持续监控管道#
本教程描述了在Azure ML管道中运行流程的高级用例。
关于先决条件和原则的详细解释可以在上述文章中找到。
持续监控对于维护生成式AI应用程序的质量、性能和效率是必要的。
这些因素直接影响用户体验和运营成本。
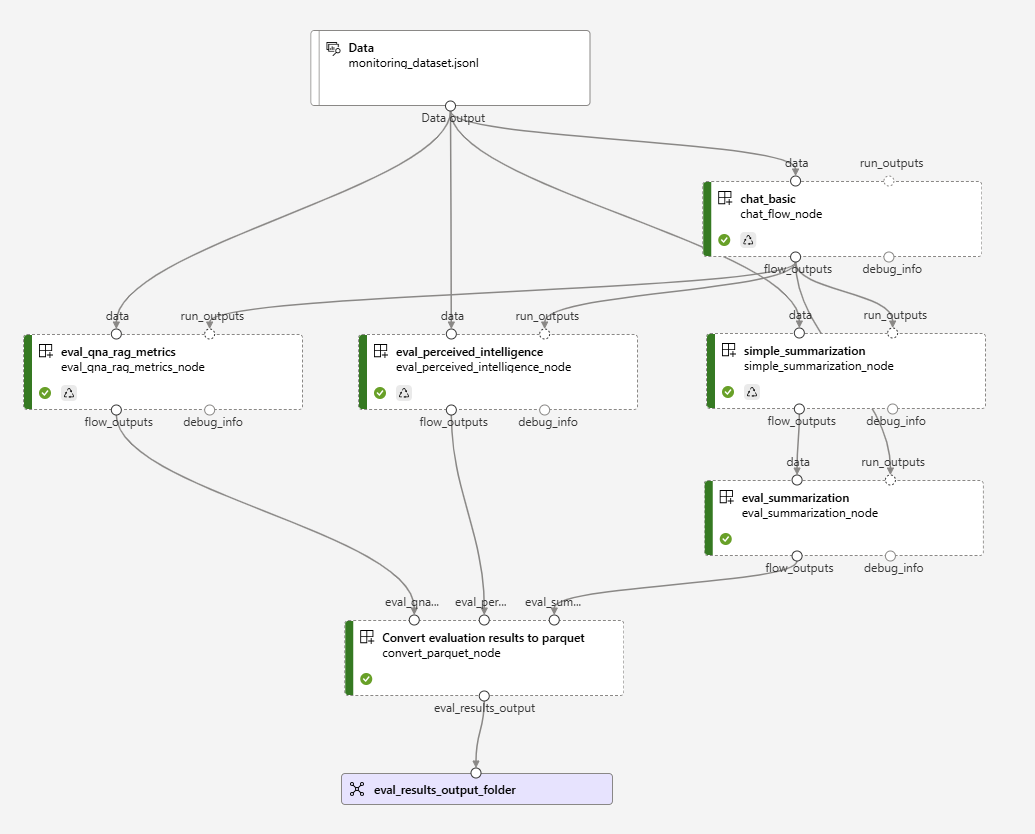
我们将对一个基本的聊天机器人流程进行评估,然后汇总结果以导出并可视化指标。
此管道中使用的流程如下所述:
1.1 导入所需的库#
安装所需的python包#
确保‘azure-ai-ml’的版本高于1.12.0
# import required libraries
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential, InteractiveBrowserCredential
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient, load_component, Input, Output
from azure.ai.ml.constants import AssetTypes
from azure.ai.ml.dsl import pipeline
from datetime import datetime
1.2 配置凭证#
try:
credential = DefaultAzureCredential()
# Check if given credential can get token successfully.
credential.get_token("https://management.azure.com/.default")
except Exception as ex:
# Fall back to InteractiveBrowserCredential in case DefaultAzureCredential not work
credential = InteractiveBrowserCredential()
1.3 获取工作区的句柄#
# Get a handle to workspace
ml_client = MLClient.from_config(credential=credential)
1.4.1 验证基本聊天流程#
导入流程所需的包#
pip install -r ../../../flows/chat/chat-basic/requirements.txt
!pf flow validate --source ../../../flows/chat/chat-basic
1.4.2 验证问答RAG评估流程#
导入流程所需的包#
pip install -r ../../../flows/evaluation/eval-qna-rag-metrics/requirements.txt
!pf flow validate --source ../../../flows/evaluation/eval-qna-rag-metrics
1.4.3 验证感知智能评估流程#
导入流程所需的包#
pip install -r ../../../flows/evaluation/eval-perceived-intelligence/requirements.txt
!pf flow validate --source ../../../flows/evaluation/eval-perceived-intelligence
1.4.4 验证摘要流程#
pip install -r ../flows/standard/simple-summarization/requirements.txt
!pf flow validate --source ./flows/standard/simple-summarization
1.4.5 验证摘要评估流程#
pip install -r ../../../flows/evaluation/eval-summarization/requirements.txt
!pf flow validate --source ../../../flows/evaluation/eval-summarization
2. 加载聊天流程作为组件#
chat_flow_component = load_component("../../../flows/chat/chat-basic/flow.dag.yaml")
2.1 加载QnA RAG评估流程作为组件#
eval_qna_rag_metrics_component = load_component(
"../../../flows/evaluation/eval-qna-rag-metrics/flow.dag.yaml"
)
2.2 加载感知智能流作为组件#
eval_perceived_intelligence_component = load_component(
"../../../flows/evaluation/eval-perceived-intelligence/flow.dag.yaml"
)
2.3 加载汇总流程作为组件#
simple_summarization_component = load_component(
"./flows/standard/simple-summarization/flow.dag.yaml"
)
2.4 加载汇总评估流程作为组件#
eval_summarization_component = load_component(
"../../../flows/evaluation/eval-summarization/flow.dag.yaml"
)
2.3 加载Parquet转换器#
Parquet转换器是一个命令组件,它聚合评估节点的结果并将指标记录到ML管道中。
convert_parquet_component = load_component(
"./components/convert_parquet/convert_parquet.yaml"
)
3.1 声明输入和输出#
data_input = Input(
path="./data/monitoring_dataset.jsonl",
type=AssetTypes.URI_FILE,
mode="mount",
)
eval_results_output = Output(
# Provide custom flow output file path if needed
# path="azureml://datastores/<data_store_name>/paths/<path>",
type=AssetTypes.URI_FOLDER,
# rw_mount is suggested for flow output
mode="rw_mount",
)
3.2.1 使用单一流程组件运行管道#
# Define the pipeline as a function
@pipeline()
def continuous_monitoring(
# Function inputs will be treated as pipeline input data or parameters.
# Pipeline input could be linked to step inputs to pass data between steps.
# Users are not required to define pipeline inputs.
# With pipeline inputs, user can provide the different data or values when they trigger different pipeline runs.
pipeline_input_data: Input,
parallel_node_count: int = 1,
):
# Declare pipeline step 'flow_node' by using flow component
chat_flow_node = chat_flow_component(
# Bind the pipeline input data to the port 'data' of the flow component
# If you don't have pipeline input, you can directly pass the 'data_input' object to the 'data'
# But with this approach, you can't provide different data when you trigger different pipeline runs.
data=pipeline_input_data,
# Declare which column of input data should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${data.<column_name_from_data_input>}
chat_history="${data.chat_history}",
question="${data.question}",
# Provide the connection values of the flow component
# The value of connection and deployment_name should align with your workspace connection settings.
connections={
"chat": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
"deployment_name": "gpt-35-turbo",
}
},
)
