torch.meshgrid¶
- torch.meshgrid(*tensors, indexing=None)[源代码]¶
创建由attr:tensors中的一维输入指定的坐标网格。
当你想要在某个输入范围内可视化数据时,这非常有用。请参见下面的绘图示例。
给定 个一维张量 作为 输入,其对应的大小为 , 这将创建 个N维张量 ,每个张量的形状为 ,其中 输出 是通过扩展 到结果形状构建的。
注意
0D 输入被视为与包含单个元素的 1D 输入等效。
警告
torch.meshgrid(*tensors) 目前具有与调用 numpy.meshgrid(*arrays, indexing=’ij’) 相同的行为。
在未来,torch.meshgrid 将默认转换为 indexing=’xy’。
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/50276 跟踪此问题,目标是迁移到NumPy的行为。
另请参阅
torch.cartesian_prod()具有相同的效果,但它将数据收集在一个向量张量中。- Parameters
- Returns
如果输入有 个大小为 ,那么输出也将有 个张量,其中每个张量的形状为 。
- Return type
seq (张量的序列)
示例:
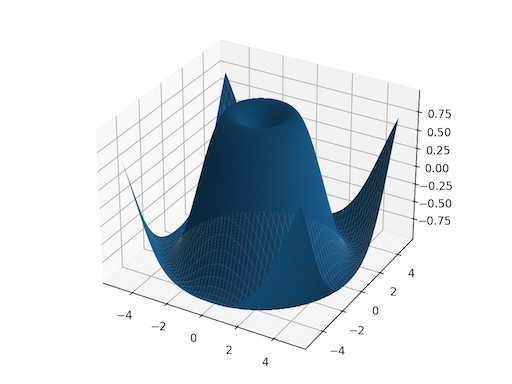
>>> x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) >>> y = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) 观察网格上的元素对,(1, 4), (1, 5), ..., (3, 6)。这与笛卡尔积相同。 >>> grid_x, grid_y = torch.meshgrid(x, y, indexing='ij') >>> grid_x tensor([[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3]]) >>> grid_y tensor([[4, 5, 6], [4, 5, 6], [4, 5, 6]]) 当这些网格被正确堆叠时,可以看到这种对应关系。 >>> torch.equal(torch.cat(tuple(torch.dstack([grid_x, grid_y]))), ... torch.cartesian_prod(x, y)) True `torch.meshgrid` 通常用于生成网格以进行绘图。 >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> xs = torch.linspace(-5, 5, steps=100) >>> ys = torch.linspace(-5, 5, steps=100) >>> x, y = torch.meshgrid(xs, ys, indexing='xy') >>> z = torch.sin(torch.sqrt(x * x + y * y)) >>> ax = plt.axes(projection='3d') >>> ax.plot_surface(x.numpy(), y.numpy(), z.numpy()) >>> plt.show()