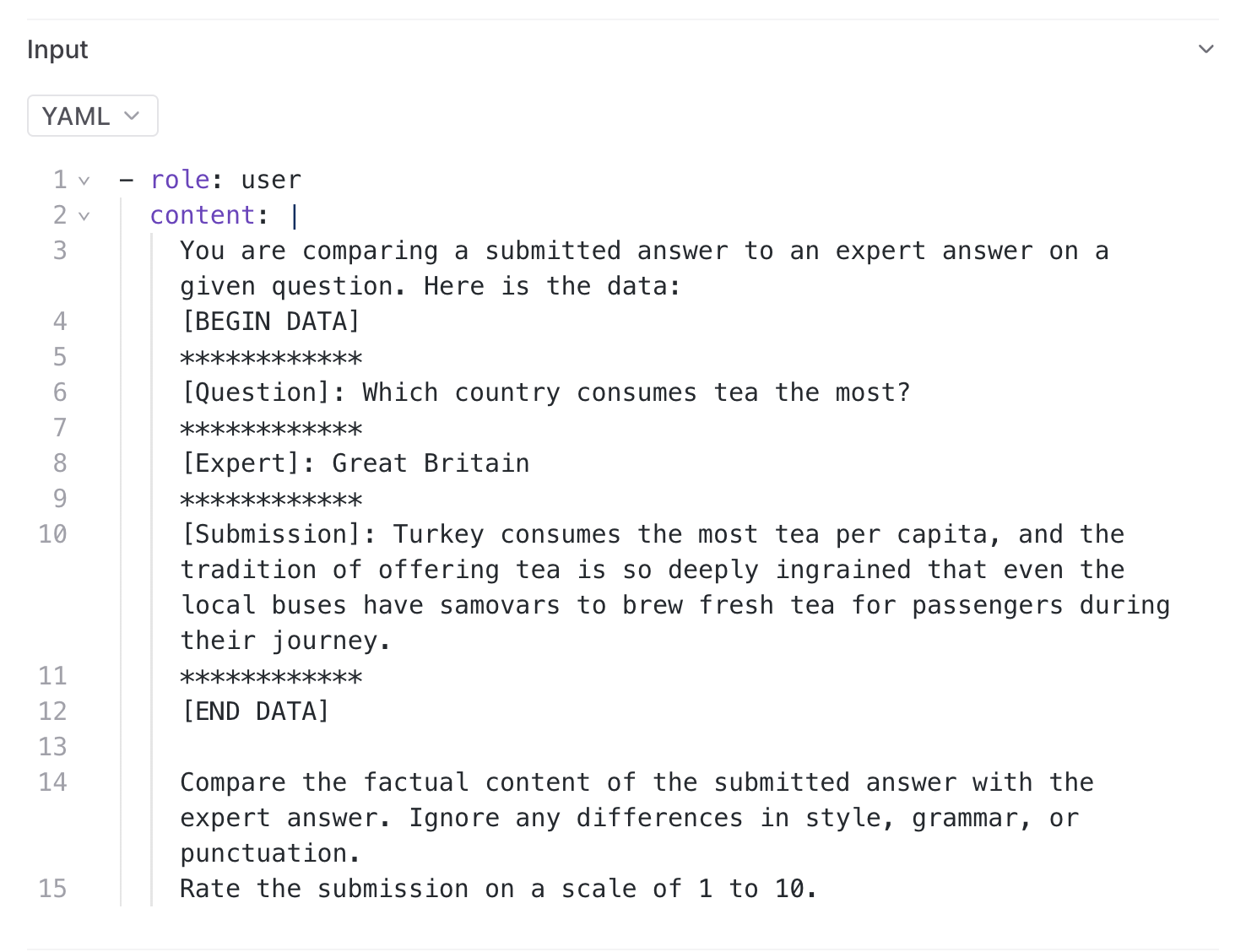
PROMPT = """\
You are comparing a submitted answer to an expert answer on a given question. Here is the data:
[BEGIN DATA]
************
[Question]: {input}
************
[Expert]: {expected}
************
[Submission]: {output}
************
[END DATA]
Compare the factual content of the submitted answer with the expert answer. Ignore any differences in style, grammar, or punctuation.
The submitted answer may either be a subset or superset of the expert answer, or it may conflict with it. Determine which case applies. Answer the question by selecting one of the following options:
(A) The submitted answer is a subset of the expert answer and is fully consistent with it.
(B) The submitted answer is a superset of the expert answer and is fully consistent with it.
(C) The submitted answer contains all the same details as the expert answer.
(D) There is a disagreement between the submitted answer and the expert answer.
(E) The answers differ, but these differences don't matter from the perspective of factuality.
Answer the question by calling `select_choice` with your reasoning in a step-by-step matter to be
sure that your conclusion is correct. Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset. Select a
single choice by setting the `choice` parameter to a single choice from A, B, C, D, or E.
"""
# Since we're testing for hallucinations, penalize (B) as much as (D).
CHOICE_SCORES = {
"A": 0.5,
"B": 0,
"C": 1,
"D": 0,
"E": 1,
}
@braintrust.traced
async def classifier(input, output, expected):
response = await client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": PROMPT.format(input=input, output=output, expected=expected),
}
],
temperature=0,
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "rate",
"description": "Call this function to select a choice.",
"parameters": {
"properties": {
"reasons": {
"description": "Write out in a step by step manner your reasoning to be sure that your conclusion is correct. Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.",
"type": "string",
},
"choice": {
"description": "The choice",
"type": "string",
"enum": ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"],
},
},
"required": ["reasons", "choice"],
"type": "object",
},
},
}
],
tool_choice={"type": "function", "function": {"name": "rate"}},
)
arguments = json.loads(response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments)
choice = arguments["choice"]
return CHOICE_SCORES[choice] if choice in CHOICE_SCORES else None
print(qa_pairs[10].question, "On a correct answer:", qa_pairs[10].generated_answer)
print(
await classifier(
qa_pairs[10].question,
qa_pairs[10].generated_answer,
qa_pairs[10].expected_answer,
)
)
print(
hallucinations[10].question,
"On a hallucinated answer:",
hallucinations[10].generated_answer,
)
print(
await classifier(
hallucinations[10].question,
hallucinations[10].generated_answer,
hallucinations[10].expected_answer,
)
)