sktime 简介#
愿景声明#
一个易于使用、易于扩展、全面的 Python 框架,用于时间序列的机器学习和人工智能
开源, 宽松许可证, 免费使用
公开透明地治理
友好、响应迅速、善良且包容 的社区,积极致力于确保公平和机会均等
一个学术和商业上的 中立空间,具有 生态系统整合 的雄心和客观的视角
一个**教育平台**,为所有职业阶段提供指导和技能提升机会,特别是职业生涯早期
sktime 是一个充满活力、欢迎新人的社区,提供指导机会!
进一步阅读:
sktime在 binder 上的笔记本教程录制的 视频教程
发现错误或类型?教程反馈线程
目录#
sktime 提供了一个统一的、类似于 scikit-learn 的工具箱接口,用于多个时间序列学习任务。
第1节 解释了什么是 scikit-learn 类似的工具箱,以 scikit-learn 为例。
第2节 概述了时间序列学习及其在该领域中的挑战。
第3节 提供了 sktime 的高层次工程概述。
1. sklearn 统一接口 - 策略模式#
sktime 遵循 sklearn / skbase 接口:
对象/估计器的统一接口
模块化设计,策略模式
可组合的,复合物是接口同质的
简单的规范语言和参数接口
视觉上信息丰富的漂亮打印
sklearn 提供了一个统一的接口,用于多种学习任务,包括分类和回归。
任何(有监督的)估计器都有以下接口点
实例化 你选择的模型,并设置参数
拟合 你的模型实例
使用那个拟合好的实例来 预测 新数据!
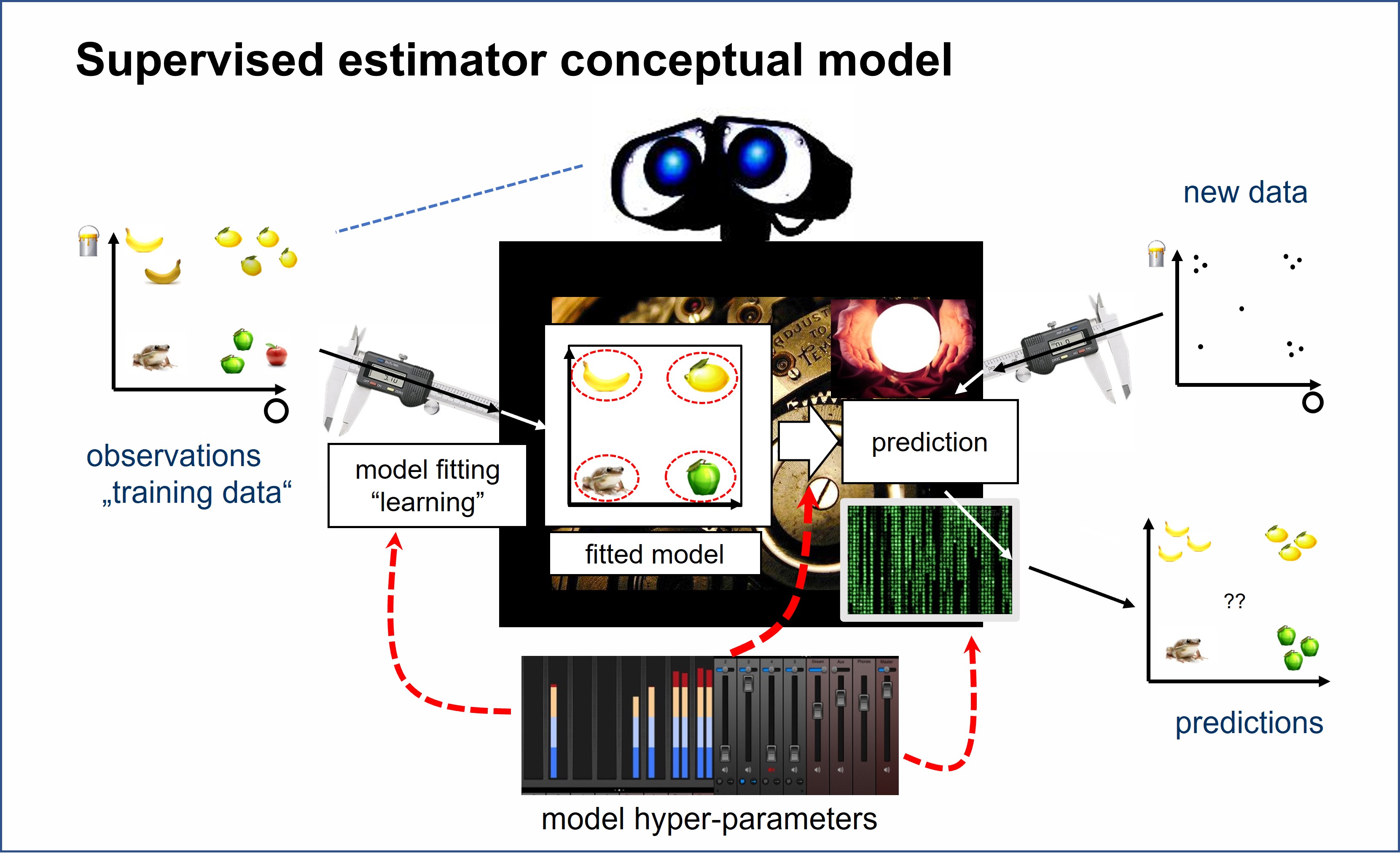
上述内容在代码中:
[1]:
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
[2]:
# get data to use the model on
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True, as_frame=True)
random_seed = 60
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=random_seed)
[3]:
X_train.head()
[3]:
| sepal length (cm) | sepal width (cm) | petal length (cm) | petal width (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59 | 5.2 | 2.7 | 3.9 | 1.4 |
| 52 | 6.9 | 3.1 | 4.9 | 1.5 |
| 108 | 6.7 | 2.5 | 5.8 | 1.8 |
| 36 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| 134 | 6.1 | 2.6 | 5.6 | 1.4 |
[4]:
y_train.head()
[4]:
59 1
52 1
108 2
36 0
134 2
Name: target, dtype: int64
[5]:
X_test.head()
[5]:
| sepal length (cm) | sepal width (cm) | petal length (cm) | petal width (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69 | 5.6 | 2.5 | 3.9 | 1.1 |
| 71 | 6.1 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 1.3 |
| 97 | 6.2 | 2.9 | 4.3 | 1.3 |
| 42 | 4.4 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| 73 | 6.1 | 2.8 | 4.7 | 1.2 |
[6]:
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# 1. Instantiate SVC with parameters gamma, C
clf = SVC(gamma=0.001, C=100.0)
# 2. Fit clf to training data
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 3. Predict labels on test data
y_test_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
y_test_pred
[6]:
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 2, 2, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0])
重要提示:要使用另一个分类器,只需更改规范行,部分1!
SVC 本可以是 RandomForest,步骤 2 和 3 保持不变 - 统一接口:
[7]:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# 1. Instantiate SVC with parameters gamma, C
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
# 2. Fit clf to training data
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 3. Predict labels on test data
y_test_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
y_test_pred
[7]:
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 2, 2, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0])
在面向对象设计的术语中,这被称为 “策略模式”
= 不同的估计器可以在不改变接口的情况下进行切换
= 就像一个电源插头适配器,如果它符合接口,它就是即插即用的。
图示总结:
可以通过 get_params、set_params 访问和设置参数:
[8]:
clf.get_params()
[8]:
{'bootstrap': True,
'ccp_alpha': 0.0,
'class_weight': None,
'criterion': 'gini',
'max_depth': None,
'max_features': 'sqrt',
'max_leaf_nodes': None,
'max_samples': None,
'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0,
'min_samples_leaf': 1,
'min_samples_split': 2,
'min_weight_fraction_leaf': 0.0,
'monotonic_cst': None,
'n_estimators': 100,
'n_jobs': None,
'oob_score': False,
'random_state': None,
'verbose': 0,
'warm_start': False}
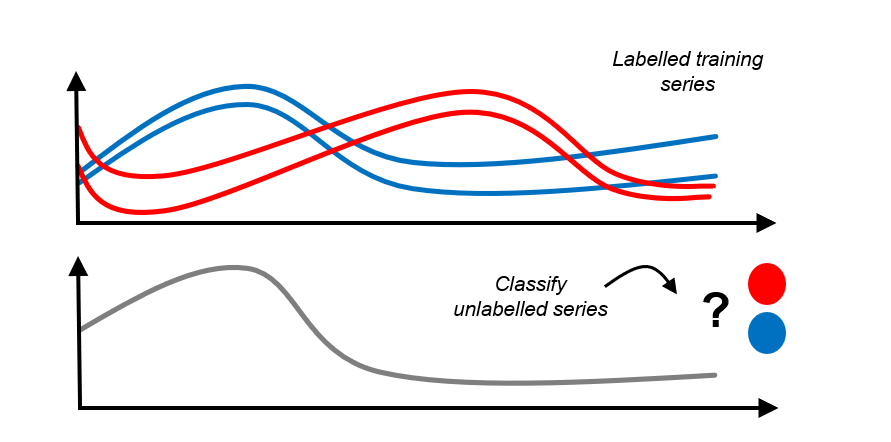
2. sktime 致力于时间序列数据分析#
与“表格”相比,更丰富的时序任务空间:
预测 - 基于过去几周的数据,预测明天的能源消耗
分类 - 根据先前的示例,将心电图分类为健康/患病
回归 - 基于温度/压力曲线预测生物反应器中的化合物纯度
聚类 - 将树形结构的叶子大纲分类为少量相似的类别
注解 - 识别数据流中的跳跃、异常、事件
sktime 旨在为这些提供类似于 sklearn 的、模块化的、可组合的接口!
任务 |
状态 |
链接 |
|---|---|---|
预测 |
稳定 |
|
时间序列分类 |
稳定 |
|
时间序列回归 |
稳定 |
|
变换 |
稳定 |
|
预测的性能指标 |
稳定 |
|
时间序列分割/重采样 |
稳定 |
|
参数拟合 |
成熟 |
|
时间序列对齐 |
成熟 |
|
时间序列聚类 |
成熟 |
|
时间序列距离/核 |
成熟 |
|
异常, 变化点 |
实验性 |
在 skpro 配套包中:
示例 - 预测#
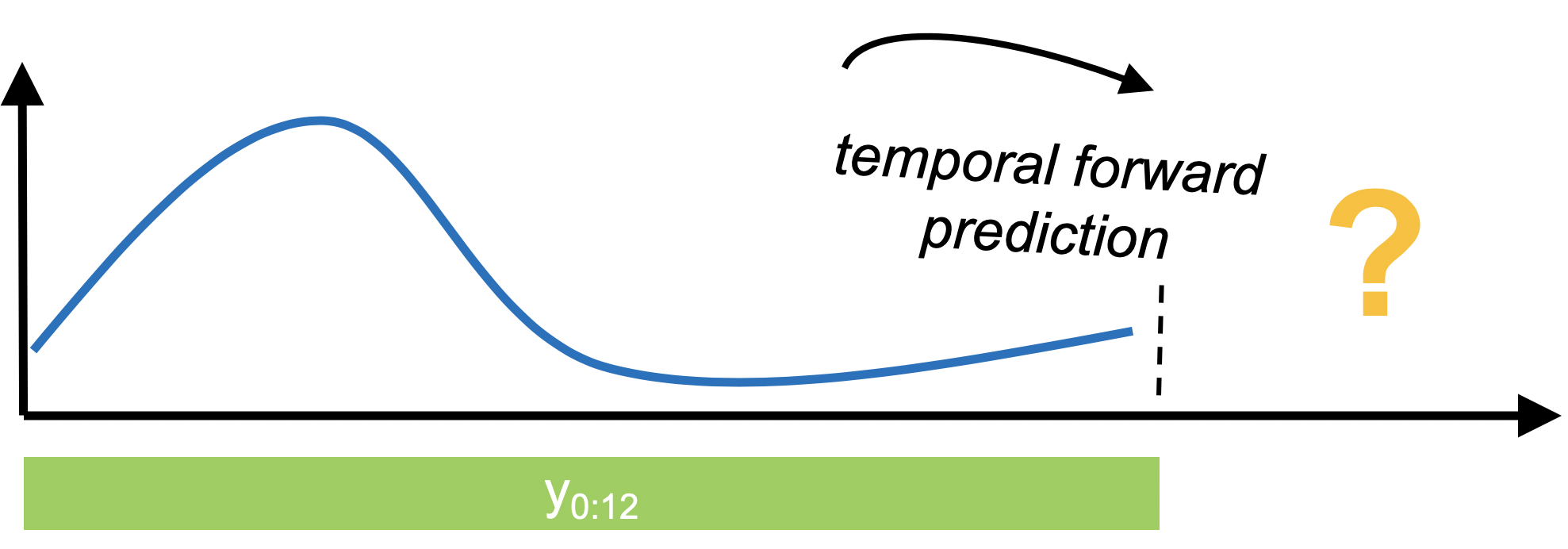
[ ]:
# get the data
from sktime.datasets import load_airline
y = load_airline()
[9]:
import numpy as np
from sktime.forecasting.naive import NaiveForecaster
# step 1: specify the forecasting algorithm
forecaster = NaiveForecaster(strategy="last", sp=12)
# step 2: specify forecasting horizon
fh = np.arange(1, 37) # we want to predict the next 36 months
# step 3: fit the forecaster
forecaster.fit(y, fh=fh)
# step 4: make the forecast
y_pred = forecaster.predict()
[10]:
from sktime.utils.plotting import plot_series
fig, ax = plot_series(y, y_pred, labels=["train", "forecast"])

示例 - 时间序列分类#

[ ]:
# get the data
from sktime.datasets import load_osuleaf
# for training
X_train, y_train = load_osuleaf(split="train", return_type="numpy3D")
# for prediction
X_new, _ = load_osuleaf(split="test", return_type="numpy3D")
X_new = X_new[:2]
[11]:
from sktime.classification.distance_based import KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier
from sktime.dists_kernels import ScipyDist
from sktime.dists_kernels.compose_tab_to_panel import AggrDist
# step 1 - specify the classifier
mean_eucl_dist = AggrDist(ScipyDist())
clf = KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier(n_neighbors=3, distance=mean_eucl_dist)
# step 2 - fit the classifier
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# step 3 - predict labels on new data
y_pred = clf.predict(X_new)
[12]:
X_train.shape
[12]:
(200, 1, 427)
[13]:
y_train.shape
[13]:
(200,)
[14]:
X_new.shape
[14]:
(2, 1, 427)
[15]:
y_pred.shape
[15]:
(2,)
3. sktime 整合了时间序列建模生态系统!#
时间序列的包空间高度分散:
有很多优秀的实现和方法!
但有许多不同的接口,不像
sklearn那样可组合

sktime 整合了生态系统 - 与所有现有的包友好合作!
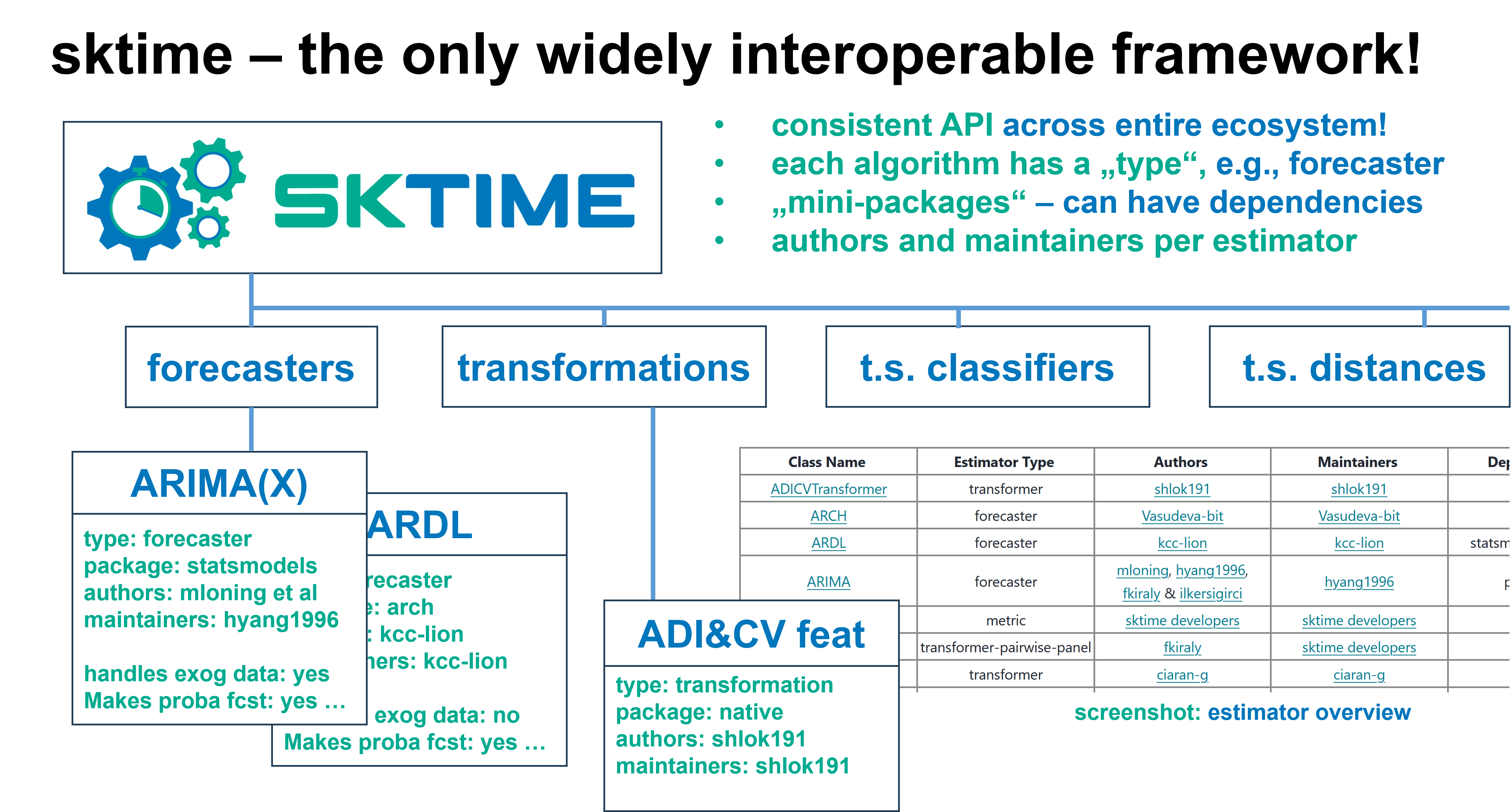
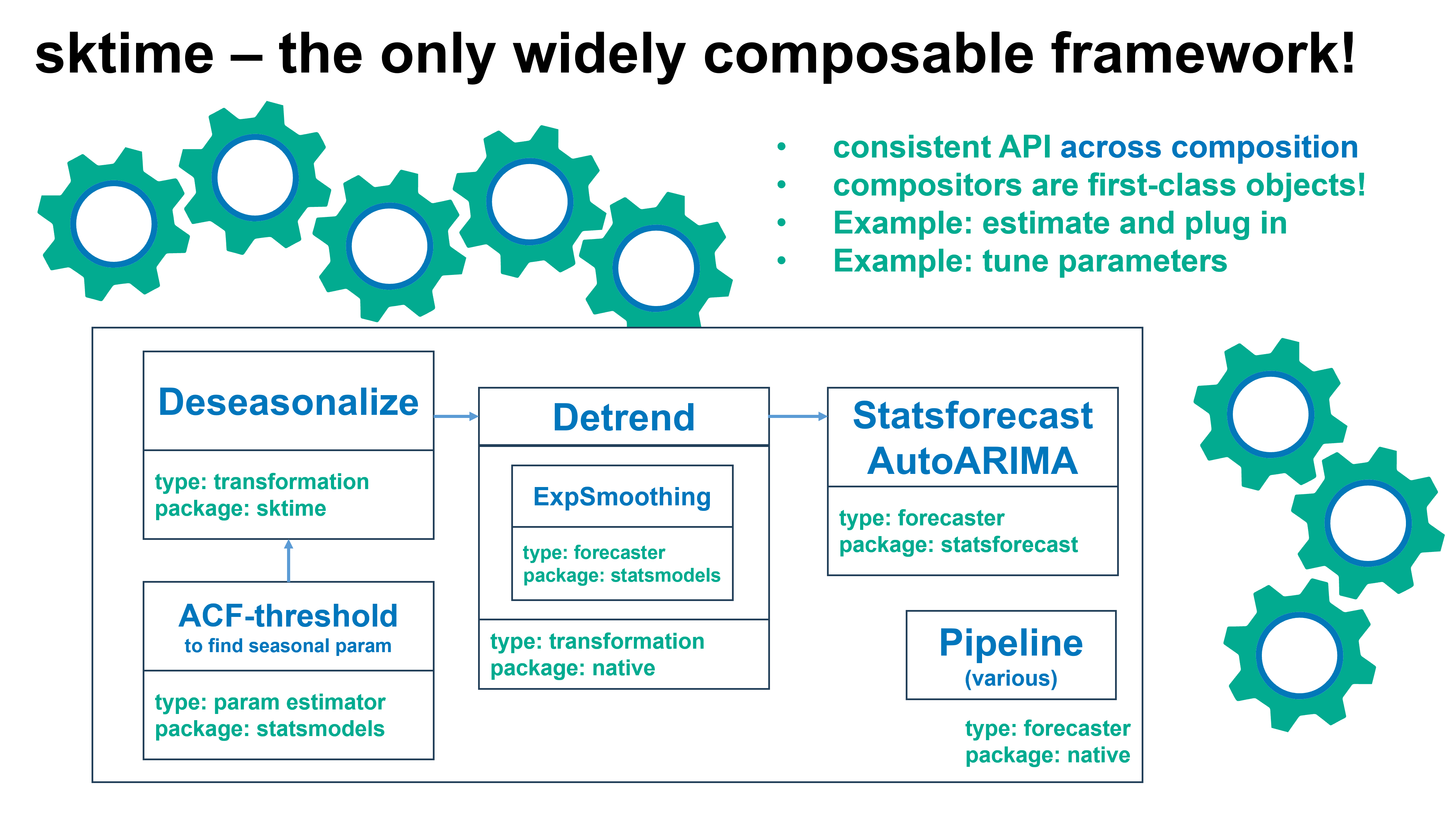
在整个生态系统中轻松搜索即插即用组件!
尝试 `sktime 估计器搜索 <https://www.sktime.net/en/latest/estimator_overview.html>`__

4. 总结#
sklearn接口:统一的接口(策略模式),模块化,组合稳定,易于指定的语言sktime演化了时间序列学习任务的接口sktime整合了一个碎片化的生态系统,包括接口、组合性和依赖管理。
致谢:笔记本 0 - sktime 和 sklearn 简介#
笔记本创建:fkiraly, marrov
基于现有 sktime 教程的一些案例,作者:fkiraly, miraep8
幻灯片(png/jpg):* 来自fkiraly在UCL的研究生课程,数据科学软件工程的原理与模式 * 生态系统幻灯片:fkiraly, mloning * 学习任务:fkiraly, mloning
学术研究论文中的引用与致谢:
sktime 工具箱: sktime: 时间序列机器学习的统一接口
sktime 设计原则: 设计机器学习工具箱:概念、原则和模式
使用 nbsphinx 生成。Jupyter 笔记本可以在这里找到。
