参数¶
参数(Params)允许您为任务提供运行时配置。您可以在DAG代码中配置默认参数,并在触发DAG时提供额外参数或覆盖参数值。Param值会通过JSON Schema进行验证。对于计划执行的DAG运行,将使用默认的Param值。
已定义的参数用于在手动触发时呈现良好的用户界面。 当您手动触发DAG时,可以在dagrun开始前修改其参数。 如果用户提供的值未通过验证,Airflow会显示警告而非创建dagrun。
DAG级别参数¶
要向DAG添加参数,请使用params关键字参数初始化它。
使用一个将参数名称映射到Param或指示参数默认值的对象的字典。
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.decorators import task
from airflow.models.param import Param
with DAG(
"the_dag",
params={
"x": Param(5, type="integer", minimum=3),
"my_int_param": 6
},
) as dag:
@task.python
def example_task(params: dict):
# This will print the default value, 6:
dag.log.info(dag.params['my_int_param'])
# This will print the manually-provided value, 42:
dag.log.info(params['my_int_param'])
# This will print the default value, 5, since it wasn't provided manually:
dag.log.info(params['x'])
example_task()
if __name__ == "__main__":
dag.test(
run_conf={"my_int_param": 42}
)
注意
DAG级别的参数是传递给任务的默认值。这些不应与通过UI表单或CLI手动提供的值混淆,后者仅存在于DagRun和TaskInstance的上下文中。这一区别对于TaskFlow DAG至关重要,因为其中可能包含with DAG(...) as dag:代码块内的逻辑。在这种情况下,用户可能尝试使用dag对象访问手动提供的参数值,但该对象始终只包含默认值。为确保访问手动提供的值,请在任务中使用模板变量如params或ti。
任务级参数¶
你也可以为单个任务添加参数。
def print_my_int_param(params):
print(params.my_int_param)
PythonOperator(
task_id="print_my_int_param",
params={"my_int_param": 10},
python_callable=print_my_int_param,
)
任务级参数优先于DAG级参数,而用户提供的参数(在触发DAG时)优先于任务级参数。
在任务中引用参数¶
参数可以在模板字符串中通过params引用。例如:
PythonOperator(
task_id="from_template",
op_args=[
"{{ params.my_int_param + 10 }}",
],
python_callable=(
lambda my_int_param: print(my_int_param)
),
)
尽管Params可以使用多种类型,但模板的默认行为是为您的任务提供字符串。
您可以通过在初始化DAG时设置render_template_as_native_obj=True来更改此行为。
with DAG(
"the_dag",
params={"my_int_param": Param(5, type="integer", minimum=3)},
render_template_as_native_obj=True
):
这样,当Param被提供给您的任务时,其类型会得到遵循:
# prints <class 'str'> by default
# prints <class 'int'> if render_template_as_native_obj=True
PythonOperator(
task_id="template_type",
op_args=[
"{{ params.my_int_param }}",
],
python_callable=(
lambda my_int_param: print(type(my_int_param))
),
)
另一种访问参数的方式是通过任务的context关键字参数。
def print_my_int_param(**context):
print(context["params"]["my_int_param"])
PythonOperator(
task_id="print_my_int_param",
python_callable=print_my_int_param,
params={"my_int_param": 12345},
)
JSON 模式验证¶
Param makes use of JSON Schema, so you can use the full JSON Schema specifications mentioned at https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/json-schema-validation.html to define Param objects.
with DAG(
"my_dag",
params={
# an int with a default value
"my_int_param": Param(10, type="integer", minimum=0, maximum=20),
# a required param which can be of multiple types
# a param must have a default value
"multi_type_param": Param(5, type=["null", "number", "string"]),
# an enum param, must be one of three values
"enum_param": Param("foo", enum=["foo", "bar", 42]),
# a param which uses json-schema formatting
"email": Param(
default="example@example.com",
type="string",
format="idn-email",
minLength=5,
maxLength=255,
),
},
):
注意
如果为DAG定义了schedule,则带有默认值的参数必须有效。这会在DAG解析期间进行验证。
如果schedule=None,则参数不会在DAG解析期间验证,而是在触发DAG之前验证。
这在DAG作者不想提供默认值但希望强制用户在触发时提供有效参数的情况下非常有用。
使用参数提供触发器UI表单¶
在2.6.0版本中新增。
DAG 级别的参数用于渲染用户友好的触发表单。
当用户点击“Trigger DAG”按钮时,会显示此表单。
触发器UI表单是基于预定义的DAG参数渲染的。如果DAG没有定义参数,则跳过触发表单。
表单元素可以通过Param类来定义,其属性决定了表单字段的显示方式。
Trigger UI 表单支持以下功能:
来自顶层DAG参数的直接标量值(布尔值、整数、字符串、列表、字典)会自动封装到
Param对象中。系统会根据原生Python数据类型自动检测type属性。因此这些简单类型会渲染为对应的字段类型。参数名称会被用作标签,且不进行额外验证,所有值都被视为可选。如果使用
Param类作为参数值的定义,可以添加以下属性:Param属性title用于渲染输入框的表单字段标签。 如果未定义title,则使用参数名称/键代替。Param属性description会在输入框下方以灰色帮助文本的形式呈现。 如需提供特殊格式或链接,需使用 Param 属性description_md。具体示例可参考教程 DAG Params UI example DAG。Param属性的type会影响字段的渲染方式。支持以下类型:参数类型
表单元素类型
额外支持的属性
示例
string生成一个单行文本框或文本区域用于编辑文本。
minLength: 最小文本长度maxLength: 最大文本长度format="date": 生成日期选择器带日历弹窗format="date-time": 生成一个带有日历弹窗的日期和时间选择器format="time": 生成一个时间选择器format="multiline": 生成一个多行文本框enum=["a", "b", "c"]: 生成一个用于标量值的下拉选择列表。根据JSON验证规则,必须选择一个值或者将该字段明确标记为可选。更多详情请参阅values_display={"a": "Alpha", "b": "Beta"}:对于通过enum生成的下拉选择框,您可以添加属性values_display并使用字典将数据值映射到显示标签。examples=["One", "Two", "Three"]: 如果你想提供可选值建议(不像上面的enum那样限制用户只能选择固定值),可以使用examples这是一个项目列表。
Param("default", type="string", maxLength=10)Param(f"{datetime.date.today()}", type="string", format="date")number或integer生成一个限制添加的字段numeric values only. The HTML browser通常还会在上添加一个加载动画右侧可增加或减少value.integeronly permits intnumbers,numberallows also分数值。minimum: 最小值maximum: 最大值
Param(42, type="integer", minimum=14, multipleOf=7)boolean生成一个用于切换的按钮asTrueorFalse.无。
Param(True, type="boolean")arrayGenerates a HTML multi line text field,每行编辑的内容都将被转换为字符串数组作为值。- 如果添加属性
examples并指定一个列表,将会生成多选下拉框而不是自由文本输入框。 values_display={"a": "Alpha", "b": "Beta"}:对于多值选择examples,您可以添加属性values_display,使用字典将数据值映射到显示标签。- 如果添加属性
items并附带一个包含type字段的字典,且该字段值不是"string"时,将会生成JSON条目字段以支持更多数组类型和额外的类型验证,具体描述请参考
Param(["a", "b", "c"], type="array")Param(["two", "three"], type="array", examples=["one", "two", "three", "four", "five"])Param(["one@example.com", "two@example.com"], type="array", items={"type": "string", "format": "idn-email"})object生成一个包含JSON的输入字段文本验证。Param({"key": "value"}, type=["object", "null"])null指定不期望有任何内容。单独使用这个功能意义不大但对于类型组合很有用liketype=["null", "string"]as thetype属性也接受一个列表类型。默认情况下,如果您指定一个类型,则该字段将被设为必填项输入 - 由于JSON验证。如果您希望某个字段的值添加了可选参数,您必须允许允许空值的JSON模式验证值。Param(None, type=["null", "string"])
如果表单字段留空,它将以
None值传递给params字典。表单字段按照DAG中
params定义的顺序呈现。如果想在表单中添加分区,请为每个字段添加
section属性。该文本将用作分区标签。 没有section的字段将在默认区域呈现。 其他分区默认会折叠显示。如果希望某些参数不显示,可以使用
const属性。这些参数会被提交但在表单中隐藏。const值必须与默认值匹配才能通过JSON Schema验证。在表单底部可以展开生成的JSON配置。如需手动修改值,可以调整JSON配置。当表单字段变更时,手动修改会被覆盖。
要在发布触发器表单链接时预填充表单中的值,您可以调用触发器URL
/dags/,并在URL中添加查询参数,格式为/trigger name=value,例如/dags/example_params_ui_tutorial/trigger?required_field=some%20text。要预定义DAG运行的运行ID,请使用URL参数run_id。字段可以是必填或选填。默认情况下,类型化字段是必填的,以确保它们通过JSON模式验证。要使类型化字段变为选填,必须允许"null"类型。
没有“部分”的字段将在默认区域呈现。其他部分默认会折叠显示。
注意
如果该字段是必填项,默认值也必须符合模式要求。如果DAG定义为schedule=None,参数值验证将在触发时进行。
例如,请查看提供的两个示例DAG:参数触发示例DAG和参数界面示例DAG。
with DAG(
dag_id=Path(__file__).stem,
dag_display_name="Params Trigger UI",
description=__doc__.partition(".")[0],
doc_md=__doc__,
schedule=None,
start_date=datetime.datetime(2022, 3, 4),
catchup=False,
tags=["example", "params"],
params={
"names": Param(
["Linda", "Martha", "Thomas"],
type="array",
description="Define the list of names for which greetings should be generated in the logs."
" Please have one name per line.",
title="Names to greet",
),
"english": Param(True, type="boolean", title="English"),
"german": Param(True, type="boolean", title="German (Formal)"),
"french": Param(True, type="boolean", title="French"),
},
) as dag:
@task(task_id="get_names", task_display_name="Get names")
def get_names(**kwargs) -> list[str]:
params: ParamsDict = kwargs["params"]
if "names" not in params:
print("Uuups, no names given, was no UI used to trigger?")
return []
return params["names"]
@task.branch(task_id="select_languages", task_display_name="Select languages")
def select_languages(**kwargs) -> list[str]:
params: ParamsDict = kwargs["params"]
selected_languages = []
for lang in ["english", "german", "french"]:
if params[lang]:
selected_languages.append(f"generate_{lang}_greeting")
return selected_languages
@task(task_id="generate_english_greeting", task_display_name="Generate English greeting")
def generate_english_greeting(name: str) -> str:
return f"Hello {name}!"
@task(task_id="generate_german_greeting", task_display_name="Erzeuge Deutsche Begrüßung")
def generate_german_greeting(name: str) -> str:
return f"Sehr geehrter Herr/Frau {name}."
@task(task_id="generate_french_greeting", task_display_name="Produire un message d'accueil en français")
def generate_french_greeting(name: str) -> str:
return f"Bonjour {name}!"
@task(task_id="print_greetings", task_display_name="Print greetings", trigger_rule=TriggerRule.ALL_DONE)
def print_greetings(greetings1, greetings2, greetings3) -> None:
for g in greetings1 or []:
print(g)
for g in greetings2 or []:
print(g)
for g in greetings3 or []:
print(g)
if not (greetings1 or greetings2 or greetings3):
print("sad, nobody to greet :-(")
lang_select = select_languages()
names = get_names()
english_greetings = generate_english_greeting.expand(name=names)
german_greetings = generate_german_greeting.expand(name=names)
french_greetings = generate_french_greeting.expand(name=names)
lang_select >> [english_greetings, german_greetings, french_greetings]
results_print = print_greetings(english_greetings, german_greetings, french_greetings)
params={
# Let's start simple: Standard dict values are detected from type and offered as entry form fields.
# Detected types are numbers, text, boolean, lists and dicts.
# Note that such auto-detected parameters are treated as optional (not required to contain a value)
"x": 3,
"text": "Hello World!",
"flag": False,
"a_simple_list": ["one", "two", "three", "actually one value is made per line"],
# But of course you might want to have it nicer! Let's add some description to parameters.
# Note if you can add any Markdown formatting to the description, you need to use the description_md
# attribute.
"most_loved_number": Param(
42,
type="integer",
title="Your favorite number",
description_md="Everybody should have a **favorite** number. Not only _math teachers_. "
"If you can not think of any at the moment please think of the 42 which is very famous because"
"of the book [The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy]"
"(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phrases_from_The_Hitchhiker%27s_Guide_to_the_Galaxy#"
"The_Answer_to_the_Ultimate_Question_of_Life,_the_Universe,_and_Everything_is_42).",
),
# If you want to have a selection list box then you can use the enum feature of JSON schema
"pick_one": Param(
"value 42",
type="string",
title="Select one Value",
description="You can use JSON schema enum's to generate drop down selection boxes.",
enum=[f"value {i}" for i in range(16, 64)],
),
"required_field": Param(
# In this example we have no default value
# Form will enforce a value supplied by users to be able to trigger
type="string",
title="Required text field",
description="This field is required. You can not submit without having text in here.",
),
"optional_field": Param(
"optional text, you can trigger also w/o text",
type=["null", "string"],
title="Optional text field",
description_md="This field is optional. As field content is JSON schema validated you must "
"allow the `null` type.",
),
@task(task_display_name="Show used parameters")
def show_params(**kwargs) -> None:
params: ParamsDict = kwargs["params"]
print(f"This DAG was triggered with the following parameters:\n\n{json.dumps(params, indent=4)}\n")
show_params()
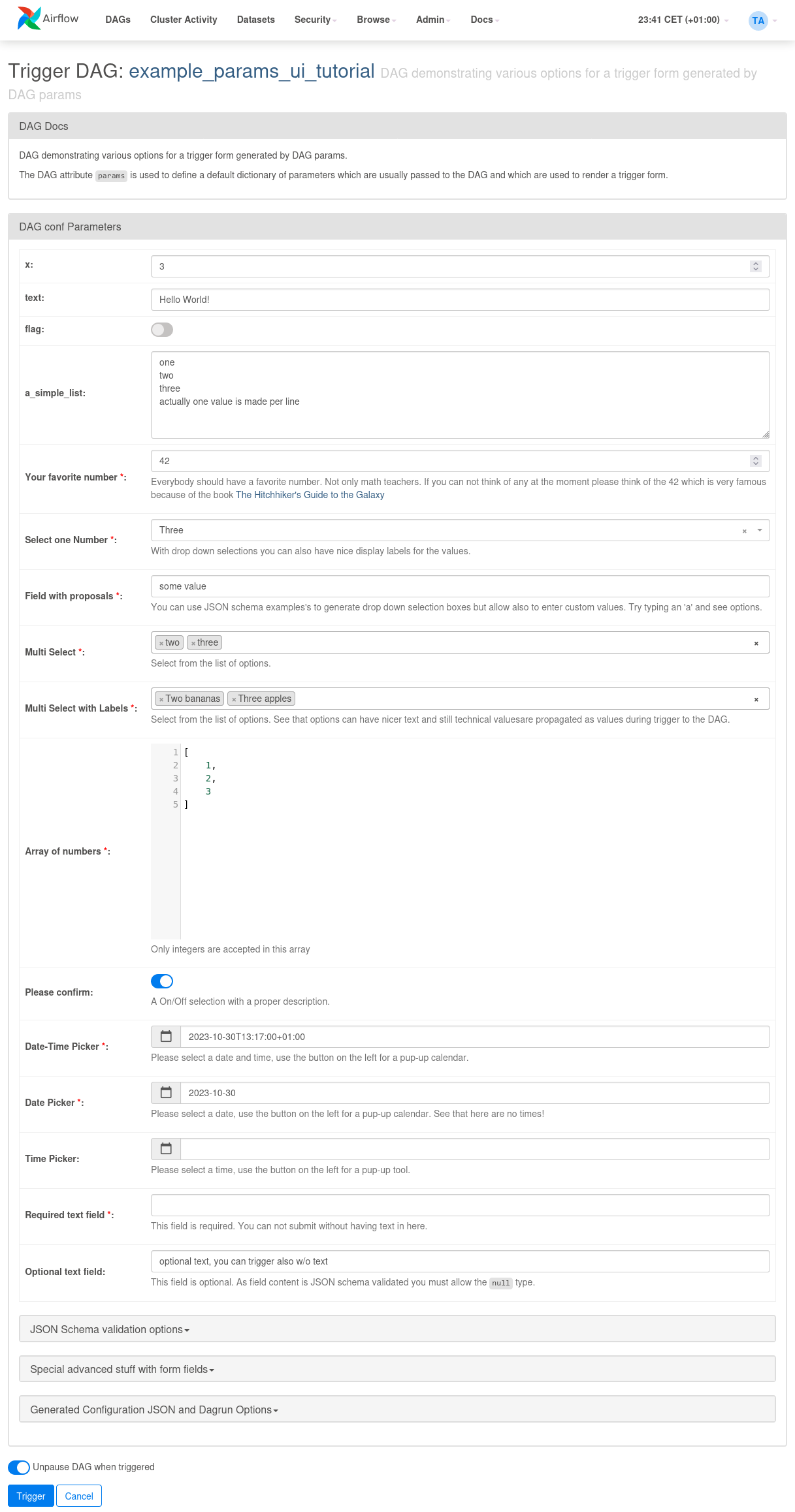
在版本2.7.0中新增:即使没有定义参数,也可以通过配置开关webserver.show_trigger_form_if_no_params强制显示触发器表单。
Changed in version 2.8.0: By default custom HTML is not allowed to prevent injection of scripts or other malicious HTML code. If you trust your DAG authors
you can change the trust level of parameter descriptions to allow raw HTML by setting the configuration entry
webserver.allow_raw_html_descriptions to True. With the default setting all HTML will be displayed as plain text.
This relates to the previous feature to enable rich formatting with the attribute description_html which is now super-seeded
with the attribute description_md.
Custom form elements using the attribute custom_html_form allow a DAG author to specify raw HTML form templates. These
custom HTML form elements are deprecated as of version 2.8.0.
禁用运行时参数修改¶
在触发DAG时更新参数的能力取决于标志core.dag_run_conf_overrides_params。将此配置设置为False将有效地将您的默认参数变为常量。