pyts.transformation.BOSS¶
-
class
pyts.transformation.BOSS(word_size=4, n_bins=4, strategy='quantile', window_size=10, window_step=1, anova=False, drop_sum=False, norm_mean=False, norm_std=False, numerosity_reduction=True, sparse=True, alphabet=None)[来源]¶ 符号傅里叶近似符号包。
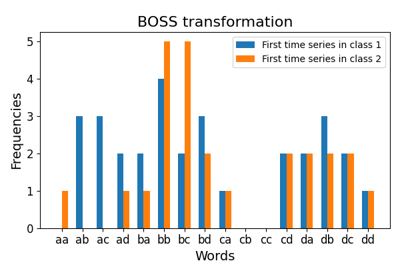
对于每个时间序列,使用滑动窗口提取子序列。 然后通过符号傅里叶近似(SFA)算法将这些子序列转换为单词。对于每个时间序列, 这些单词会被分组统计,并创建一个记录每个单词出现次数的直方图。
Parameters: - word_size : int (default = 4)
每个单词的大小。
- n_bins : int (default = 4)
要生成的区间数量。该值必须在2到26之间。
- strategy : str (default = ‘quantile’)
用于定义分箱宽度的策略:
- ‘uniform’: 每个样本中的所有箱宽度相同
- 'quantile': 每个样本中的所有分箱具有相同数量的数据点
- ‘normal’: 箱边缘为标准正态分布的分位数
- ‘entropy’: 使用信息增益计算分箱边界
- window_size : int or float (default = 10)
滑动窗口的大小。如果是浮点数,表示每个时间序列大小的百分比,必须在0到1之间。窗口大小将计算为
ceil(window_size * n_timestamps)。- window_step : int or float (default = 1)
滑动窗口的步长。如果是浮点数,表示每个时间序列大小的百分比,必须在0到1之间。窗口大小将计算为
ceil(window_step * n_timestamps)。- anova : bool (default = False)
如果为True,则通过单向ANOVA检验选择傅里叶系数。如果为False,则选择前几个傅里叶系数。
- drop_sum : bool (default = False)
如果为True,则丢弃第一个傅里叶系数(即子序列之和)。否则,保留该系数。
- norm_mean : bool (default = False)
如果为True,在缩放前对每个子序列进行居中处理。
- norm_std : bool (default = False)
如果为True,将每个子序列缩放为单位方差。
- numerosity_reduction : bool (default = True)
如果为True,则删除样本中除一个之外的所有连续出现的相同单词。
- sparse : bool (default = True)
如果为True则返回稀疏矩阵,否则返回数组。
- alphabet : None, ‘ordinal’ or array-like, shape = (n_bins,)
使用的字母表。如果为None,则使用拉丁字母表的前n_bins个字母。
参考文献
[1] P. Schäfer, "BOSS专注于在噪声存在情况下的时间序列分类"。数据挖掘与知识发现, 29(6), 1505-1530 (2015). 示例
>>> from pyts.datasets import load_gunpoint >>> from pyts.transformation import BOSS >>> X_train, X_test, _, _ = load_gunpoint(return_X_y=True) >>> boss = BOSS(word_size=2, n_bins=2, sparse=False) >>> boss.fit(X_train) BOSS(...) >>> sorted(boss.vocabulary_.values()) ['aa', 'ab', 'ba', 'bb'] >>> boss.transform(X_test) array(...)
属性: - vocabulary_ : dict
特征索引到术语的映射。
方法
__init__([word_size, n_bins, strategy, …])Initialize self. fit(X[, y])Fit the model according to the given training data. fit_transform(X[, y])Fit the data then transform it. get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator. set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator. transform(X)Transform the provided data. -
__init__(word_size=4, n_bins=4, strategy='quantile', window_size=10, window_step=1, anova=False, drop_sum=False, norm_mean=False, norm_std=False, numerosity_reduction=True, sparse=True, alphabet=None)[来源]¶ 初始化自身。查看 help(type(self)) 获取准确的签名信息。
-
fit(X, y=None)[来源]¶ 根据给定的训练数据拟合模型。
参数: - X : array-like, shape = (n_samples, n_timestamps)
训练向量。
- y : None or array-like, shape = (n_samples,)
每个数据样本的类别标签。
返回值: - self : object
-
fit_transform(X, y=None)[来源]¶ 拟合数据然后进行转换。
参数: - X : array-like, shape = (n_samples, n_timestamps)
训练向量。
- y : None or array-like, shape = (n_samples,)
每个数据样本的类别标签。
返回值: - X_new : 稀疏矩阵, 形状 = (n_samples, n_words)
文档-词项矩阵。
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ 获取此估计器的参数。
参数: - deep : bool, default=True
如果为True,将返回此估计器及其包含的子估计器的参数。
返回值: - params : dict
参数名称映射到对应的值。