使用Label Studio实现OpenAI结构化输出

利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行标注任务可以显著提升效率。然而,这些模型通常生成自由格式的文本,通常需要额外预处理才能将输出格式化为可用结构。OpenAI新推出的结构化输出功能可确保输出符合预定义的JSON结构,使其成为与Label Studio等工具集成的理想选择。本文将探讨如何利用该功能完成各类标注任务。
为何在Label Studio中使用结构化输出?
Label Studio支持一种预标注格式用于将预测结果整合到标注工作流中,但集成LLM的输出可能具有挑战性。自由格式的输出通常需要大量前后处理才能匹配特定数据格式,这会增加开发时间和错误概率。此外,模型输出可能不一致地变化,经常包含解释或不同的结果格式。结构化输出通过允许开发者预先定义所需的JSON结构来解决这些问题,确保结果的一致性和可预测性。
直接使用JSON模式定义数据结构可能既繁琐又容易出错,尤其是与Pydantic等原生Python库相比。JSON模式需要手动精确定义每个字段,缺乏与Python类型系统的直接集成,并使验证过程复杂化。相比之下,Pydantic通过支持使用带类型提示的Python类来定义模式,从而简化了这一过程,同时提高了代码可读性和错误处理能力。
例如,考虑定义一个包含姓名和年龄的简单用户模式:
使用JSON Schema:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"age": {"type": "integer", "minimum": 0}
},
"required": ["name", "age"]
}使用Pydantic:
from pydantic import BaseModel, conint
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
age: conint(ge=0)使用Pydantic时,数据模式更加简洁,能与Python代码无缝集成,并在开发过程中提供类型检查和验证等额外优势,这使其成为Python应用中管理数据模式的首选方案。
示例
本博客附带了一个配套笔记本,让您能够边阅读内容边与代码和示例互动。
让我们探索如何利用OpenAI结构化输出来为不同任务生成预测。在继续之前,我们将先初始化OpenAI客户端。
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()摘要
摘要任务旨在从较长文本中提取关键信息,生成简洁版本。这在内容精选、文档索引或研究论文摘要等场景中非常实用。通过定义指定必填字段(如摘要文本和置信度分数)的标注方案,可确保模型输出与Label Studio的要求直接匹配,从而减少后处理需求,实现无缝集成。
首先,我们将使用Pydantic定义Label Studio的架构。
from enum import Enum
from typing import List, Union, Optional, Literal
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Label(BaseModel):
score: float
text: str
class ResultItem(BaseModel):
id: str
from_name: Literal["answer"] = "answer"
to_name: Literal["text"] = "text"
type: Literal["textarea"] = "textarea"
value: Label
class Prediction(BaseModel):
model_version: str
result: List[ResultItem]
class Data(BaseModel):
text: str
class Summarization(BaseModel):
data: Data
predictions: List[Prediction]定义完模式后,我们通过将模式作为response_format传递来请求预测。
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": """You are a Summarization assistant.
Your job is to identify a best, single sentence summary
for a given piece of text. Ensure that there is only a single
summary for the given text.""",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "The 2024 Summer Olympics,[a] officially the Games of the XXXIII Olympiad[b] and branded as Paris 2024, were an international multi-sport event that occurred from 26 July to 11 August 2024 in France, with the opening ceremony having taken place on 26 July. Paris was the host city, with events (mainly football) held in 16 additional cities spread across metropolitan France, including the sailing centre in the second-largest city of France, Marseille on the Mediterranean Sea, as well as one subsite for surfing in Tahiti, French Polynesia."
}
],
response_format=Summarization
)输出按预期填充了我们的模式:
{
"data": {
"text": "The 2024 Summer Olympics, branded as Paris 2024, were an international multi-sport event held from 26 July to 11 August 2024 in Paris and 16 additional cities across France, with surfing events in Tahiti."
},
"predictions": [
{
"model_version": "1",
"result": [
{
"id": "result",
"from_name": "answer",
"to_name": "text",
"type": "textarea",
"value": {
"score": 1.0,
"text": "The 2024 Summer Olympics were held in Paris and other locations across France and French Polynesia from 26 July to 11 August 2024."
}
}
]
}
]
}该JSON结果可直接导入Label Studio的文本摘要项目中。
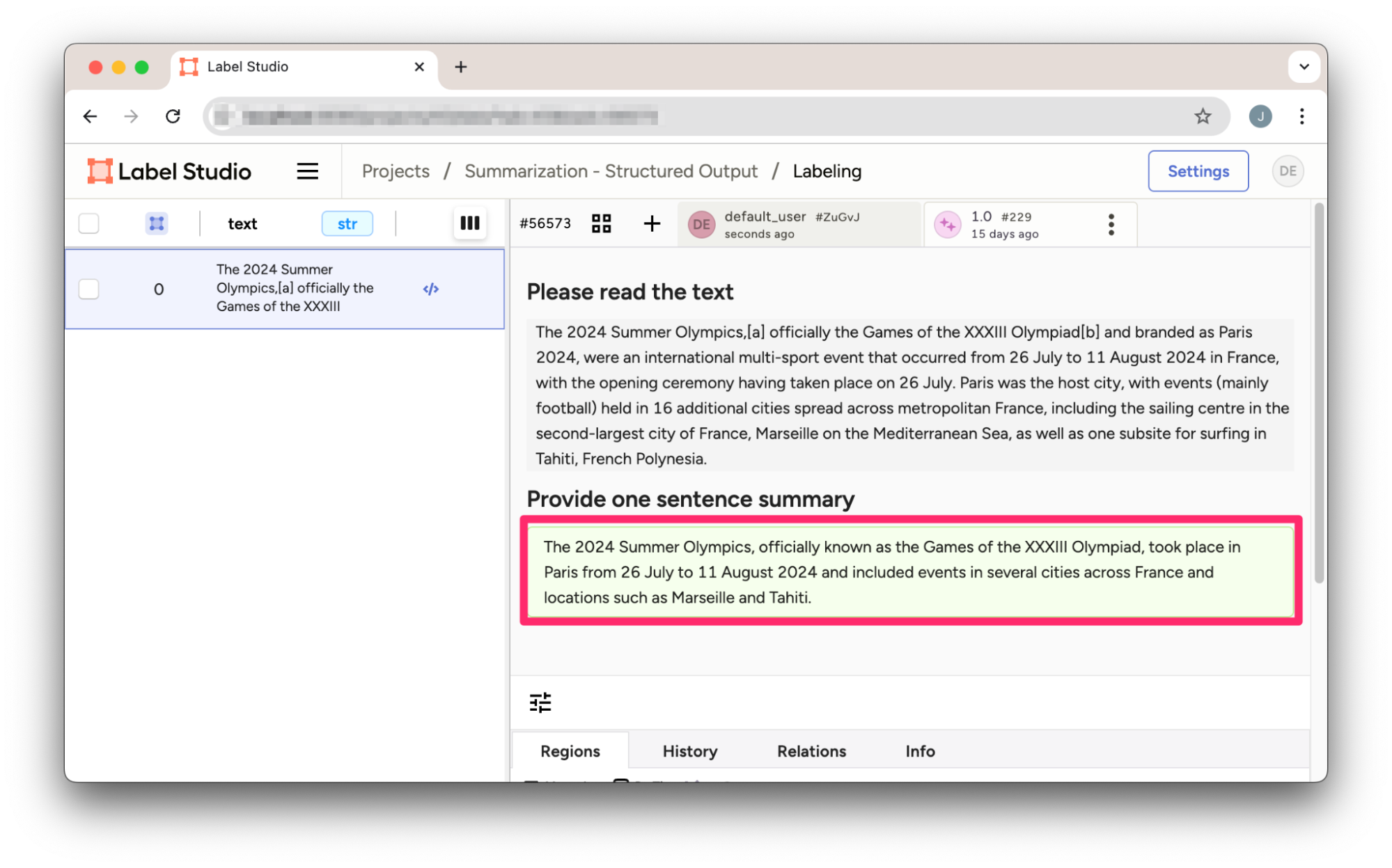
图1:从OpenAI结构化输出结果导入至Label Studio的摘要预测。
文本分类
文本分类涉及将一段文本分配到预定义的类别中,例如情感分析(如正面、负面、中性)、主题分类或垃圾邮件检测。在使用LLMs预测标签时,分类通常会稍微复杂一些,因为在生成过程中可能会混淆确切的类别。
在文本分类中使用结构化输出,可以让我们定义精确的模式来控制分类结果。我们不仅能控制返回的类别标签名称,还能在预测结果不明确时加入置信分数和额外元数据。通过这种方法,输出可直接导入Label Studio,结合人工审核来构建高质量的数据集。让我们看看如何在情感分析项目模板中实现这一点。
我们将再次在Pydantic中定义Label Studio的架构。
class EntityType(str, Enum):
positive = "Positive"
negative = "Negative"
neutral = "Neutral"
class Label(BaseModel):
score: float
choices: List[EntityType]
class ResultItem(BaseModel):
id: str
from_name: Literal["sentiment"] = "sentiment"
to_name: Literal["text"] = "text"
type: Literal["choices"] = "choices"
value: Label
class Prediction(BaseModel):
model_version: str
result: List[ResultItem]
class Data(BaseModel):
text: str
class Classification(BaseModel):
data: Data
predictions: List[Prediction]定义好模式后,我们就可以请求预测了,将模式作为response_format参数传入。
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": """You are a Sentiment analysis assistant.
Your job is to provide the sentiment for
for a given piece of text. Ensure that there is only a single
sentiment for the given text.""",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "We're excited to announce the 1.13 release of Label Studio! This update includes a refreshed UI and some new Generative AI templates for you to use."
}
],
response_format=Classification
)当我们检查输出时,可以看到补全内容完全按照我们的预期填充了模式。
{
"data": {
"text": "We\u2019re excited to announce the 1.13 release of Label Studio! This update includes a refreshed UI and some new Generative AI templates for you to use."
},
"predictions": [
{
"model_version": "1.3",
"result": [
{
"id": "1",
"from_name": "sentiment",
"to_name": "text",
"type": "choices",
"value": {
"score": 0.98,
"choices": [
"Positive"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}保存JSON结果后,我们可以直接将其导入Label Studio。
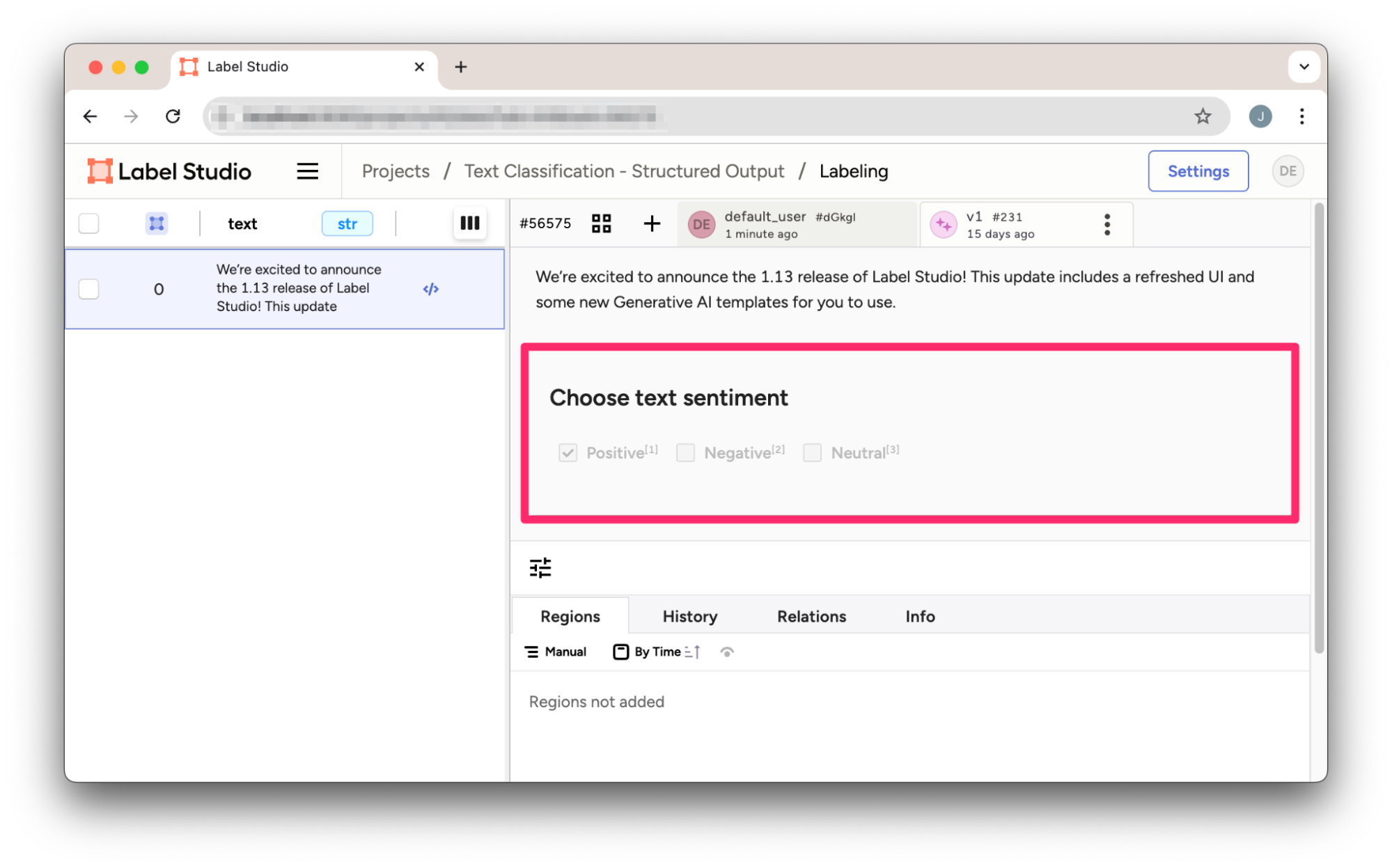
图2:Label Studio中从OpenAI结构化输出结果导入的文本分类预测。
命名实体识别
命名实体识别(NER)涉及识别文本中的人名、组织名、地名和日期等实体。这项任务更为复杂,因为它需要识别实体名称及其在文本中的位置。虽然大语言模型(LLMs)可以识别实体,但获取精确的字符偏移量(起始和结束位置)可能具有挑战性。通过定义包含这些细节的schema,您可以为Label Studio格式化输出,其中将包含这些条目的生成预测,但正确性可能不可靠。正如我们将在本例中看到的,可能仍需要进行一些后处理调整。
我们使用Pydantic为NER模板定义Label Studio的schema:
class EntityType(str, Enum):
person = "Person"
organization = "Organization"
location = "Location"
datetime = "DateTime"
product = "Product"
percent = "Percent"
fact = "Fact"
money = "Money"
class Label(BaseModel):
start: int
end: int
score: float
text: str
labels: List[EntityType]
class ResultItem(BaseModel):
id: str
from_name: Literal["label"] = "label"
to_name: Literal["text"] = "text"
type: Literal["labels"] = "labels"
value: Label
class Prediction(BaseModel):
model_version: str
result: List[ResultItem]
class Data(BaseModel):
text: str
class NamedEntities(BaseModel):
data: Data
predictions: List[Prediction]定义好模式后,我们就可以请求预测了,将模式作为`response_format`参数传入。
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": """You are a Named Entity Recognition (NER) assistant.
Your job is to identify and return all entity names and their
types for a given piece of text. You are to strictly conform
only to the following entity types: Person, Location, Organization
and DateTime. If uncertain about entity type, please ignore it.
Be careful of certain acronyms, such as role titles "CEO", "CTO",
"VP", etc - these are to be ignore.""",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Samuel Harris Altman (born April 22, 1985) is an American entrepreneur and investor best known as the CEO of OpenAI since 2019 (he was briefly fired and reinstated in November 2023)."
}
],
response_format=NamedEntities
)在检查输出结果时,我们可以看到补全内容完全按照预期填充了我们的模式。不过,我们应该对起始和结束字符偏移量保持审慎态度。我们将把数据导入Label Studio来查看实际效果。
{
"data": {
"text": "Samuel Harris Altman (born April 22, 1985) is an American entrepreneur and investor best known as the CEO of OpenAI since 2019 (he was briefly fired and reinstated in November 2023)."
},
"predictions": [
{
"model_version": "2023.10.01",
"result": [
{
"id": "1",
"from_name": "label",
"to_name": "text",
"type": "labels",
"value": {
"start": 0,
"end": 19,
"score": 0.95,
"text": "Samuel Harris Altman",
"labels": [
"Person"
]
}
},
{
"id": "2",
...
]
}
]
}模型能准确识别实体,但在提供Label Studio所需的正确字符偏移量以精确定位它们在文本中的位置时存在困难。

图3:从OpenAI结构化输出结果导入Label Studio的NER预测。请注意字符偏移量与识别出的实体未能正确对齐。
虽然识别实体是更复杂的任务,但模型的字符偏移量(指示实体在文本中的位置)并不准确。由于通过编程方式确定字符串中字符的确切位置相对简单,可以使用正则表达式或类似的后处理技术来正确调整和对齐实体。以下是一个简单的Python代码片段来解决此问题。
import re
json_data = json.loads(completion.choices[0].message.content)
# Extract the text to search in
text = json_data["data"]["text"]
# Iterate over each result in predictions to update start and end indexes
for prediction in json_data["predictions"]:
for result in prediction["result"]:
# Get the text to find in the main text
search_text = result["value"]["text"]
# Use regex to find the exact position of the search_text in text
match = re.search(re.escape(search_text), text)
if match:
# Update start and end indexes with exact positions
result["value"]["start"] = match.start()
result["value"]["end"] = match.end()
# Print the updated JSON
print(json.dumps(json_data, indent=4))完成这些调整后,输出结果可以导入Label Studio进行进一步审查或验证。
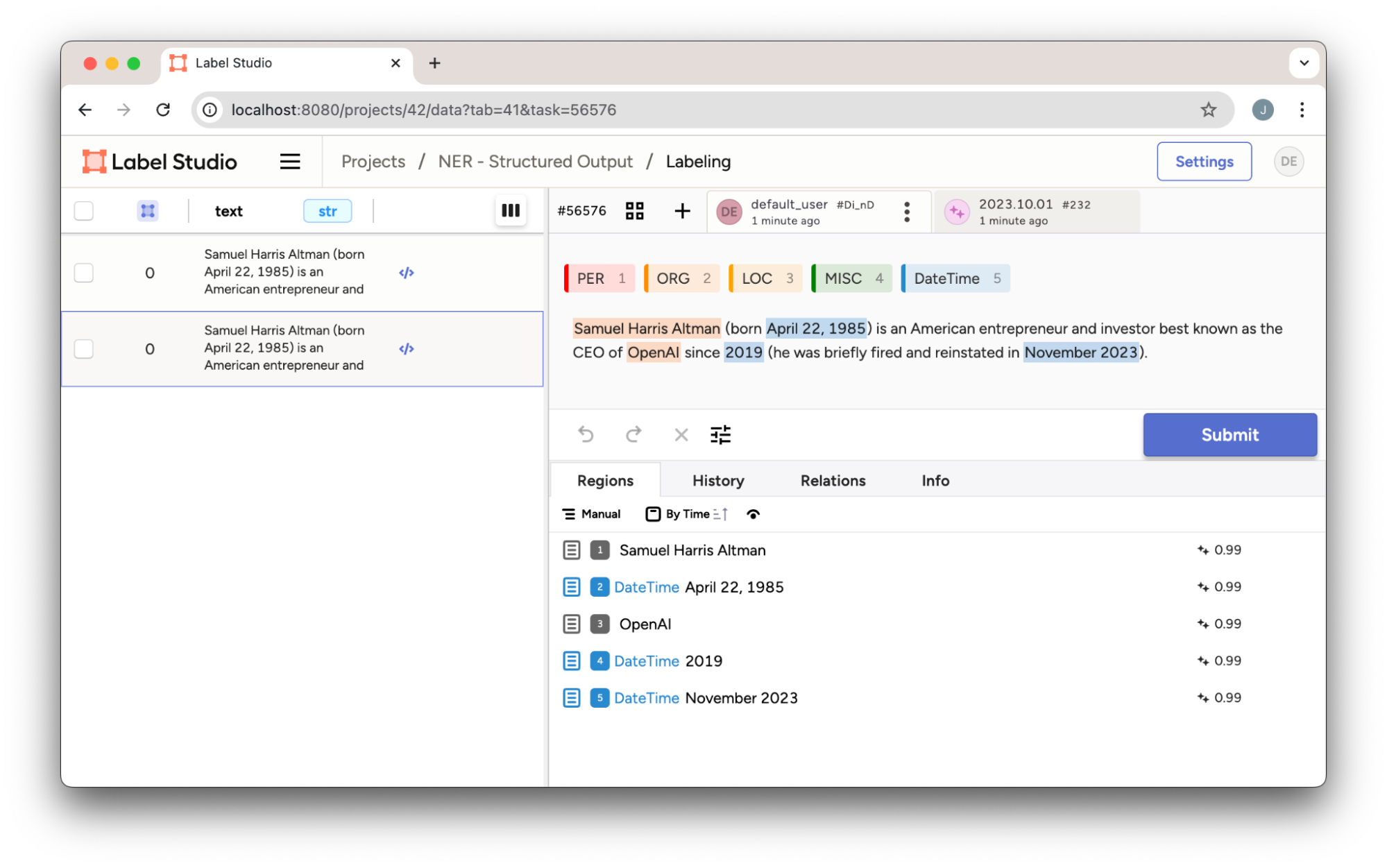
图4:经过后处理OpenAI结构化输出结果后,Label Studio中对齐的NER预测。请注意,与图3不同,字符偏移量正确地对齐到实体。
我们可以看到预测结果现在已与文本对齐。
高效使用结构化输出的技巧
- 选择合适的模型和参数: 选择适当的模型(例如 gpt-4o-2024-08-06)并调整温度、最大令牌数和停止序列等参数以优化输出质量。
- 编写有效的提示词: 请记住任务提示词会显著影响结构化输出。确保您的提示词清晰明确,并与Label Studio项目预期的格式保持一致,以获得一致的结果。
- 后处理技术: 对于需要精确细节的任务,如命名实体识别(NER),可使用正则表达式或字符串匹配等后处理方法校正偏移量或优化输出。同时必须验证关键元素(如URL)并在必要时确认响应的准确性。
- 模式验证:在使用前验证您的模式,以便及早发现并解决任何错误。此步骤有助于确保您的结构化输出与定义的模式保持一致,减少与Label Studio的集成问题。
结论
OpenAI的结构化输出功能极大地增强了数据标注预测的生成能力。通过确保输出符合预定义模式、提高可靠性并减少预处理工作,您可以显著提升Label Studio工作流的整体效率。我们列举了几个示例来展示如何使用结构化输出,但这些示例的灵活性应能让您将其扩展并适配到广泛的用例场景,使其成为应对不同项目中各类数据标注挑战的强大解决方案。