第2章:bookdelegate.cpp 到 bookdelegate.py¶
现在您的数据库已经就绪,移植用于BookDelegate类的C++代码。这个类提供了一个委托来展示和编辑QTableView中的数据。它继承了QSqlRelationalDelegate接口,该接口提供了处理关系数据库的特定功能,例如用于外键字段的组合框编辑器。首先,创建bookdelegate.py并向其中添加以下导入:
1from __future__ import annotations
2
3import copy
4import os
5from pathlib import Path
6
7from PySide6.QtSql import QSqlRelationalDelegate
8from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QItemDelegate, QSpinBox, QStyledItemDelegate,
在必要的import语句之后,移植BookDelegate类的构造函数代码。这段代码的C++和Python版本都初始化了一个QSqlRelationalDelegate和QPixmap实例。以下是它们的样子:
C++ 版本¶
1 QStyleOptionViewItem opt = option;
2 // Since we draw the grid ourselves:
3 opt.rect.adjust(0, 0, -1, -1);
4 QSqlRelationalDelegate::paint(painter, opt, index);
5 } else {
6 const QAbstractItemModel *model = index.model();
Python 版本¶
1from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QItemDelegate, QSpinBox, QStyledItemDelegate,
2 QStyle, QStyleOptionViewItem)
3from PySide6.QtGui import QMouseEvent, QPixmap, QPalette, QImage
4from PySide6.QtCore import QEvent, QSize, Qt, QUrl
5
6
7class BookDelegate(QSqlRelationalDelegate):
8 """Books delegate to rate the books"""
注意
Python 版本使用本地文件系统中 star.png 的绝对路径加载 QPixmap。
由于QSqlRelationalDelegate提供的默认功能不足以展示书籍数据,您必须重新实现一些函数。例如,绘制星星来表示表中每本书的评分。以下是重新实现代码的样子:
C++ 版本 (bookdelegate)¶
1 const QAbstractItemModel *model = index.model();
2 QPalette::ColorGroup cg = (option.state & QStyle::State_Enabled) ?
3 (option.state & QStyle::State_Active) ?
4 QPalette::Normal :
5 QPalette::Inactive :
6 QPalette::Disabled;
7
8 if (option.state & QStyle::State_Selected)
9 painter->fillRect(
10 option.rect,
11 option.palette.color(cg, QPalette::Highlight));
12
13 int rating = model->data(index, Qt::DisplayRole).toInt();
14 int width = star.width();
15 int height = star.height();
16 int x = option.rect.x();
17 int y = option.rect.y() + (option.rect.height() / 2) - (height / 2);
18 for (int i = 0; i < rating; ++i) {
19 painter->drawPixmap(x, y, star);
20 x += width;
21 }
22 // Since we draw the grid ourselves:
23 drawFocus(painter, option, option.rect.adjusted(0, 0, -1, -1));
24 }
25
26 QPen pen = painter->pen();
27 painter->setPen(option.palette.color(QPalette::Mid));
28 painter->drawLine(option.rect.bottomLeft(), option.rect.bottomRight());
29 painter->drawLine(option.rect.topRight(), option.rect.bottomRight());
30 painter->setPen(pen);
31}
32
33QSize BookDelegate::sizeHint(const QStyleOptionViewItem &option,
34 const QModelIndex &index) const
35{
36 if (index.column() == 5)
37 return QSize(5 * star.width(), star.height()) + QSize(1, 1);
38 // Since we draw the grid ourselves:
39 return QSqlRelationalDelegate::sizeHint(option, index) + QSize(1, 1);
40}
41
42bool BookDelegate::editorEvent(QEvent *event, QAbstractItemModel *model,
43 const QStyleOptionViewItem &option,
44 const QModelIndex &index)
45{
46 if (index.column() != 5)
47 return QSqlRelationalDelegate::editorEvent(event, model, option, index);
48
49 if (event->type() == QEvent::MouseButtonPress) {
50 QMouseEvent *mouseEvent = static_cast<QMouseEvent*>(event);
51 int stars = qBound(0, int(0.7 + qreal(mouseEvent->pos().x()
52 - option.rect.x()) / star.width()), 5);
53 model->setData(index, QVariant(stars));
54 // So that the selection can change:
55 return false;
56 }
57
58 return true;
59}
60
61QWidget *BookDelegate::createEditor(QWidget *parent,
62 const QStyleOptionViewItem &option,
63 const QModelIndex &index) const
64{
65 if (index.column() != 4)
66 return QSqlRelationalDelegate::createEditor(parent, option, index);
67
68 // For editing the year, return a spinbox with a range from -1000 to 2100.
69 QSpinBox *sb = new QSpinBox(parent);
70 sb->setFrame(false);
71 sb->setMaximum(2100);
72 sb->setMinimum(-1000);
73
74 return sb;
75}
Python 版本 (bookdelegate)¶
1
2 def __init__(self, parent=None):
3 QSqlRelationalDelegate.__init__(self, parent)
4 star_png = Path(__file__).parent / "images" / "star.png"
5 self.star = QPixmap(star_png)
6
7 def paint(self, painter, option, index):
8 """ Paint the items in the table.
9
10 If the item referred to by <index> is a StarRating, we
11 handle the painting ourselves. For the other items, we
12 let the base class handle the painting as usual.
13
14 In a polished application, we'd use a better check than
15 the column number to find out if we needed to paint the
16 stars, but it works for the purposes of this example.
