回归诊断¶
这个示例文件展示了如何在实际生活中使用一些statsmodels回归诊断测试。你可以在回归诊断页面上了解更多测试并获取更多信息。
请注意,这里描述的大多数测试只返回一个数字元组,没有任何注释。输出的完整描述总是包含在docstring和在线的statsmodels文档中。为了演示目的,我们在下面的示例中使用zip(name,test)构造来美观地打印简短描述。
估计一个回归模型¶
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
[2]:
from statsmodels.compat import lzip
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
import statsmodels.stats.api as sms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load data
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vincentarelbundock/Rdatasets/master/csv/HistData/Guerry.csv"
dat = pd.read_csv(url)
# Fit regression model (using the natural log of one of the regressors)
results = smf.ols("Lottery ~ Literacy + np.log(Pop1831)", data=dat).fit()
# Inspect the results
print(results.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: Lottery R-squared: 0.348
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.333
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 22.20
Date: Wed, 16 Oct 2024 Prob (F-statistic): 1.90e-08
Time: 18:27:14 Log-Likelihood: -379.82
No. Observations: 86 AIC: 765.6
Df Residuals: 83 BIC: 773.0
Df Model: 2
Covariance Type: nonrobust
===================================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 246.4341 35.233 6.995 0.000 176.358 316.510
Literacy -0.4889 0.128 -3.832 0.000 -0.743 -0.235
np.log(Pop1831) -31.3114 5.977 -5.239 0.000 -43.199 -19.424
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 3.713 Durbin-Watson: 2.019
Prob(Omnibus): 0.156 Jarque-Bera (JB): 3.394
Skew: -0.487 Prob(JB): 0.183
Kurtosis: 3.003 Cond. No. 702.
==============================================================================
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
残差的正态性¶
Jarque-Bera 检验:
[3]:
name = ["Jarque-Bera", "Chi^2 two-tail prob.", "Skew", "Kurtosis"]
test = sms.jarque_bera(results.resid)
lzip(name, test)
[3]:
[('Jarque-Bera', np.float64(3.3936080248431657)),
('Chi^2 two-tail prob.', np.float64(0.1832683123166338)),
('Skew', np.float64(-0.4865803431122337)),
('Kurtosis', np.float64(3.0034177578816323))]
全渠道测试:
[4]:
name = ["Chi^2", "Two-tail probability"]
test = sms.omni_normtest(results.resid)
lzip(name, test)
[4]:
[('Chi^2', np.float64(3.71343781159718)),
('Two-tail probability', np.float64(0.15618424580304832))]
影响测试¶
一旦创建,类 OLSInfluence 的对象会保存属性和方法,允许用户评估每个观测值的影响。例如,我们可以通过以下方式计算并提取 DFbetas 的前几行:
[5]:
from statsmodels.stats.outliers_influence import OLSInfluence
test_class = OLSInfluence(results)
test_class.dfbetas[:5, :]
[5]:
array([[-0.00301154, 0.00290872, 0.00118179],
[-0.06425662, 0.04043093, 0.06281609],
[ 0.01554894, -0.03556038, -0.00905336],
[ 0.17899858, 0.04098207, -0.18062352],
[ 0.29679073, 0.21249207, -0.3213655 ]])
通过输入 dir(influence_test) 探索其他选项
关于杠杆的有用信息也可以绘制:
[6]:
from statsmodels.graphics.regressionplots import plot_leverage_resid2
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
fig = plot_leverage_resid2(results, ax=ax)
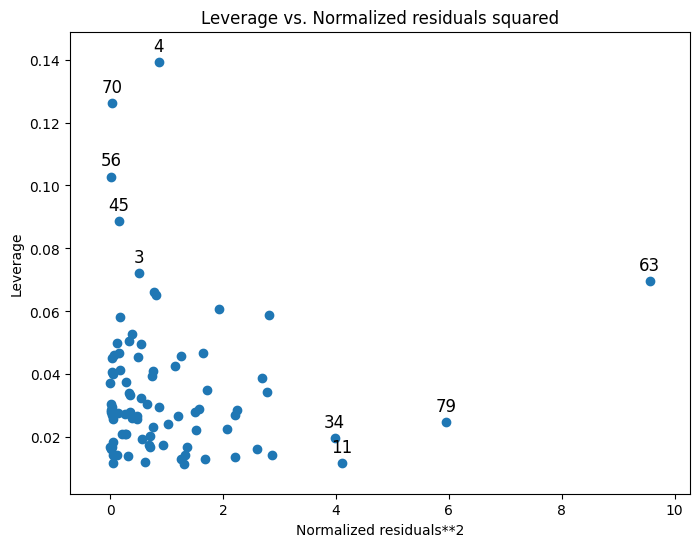
其他绘图选项可以在图形页面上找到。
多重共线性¶
条件数:
[7]:
np.linalg.cond(results.model.exog)
[7]:
np.float64(702.1792145490065)
异方差性检验¶
Breush-Pagan 检验:
[8]:
name = ["Lagrange multiplier statistic", "p-value", "f-value", "f p-value"]
test = sms.het_breuschpagan(results.resid, results.model.exog)
lzip(name, test)
[8]:
[('Lagrange multiplier statistic', np.float64(4.893213374093985)),
('p-value', np.float64(0.08658690502352087)),
('f-value', np.float64(2.503715946256453)),
('f p-value', np.float64(0.08794028782672857))]
Goldfeld-Quandt 检验
[9]:
name = ["F statistic", "p-value"]
test = sms.het_goldfeldquandt(results.resid, results.model.exog)
lzip(name, test)
[9]:
[('F statistic', np.float64(1.1002422436378152)),
('p-value', np.float64(0.3820295068692518))]
线性¶
Harvey-Collier 乘数检验,用于检验线性规范正确的零假设:
[10]:
name = ["t value", "p value"]
test = sms.linear_harvey_collier(results)
lzip(name, test)
[10]:
[('t value', np.float64(-1.0796490077784027)),
('p value', np.float64(0.2834639247558495))]
Last update:
Oct 16, 2024