注意
Go to the end 以下载完整的示例代码。
比较结合过采样和欠采样的采样器#
此示例展示了在SMOTE过采样后应用欠采样算法的效果。在文献中,Tomek's link和编辑最近邻是两种已被使用并在imbalanced-learn中可用的方法。
# Authors: Guillaume Lemaitre <g.lemaitre58@gmail.com>
# License: MIT
print(__doc__)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_context("poster")
数据集生成#
我们将创建一个包含几个样本的不平衡数据集。我们将使用
make_classification 来生成这个数据集。
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
_ = ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, alpha=0.8, edgecolor="k")
以下函数将用于绘制重采样后的样本空间,以说明算法的特性。
from collections import Counter
def plot_resampling(X, y, sampler, ax):
"""Plot the resampled dataset using the sampler."""
X_res, y_res = sampler.fit_resample(X, y)
ax.scatter(X_res[:, 0], X_res[:, 1], c=y_res, alpha=0.8, edgecolor="k")
sns.despine(ax=ax, offset=10)
ax.set_title(f"Decision function for {sampler.__class__.__name__}")
return Counter(y_res)
以下函数将用于绘制给定一些数据的分类器的决策函数。
import numpy as np
def plot_decision_function(X, y, clf, ax):
"""Plot the decision function of the classifier and the original data"""
plot_step = 0.02
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step), np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step)
)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], alpha=0.8, c=y, edgecolor="k")
ax.set_title(f"Resampling using {clf[0].__class__.__name__}")
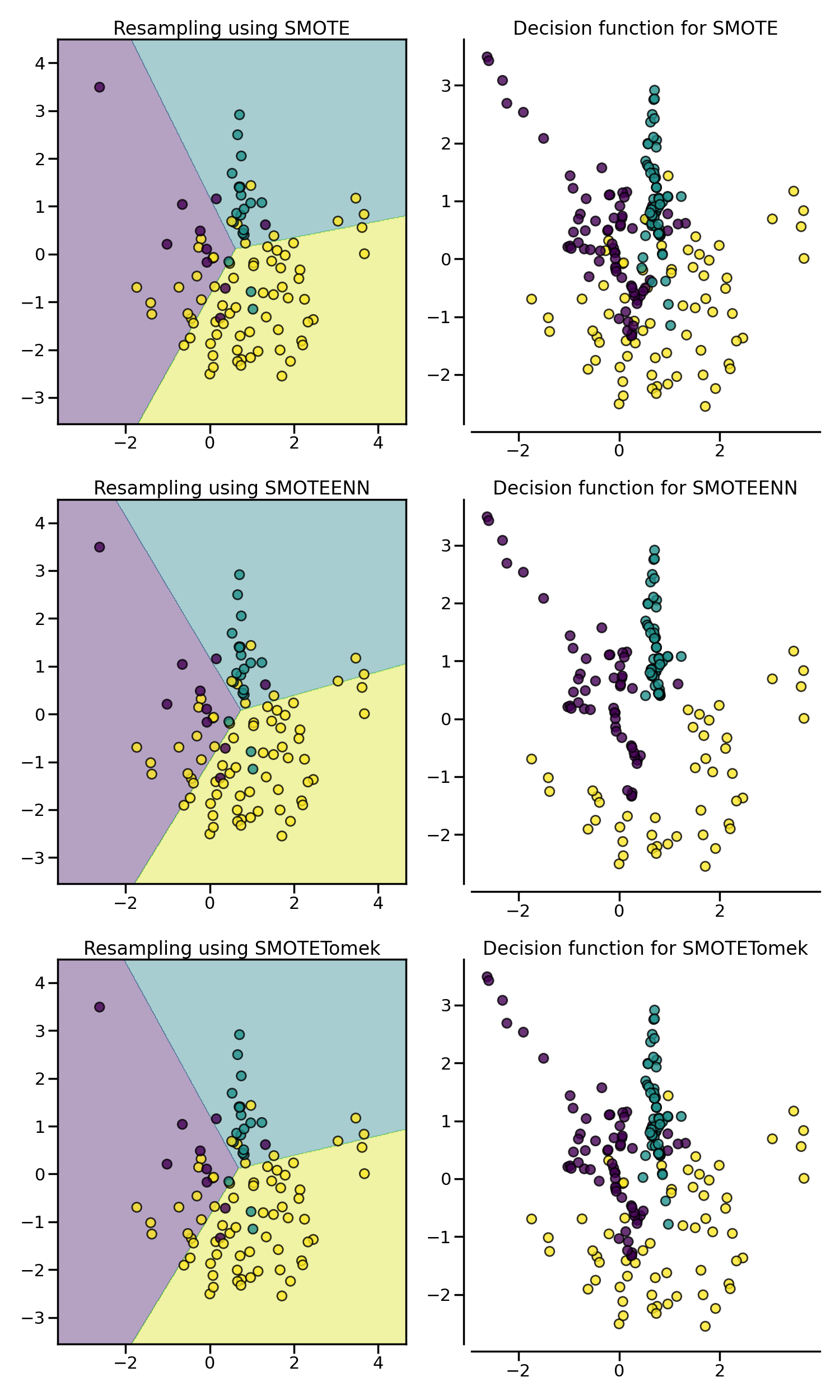
SMOTE 允许生成样本。然而,这种过采样方法对底层分布没有任何了解。因此,可能会生成一些噪声样本,例如当不同类别无法很好分离时。因此,应用欠采样算法来清理噪声样本可能是有益的。文献中通常使用两种方法:(i) Tomek’s link 和 (ii) 编辑最近邻清理方法。Imbalanced-learn 提供了两种现成的采样器 SMOTETomek 和 SMOTEENN。通常,SMOTEENN 比 SMOTETomek 清理更多的噪声数据。
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from imblearn.combine import SMOTEENN, SMOTETomek
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
from imblearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
samplers = [SMOTE(random_state=0), SMOTEENN(random_state=0), SMOTETomek(random_state=0)]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize=(15, 25))
for ax, sampler in zip(axs, samplers):
clf = make_pipeline(sampler, LogisticRegression()).fit(X, y)
plot_decision_function(X, y, clf, ax[0])
plot_resampling(X, y, sampler, ax[1])
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间: (0 分钟 2.354 秒)
预计内存使用量: 199 MB

