BBO基准测试函数
在这个开源的Python模块中,我们提供了一组基准/测试函数,这些函数在黑箱优化/零阶优化/无梯度优化/无导数优化/全局优化/直接搜索/随机优化/元启发式/进化算法/群体智能社区中已被广泛使用。
注意
在接下来的日子里,我们计划从各种实际应用中添加一些具有挑战性的BBO模型。由于这是一个长期开发项目,欢迎任何人对其进行开源贡献。
对于一组23个基准/测试函数,它们的基本形式、平移/变换形式、旋转形式以及旋转-平移形式已经被编码并经过充分测试。通常,在BBO的比较实验中应使用它们的旋转-平移形式,以避免对某些搜索点(例如原点)或可分离性可能产生的偏见。
检查编码正确性
有关所有基准测试函数的测试代码,请参考以下公开访问链接以获取详细信息(事实上,我们花费了大量时间来检查Python代码的正确性):
基础函数
在这里,我们介绍一些常见的基准函数的基本形式,如下所示:
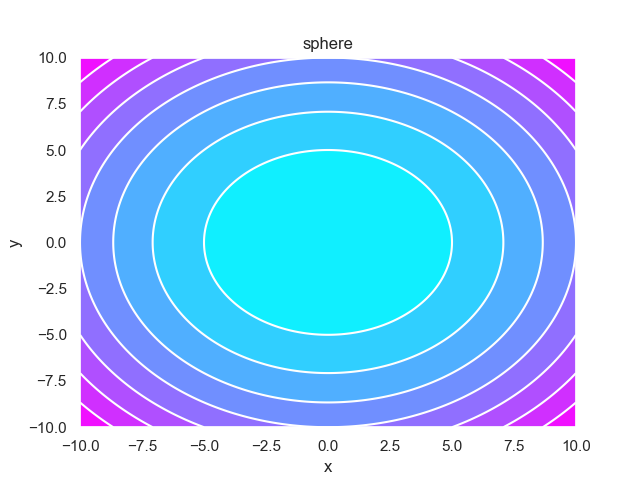
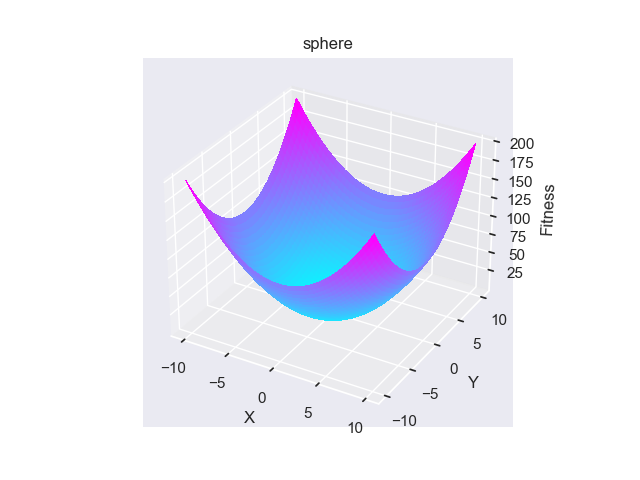
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.sphere(x)[source]
Sphere 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
周, Q. 和 李, Y., 2003. 进化策略中的定向变异. IEEE 进化计算汇刊, 7(4), 页码 356-366.
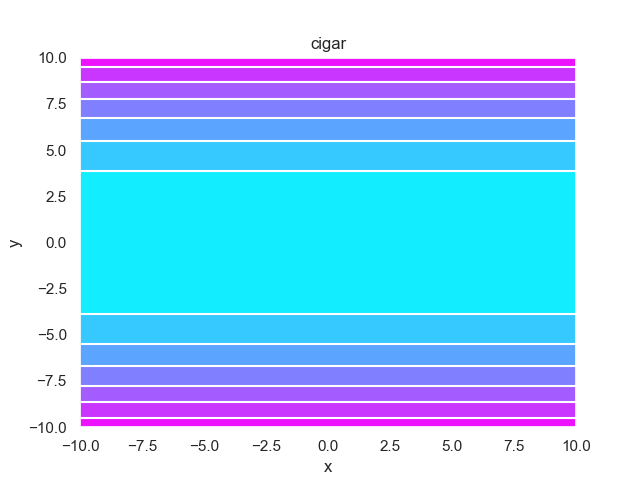
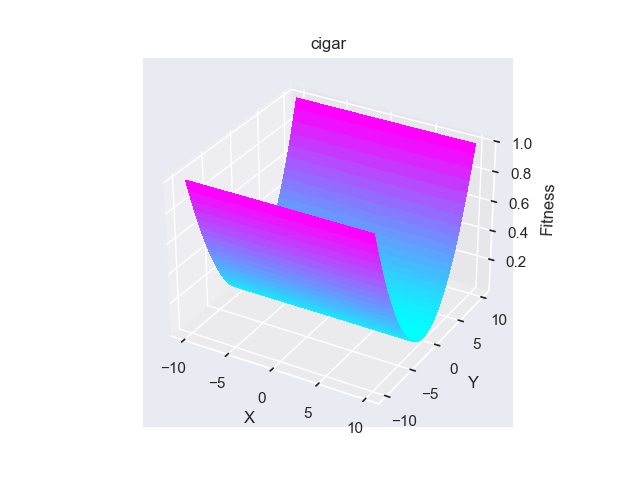
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.cigar(x)[source]
Cigar 测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
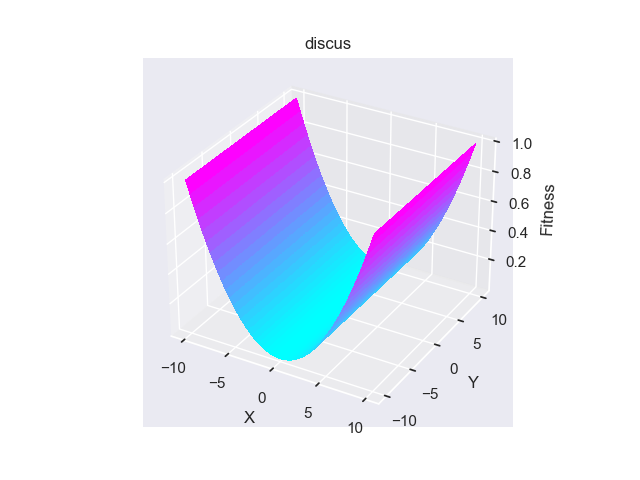
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.discus(x)[source]
Discus(也称为Tablet)测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (第2814-2821页). IEEE.
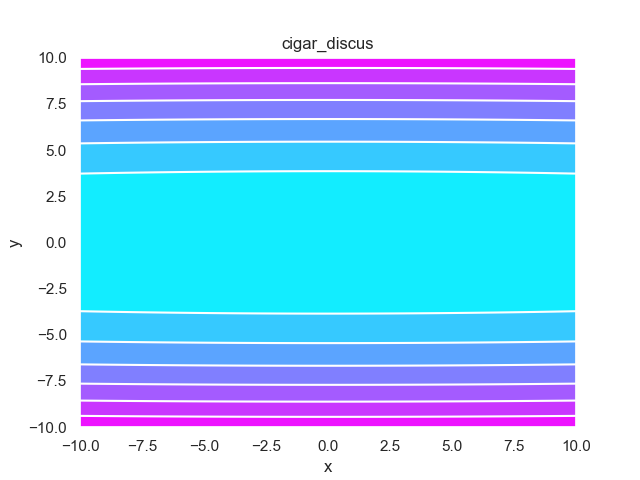
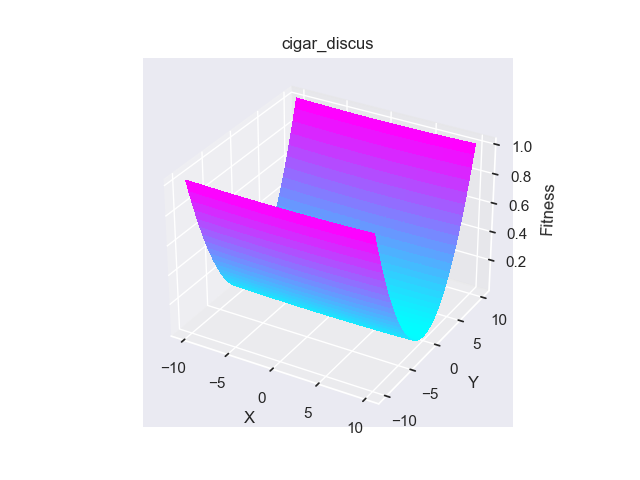
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.cigar_discus(x)[source]
Cigar-Discus 测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
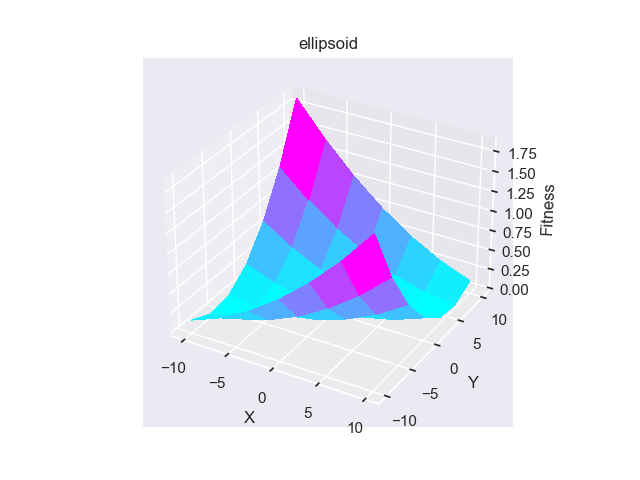
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.ellipsoid(x)[source]
椭球 测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.different_powers(x)[source]
Different-Powers 测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
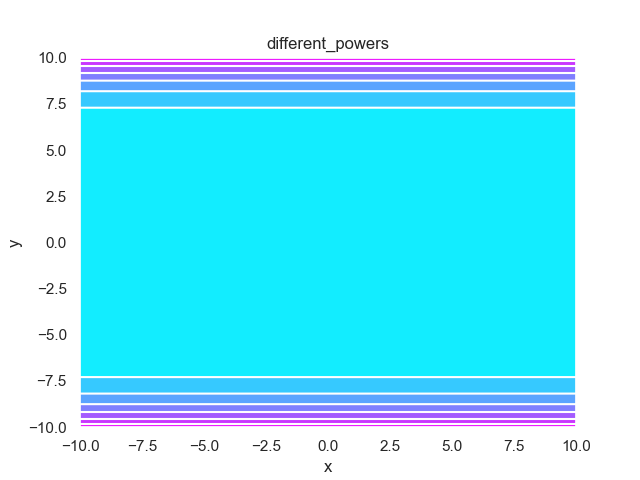
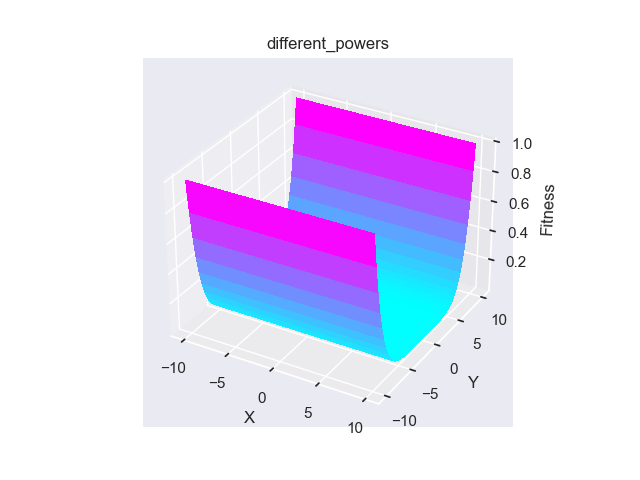
Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schwefel221(x)[source]
Schwefel221 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数


- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.step(x)[source]
步骤 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
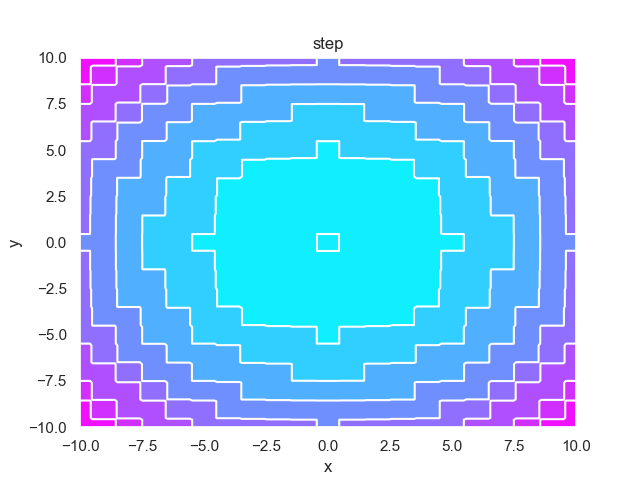
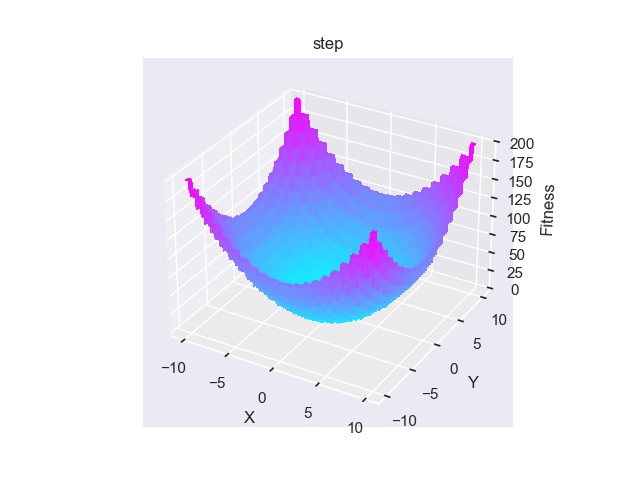
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schwefel222(x)[source]
Schwefel222 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.rosenbrock(x)[source]
Rosenbrock 测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

Jastrebski, G.A. 和 Arnold, D.V., 2006年7月. 通过主动协方差矩阵适应改进进化策略. 在IEEE国际进化计算会议上 (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
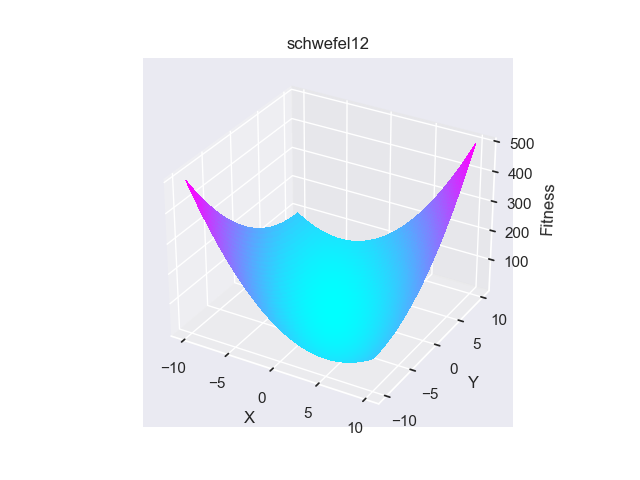
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schwefel12(x)[source]
Schwefel12 测试函数。
注意
它的维度应该> 1。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
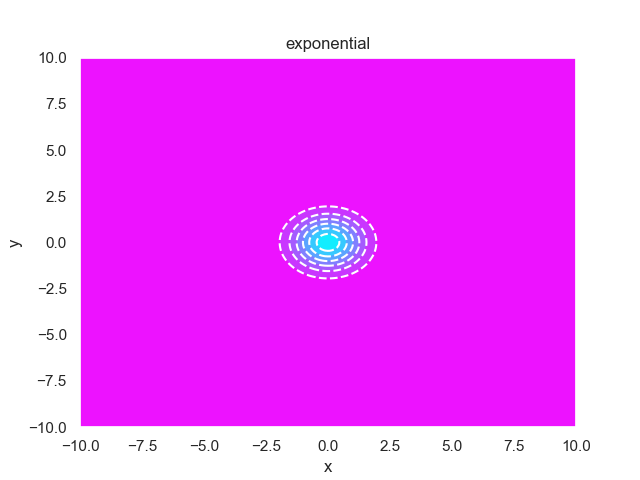
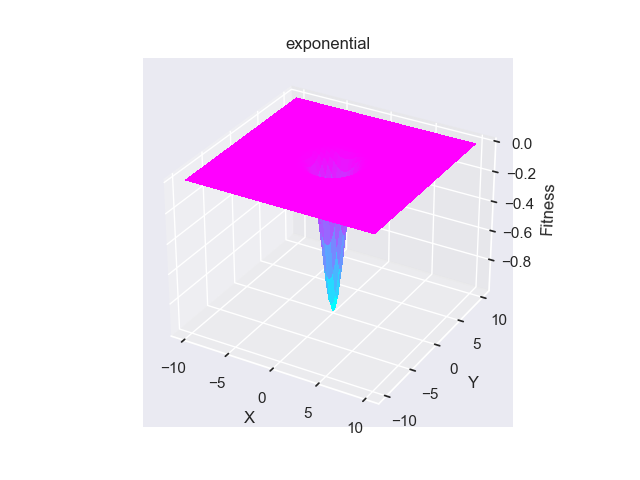
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.exponential(x)[source]
指数 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
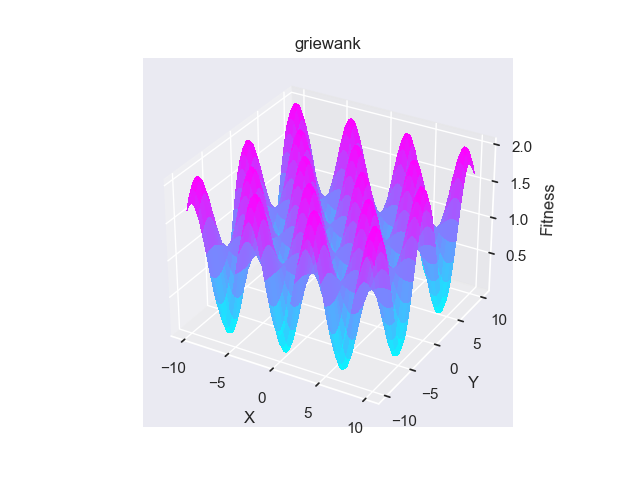
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.griewank(x)[source]
Griewank 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.bohachevsky(x)[source]
Bohachevsky 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.ackley(x)[source]
Ackley 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
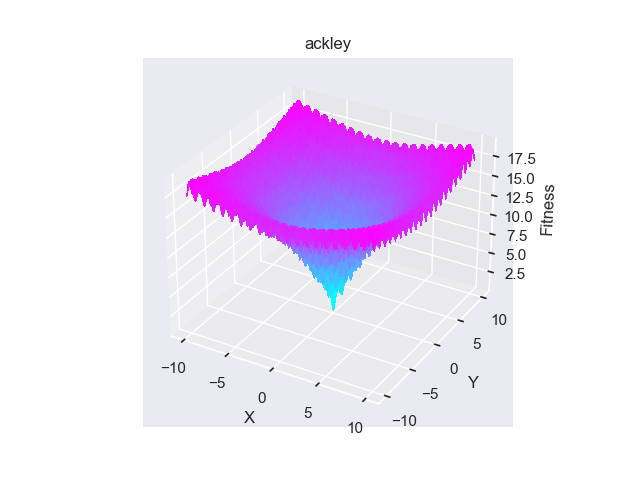
Carrillo, J.A., Choi, Y.P., Totzeck, C. 和 Tse, O., 2018. 基于共识的全局优化方法的分析框架。 《应用科学中的数学模型与方法》, 28(06), 第1037-1066页。
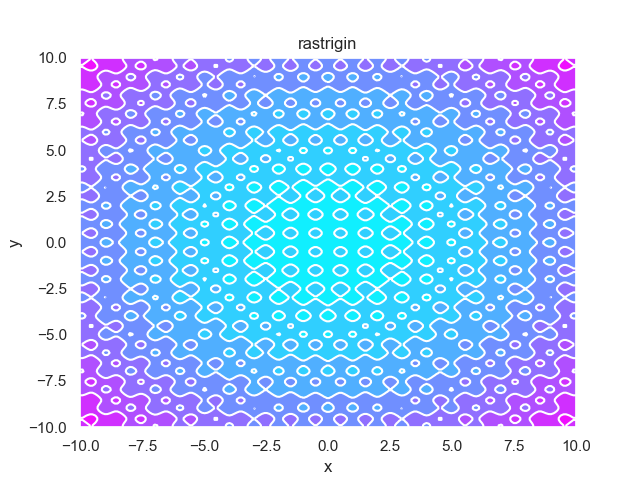
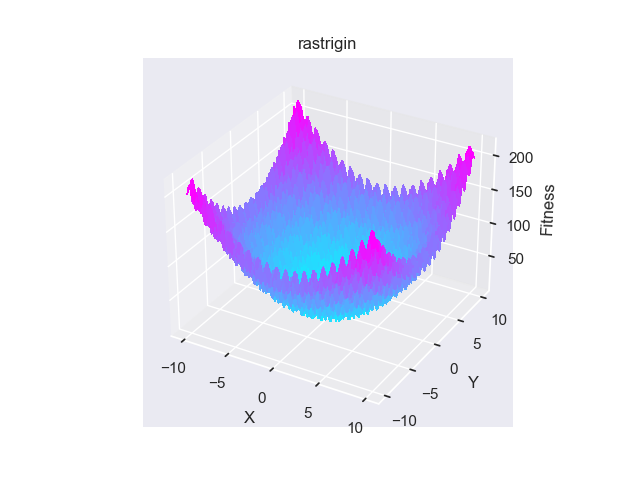
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.rastrigin(x)[source]
Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是 $10 n + sum_{i = 1}^{n} (x_i^2 - 10 cos(2 pi x_i))$。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
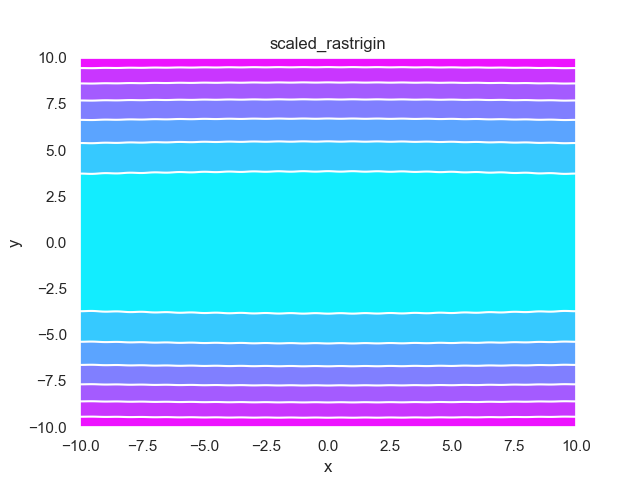
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x)[source]
Scaled-Rastrigin 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.skew_rastrigin(x)[source]
Skew-Rastrigin 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.levy_montalvo(x)[source]
Levy-Montalvo 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.michalewicz(x)[source]
Michalewicz 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.salomon(x)[source]
Salomon 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数

- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.shubert(x)[source]
Shubert 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schaffer(x)[source]
Schaffer 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
移位/变换形式
接下来,我们将介绍上述基础函数的移位/变换形式,如下所示:
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.generate_shift_vector(func, ndim, low, high, seed=None)[source]
生成一个维度为ndim的随机偏移向量,均匀采样于low(包含)和high(不包含)之间。
注意
生成的位移向量将自动以txt形式存储以供进一步使用。
- Parameters:
func (str 或 func) – 函数名称。
ndim (int) – 位移向量的维度数。
low (float 或 array_like) – 平移向量的下界。
high (float 或 array_like) – 位移向量的上边界。
seed (int) – 随机数生成器 (RNG) 的标量种子。
- Returns:
shift_vector – 一个在大小为ndim的[low, high)范围内均匀采样的位移向量。
- Return type:
ndarray(数据类型为 np.float64)
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.load_shift_vector(func, x, shift_vector=None)[source]
加载需要预先生成的偏移向量。
注意
当None时,位移向量应该已经生成并以txt形式预先存储。
- Parameters:
func (func) – 函数名称。
x (array_like) – 决策向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 一个与x大小相同的位移向量。
- Returns:
shift_vector – 一个与x大小相同的偏移向量。
- Return type:
ndarray(数据类型为 np.float64)
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.sphere(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Sphere 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是 $sum_{i=1}^{n}x_i^2$。 如果其参数 shift_vector 是 None,请使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 来 提前生成它(以 txt 形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.cigar(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Cigar 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.discus(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Discus 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.cigar_discus(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Cigar-Discus 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.ellipsoid(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
椭球 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.different_powers(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Different-Powers 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector是None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.schwefel221(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Schwefel221 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.step(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
步骤 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector是None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.schwefel222(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Schwefel222 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.rosenbrock(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Rosenbrock 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.schwefel12(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Schwefel12 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.exponential(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
指数 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.griewank(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Griewank 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.bohachevsky(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Bohachevsky 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.ackley(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Ackley 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Scaled-Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.skew_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Skew-Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.levy_montalvo(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Levy-Montalvo 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.michalewicz(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Michalewicz 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.salomon(x, shift_vector=None)[source]
Salomon 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数shift_vector为None,请使用函数generate_shift_vector()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 一个与x大小相同的向量。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
旋转形式
接下来,我们将介绍上述基础函数的旋转形式,如下所示:
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.generate_rotation_matrix(func, ndim, seed)[source]
生成一个维度为[ndim * ndim]的随机旋转矩阵,通常采样。
注意
生成的旋转矩阵将自动以txt形式存储以供进一步使用。
- Parameters:
func (str 或 func) – 函数名称。
ndim (int) – 旋转矩阵的维度数。
seed (int) – 随机数生成器 (RNG) 的标量种子。
- Returns:
rotation_matrix – 大小为 [ndim * ndim] 的旋转矩阵。
- Return type:
ndarray
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.load_rotation_matrix(func, x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
加载需要预先生成的旋转矩阵。
注意
当None时,旋转矩阵应该已经生成并以txt形式预先存储。
- Parameters:
func (str 或 func) – 函数名称。
x (array_like) – 决策向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
rotation_matrix – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Return type:
ndarray
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.sphere(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Sphere 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$sum_{i=1}^{n}x_i^2$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上与x大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.cigar(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Cigar 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.discus(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Discus/Tablet 测试功能。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.cigar_discus(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Cigar-Discus 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.ellipsoid(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
椭球 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.different_powers(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Different-Powers 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schwefel221(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schwefel221 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.step(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
步骤 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schwefel222(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schwefel222 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()来 提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.rosenbrock(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Rosenbrock 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schwefel12(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schwefel12 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.exponential(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
指数 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.griewank(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Griewank 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.bohachevsky(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Bohachevsky 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.ackley(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Ackley 