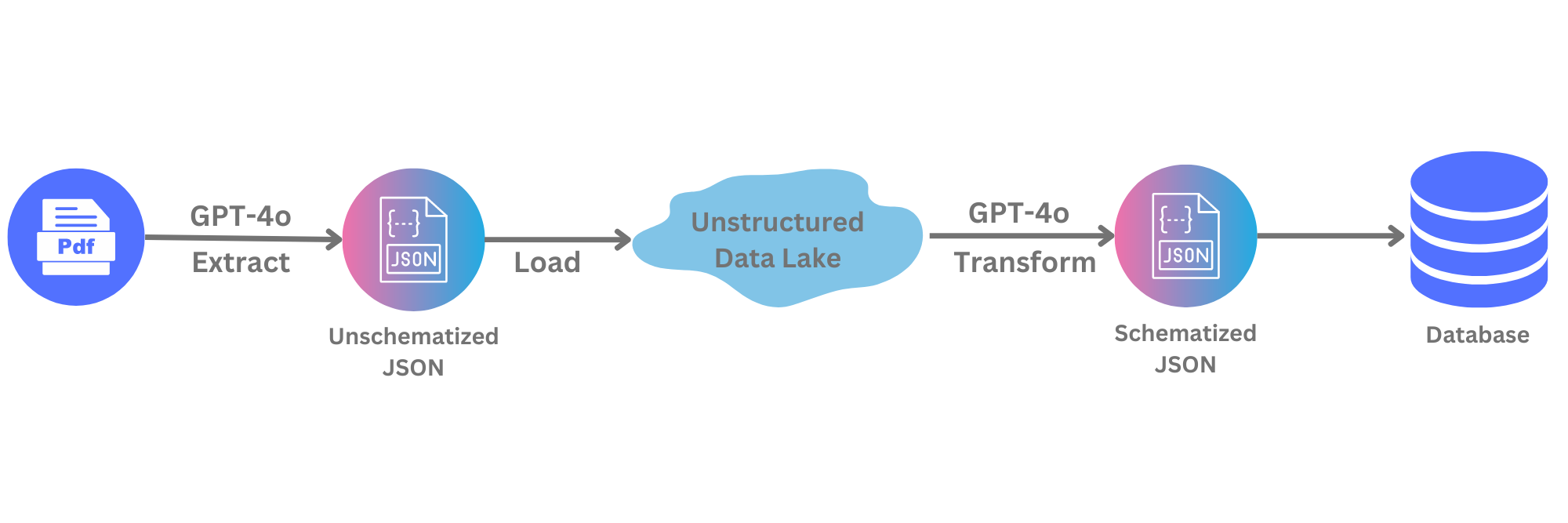
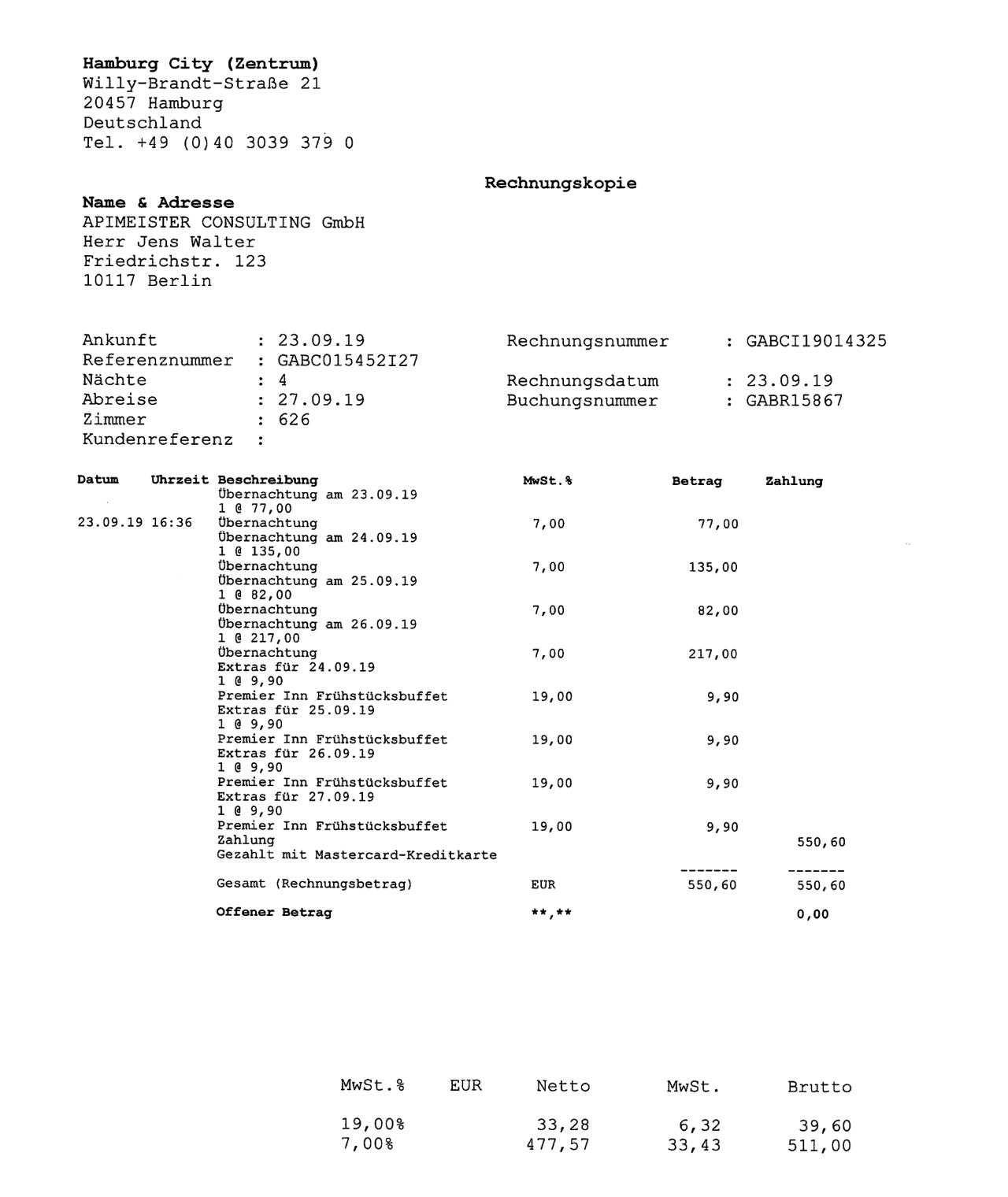
import os
import json
import sqlite3
def ingest_transformed_jsons(json_folder_path, db_path):
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Create necessary tables
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Hotels (
hotel_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
street TEXT,
city TEXT,
country TEXT,
postal_code TEXT,
phone TEXT,
fax TEXT,
email TEXT,
website TEXT
)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Invoices (
invoice_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
hotel_id INTEGER,
invoice_number TEXT,
reservation_number TEXT,
date TEXT,
room_number TEXT,
check_in_date TEXT,
check_out_date TEXT,
currency TEXT,
total_net REAL,
total_tax REAL,
total_gross REAL,
total_charge REAL,
total_credit REAL,
balance_due REAL,
guest_company TEXT,
guest_address TEXT,
guest_name TEXT,
FOREIGN KEY(hotel_id) REFERENCES Hotels(hotel_id)
)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Charges (
charge_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
invoice_id INTEGER,
date TEXT,
description TEXT,
charge REAL,
credit REAL,
FOREIGN KEY(invoice_id) REFERENCES Invoices(invoice_id)
)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Taxes (
tax_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
invoice_id INTEGER,
tax_type TEXT,
tax_rate TEXT,
net_amount REAL,
tax_amount REAL,
gross_amount REAL,
FOREIGN KEY(invoice_id) REFERENCES Invoices(invoice_id)
)
''')
# Loop over all JSON files in the specified folder
for filename in os.listdir(json_folder_path):
if filename.endswith(".json"):
file_path = os.path.join(json_folder_path, filename)
# Load the JSON data
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# Insert Hotel Information
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO Hotels (name, street, city, country, postal_code, phone, fax, email, website)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
data["hotel_information"]["name"],
data["hotel_information"]["address"]["street"],
