概述
本笔记本为初学者提供了一个清晰实用的指南,帮助您快速上手使用OpenAI API进行语音转文字(STT)。您将探索多种实用方法、它们的应用场景以及注意事项。
最终你将能够为你的使用场景选择并使用合适的转录方法。
注意:为简化使用流程,本笔记本采用WAV音频文件。未启用实时麦克风流式传输(例如来自网页应用或麦克风)。
本笔记本为初学者提供了一个清晰实用的指南,帮助您快速上手使用OpenAI API进行语音转文字(STT)。您将探索多种实用方法、它们的应用场景以及注意事项。
最终你将能够为你的使用场景选择并使用合适的转录方法。
注意:为简化使用流程,本笔记本采用WAV音频文件。未启用实时麦克风流式传输(例如来自网页应用或麦克风)。
| 模式 | 首个token的延迟 | 最佳适用场景(实际案例) | 优势 | 主要限制 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
File upload + stream=False (blocking) | seconds | Voicemail, meeting recordings | Simple to set up | • No partial results, users see nothing until file finishes • Max 25 MB per request (you must chunk long audio) |
File upload + stream=True | subseconds | Voice memos in mobile apps | Simple to set up & provides a “live” feel via token streaming | • Still requires a completed file • You implement progress bars / chunked uploads |
| 实时WebSocket | 亚秒级 | 网络研讨会中的实时字幕 | 真正实时;支持连续音频流 | • 音频格式必须为pcm16、g711_ulaw或g711_alaw • 会话时长≤30分钟,支持重连拼接 • 需自行处理说话人轮换格式以构建完整文本记录 |
| Agents SDK VoicePipeline | subseconds | 内部帮助台助手 | 实时流式处理,轻松构建智能体工作流 | • 仅限Python测试版 • API接口可能变更 |
要设置您的环境,请在新Python环境中取消注释并运行以下单元格:
!pip install --upgrade -q openai openai-agents websockets sounddevice pyaudio nest_asyncio resampy httpx websocket-client这将安装运行笔记本所需的必要软件包。
在继续之前,请确保您已将OpenAI API密钥设置为名为OPENAI_API_KEY的环境变量。通常可以在终端或笔记本环境中设置:export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key-here"
通过运行下一个单元格来验证您的API密钥是否设置正确。
# ─── Standard Library ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
import asyncio
import struct
import base64 # encode raw PCM bytes → base64 before sending JSON
import json # compose/parse WebSocket messages
import os
import time
from typing import List
from pathlib import Path
# ─── Third-Party ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
import nest_asyncio
import numpy as np
from openai import OpenAI
import resampy # high-quality sample-rate conversion
import soundfile as sf # reads many audio formats into float32 arrays
import websockets # asyncio-based WebSocket client
from agents import Agent
from agents.voice import (
SingleAgentVoiceWorkflow,
StreamedAudioInput,
VoicePipeline,
VoicePipelineConfig,
)
from IPython.display import Audio, display
# ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
nest_asyncio.apply()
# ✏️ Put your key in an env-var or just replace the call below.
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
print("✅ OpenAI client ready")✅ OpenAI client ready
model = gpt-4o-transcribe
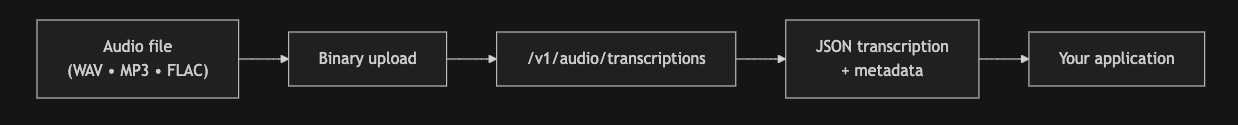
让我们先预览一下音频文件。我已从此处下载了该音频文件。
AUDIO_PATH = Path('./data/sample_audio_files/lotsoftimes-78085.mp3') # change me
MODEL_NAME = "gpt-4o-transcribe"
if AUDIO_PATH.exists():
display(Audio(str(AUDIO_PATH)))
else:
print('⚠️ Provide a valid audio file')现在,我们可以调用STT端点来转录音频。
if AUDIO_PATH.exists():
with AUDIO_PATH.open('rb') as f:
transcript = client.audio.transcriptions.create(
file=f,
model=MODEL_NAME,
response_format='text',
)
print('\n--- TRANSCRIPT ---\n')
print(transcript)--- TRANSCRIPT --- And lots of times you need to give people more than one link at a time. A band could give their fans a couple new videos from a live concert, a behind-the-scenes photo gallery, an album to purchase, like these next few links.
model = gpt-4o-transcribe
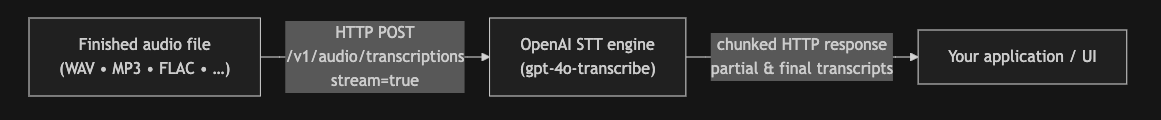
if AUDIO_PATH.exists():
with AUDIO_PATH.open('rb') as f:
stream = client.audio.transcriptions.create(
file=f,
model=MODEL_NAME,
response_format='text',
stream=True
)
for event in stream:
# If this is an incremental update, you can get the delta using `event.delta`
if getattr(event, "delta", None):
print(event.delta, end="", flush=True)
time.sleep(0.05) # simulate real-time pacing
# When transcription is complete, you can get the final transcript using `event.text`
elif getattr(event, "text", None):
print()
print("\n" + event.text)And lots of times you need to give people more than one link at a time. A band could give their fans a couple new videos from a live concert, a behind-the-scenes photo gallery, an album to purchase, like these next few links. And lots of times you need to give people more than one link at a time. A band could give their fans a couple new videos from a live concert, a behind-the-scenes photo gallery, an album to purchase, like these next few links.
model = gpt-4o-transcribe
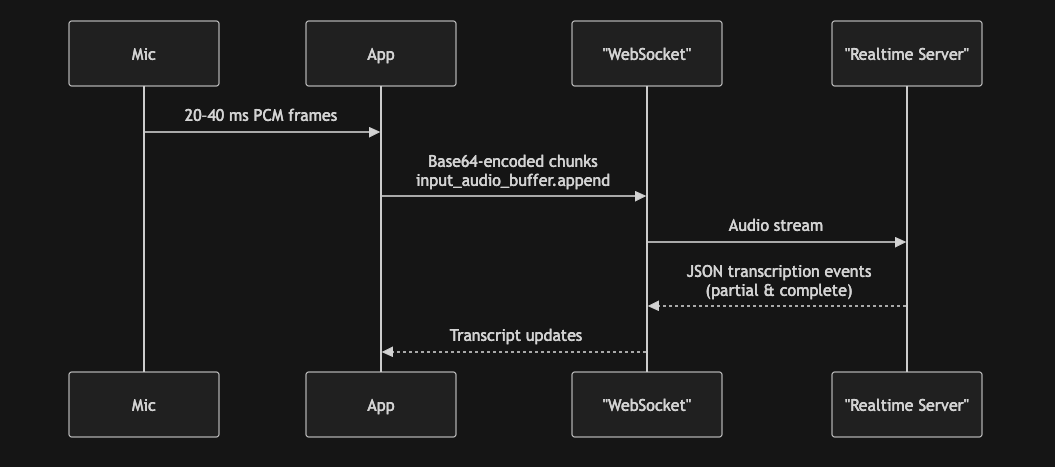
TARGET_SR = 24_000
PCM_SCALE = 32_767
CHUNK_SAMPLES = 3_072 # ≈128 ms at 24 kHz
RT_URL = "wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?intent=transcription"
EV_DELTA = "conversation.item.input_audio_transcription.delta"
EV_DONE = "conversation.item.input_audio_transcription.completed"
# ── helpers ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
def float_to_16bit_pcm(float32_array):
clipped = [max(-1.0, min(1.0, x)) for x in float32_array]
pcm16 = b''.join(struct.pack('<h', int(x * 32767)) for x in clipped)
return pcm16
def base64_encode_audio(float32_array):
pcm_bytes = float_to_16bit_pcm(float32_array)
encoded = base64.b64encode(pcm_bytes).decode('ascii')
return encoded
def load_and_resample(path: str, sr: int = TARGET_SR) -> np.ndarray:
"""Return mono PCM-16 as a NumPy array."""
data, file_sr = sf.read(path, dtype="float32")
if data.ndim > 1:
data = data.mean(axis=1)
if file_sr != sr:
data = resampy.resample(data, file_sr, sr)
return data
async def _send_audio(ws, pcm: np.ndarray, chunk: int, sr: int) -> None:
"""Producer: stream base-64 chunks at real-time pace, then signal EOF."""
dur = 0.025 # Add pacing to ensure real-time transcription
t_next = time.monotonic()
for i in range(0, len(pcm), chunk):
float_chunk = pcm[i:i + chunk]
payload = {
"type": "input_audio_buffer.append",
"audio": base64_encode_audio(float_chunk),
}
await ws.send(json.dumps(payload))
t_next += dur
await asyncio.sleep(max(0, t_next - time.monotonic()))
await ws.send(json.dumps({"type": "input_audio_buffer.end"}))
async def _recv_transcripts(ws, collected: List[str]) -> None:
"""
Consumer: build `current` from streaming deltas, promote it to `collected`
whenever a …completed event arrives, and flush the remainder on socket
close so no words are lost.
"""
current: List[str] = []
try:
async for msg in ws:
ev = json.loads(msg)
typ = ev.get("type")
if typ == EV_DELTA:
delta = ev.get("delta")
if delta:
current.append(delta)
print(delta, end="", flush=True)
elif typ == EV_DONE:
# sentence finished → move to permanent list
collected.append("".join(current))
current.clear()
except websockets.ConnectionClosedOK:
pass
# socket closed → flush any remaining partial sentence
if current:
collected.append("".join(current))
def _session(model: str, vad: float = 0.5) -> dict:
return {
"type": "transcription_session.update",
"session": {
"input_audio_format": "pcm16",
"turn_detection": {"type": "server_vad", "threshold": vad},
"input_audio_transcription": {"model": model},
},
}
async def transcribe_audio_async(
wav_path,
api_key,
*,
model: str = MODEL_NAME,
chunk: int = CHUNK_SAMPLES,
) -> str:
pcm = load_and_resample(wav_path)
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}", "OpenAI-Beta": "realtime=v1"}
async with websockets.connect(RT_URL, additional_headers=headers, max_size=None) as ws:
await ws.send(json.dumps(_session(model)))
transcripts: List[str] = []
await asyncio.gather(
_send_audio(ws, pcm, chunk, TARGET_SR),
_recv_transcripts(ws, transcripts),
) # returns when server closes
return " ".join(transcripts)transcript = await transcribe_audio_async(AUDIO_PATH, OPENAI_API_KEY)
transcriptAnd lots of times you need to give people more than one link at a time.A band could give their fans a couple new videos from a live concert, a behind-the-scenes photo galleryLike these next few linksAn album to purchase.
'And lots of times you need to give people more than one link at a time. A band could give their fans a couple new videos from a live concert, a behind-the-scenes photo gallery Like these next few linksAn album to purchase. '
模型 = gpt-4o-transcribe, gpt-4o-mini

优势
VoicePipeline 处理重采样、语音活动检测、缓冲、令牌认证和重新连接。限制
# ── 1 · agent that replies in French ---------------------------------------
fr_agent = Agent(
name="Assistant-FR",
instructions=
"Translate the user's words into French.",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
)
# ── 2 · workflow that PRINTS what it yields --------------------------------
class PrintingWorkflow(SingleAgentVoiceWorkflow):
"""Subclass that prints every chunk it yields (the agent's reply)."""
async def run(self, transcription: str):
# Optionally: also print the user transcription
print()
print("[User]:", transcription)
print("[Assistant]: ", end="", flush=True)
async for chunk in super().run(transcription):
print(chunk, end="", flush=True) # <-- agent (French) text
yield chunk # still forward to TTS
pipeline = VoicePipeline(
workflow=PrintingWorkflow(fr_agent),
stt_model=MODEL_NAME,
config=VoicePipelineConfig(tracing_disabled=True),
)
# ── 3 · helper to stream ~40 ms chunks at 24 kHz ---------------------------
def load_and_resample(path: str, sr: int = 24_000) -> np.ndarray:
"""Return mono PCM-16 as a NumPy array."""
data, file_sr = sf.read(path, dtype="float32")
if data.ndim > 1:
data = data.mean(axis=1)
if file_sr != sr:
data = resampy.resample(data, file_sr, sr)
return data
def audio_chunks(path: str, target_sr: int = 24_000, chunk_ms: int = 40):
# 1️⃣ reuse the helper
audio = load_and_resample(path, target_sr)
# 2️⃣ float-32 → int16 NumPy array
pcm = (np.clip(audio, -1, 1) * 32_767).astype(np.int16)
# 3️⃣ yield real-time sized hops
hop = int(target_sr * chunk_ms / 1_000)
for off in range(0, len(pcm), hop):
yield pcm[off : off + hop]
# ── 4 · stream the file ----------------------------------------------------
async def stream_audio(path: str):
sai = StreamedAudioInput()
run_task = asyncio.create_task(pipeline.run(sai))
for chunk in audio_chunks(path):
await sai.add_audio(chunk)
await asyncio.sleep(len(chunk) / 24_000) # real-time pacing
# just stop pushing; session ends automatically
await run_task # wait for pipeline to finishawait stream_audio(AUDIO_PATH)[User]: And lots of times you need to give people more than one link at a time. [Assistant]: Et souvent, vous devez donner aux gens plusieurs liens à la fois. [User]: A band could give their fans a couple new videos from a live concert, a behind-the-scenes photo gallery. [Assistant]: Un groupe pourrait donner à ses fans quelques nouvelles vidéos d'un concert live, ainsi qu'une galerie de photos des coulisses. [User]: An album to purchase. [Assistant]:
Un album à acheter. [User]: like these next few links. [Assistant]: comme ces quelques liens suivants.
在本笔记本中,您探索了使用OpenAI API和智能体SDK将语音转换为文本的多种方法,从简单的文件上传到完全交互式的实时流媒体。每种工作流程在不同场景下各具优势,请选择最符合您产品需求的方案。