# Provide run settings of your flow component
# Only 'compute' is required and other setting will keep default value if not provided.
# If the workspace has been created with Azure AI Studio is inside a hub,
# a Compute Cluster cannot be used, use a Serverless instance instead.
chat_flow_node.environment_variables = {
"PF_INPUT_FORMAT": "jsonl",
}
chat_flow_node.compute = "serverless"
chat_flow_node.resources = {"instance_count": parallel_node_count}
chat_flow_node.mini_batch_size = 5
chat_flow_node.max_concurrency_per_instance = 2
chat_flow_node.retry_settings = {
"max_retries": 1,
"timeout": 1200,
}
chat_flow_node.error_threshold = -1
chat_flow_node.mini_batch_error_threshold = -1
chat_flow_node.logging_level = "DEBUG"
# QnA RAG Metrics Evaluation Node
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node = eval_qna_rag_metrics_component(
# Bind the pipeline input data to the port 'data' of the flow component
# If you don't have pipeline input, you can directly pass the 'data_input' object to the 'data'
# But with this approach, you can't provide different data when you trigger different pipeline runs.
data=pipeline_input_data,
# run_outputs connects the output of a previous node
run_outputs=chat_flow_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
# Declare which column of input data should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${data.<column_name_from_data_input>}
documents="${data.documents}",
question="${data.question}",
# Declare which column of previous node output should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${run.outputs.<column_name_from_data_input>}
answer="${run.outputs.answer}",
# Provide the connection values of the flow component
# The value of connection and deployment_name should align with your workspace connection settings.
connections={
"gpt_groundedness": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
"deployment_name": "gpt-35-turbo",
},
"gpt_relevance": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
"deployment_name": "gpt-35-turbo",
},
"gpt_retrieval_score": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
"deployment_name": "gpt-35-turbo",
},
},
)
# Provide run settings of your flow component
# Only 'compute' is required and other setting will keep default value if not provided.
# If the workspace has been created with Azure AI Studio is inside a hub,
# a Compute Cluster cannot be used, use a Serverless instance instead.
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.environment_variables = {
"PF_INPUT_FORMAT": "jsonl",
}
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.compute = "serverless"
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.resources = {"instance_count": parallel_node_count}
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.mini_batch_size = 5
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.max_concurrency_per_instance = 2
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.retry_settings = {
"max_retries": 1,
"timeout": 1200,
}
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.error_threshold = -1
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.mini_batch_error_threshold = -1
eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.logging_level = "DEBUG"
# Perceived Intelligence Evaluation Node
eval_perceived_intelligence_node = eval_perceived_intelligence_component(
# Bind the pipeline input data to the port 'data' of the flow component
# If you don't have pipeline input, you can directly pass the 'data_input' object to the 'data'
# But with this approach, you can't provide different data when you trigger different pipeline runs.
data=pipeline_input_data,
# run_outputs connects the output of a previous node
run_outputs=chat_flow_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
# Declare which column of input data should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${data.<column_name_from_data_input>}
question="${data.question}",
context="${data.context}",
# Declare which column of previous node output should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${run.outputs.<column_name_from_data_input>}
answer="${run.outputs.answer}",
# Provide the connection values of the flow component
# The value of connection and deployment_name should align with your workspace connection settings.
connections={
"gpt_perceived_intelligence": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
"deployment_name": "gpt-35-turbo",
}
},
)
# Provide run settings of your flow component
# Only 'compute' is required and other setting will keep default value if not provided.
# If the workspace has been created with Azure AI Studio is inside a hub,
# a Compute Cluster cannot be used, use a Serverless instance instead.
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.environment_variables = {
"PF_INPUT_FORMAT": "jsonl",
}
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.compute = "serverless"
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.resources = {"instance_count": parallel_node_count}
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.mini_batch_size = 5
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.max_concurrency_per_instance = 2
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.retry_settings = {
"max_retries": 1,
"timeout": 1200,
}
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.error_threshold = -1
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.mini_batch_error_threshold = -1
eval_perceived_intelligence_node.logging_level = "DEBUG"
# Summarization Node
simple_summarization_node = simple_summarization_component(
# Bind the pipeline input data to the port 'data' of the flow component
# If you don't have pipeline input, you can directly pass the 'data_input' object to the 'data'
# But with this approach, you can't provide different data when you trigger different pipeline runs.
data=pipeline_input_data,
# run_outputs connects the output of a previous node
run_outputs=chat_flow_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
# Declare which column of previous node output should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${run.outputs.<column_name_from_data_input>}
answer="${run.outputs.answer}",
# Provide the connection values of the flow component
# The value of connection and deployment_name should align with your workspace connection settings.
connections={
"summarize_text_content": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
"deployment_name": "gpt-35-turbo",
}
},
)