data["hotel_information"]["address"]["city"],
data["hotel_information"]["address"]["country"],
data["hotel_information"]["address"]["postal_code"],
data["hotel_information"]["contact"]["phone"],
data["hotel_information"]["contact"]["fax"],
data["hotel_information"]["contact"]["email"],
data["hotel_information"]["contact"]["website"]
))
hotel_id = cursor.lastrowid
# Insert Invoice Information
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO Invoices (hotel_id, invoice_number, reservation_number, date, room_number, check_in_date, check_out_date, currency, total_net, total_tax, total_gross, total_charge, total_credit, balance_due, guest_company, guest_address, guest_name)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
hotel_id,
data["invoice_information"]["invoice_number"],
data["invoice_information"]["reservation_number"],
data["invoice_information"]["date"],
data["invoice_information"]["room_number"],
data["invoice_information"]["check_in_date"],
data["invoice_information"]["check_out_date"],
data["totals_summary"]["currency"],
data["totals_summary"]["total_net"],
data["totals_summary"]["total_tax"],
data["totals_summary"]["total_gross"],
data["totals_summary"]["total_charge"],
data["totals_summary"]["total_credit"],
data["totals_summary"]["balance_due"],
data["guest_information"]["company"],
data["guest_information"]["address"],
data["guest_information"]["guest_name"]
))
invoice_id = cursor.lastrowid
# Insert Charges
for charge in data["charges"]:
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO Charges (invoice_id, date, description, charge, credit)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
invoice_id,
charge["date"],
charge["description"],
charge["charge"],
charge["credit"]
))
# Insert Taxes
for tax in data["taxes"]:
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO Taxes (invoice_id, tax_type, tax_rate, net_amount, tax_amount, gross_amount)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
invoice_id,
tax["tax_type"],
tax["tax_rate"],
tax["net_amount"],
tax["tax_amount"],
tax["gross_amount"]
))
conn.commit()
conn.close()