17 """
18 if index.column() != 5:
19 # Since we draw the grid ourselves:
20 opt = copy.copy(option)
21 opt.rect = option.rect.adjusted(0, 0, -1, -1)
22 QSqlRelationalDelegate.paint(self, painter, opt, index)
23 else:
24 model = index.model()
25 if option.state & QStyle.State_Enabled:
26 if option.state & QStyle.State_Active:
27 color_group = QPalette.Normal
28 else:
29 color_group = QPalette.Inactive
30 else:
31 color_group = QPalette.Disabled
32
33 if option.state & QStyle.State_Selected:
34 painter.fillRect(option.rect,
35 option.palette.color(color_group, QPalette.Highlight))
36 rating = model.data(index, Qt.DisplayRole)
37 width = self.star.width()
38 height = self.star.height()
39 x = option.rect.x()
40 y = option.rect.y() + (option.rect.height() / 2) - (height / 2)
41 for i in range(rating):
42 painter.drawPixmap(x, y, self.star)
43 x += width
44
45 # Since we draw the grid ourselves:
46 self.drawFocus(painter, option, option.rect.adjusted(0, 0, -1, -1))
47
48 pen = painter.pen()
49 painter.setPen(option.palette.color(QPalette.Mid))
50 painter.drawLine(option.rect.bottomLeft(), option.rect.bottomRight())
51 painter.drawLine(option.rect.topRight(), option.rect.bottomRight())
52 painter.setPen(pen)
53
54 def sizeHint(self, option, index):
55 """ Returns the size needed to display the item in a QSize object. """
56 if index.column() == 5:
57 size_hint = QSize(5 * self.star.width(), self.star.height()) + QSize(1, 1)
58 return size_hint
59 # Since we draw the grid ourselves:
60 return QSqlRelationalDelegate.sizeHint(self, option, index) + QSize(1, 1)
61
62 def editorEvent(self, event, model, option, index):
63 if index.column() != 5:
64 return False
65
66 if event.type() == QEvent.MouseButtonPress:
67 mouse_pos = event.pos()
68 new_stars = int(0.7 + (mouse_pos.x() - option.rect.x()) / self.star.width())
69 stars = max(0, min(new_stars, 5))
70 model.setData(index, stars)
71 # So that the selection can change
72 return False
73
74 return True
75
76 def createEditor(self, parent, option, index):
77 if index.column() != 4:
78 return QSqlRelationalDelegate.createEditor(self, parent, option, index)
79
80 # For editing the year, return a spinbox with a range from -1000 to 2100.
81 spinbox = QSpinBox(parent)
82 spinbox.setFrame(False)
83 spinbox.setMaximum(2100)
84 spinbox.setMinimum(-1000)
85 return spinbox
现在委托已经就位,运行以下
main.py 以查看数据的呈现方式:
1from __future__ import annotations
2
3import sys
4
5from PySide6.QtCore import Qt
6from PySide6.QtSql import QSqlQueryModel
7from PySide6.QtWidgets import QTableView, QApplication
8
9import createdb
10from bookdelegate import BookDelegate
11
12if __name__ == "__main__":
13 app = QApplication()
14 createdb.init_db()
15
16 model = QSqlQueryModel()
17 model.setQuery("select title, author, genre, year, rating from books")
18
19 table = QTableView()
20 table.setModel(model)
21 table.setItemDelegate(BookDelegate())
22 table.resize(800, 600)
23 table.show()
24
25 sys.exit(app.exec())
这是应用程序运行时的外观:
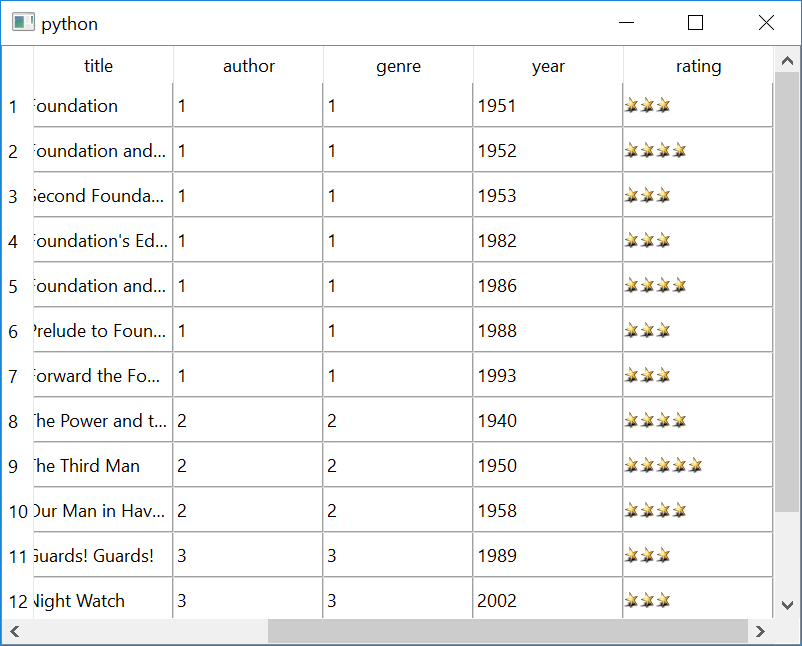
你现在会注意到与第1章相比的唯一区别是rating列看起来不同。
尝试通过添加这些功能进一步改进表格:
每列的标题
用于
author_id和genre_id列的SQL关系为窗口设置一个标题
有了这些功能,你的表格将会是这样的: