Ragas 实验性
一个将评估驱动开发(EDD)应用于人工智能应用的框架。
Ragas Experimental的目标是将Ragas发展成一个面向AI应用的通用评估框架。它帮助团队设计、运行并推理任何AI工作流中的评估。除了工具本身,它还提供了一种思维模型,将评估不仅视为诊断工具,更作为迭代改进的支柱。
✨ 简介
-
🚀 教程
循序渐进的指南,帮助您开始使用 Ragas Experimental。通过实用示例学习如何评估像 RAGs 和智能体这样的人工智能应用。
-
📚 核心概念
深入探讨评估的原则,以及 Ragas Experimental 如何支持面向人工智能应用的评估驱动开发。
你好,世界 👋
1. 使用本地后端安装 Ragas Experimental
2. 将此代码片段复制到名为 hello_world.py 的文件中并运行 python hello_world.py
import numpy as np
from ragas_experimental import Dataset
from ragas import experiment
from ragas_experimental.metrics import MetricResult, discrete_metric
# Define a custom metric for accuracy
@discrete_metric(name="accuracy_score", allowed_values=["pass", "fail"])
def accuracy_score(response: str, expected: str):
result = "pass" if expected.lower().strip() == response.lower().strip() else "fail"
return MetricResult(value=result, reason=f"Match: {result == 'pass'}")
# Mock application endpoint that simulates an AI application response
def mock_app_endpoint(**kwargs) -> str:
return np.random.choice(["Paris", "4", "Blue Whale", "Einstein", "Python"])
# Create an experiment that uses the mock application endpoint and the accuracy metric
@experiment()
async def run_experiment(row):
response = mock_app_endpoint(query=row.get("query"))
accuracy = accuracy_score.score(response=response, expected=row.get("expected_output"))
return {**row, "response": response, "accuracy": accuracy.value}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
# Create dataset inline
dataset = Dataset(name="test_dataset", backend="local/csv", root_dir=".")
test_data = [
{"query": "What is the capital of France?", "expected_output": "Paris"},
{"query": "What is 2 + 2?", "expected_output": "4"},
{"query": "What is the largest animal?", "expected_output": "Blue Whale"},
{"query": "Who developed the theory of relativity?", "expected_output": "Einstein"},
{"query": "What programming language is named after a snake?", "expected_output": "Python"},
]
for sample in test_data:
dataset.append(sample)
dataset.save()
# Run experiment
results = asyncio.run(run_experiment.arun(dataset, name="first_experiment"))
3. 检查当前目录结构以查看创建的数据集和实验结果。
输出:
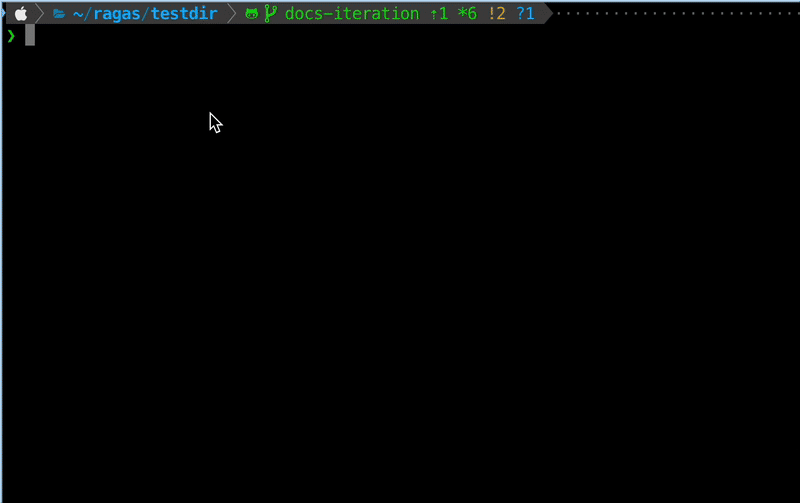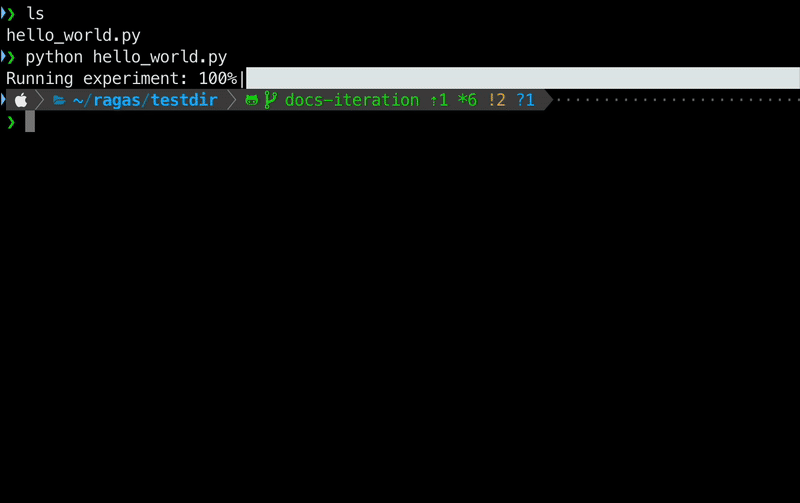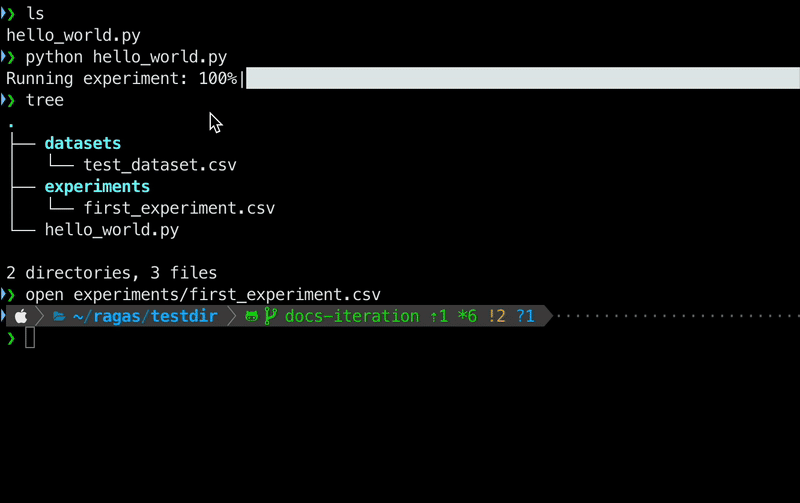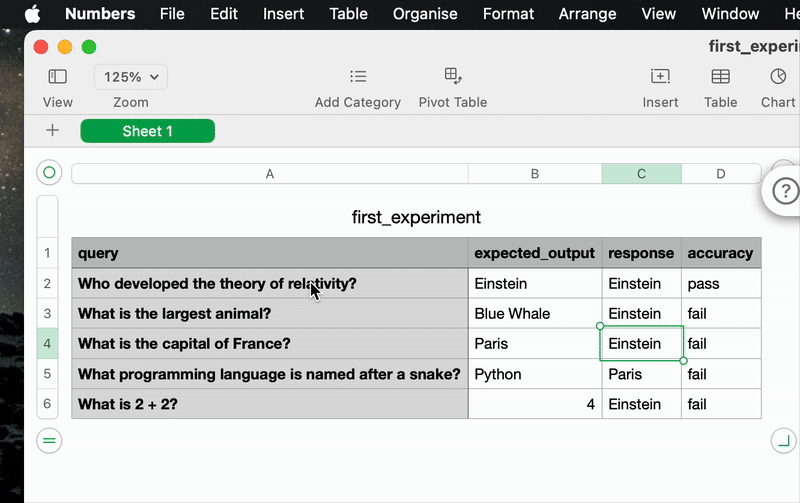
4. 查看您第一个实验的结果
输出: