版本 0.17.0 (2015年10月9日)#
这是从 0.16.2 版本以来的一个重大发布,包括少量 API 更改、几个新功能、增强功能和性能改进,以及大量错误修复。我们建议所有用户升级到此版本。
警告
pandas >= 0.17.0 将不再支持与 Python 版本 3.2 的兼容性 (GH 9118)
警告
pandas.io.data 包已被弃用,并将被 pandas-datareader 包 取代。这将允许数据模块独立于您的 pandas 安装进行更新。pandas-datareader v0.1.1 的 API 与 pandas v0.17.0 中的完全相同 (GH 8961, GH 10861)。
安装 pandas-datareader 后,您可以轻松更改导入:
from pandas.io import data, wb
变为
from pandas_datareader import data, wb
亮点包括:
在某些 cython 操作上释放全局解释器锁 (GIL),请参见 这里
绘图方法现在可以通过
.plot访问器作为属性使用,详见 这里排序 API 已经进行了改进,以消除一些长期存在的不一致性,请参见 这里
支持
datetime64[ns]带时区作为第一类数据类型,参见 这里to_datetime的默认行为现在将在遇到不可解析的格式时raise,之前这将返回原始输入。此外,日期解析函数现在返回一致的结果。请参见 这里在
HDFStore中dropna的默认值已更改为False,以默认存储所有行,即使它们全部是NaN,请参见 这里Datetime 访问器 (
dt) 现在支持Series.dt.strftime以生成格式化的字符串用于 datetime-like 对象,以及Series.dt.total_seconds以生成 timedelta 的每个持续时间(以秒为单位)。请参见 这里Period和PeriodIndex可以处理乘法频率,如3D,这对应于 3 天的跨度。请参见 这里现在安装的 pandas 开发版本将具有符合
PEP440的版本字符串 (GH 9518)使用 Air Speed Velocity 库 进行基准测试的开发支持 (GH 8361)
支持读取 SAS xport 文件,请参见 这里
比较 SAS 与 pandas 的文档,见 这里
移除自 0.8.0 版本以来已弃用的自动 TimeSeries 广播,详见 这里
使用纯文本的显示格式可以选择与 Unicode 东亚宽度对齐,请参见 这里
与 Python 3.5 的兼容性 (GH 11097)
与 matplotlib 1.5.0 的兼容性 (GH 11111)
v0.17.0 中的新内容
新功能#
带时区的日期时间#
我们正在添加一个原生支持带时区的datetime的实现。一个 Series 或一个 DataFrame 列之前 可以 被分配一个带时区的datetime,并且会作为一个 object dtype 工作。这在行数较多时存在性能问题。更多详情请参见 文档 。(GH 8260, GH 10763, GH 11034)。
新的实现允许在所有行中使用单一时区,并以高效的方式进行操作。
In [1]: df = pd.DataFrame(
...: {
...: "A": pd.date_range("20130101", periods=3),
...: "B": pd.date_range("20130101", periods=3, tz="US/Eastern"),
...: "C": pd.date_range("20130101", periods=3, tz="CET"),
...: }
...: )
...:
In [2]: df
Out[2]:
A B C
0 2013-01-01 2013-01-01 00:00:00-05:00 2013-01-01 00:00:00+01:00
1 2013-01-02 2013-01-02 00:00:00-05:00 2013-01-02 00:00:00+01:00
2 2013-01-03 2013-01-03 00:00:00-05:00 2013-01-03 00:00:00+01:00
[3 rows x 3 columns]
In [3]: df.dtypes
Out[3]:
A datetime64[ns]
B datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]
C datetime64[ns, CET]
Length: 3, dtype: object
In [4]: df.B
Out[4]:
0 2013-01-01 00:00:00-05:00
1 2013-01-02 00:00:00-05:00
2 2013-01-03 00:00:00-05:00
Name: B, Length: 3, dtype: datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]
In [5]: df.B.dt.tz_localize(None)
Out[5]:
0 2013-01-01
1 2013-01-02
2 2013-01-03
Name: B, Length: 3, dtype: datetime64[ns]
这还使用了一种新的数据类型表示,它在外观和感觉上与它的numpy表亲 datetime64[ns] 非常相似。
In [6]: df["B"].dtype
Out[6]: datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]
In [7]: type(df["B"].dtype)
Out[7]: pandas.core.dtypes.dtypes.DatetimeTZDtype
备注
由于数据类型变化,底层 DatetimeIndex 的字符串表示略有不同,但功能上这些是相同的。
之前的行为:
In [1]: pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3, tz='US/Eastern')
Out[1]: DatetimeIndex(['2013-01-01 00:00:00-05:00', '2013-01-02 00:00:00-05:00',
'2013-01-03 00:00:00-05:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D', tz='US/Eastern')
In [2]: pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3, tz='US/Eastern').dtype
Out[2]: dtype('<M8[ns]')
新行为:
In [8]: pd.date_range("20130101", periods=3, tz="US/Eastern")
Out[8]:
DatetimeIndex(['2013-01-01 00:00:00-05:00', '2013-01-02 00:00:00-05:00',
'2013-01-03 00:00:00-05:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]', freq='D')
In [9]: pd.date_range("20130101", periods=3, tz="US/Eastern").dtype
Out[9]: datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]
释放GIL#
我们正在某些cython操作中释放全局解释器锁(GIL)。这将允许其他线程在计算期间同时运行,潜在地允许通过多线程提高性能。值得注意的是,groupby、nsmallest、value_counts 和一些索引操作受益于此。(GH 8882)
例如,以下代码中的 groupby 表达式在因式分解步骤中会释放 GIL,例如 df.groupby('key') 以及 .sum() 操作。
N = 1000000
ngroups = 10
df = DataFrame(
{"key": np.random.randint(0, ngroups, size=N), "data": np.random.randn(N)}
)
df.groupby("key")["data"].sum()
释放GIL可以有利于使用线程进行用户交互(例如QT)或执行多线程计算的应用程序。一个很好的可以处理这些类型并行计算的库例子是dask_库。
绘图子方法#
Series 和 DataFrame 的 .plot() 方法允许通过提供 kind 关键字参数来自定义 图表类型。不幸的是,许多这类图表使用不同的必需和可选关键字参数,这使得很难发现任何给定图表类型使用了数十种可能参数中的哪些。
为了缓解这个问题,我们添加了一个新的、可选的绘图接口,该接口将每种类型的图表作为 .plot 属性的方法公开。现在,您不仅可以使用 series.plot(kind=<kind>, ...),还可以使用 series.plot.<kind>(...):
In [10]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 2), columns=['a', 'b'])
In [11]: df.plot.bar()
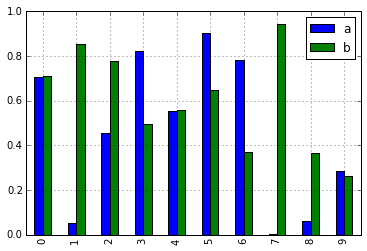
由于这一更改,这些方法现在都可以通过选项卡补全功能找到:
In [12]: df.plot.<TAB> # noqa: E225, E999
df.plot.area df.plot.barh df.plot.density df.plot.hist df.plot.line df.plot.scatter
df.plot.bar df.plot.box df.plot.hexbin df.plot.kde df.plot.pie
每个方法签名仅包括相关的参数。目前,这些仅限于必需的参数,但在未来,这些还将包括可选参数。有关概述,请参阅新的 绘图 API 文档。
dt 访问器的其他方法#
Series.dt.strftime#
我们现在支持一个 Series.dt.strftime 方法用于生成格式化字符串的日期时间类型 (GH 10110)。示例:
# DatetimeIndex
In [13]: s = pd.Series(pd.date_range("20130101", periods=4))
In [14]: s
Out[14]:
0 2013-01-01
1 2013-01-02
2 2013-01-03
3 2013-01-04
Length: 4, dtype: datetime64[ns]
In [15]: s.dt.strftime("%Y/%m/%d")
Out[15]:
0 2013/01/01
1 2013/01/02
2 2013/01/03
3 2013/01/04
Length: 4, dtype: object
# PeriodIndex
In [16]: s = pd.Series(pd.period_range("20130101", periods=4))
In [17]: s
Out[17]:
0 2013-01-01
1 2013-01-02
2 2013-01-03
3 2013-01-04
Length: 4, dtype: period[D]
In [18]: s.dt.strftime("%Y/%m/%d")
Out[18]:
0 2013/01/01
1 2013/01/02
2 2013/01/03
3 2013/01/04
Length: 4, dtype: object
字符串格式与Python标准库相同,详细信息可以在 这里 找到
Series.dt.total_seconds#
pd.Series 类型为 timedelta64 有新的方法 .dt.total_seconds() 返回 timedelta 的持续时间(以秒为单位)(GH 10817)
# TimedeltaIndex
In [19]: s = pd.Series(pd.timedelta_range("1 minutes", periods=4))
In [20]: s
Out[20]:
0 0 days 00:01:00
1 1 days 00:01:00
2 2 days 00:01:00
3 3 days 00:01:00
Length: 4, dtype: timedelta64[ns]
In [21]: s.dt.total_seconds()
Out[21]:
0 60.0
1 86460.0
2 172860.0
3 259260.0
Length: 4, dtype: float64
周期频率增强#
Period、PeriodIndex 和 period_range 现在可以接受乘法频率。此外,Period.freq 和 PeriodIndex.freq 现在存储为 DateOffset 实例,类似于 DatetimeIndex,而不是 str (GH 7811)
一个乘以的 freq 表示相应长度的跨度。下面的示例创建了一个为期3天的周期。加法和减法将按其跨度移动周期。
In [22]: p = pd.Period("2015-08-01", freq="3D")
In [23]: p
Out[23]: Period('2015-08-01', '3D')
In [24]: p + 1
Out[24]: Period('2015-08-04', '3D')
In [25]: p - 2
Out[25]: Period('2015-07-26', '3D')
In [26]: p.to_timestamp()
Out[26]: Timestamp('2015-08-01 00:00:00')
In [27]: p.to_timestamp(how="E")
Out[27]: Timestamp('2015-08-03 23:59:59.999999999')
你可以在 PeriodIndex 和 period_range 中使用乘法频率。
In [28]: idx = pd.period_range("2015-08-01", periods=4, freq="2D")
In [29]: idx
Out[29]: PeriodIndex(['2015-08-01', '2015-08-03', '2015-08-05', '2015-08-07'], dtype='period[2D]')
In [30]: idx + 1
Out[30]: PeriodIndex(['2015-08-03', '2015-08-05', '2015-08-07', '2015-08-09'], dtype='period[2D]')
SAS XPORT 文件支持#
read_sas() 提供了对读取 SAS XPORT 格式文件的支持。(GH 4052)。
df = pd.read_sas("sas_xport.xpt")
也可以获取一个迭代器并增量读取 XPORT 文件。
for df in pd.read_sas("sas_xport.xpt", chunksize=10000):
do_something(df)
查看 文档 了解更多细节。
在 .eval() 中对数学函数的支持#
df = pd.DataFrame({"a": np.random.randn(10)})
df.eval("b = sin(a)")
支持的数学函数有 sin, cos, exp, log, expm1, log1p, sqrt, sinh, cosh, tanh, arcsin, arccos, arctan, arccosh, arcsinh, arctanh, abs 和 arctan2。
这些函数映射到 NumExpr 引擎的内在函数。对于 Python 引擎,它们映射到 NumPy 调用。
对 Excel 的更改与 MultiIndex#
在版本 0.16.2 中,带有 MultiIndex 列的 DataFrame 无法通过 to_excel 写入 Excel。该功能已添加(GH 10564),同时还更新了 read_excel,以便可以通过指定 header 和 index_col 参数中的哪些列/行构成 MultiIndex 来读回数据,且不会丢失信息(GH 4679)
查看 文档 了解更多详情。
In [31]: df = pd.DataFrame(
....: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]],
....: columns=pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
....: [["foo", "bar"], ["a", "b"]], names=["col1", "col2"]
....: ),
....: index=pd.MultiIndex.from_product([["j"], ["l", "k"]], names=["i1", "i2"]),
....: )
....:
In [32]: df
Out[32]:
col1 foo bar
col2 a b a b
i1 i2
j l 1 2 3 4
k 5 6 7 8
[2 rows x 4 columns]
In [33]: df.to_excel("test.xlsx")
In [34]: df = pd.read_excel("test.xlsx", header=[0, 1], index_col=[0, 1])
In [35]: df
Out[35]:
col1 foo bar
col2 a b a b
i1 i2
j l 1 2 3 4
k 5 6 7 8
[2 rows x 4 columns]
之前,如果序列化数据有索引名称,则需要在 read_excel 中指定 has_index_names 参数。对于版本 0.17.0,to_excel 的输出格式已更改,使得此关键字不再必要 - 更改如下所示。
旧
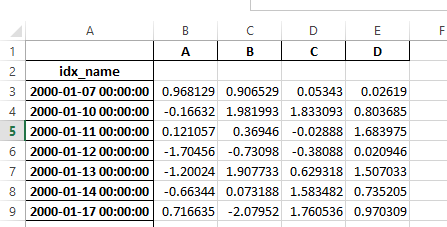
新
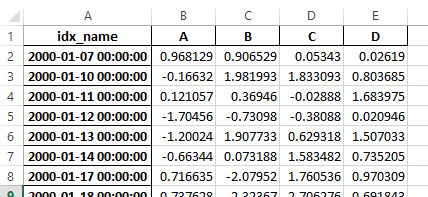
警告
在0.16.2或更早版本中保存的带有索引名称的Excel文件仍然可以读取,但必须将 has_index_names 参数指定为 True。
Google BigQuery 增强功能#
增加了在目标表/数据集不存在时,使用
pandas.io.gbq.to_gbq()函数自动创建表/数据集的功能。(GH 8325, GH 11121)。在调用
pandas.io.gbq.to_gbq()函数时,通过if_exists参数增加了替换现有表和模式的能力。更多详情请参见 文档 (GH 8325)。在 gbq 模块中,
InvalidColumnOrder和InvalidPageToken将引发ValueError而不是IOError。generate_bq_schema()函数现已弃用,并将在未来版本中移除 (GH 11121)gbq 模块现在将支持 Python 3 (GH 11094)。
使用 Unicode 东亚宽度进行显示对齐#
警告
启用此选项将影响 DataFrame 和 Series 的打印性能(大约慢2倍)。仅在实际需要时使用。
一些东亚国家使用的 Unicode 字符其宽度相当于 2 个字母。如果一个 DataFrame 或 Series 包含这些字符,默认输出将无法正确对齐。以下选项被添加以启用对这些字符的精确处理。
display.unicode.east_asian_width: 是否使用 Unicode 东亚宽度来计算显示文本宽度。(GH 2612)display.unicode.ambiguous_as_wide: 是否将属于 Ambiguous 的 Unicode 字符作为 Wide 处理。(GH 11102)
In [36]: df = pd.DataFrame({u"国籍": ["UK", u"日本"], u"名前": ["Alice", u"しのぶ"]})
In [37]: df
Out[37]:
国籍 名前
0 UK Alice
1 日本 しのぶ
[2 rows x 2 columns]
In [38]: pd.set_option("display.unicode.east_asian_width", True)
In [39]: df
Out[39]:
国籍 名前
0 UK Alice
1 日本 しのぶ
[2 rows x 2 columns]
欲了解更多详情,请参见 这里
其他增强功能#
对
openpyxl>= 2.2 的支持。样式支持的 API 现在已稳定 (GH 10125)merge现在接受参数indicator,它会在输出对象中添加一个类别类型的列(默认称为_merge),该列的取值为 (GH 8790)观察原点
_merge值仅在
'left'帧中合并键left_only仅在
'right'帧中合并键right_only两个帧中的合并键
bothIn [40]: df1 = pd.DataFrame({"col1": [0, 1], "col_left": ["a", "b"]}) In [41]: df2 = pd.DataFrame({"col1": [1, 2, 2], "col_right": [2, 2, 2]}) In [42]: pd.merge(df1, df2, on="col1", how="outer", indicator=True) Out[42]: col1 col_left col_right _merge 0 0 a NaN left_only 1 1 b 2.0 both 2 2 NaN 2.0 right_only 3 2 NaN 2.0 right_only [4 rows x 4 columns]
更多信息,请参见 更新的文档
pd.to_numeric是一个新的函数,用于将字符串强制转换为数字(可能带有强制转换) (GH 11133)pd.merge现在允许在未合并的列名中存在重复项(GH 10639)。pd.pivot现在允许传递None作为索引 (GH 3962)。pd.concat现在如果提供了的话,将使用现有的 Series 名称 (GH 10698)。In [43]: foo = pd.Series([1, 2], name="foo") In [44]: bar = pd.Series([1, 2]) In [45]: baz = pd.Series([4, 5])
之前的行为:
In [1]: pd.concat([foo, bar, baz], axis=1) Out[1]: 0 1 2 0 1 1 4 1 2 2 5
新行为:
In [46]: pd.concat([foo, bar, baz], axis=1) Out[46]: foo 0 1 0 1 1 4 1 2 2 5 [2 rows x 3 columns]
DataFrame获得了nlargest和nsmallest方法 (GH 10393)添加一个
limit_direction关键字参数,该参数与limit一起工作,以使interpolate能够向前、向后或双向填充NaN值(GH 9218, GH 10420, GH 11115)In [47]: ser = pd.Series([np.nan, np.nan, 5, np.nan, np.nan, np.nan, 13]) In [48]: ser.interpolate(limit=1, limit_direction="both") Out[48]: 0 NaN 1 5.0 2 5.0 3 7.0 4 NaN 5 11.0 6 13.0 Length: 7, dtype: float64
添加了一个
DataFrame.round方法,用于将数值四舍五入到可变的小数位数 (GH 10568)。In [49]: df = pd.DataFrame( ....: np.random.random([3, 3]), ....: columns=["A", "B", "C"], ....: index=["first", "second", "third"], ....: ) ....: In [50]: df Out[50]: A B C first 0.126970 0.966718 0.260476 second 0.897237 0.376750 0.336222 third 0.451376 0.840255 0.123102 [3 rows x 3 columns] In [51]: df.round(2) Out[51]: A B C first 0.13 0.97 0.26 second 0.90 0.38 0.34 third 0.45 0.84 0.12 [3 rows x 3 columns] In [52]: df.round({"A": 0, "C": 2}) Out[52]: A B C first 0.0 0.966718 0.26 second 1.0 0.376750 0.34 third 0.0 0.840255 0.12 [3 rows x 3 columns]
drop_duplicates和duplicated现在接受一个keep关键字来针对第一个、最后一个和所有重复项。take_last关键字已被弃用,请参见 这里 (GH 6511, GH 8505)In [53]: s = pd.Series(["A", "B", "C", "A", "B", "D"]) In [54]: s.drop_duplicates() Out[54]: 0 A 1 B 2 C 5 D Length: 4, dtype: object In [55]: s.drop_duplicates(keep="last") Out[55]: 2 C 3 A 4 B 5 D Length: 4, dtype: object In [56]: s.drop_duplicates(keep=False) Out[56]: 2 C 5 D Length: 2, dtype: object
Reindex 现在有一个
tolerance参数,允许对 重新索引时的填充限制 进行更精细的控制 (GH 10411):In [57]: df = pd.DataFrame({"x": range(5), "t": pd.date_range("2000-01-01", periods=5)}) In [58]: df.reindex([0.1, 1.9, 3.5], method="nearest", tolerance=0.2) Out[58]: x t 0.1 0.0 2000-01-01 1.9 2.0 2000-01-03 3.5 NaN NaT [3 rows x 2 columns]
当在
DatetimeIndex、TimedeltaIndex或PeriodIndex上使用时,tolerance将会尽可能地被强制转换为Timedelta。这允许你用字符串指定容差:In [59]: df = df.set_index("t") In [60]: df.reindex(pd.to_datetime(["1999-12-31"]), method="nearest", tolerance="1 day") Out[60]: x 1999-12-31 0 [1 rows x 1 columns]
tolerance也通过较低级别的Index.get_indexer和Index.get_loc方法暴露出来。在重采样
TimeDeltaIndex时增加了使用base参数的功能 (GH 10530)DatetimeIndex可以使用包含NaT的字符串来实例化 (GH 7599)to_datetime现在可以接受yearfirst关键字 (GH 7599)pandas.tseries.offsets大于Day偏移的现在可以与Series一起用于加法/减法 (GH 10699)。更多详情请参见 文档。pd.Timedelta.total_seconds()现在返回 Timedelta 持续时间到 ns 精度(之前是微秒精度)(GH 10939)PeriodIndex现在支持与np.ndarray的算术运算 (GH 10638)支持
Period对象的序列化 (GH 10439).as_blocks现在将接受一个copy可选参数以返回数据的副本,默认是复制(与之前版本的行为没有变化),(GH 9607)regex参数到DataFrame.filter现在可以处理数字列名,而不是引发ValueError(GH 10384)。通过URL启用读取gzip压缩文件,可以通过显式设置压缩参数或通过从响应中的HTTP Content-Encoding头推断来实现 (GH 8685)
在
ExcelWriter中启用列表和字典到字符串的序列化 (GH 8188)SQL io 函数现在接受一个 SQLAlchemy 可连接对象。(GH 7877)
pd.read_sql和to_sql可以接受数据库 URI 作为con参数 (GH 10214)read_sql_table现在允许从视图中读取 (GH 10750)。在使用
table格式时,启用将复杂值写入HDFStores的功能 (GH 10447)启用
pd.read_hdf在 HDF 文件包含单个数据集时无需指定键即可使用 (GH 10443)pd.read_stata现在可以读取 Stata 118 类型的文件。(GH 9882)msgpack子模块已更新到 0.4.6,保持向后兼容性 (GH 10581)DataFrame.to_dict现在接受orient='index'关键字参数 (GH 10844)。DataFrame.apply如果传递的函数返回一个字典并且reduce=True,将返回一个字典系列 (GH 8735)。允许传递
kwargs到插值方法 (GH 10378)。当连接一个空的
Dataframe对象的可迭代对象时,改进了错误信息 (GH 9157)pd.read_csv现在可以增量读取 bz2 压缩文件,C 解析器可以从 AWS S3 读取 bz2 压缩文件 (GH 11070, GH 11072)。在
pd.read_csv中,识别s3n://和s3a://URL 作为指定 S3 文件存储 (GH 11070, GH 11071)。从AWS S3增量读取CSV文件,而不是首先下载整个文件。(在Python 2中仍需要完整下载压缩文件。)(GH 11070, GH 11073)
pd.read_csv现在能够推断从 AWS S3 存储读取的文件的压缩类型(GH 11070, GH 11074)。
向后不兼容的 API 变化#
对排序 API 的更改#
排序 API 有一些长期的不一致性。(GH 9816, GH 8239)。
以下是 API 在 0.17.0 之前 的总结:
Series.sort是 INPLACE 的,而DataFrame.sort返回一个新对象。Series.order返回一个新对象可以使用
Series/DataFrame.sort_index通过传递by关键字按 值 进行排序。Series/DataFrame.sortlevel仅在MultiIndex上工作,用于按索引排序。
为了解决这些问题,我们重构了API:
我们引入了一种新方法,
DataFrame.sort_values(),它是DataFrame.sort()、Series.sort()和Series.order()的合并,用于处理 值 的排序。现有的方法
Series.sort(),Series.order(), 和DataFrame.sort()已被弃用,并将在未来版本中移除。DataFrame.sort_index()的by参数已被弃用,并将在未来版本中移除。现有的方法
.sort_index()将获得level关键字,以启用级别排序。
我们现在有两种不同的且不重叠的排序方法。一个 * 标记的项目将显示一个 FutureWarning。
要按 值 排序:
上一个 |
Replacement |
|---|---|
* |
|
* |
|
* |
|
按 索引 排序:
上一个 |
Replacement |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
|
我们还弃用了两个类似 Series 的类 Index 和 Categorical 中的类似方法,并进行了更改。
上一个 |
Replacement |
|---|---|
* |
|
* |
|
对 to_datetime 和 to_timedelta 的更改#
错误处理#
pd.to_datetime 的错误处理默认值已更改为 errors='raise'。在之前的版本中,它是 errors='ignore'。此外,coerce 参数已被弃用,取而代之的是 errors='coerce'。这意味着无效的解析将引发错误,而不是像以前版本那样返回原始输入。(GH 10636)
之前的行为:
In [2]: pd.to_datetime(['2009-07-31', 'asd'])
Out[2]: array(['2009-07-31', 'asd'], dtype=object)
新行为:
In [3]: pd.to_datetime(['2009-07-31', 'asd'])
ValueError: Unknown string format
当然,你也可以强制这样做。
In [61]: pd.to_datetime(["2009-07-31", "asd"], errors="coerce")
Out[61]: DatetimeIndex(['2009-07-31', 'NaT'], dtype='datetime64[s]', freq=None)
要保留之前的行为,你可以使用 errors='ignore':
In [4]: pd.to_datetime(["2009-07-31", "asd"], errors="ignore")
Out[4]: Index(['2009-07-31', 'asd'], dtype='object')
此外,pd.to_timedelta 获得了类似的 API,即 errors='raise'|'ignore'|'coerce',并且 coerce 关键字已被弃用,取而代之的是 errors='coerce'。
一致的解析#
to_datetime、Timestamp 和 DatetimeIndex 的字符串解析已经保持一致。(GH 7599)
在 v0.17.0 之前,Timestamp 和 to_datetime 可能会使用今天的日期错误地解析仅包含年份的日期时间字符串,否则 DatetimeIndex 使用该年份的开始。Timestamp 和 to_datetime 可能会在某些类型的日期时间字符串上引发 ValueError,而 DatetimeIndex 可以解析这些字符串,例如季度字符串。
之前的行为:
In [1]: pd.Timestamp('2012Q2')
Traceback
...
ValueError: Unable to parse 2012Q2
# Results in today's date.
In [2]: pd.Timestamp('2014')
Out [2]: 2014-08-12 00:00:00
v0.17.0 可以如下解析它们。它也适用于 DatetimeIndex。
新行为:
In [62]: pd.Timestamp("2012Q2")
Out[62]: Timestamp('2012-04-01 00:00:00')
In [63]: pd.Timestamp("2014")
Out[63]: Timestamp('2014-01-01 00:00:00')
In [64]: pd.DatetimeIndex(["2012Q2", "2014"])
Out[64]: DatetimeIndex(['2012-04-01', '2014-01-01'], dtype='datetime64[s]', freq=None)
备注
如果你想基于今天的日期进行计算,使用 Timestamp.now() 和 pandas.tseries.offsets。
In [65]: import pandas.tseries.offsets as offsets
In [66]: pd.Timestamp.now()
Out[66]: Timestamp('2024-08-26 03:54:36.458413')
In [67]: pd.Timestamp.now() + offsets.DateOffset(years=1)
Out[67]: Timestamp('2025-08-26 03:54:36.459509')
索引比较的更改#
在 Index 上的操作符等于应该与 Series 的行为相似(GH 9947, GH 10637)
从 v0.17.0 开始,比较不同长度的 Index 对象将引发 ValueError。这是为了与 Series 的行为保持一致。
之前的行为:
In [2]: pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) == pd.Index([1, 4, 5])
Out[2]: array([ True, False, False], dtype=bool)
In [3]: pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) == pd.Index([2])
Out[3]: array([False, True, False], dtype=bool)
In [4]: pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) == pd.Index([1, 2])
Out[4]: False
新行为:
In [8]: pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) == pd.Index([1, 4, 5])
Out[8]: array([ True, False, False], dtype=bool)
In [9]: pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) == pd.Index([2])
ValueError: Lengths must match to compare
In [10]: pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) == pd.Index([1, 2])
ValueError: Lengths must match to compare
请注意,这与 numpy 的行为不同,在 numpy 中比较可以广播:
In [68]: np.array([1, 2, 3]) == np.array([1])
Out[68]: array([ True, False, False])
或者如果广播不能完成,它可以返回 False:
In [11]: np.array([1, 2, 3]) == np.array([1, 2])
Out[11]: False
布尔比较与 None 的变化#
Series 与 None 的布尔比较现在将等同于与 np.nan 比较,而不是引发 TypeError。(GH 1079)。
In [69]: s = pd.Series(range(3), dtype="float")
In [70]: s.iloc[1] = None
In [71]: s
Out[71]:
0 0.0
1 NaN
2 2.0
Length: 3, dtype: float64
之前的行为:
In [5]: s == None
TypeError: Could not compare <type 'NoneType'> type with Series
新行为:
In [72]: s == None
Out[72]:
0 False
1 False
2 False
Length: 3, dtype: bool
通常你只是想知道哪些值是空的。
In [73]: s.isnull()
Out[73]:
0 False
1 True
2 False
Length: 3, dtype: bool
警告
通常你会想使用 isnull/notnull 来进行这些类型的比较,因为 isnull/notnull 告诉你哪些元素是空的。需要注意的是 nan 不等于 nan,但 None 等于 None。注意 pandas/numpy 使用了 np.nan != np.nan 这一事实,并将 None 视为 np.nan。
In [74]: None == None
Out[74]: True
In [75]: np.nan == np.nan
Out[75]: False
HDFStore dropna 行为#
对于 format='table' 的 HDFStore 写函数,默认行为现在是保留所有缺失的行。以前的行为是删除所有缺失的行(保存索引除外)。以前的行为可以通过使用 dropna=True 选项来复制。(GH 9382)
之前的行为:
In [76]: df_with_missing = pd.DataFrame(
....: {"col1": [0, np.nan, 2], "col2": [1, np.nan, np.nan]}
....: )
....:
In [77]: df_with_missing
Out[77]:
col1 col2
0 0.0 1.0
1 NaN NaN
2 2.0 NaN
[3 rows x 2 columns]
In [27]:
df_with_missing.to_hdf('file.h5',
key='df_with_missing',
format='table',
mode='w')
In [28]: pd.read_hdf('file.h5', 'df_with_missing')
Out [28]:
col1 col2
0 0 1
2 2 NaN
新行为:
In [78]: df_with_missing.to_hdf("file.h5", key="df_with_missing", format="table", mode="w")
In [79]: pd.read_hdf("file.h5", "df_with_missing")
Out[79]:
col1 col2
0 0.0 1.0
1 NaN NaN
2 2.0 NaN
[3 rows x 2 columns]
查看 文档 了解更多细节。
对 display.precision 选项的更改#
display.precision 选项已澄清,指代小数位数 (GH 10451)。
早期版本的 pandas 会将浮点数格式化为比 display.precision 中的值少一个小数位。
In [1]: pd.set_option('display.precision', 2)
In [2]: pd.DataFrame({'x': [123.456789]})
Out[2]:
x
0 123.5
如果将精度解释为“有效数字”,这在科学计数法中确实有效,但同样的解释在标准格式值中并不适用。这与numpy处理格式的方式也不一致。
向前推进,display.precision 的值将直接控制小数点后的位数,用于常规格式化以及科学记数法,类似于 numpy 的 precision 打印选项的工作方式。
In [80]: pd.set_option("display.precision", 2)
In [81]: pd.DataFrame({"x": [123.456789]})
Out[81]:
x
0 123.46
[1 rows x 1 columns]
为了保持与先前版本的输出行为一致,display.precision 的默认值已从 7 减少到 6。
对 Categorical.unique 的更改#
Categorical.unique 现在返回具有唯一 categories 和 codes 的新 Categoricals,而不是返回 np.array (GH 10508)
无序类别:值和类别按出现顺序排序。
有序类别:值按出现顺序排序,类别保持现有顺序。
In [82]: cat = pd.Categorical(["C", "A", "B", "C"], categories=["A", "B", "C"], ordered=True)
In [83]: cat
Out[83]:
['C', 'A', 'B', 'C']
Categories (3, object): ['A' < 'B' < 'C']
In [84]: cat.unique()
Out[84]:
['C', 'A', 'B']
Categories (3, object): ['A' < 'B' < 'C']
In [85]: cat = pd.Categorical(["C", "A", "B", "C"], categories=["A", "B", "C"])
In [86]: cat
Out[86]:
['C', 'A', 'B', 'C']
Categories (3, object): ['A', 'B', 'C']
In [87]: cat.unique()
Out[87]:
['C', 'A', 'B']
Categories (3, object): ['A', 'B', 'C']
在解析器中作为 header 传递的 bool 的更改#
在早期的 pandas 版本中,如果传递给 read_csv、read_excel 或 read_html 的 header 参数是一个布尔值,它会隐式转换为整数,结果是 False 对应 header=0,True 对应 header=1 (GH 6113)
header 的 bool 输入现在会引发 TypeError
In [29]: df = pd.read_csv('data.csv', header=False)
TypeError: Passing a bool to header is invalid. Use header=None for no header or
header=int or list-like of ints to specify the row(s) making up the column names
其他 API 更改#
使用
subplots=True的线和 kde 图现在使用默认颜色,不再是全黑。指定color='k'以黑色绘制所有线条 (GH 9894)在具有
categoricaldtype 的 Series 上调用.value_counts()方法现在返回一个具有CategoricalIndex的 Series (GH 10704)pandas对象子类的元数据属性现在将被序列化 (GH 10553)。
使用
Categorical的groupby遵循与上述Categorical.unique相同的规则 (GH 10508)当使用
complex64dtype 的数组构造DataFrame时,以前意味着相应的列会自动提升到complex128dtype。pandas 现在将保留复杂数据的输入项大小(GH 10952)某些数值缩减运算符在包含字符串和数字的对象类型上会返回
ValueError,而不是TypeError(GH 11131)将当前不支持的
chunksize参数传递给read_excel或ExcelFile.parse现在将引发NotImplementedError(GH 8011)允许将
ExcelFile对象传递给read_excel(GH 11198)DatetimeIndex.union如果self和输入的freq为None,则不推断freq(GH 11086)NaT的方法现在要么引发ValueError,要么返回np.nan或NaT(GH 9513)行为
方法
返回
np.nanweekday,isoweekday返回
NaTdate,now,replace,to_datetime,today返回
np.datetime64('NaT')to_datetime64(不变)引发
ValueError所有其他公共方法(名称不以下划线开头)
弃用#
对于
Series,以下索引函数已被弃用(GH 10177)。弃用函数
Replacement
.irow(i).iloc[i]或.iat[i].iget(i).iloc[i]或.iat[i].iget_value(i).iloc[i]或.iat[i]对于
DataFrame,以下索引函数已被弃用(GH 10177)。弃用函数
Replacement
.irow(i).iloc[i].iget_value(i, j).iloc[i, j]或.iat[i, j].icol(j).iloc[:, j]
备注
自 0.11.0 版本起,这些索引功能在文档中已被弃用。
Categorical.name已被弃用,以使Categorical更像numpy.ndarray。请改用Series(cat, name="whatever")(GH 10482)。在
Categorical的categories中设置缺失值(NaN)将发出警告(GH 10748)。您仍然可以在values中有缺失值。drop_duplicates和duplicated的take_last关键字已被弃用,取而代之的是keep。 (GH 6511, GH 8505)Series.nsmallest和nlargest的take_last关键字已被弃用,取而代之的是keep。 (GH 10792)DataFrame.combineAdd和DataFrame.combineMult已被弃用。它们可以很容易地被add和mul方法替代:DataFrame.add(other, fill_value=0)和DataFrame.mul(other, fill_value=1.)(GH 10735)。TimeSeries已被Series取代(注意,自 0.13.0 版本以来,这已经是一个别名),(GH 10890)SparsePanel已弃用,并将在未来版本中移除 (GH 11157)。Series.is_time_series已被弃用,取而代之的是Series.index.is_all_dates(GH 11135)遗留偏移量(如
'A@JAN')已被弃用(注意,这自 0.8.0 版本以来一直是别名)(GH 10878)WidePanel已弃用,改为使用Panel,LongPanel改为使用 ``DataFrame``(注意这些自 < 0.11.0 版本以来一直是别名),(GH 10892)DataFrame.convert_objects已被弃用,取而代之的是特定类型的函数pd.to_datetime、pd.to_timestamp和 ``pd.to_numeric``(0.17.0 新增)(GH 11133)。
移除先前版本的弃用/更改#
从
Series.order()和Series.sort()中移除na_last参数,改为使用na_position。 (GH 5231)从
.describe()中移除percentile_width,改为使用percentiles。(GH 7088)在 0.8.0 版本左右,从
DataFrame.to_string()中移除了colSpace参数,改为使用col_space。移除自动时间序列广播 (GH 2304)
In [88]: np.random.seed(1234) In [89]: df = pd.DataFrame( ....: np.random.randn(5, 2), ....: columns=list("AB"), ....: index=pd.date_range("2013-01-01", periods=5), ....: ) ....: In [90]: df Out[90]: A B 2013-01-01 0.471435 -1.190976 2013-01-02 1.432707 -0.312652 2013-01-03 -0.720589 0.887163 2013-01-04 0.859588 -0.636524 2013-01-05 0.015696 -2.242685 [5 rows x 2 columns]
之前
In [3]: df + df.A FutureWarning: TimeSeries broadcasting along DataFrame index by default is deprecated. Please use DataFrame.<op> to explicitly broadcast arithmetic operations along the index Out[3]: A B 2013-01-01 0.942870 -0.719541 2013-01-02 2.865414 1.120055 2013-01-03 -1.441177 0.166574 2013-01-04 1.719177 0.223065 2013-01-05 0.031393 -2.226989
当前
In [91]: df.add(df.A, axis="index") Out[91]: A B 2013-01-01 0.942870 -0.719541 2013-01-02 2.865414 1.120055 2013-01-03 -1.441177 0.166574 2013-01-04 1.719177 0.223065 2013-01-05 0.031393 -2.226989 [5 rows x 2 columns]
在
HDFStore.put/append中移除table关键字,改为使用format=(GH 4645)在
read_excel/ExcelFile中移除kind,因为它未被使用 (GH 4712)从
pd.read_html中移除infer_type关键字,因为它未被使用 (GH 4770, GH 7032)从
Series.tshift/shift中移除offset和timeRule关键字,改为使用freq(GH 4853, GH 4864)移除
pd.load/pd.save别名,改为使用pd.to_pickle/pd.read_pickle(GH 3787)
性能提升#
使用 Air Speed Velocity 库 进行基准测试的开发支持 (GH 8361)
为替代的 ExcelWriter 引擎和读取 Excel 文件添加了 vbench 基准测试 (GH 7171)
Categorical.value_counts中的性能改进 (GH 10804)在
SeriesGroupBy.nunique和SeriesGroupBy.value_counts以及SeriesGroupby.transform中的性能改进 (GH 10820, GH 11077)在
DataFrame.drop_duplicates中使用整数数据类型时的性能改进 (GH 10917)timedelta64和datetime64操作的8倍改进 (GH 6755)显著提升了使用切片器对
MultiIndex进行索引的性能 (GH 10287)使用类似列表的输入,
iloc提升了 8 倍 (GH 10791)改进了
Series.isin对于日期时间类型/整数 Series 的性能 (GH 10287)当类别相同时,
concat的 Categoricals 性能提升了 20 倍 (GH 10587)在指定格式字符串为ISO8601时,
to_datetime的性能得到了提升 (GH 10178)Series.value_counts对于 float 类型的 2 倍改进 (GH 10821)在
to_datetime中启用infer_datetime_format当日期组件没有0填充时 (GH 11142)从 0.16.1 版本开始在从嵌套字典构造
DataFrame时出现的回归问题 (GH 11084)DateOffset在Series或DatetimeIndex的加减操作中的性能改进 (GH 10744, GH 11205)
错误修复#
由于溢出导致的
timedelta64[ns]上的.mean()计算错误 (GH 9442)在旧版 numpy 中的
