max_steps=500,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=MAE(),
valid_loss=MAE(),
batch_size=32
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
# 情节预测
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (20, 7))
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['TSMixerx'], c='blue', label='Forecast')
ax.set_title('AirPassengers Forecast', fontsize=22)
ax.set_ylabel('Monthly Passengers', fontsize=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Year', fontsize=20)
ax.legend(prop={'size': 15})
ax.grid()使用cross_validation来预测多个历史值。
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
forecasts = fcst.cross_validation(df=AirPassengersPanel, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, n_windows=2, step_size=12)
# 情节预测
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (20, 7))
Y_hat_df = forecasts.loc['Airline1']
Y_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel['unique_id']=='Airline1']
plt.plot(Y_df['ds'], Y_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(Y_hat_df['ds'], Y_hat_df['TSMixerx'], c='blue', label='Forecast')
ax.set_title('AirPassengers Forecast', fontsize=22)
ax.set_ylabel('Monthly Passengers', fontsize=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Year', fontsize=20)
ax.legend(prop={'size': 15})
ax.grid()Give us a ⭐ on Github