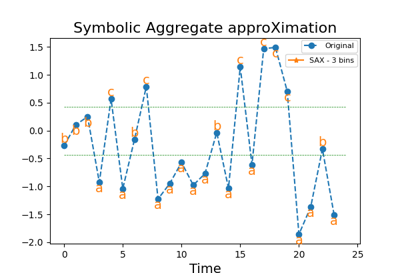
pyts.approximation.SymbolicAggregateApproximation¶
-
class
pyts.approximation.SymbolicAggregateApproximation(n_bins=4, strategy='quantile', raise_warning=True, alphabet=None)[来源]¶ 符号聚合近似。
Parameters: - n_bins : int (default = 4)
要生成的箱数。必须在2到
min(n_timestamps, 26)之间。- strategy : ‘uniform’, ‘quantile’ or ‘normal’ (default = ‘quantile’)
用于定义分箱宽度的策略:
- ‘uniform’: 每个样本中的所有箱宽度相同
- 'quantile': 每个样本中的所有分箱具有相同数量的数据点
- ‘normal’: 箱边缘为标准正态分布的分位数
- raise_warning : bool (default = True)
如果为True,当至少一个样本的分箱数较小时会发出警告。在这种情况下,您应考虑减少分箱数或移除这些样本。
- alphabet : None, ‘ordinal’ or array-like, shape = (n_bins,)
使用的字母表。如果为None,则使用拉丁字母表的前n_bins个字母。如果为'ordinal',则使用整数。
参考文献
[1] J. Lin, E. Keogh, L. Wei 和 S. Lonardi, "体验SAX:一种新颖的时间序列符号表示方法". 数据挖掘与知识发现, 15(2), 107-144 (2007). 示例
>>> from pyts.approximation import SymbolicAggregateApproximation >>> X = [[0, 4, 2, 1, 7, 6, 3, 5], ... [2, 5, 4, 5, 3, 4, 2, 3]] >>> transformer = SymbolicAggregateApproximation() >>> print(transformer.transform(X)) [['a' 'c' 'b' 'a' 'd' 'd' 'b' 'c'] ['a' 'd' 'c' 'd' 'b' 'c' 'a' 'b']]
方法
__init__([n_bins, strategy, raise_warning, …])Initialize self. fit([X, y])Pass. fit_transform(X[, y])Fit to data, then transform it. get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator. set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator. transform(X)Bin the data with the given alphabet. -
__init__(n_bins=4, strategy='quantile', raise_warning=True, alphabet=None)[来源]¶ 初始化自身。查看 help(type(self)) 获取准确的签名信息。
-
fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)¶ 拟合数据,然后进行转换。
使用可选参数fit_params将转换器适配到X和y,并返回转换后的X版本。
参数: - X : array-like, shape = (n_samples, n_timestamps)
单变量时间序列。
- y : None or array-like, shape = (n_samples,) (default = None)
目标值(无监督转换时为None)。
- **fit_params : dict
额外的拟合参数。
返回值: - X_new : array
转换后的数组。
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ 获取此估计器的参数。
参数: - deep : bool, default=True
如果为True,将返回此估计器及其包含的子估计器的参数。
返回值: - params : dict
参数名称映射到对应的值。