# Provide run settings of your flow component
# Only 'compute' is required and other setting will keep default value if not provided.
# If the workspace has been created with Azure AI Studio is inside a hub,
# a Compute Cluster cannot be used, use a Serverless instance instead.
simple_summarization_node.environment_variables = {
"PF_INPUT_FORMAT": "jsonl",
}
simple_summarization_node.compute = "serverless"
simple_summarization_node.resources = {"instance_count": parallel_node_count}
simple_summarization_node.mini_batch_size = 5
simple_summarization_node.max_concurrency_per_instance = 2
simple_summarization_node.retry_settings = {
"max_retries": 1,
"timeout": 1200,
}
simple_summarization_node.error_threshold = -1
simple_summarization_node.mini_batch_error_threshold = -1
simple_summarization_node.logging_level = "DEBUG"
# Summarization Evaluation Node
eval_summarization_node = eval_summarization_component(
# Bind the pipeline input data to the port 'data' of the flow component
# If you don't have pipeline input, you can directly pass the 'data_input' object to the 'data'
# But with this approach, you can't provide different data when you trigger different pipeline runs.
data=simple_summarization_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
# run_outputs connects the output of a previous node
run_outputs=chat_flow_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
# Declare which column of input data should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${data.<column_name_from_data_input>}
summary="${data.summary}",
# Declare which column of previous node output should be mapped to flow input
# the value pattern follows ${run.outputs.<column_name_from_data_input>}
document="${run.outputs.answer}",
# Provide the connection values of the flow component
# The value of connection and deployment_name should align with your workspace connection settings.
connections={
"score_fluency": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
},
"score_consistency": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
},
"score_relevance": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
},
"score_coherence": {
"connection": "azure_open_ai_connection",
},
},
)
# Provide run settings of your flow component
# Only 'compute' is required and other setting will keep default value if not provided.
# If the workspace has been created with Azure AI Studio is inside a hub,
# a Compute Cluster cannot be used, use a Serverless instance instead.
eval_summarization_node.environment_variables = {
"PF_INPUT_FORMAT": "jsonl",
}
eval_summarization_node.compute = "serverless"
eval_summarization_node.resources = {"instance_count": parallel_node_count}
eval_summarization_node.mini_batch_size = 5
eval_summarization_node.max_concurrency_per_instance = 2
eval_summarization_node.retry_settings = {
"max_retries": 1,
"timeout": 1200,
}
eval_summarization_node.error_threshold = -1
eval_summarization_node.mini_batch_error_threshold = -1
eval_summarization_node.logging_level = "DEBUG"
convert_parquet_node = convert_parquet_component(
# Bind the evaluation nodes outputs to the command component's input
eval_qna_rag_metrics_output_folder=eval_qna_rag_metrics_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
eval_perceived_intelligence_output_folder=eval_perceived_intelligence_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
eval_summarization_output_folder=eval_summarization_node.outputs.flow_outputs,
)
# Provide run settings of your flow component
# Only 'compute' is required and other setting will keep default value if not provided.
# If the workspace has been created with Azure AI Studio is inside a hub,
# a Compute Cluster cannot be used, use a Serverless instance instead.
convert_parquet_node.compute = "serverless"
# Function return will be treated as pipeline output. This is not required.
return {
"eval_results_output_folder": convert_parquet_node.outputs.eval_results_output
}
# create pipeline instance
pipeline_job_def = continuous_monitoring(pipeline_input_data=data_input)
pipeline_job_def.outputs.eval_results_output_folder = eval_results_output
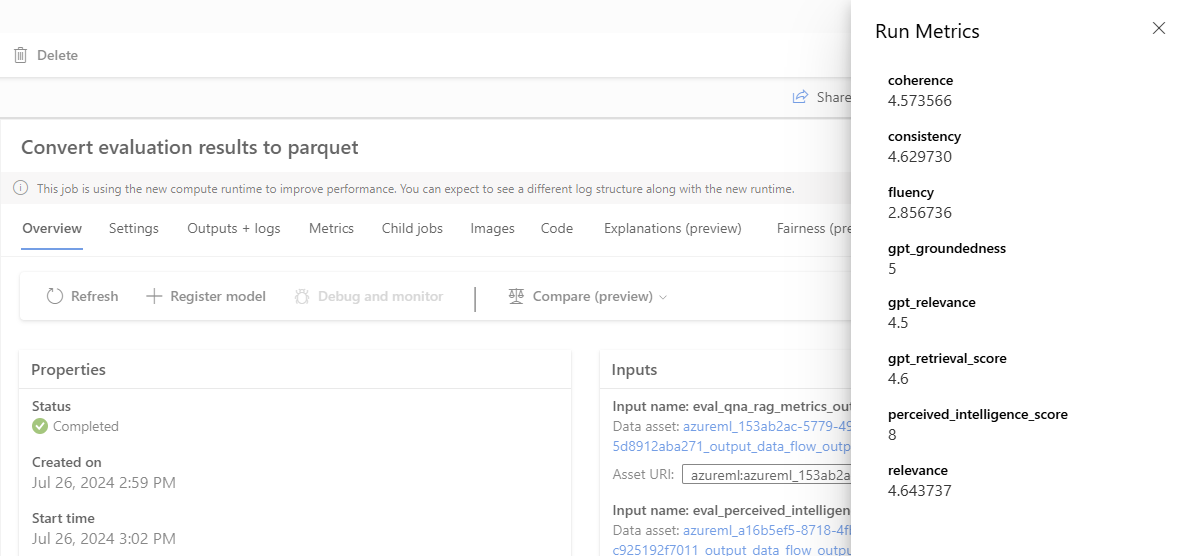
3.2.2 提交任务#
# Submit the pipeline job to your workspace
pipeline_job_run = ml_client.jobs.create_or_update(
pipeline_job_def, experiment_name="Continuous Monitoring"
)
pipeline_job_run
ml_client.jobs.stream(pipeline_job_run.name)
4.1 下一步 - 为您的管道设置调度器#
from datetime import datetime
from azure.ai.ml.entities import JobSchedule, RecurrenceTrigger, RecurrencePattern
from azure.ai.ml.constants import TimeZone
schedule_name = "simple_sdk_create_schedule_recurrence"
schedule_start_time = datetime.utcnow()
recurrence_trigger = RecurrenceTrigger(
frequency="day", # could accept "hour", "minute", "day", "week", "month"
interval=1,
schedule=RecurrencePattern(hours=10, minutes=[0, 1]),
start_time=schedule_start_time,
time_zone=TimeZone.UTC,
)
job_schedule = JobSchedule(
name=schedule_name,
trigger=recurrence_trigger,
# Declare the pipeline job to be scheduled. Here we uses the pipeline job created in previous example.
create_job=pipeline_job_def,
)
启动调度器#
job_schedule = ml_client.schedules.begin_create_or_update(
schedule=job_schedule
).result()
print(job_schedule)
禁用或关闭正在运行的调度程序#
job_schedule = ml_client.schedules.begin_disable(name=schedule_name).result()
job_schedule.is_enabled
4.2 下一步 - 将管道部署到端点#
from azure.ai.ml.entities import BatchEndpoint, PipelineComponentBatchDeployment
# from azure.ai.ml.entities import ModelBatchDeployment, ModelBatchDeploymentSettings, Model, AmlCompute, Data, BatchRetrySettings, CodeConfiguration, Environment, Data
# from azure.ai.ml.constants import BatchDeploymentOutputAction
endpoint_name = "hello-my-pipeline-endpoint"
endpoint = BatchEndpoint(
name=endpoint_name,
description="A hello world endpoint for pipeline",
)
ml_client.batch_endpoints.begin_create_or_update(endpoint).result()