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.rastrigin(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Scaled-Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.skew_rastrigin(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Skew-Rastrigin 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.levy_montalvo(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Levy-Montalvo 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.michalewicz(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Michalewicz 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.salomon(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Salomon 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.shubert(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Shubert 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schaffer(x, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schaffer 测试函数。
注意
它的LaTeX公式是$$。 如果其参数rotation_matrix为None,请使用函数generate_rotation_matrix()提前生成它(以txt形式存储)。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个与x在每个维度上大小相同的矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
旋转-平移形式
接下来,我们将介绍上述基础函数的旋转平移形式,如下所示:
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.load_shift_and_rotation(func, x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
加载需要提前生成的平移向量和旋转矩阵。
注意
当None时,位移向量应已生成并以txt形式预先存储。当None时,旋转矩阵应已生成并以txt形式预先存储。
- Parameters:
func (str 或 func) – 函数名称。
x (array_like) – 决策向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
shift_vector (ndarray (of dtype np.float64)) – 与x大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为[len(x) * len(x)]的旋转矩阵。
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.sphere(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Sphere 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的位移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.cigar(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Cigar 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的位移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.discus(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Discus 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与x大小相同的位移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.cigar_discus(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Cigar-Discus 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.ellipsoid(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
椭球 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与x大小相同的位移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.different_powers(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Different-Power 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的位移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.schwefel221(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schwefel221 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.step(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
步骤 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.schwefel222(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schwefel222 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.rosenbrock(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Rosenbrock 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.schwefel12(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Schwefel12 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.exponential(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
指数 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.griewank(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Griewank 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.bohachevsky(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Bohachevsky 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.ackley(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Ackley 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Rastrigin 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Scaled-Rastrigin 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.skew_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Skew-Rastrigin 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.levy_montalvo(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Levy-Montalvo 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.michalewicz(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Michalewicz 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.salomon(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[source]
Salomon 测试函数。
- Parameters:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- Returns:
y – 标量适应度。
- Return type:
浮点数
大规模BBO(LBO)基准测试
这里我们提供了两种不同的基准测试案例(局部搜索 vs 全局搜索)用于大规模黑箱优化(LBO):
- class pypop7.benchmarks.lbo.Experiment(index, function, seed, ndim_problem, max_runtime)[source]
一个独立的实验。
- class pypop7.benchmarks.lbo.Experiments(start, end, ndim_problem, max_runtime, is_local=True)[source]
- pypop7.benchmarks.lbo.benchmark_local_search(optimizer, ndim=2000, max_runtime=10800, start_index=1, end_index=14, seed=20221001)[source]
测试大规模黑箱优化(LBO)的本地搜索能力。
- Parameters:
optimizer (class) – 任何黑箱优化器。
ndim (int) – 维度的数量。
max_runtime (float) – 允许的最大运行时间(秒)。
start_index (int) – 独立实验的起始索引。
end_index (int) – 独立实验的结束索引。
seed (int) – 用于随机数生成(RNG)的种子。
- Return type:
工作空间(pwd())中来自独立实验的一组数据文件。
- pypop7.benchmarks.lbo.benchmark_global_search(optimizer, ndim=2000, max_runtime=10800, start_index=1, end_index=14, seed=20221001)[source]
测试大规模黑箱优化(LBO)的全局搜索能力。
- Parameters:
optimizer (class) – 任何黑箱优化器。
ndim (int) – 维度的数量。
max_runtime (float) – 允许的最大运行时间(秒)。
start_index (int) – 独立实验的起始索引。
end_index (int) – 独立实验的结束索引。
seed (int) – 用于随机数生成(RNG)的种子。
- Return type:
工作空间(pwd())中来自独立实验的一组数据文件。
数据科学中的黑箱分类
这里我们提供了一系列来自数据科学黑箱分类的测试函数:
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.cross_entropy_loss_lr(w, x, y)[source]
逻辑回归的交叉熵损失函数(带有二元标签/类别 {0, 1} 的 LR)。
注意
这个用于二分类的损失函数无论使用什么数据集总是凸的。它在实践中经常用于执行LR。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 用于训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.cross_entropy_loss_l2(w, x, y)[source]
带有L2正则化的逻辑回归交叉熵损失函数(二元标签{0, 1}的逻辑回归)。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
https://jermwatt.github.io/machine_learning_refined/ (2020)
https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/17M1154679?journalCode=sjope8 (2018)
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.square_loss_lr(w, x, y)[source]
逻辑回归的平方损失函数(带有二元标签/类别 {0, 1} 的 LR)。
注意
这个用于二元分类的损失函数通常是非凸的(非线性最小二乘法)。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
https://jermwatt.github.io/machine_learning_refined/ (2020)
https://openreview.net/forum?id=ryxz8CVYDH (2020)
https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/1.9781611976236.23 (2020)
https://openreview.net/forum?id=BJe-DsC5Fm (2019)
https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2018/file/ba9a56ce0a9bfa26e8ed9e10b2cc8f46-Paper.pdf (2018)
https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/17M1154679?journalCode=sjope8 (2018)
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.logistic_loss_lr(w, x, y)[source]
逻辑回归的Logistic损失函数(带有二元标签/类别{-1, 1}的LR)。
注意
AKA softmax 成本(无论使用何种数据集,始终是凸的)。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00031305.2021.2006781 (2021)
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.logistic_loss_l2(w, x, y)[source]
带有L2正则化的逻辑回归损失函数(适用于二元标签/类别{-1, 1}的逻辑回归)。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/17M1154679?journalCode=sjope8 (2018)
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.tanh_loss_lr(w, x, y)[source]
逻辑回归的Tanh损失函数(带有二元类别标签{-1, 1}的LR)。
注意
这个用于二元分类的损失函数通常是非凸的(非线性最小二乘法)。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(需要优化的权重)。
x (ndarray) – 用于训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的类别标签。
- Return type:
需要最小化的损失/适应度值(float)。
参考文献
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.hinge_loss_perceptron(w, x, y)[source]
感知器的合页损失函数(带有二元标签/类别 {-1, 1})。
注意
又称感知器成本或修正线性单元成本。此成本函数始终是凸的,但在每个变量维度上都有一个不连续的导数。它总是在原点有一个平凡解,因此在实践中可能需要小心,以避免意外找到它。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.loss_margin_perceptron(w, x, y)[source]
边缘感知器的损失函数(带有二元标签/类别 {-1, 1})。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.loss_svm(w, x, y)[source]
支持向量机的损失函数(带有二元标签/类别 {-1, 1} 的SVM)。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.mpc2023_nonsmooth(w, x, y)[source]
来自MPC-2023的非光滑函数。
- Parameters:
w (ndarray) – 输入向量(权重)。
x (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的特征。
y (ndarray) – 使用的训练集中的标签。
- Return type:
损失/适应度值 (float).
参考文献
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12532-023-00233-9 (2023)
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.read_parkinson_disease_classification(is_10=True)[source]
读取数据集帕金森病分类。
注意
# 数据: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/static/public/470/parkinson+s+disease+classification.zip
# 实例数: 756
# 特性:753(从754特性中删除id)
# 类别: 0/1
# 缺失值:无
参考文献
Sakar,C., Serbes,Gorkem, Gunduz,Aysegul, Nizam,Hatice, 和 Sakar,Betul. (2018). 帕金森病分类. UCI 机器学习库. https://doi.org/10.24432/C5MS4X
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.read_semeion_handwritten_digit(is_10=True)[source]
读取数据集Semeion手写数字。
注意
# 数据: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/static/public/178/semeion+handwritten+digit.zip
# 实例数: 1593
# 特征:256(对于266个特征:最后10列是数字0-9的类别标签)
# 类别: 0/1
# 缺失值:无
参考文献
Tactile,Srl, Massimo,Buscema, 和 Stefano,Terzi (1994). Semeion 手写数字. UCI 机器学习库. https://doi.org/10.24432/C5SC8V
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.read_cnae9(is_10=True)[source]
读取数据集 CNAE-9。
注意
# 数据: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/static/public/233/cnae+9.zip
# 实例数: 1080
# 功能:856
# 类别: 0/1
# 缺失值:无
参考文献
Ciarelli,Patrick 和 Oliveira,Elias. (2012). CNAE-9. UCI 机器学习库. https://doi.org/10.24432/C51G7P.
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.read_madelon(is_10=False)[source]
读取数据集Madelon。
注意
# 数据: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/static/public/171/madelon.zip
# 实例数: 2000
# 特征:500
# 类别: -1/1
# 缺失值:无
参考文献
Guyon,Isabelle. (2008). Madelon. UCI 机器学习库. https://doi.org/10.24432/C5602H.
- pypop7.benchmarks.data_science.read_qsar_androgen_receptor(is_10=False)[source]
读取数据集QSAR雄激素受体。
注意
# 数据: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/static/public/509/qsar+androgen+receptor.zip
# 实例数: 1687
# 特征: 1024
# 班级: -1/1
# 缺失值:无
参考文献
QSAR 雄激素受体。(2019)。 UCI 机器学习库。 https://doi.org/10.24432/C53317。
在NeverGrad的光子学模型上进行基准测试
请参考NeverGrad了解光子学模型的介绍。
- pypop7.benchmarks.never_grad.benchmark_photonics(optimizer, ndim=10, max_function_evaluations=50000, seed=20221001)[source]
在NeverGrad平台上对光子学模型进行基准测试。
- Parameters:
optimizer (class) – 任何黑箱优化器。
ndim (int) – 需要最小化的适应度函数的维度数。
max_function_evaluations (int) – 函数评估的最大次数。
seed (int) – 用于随机数生成(RNG)的种子。
- Returns:
results – 最终优化结果。
- Return type:
字典
在Gymnasium上对控制器的基准测试
请参考Gymnasium以获取介绍(来自Farama Foundation)。
来自PyGMO的Lennard-Jones集群优化
请参考pagmo2了解(来自European Space Agency)关于这个444维Lennard-Jones团簇优化问题的介绍,该问题来自PyGMO。
测试类和数据
在下面,我们将提供一组用于基准测试的类和测试数据。由于这些类和数据仅用于测试目的,最终用户可以安全地跳过本节。
- class pypop7.benchmarks.cases.Cases(is_shifted=False, is_rotated=False)[source]
通过采样(测试案例)测试基准函数的正确性。
- check_origin(func, n_samples=7)[source]
通过随机抽样(测试案例)检查函数值为零的起点。
- Parameters:
func – 基准测试函数,func。
n_samples – 样本数量,int。
- Returns:
True 如果在测试用例上计算的所有函数值都为零,否则为 False;bool。
- compare(func, ndim, y_true, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None, atol=0.001)[source]
将真实函数值与使用的基准函数返回的值进行比较。
- Parameters:
func – 基准测试函数,func。
ndim – 维度数量(仅在[1, 7]范围内),int。
y_true – ndarray,其中每个元素是对应测试用例的真实函数值。
shift_vector – 平移向量,ndarray。
rotation_matrix – 旋转矩阵,ndarray。
atol – 绝对容差参数,float。
- Returns:
True 如果在测试用例上计算的所有函数值都匹配 y_true;否则,False。