.isin存在错误 (GH 11232)DataFrame.to_html(index=False)中的错误渲染了不必要的name行 (GH 10344)DataFrame.to_latex()中的column_format参数无法传递 (GH 9402)在
DatetimeIndex本地化时带有NaT的错误 (GH 10477)Series.dt操作中保留元数据的错误 (GH 10477)在传递给
to_datetime构造函数时保留NaT的错误(GH 10477)当函数返回分类系列时,
DataFrame.apply中的错误。(GH 9573)to_datetime中存在一个错误,当提供无效的日期和格式时 (GH 10154)Index.drop_duplicates中删除名称的错误 (GH 10115)Series.quantile中的错误导致名称丢失 (GH 10881)在
pd.Series中设置值时,当索引具有频率的空Series存在错误。(GH 10193)pd.Series.interpolate中order关键字值无效的错误。(GH 10633)在
DataFrame.plot中的错误在指定颜色名称由多个字符组成时引发ValueError(GH 10387)在
Index构建中存在一个包含混合元组列表的错误 (GH 10697)当索引包含
NaT时,DataFrame.reset_index中的错误。(GH 10388)当工作表为空时
ExcelReader中的错误 (GH 6403)BinGrouper.group_info中的错误,返回值与基类不兼容 (GH 10914)在
DataFrame.pop上清除缓存的错误以及随后就地操作的错误 (GH 10912)使用混合整数
Index进行索引时出现ImportError的错误 (GH 10610)当索引包含空值时
Series.count中的错误 (GH 10946)在非规则频率
DatetimeIndex中的序列化错误 (GH 11002)当框架具有对称形状时,导致
DataFrame.where不尊重axis参数的错误。(GH 9736)Table.select_column中的错误,名称未保留 (GH 10392)offsets.generate_range中的错误,其中start和end的精度比offset更高 (GH 9907)pd.rolling_*中的一个错误,其中Series.name会在输出中丢失 (GH 10565)当索引或列不唯一时,
stack中的错误。(GH 10417)当轴具有 MultiIndex 时设置
Panel的错误 (GH 10360)USFederalHolidayCalendar中的错误,其中USMemorialDay和USMartinLutherKingJr不正确 (GH 10278 和 GH 9760)在
.sample()中的错误,如果设置了返回对象,会给出不必要的SettingWithCopyWarning(GH 10738)在
.sample()中的一个错误,当权重作为Series传递时,在按位置处理之前没有沿轴对齐,如果权重索引与采样对象未对齐,可能会导致问题。(GH 10738)在 (GH 9311, GH 6620, GH 9345) 中修复了回归问题,其中 groupby 与某些聚合器一起将类似日期时间的转换为浮点数 (GH 10979)
DataFrame.interpolate中axis=1和inplace=True的错误 (GH 10395)当指定多个列作为主键时,
io.sql.get_schema中的错误 (GH 10385)。在
groupby(sort=False)中使用类似日期时间的Categorical会引发ValueError(GH 10505)groupby(axis=1)中使用filter()抛出IndexError的错误 (GH 11041)在大端构建中的
test_categorical中的错误 (GH 10425)Series.shift和DataFrame.shift中的错误不支持分类数据 (GH 9416)在
Series.map中使用分类Series引发AttributeError(GH 10324)MultiIndex.get_level_values中包含Categorical的错误引发AttributeError(GH 10460)pd.get_dummies中sparse=True时未返回SparseDataFrame的错误 (GH 10531)Index子类型(如PeriodIndex)在.drop和.insert方法中没有返回它们自己的类型 (GH 10620)当
right数组为空时,algos.outer_join_indexer中的错误 (GH 10618)filter中的错误(从 0.16.0 版本回归)和transform在按多个键分组时,其中一个键是类似日期时间的(GH 10114)to_datetime和to_timedelta中的错误导致Index名称丢失 (GH 10875)len(DataFrame.groupby)中的错误导致当存在仅包含 NaN 的列时引发IndexError(GH 11016)在重采样空系列时导致段错误的问题 (GH 10228)
DatetimeIndex和PeriodIndex.value_counts中的错误会从其结果中重置名称,但在结果的Index中保留。 (GH 10150)使用
numexpr引擎的pd.eval中的错误将单元素 numpy 数组强制转换为标量 (GH 10546)当列的数据类型为
category时,pd.concat在axis=0存在错误 (GH 10177)pd.read_csv中使用 kwargsindex_col=False,index_col=['a', 'b']或dtype的错误 (GH 10413, GH 10467, GH 10577)Series.from_csv中header关键字参数未设置Series.name或Series.index.name的错误 (GH 10483)groupby.var中的错误导致小浮点值的方差不准确 (GH 10448)Series.plot(kind='hist')中的错误:Y 标签不具有信息性 (GH 10485)当使用生成
uint8类型的转换器时,read_csv中的错误 (GH 9266)在时间序列线和面积图中存在内存泄漏的错误 (GH 9003)
当右侧是一个
DataFrame时,沿着主轴或次轴设置Panel时出现的错误 (GH 11014)当
Panel的运算符函数(例如.add)未实现时,返回None且不引发NotImplementedError的错误 (GH 7692)当
subplots=True时,线和kde图不能接受多种颜色 (GH 9894)在
DataFrame.plot中的错误在指定颜色名称由多个字符组成时引发ValueError(GH 10387)带有
MultiIndex的Series的左右align中的错误可能被颠倒 (GH 10665)左侧和右侧
join与MultiIndex的错误可能被颠倒 (GH 10741)在
columns中设置了不同顺序时读取文件时read_stata中的错误 (GH 10757)Categorical中的错误在类别包含tz或Period时可能无法正确表示 (GH 10713)Categorical.__iter__中的错误可能不会返回正确的datetime和Period(GH 10713)在具有
PeriodIndex的对象上使用PeriodIndex进行索引时出现的错误 (GH 4125)使用
engine='c'的read_csv中的错误:注释、空白行等之前的 EOF 未正确处理 (GH 10728, GH 10548)通过
DataReader读取“famafrench”数据会导致 HTTP 404 错误,因为网站 URL 已更改 (GH 10591)。read_msgpack中存在一个错误,解码的 DataFrame 具有重复的列名 (GH 9618)io.common.get_filepath_or_buffer中的错误,如果桶中还包含用户没有读取权限的键,则会导致读取有效的 S3 文件失败 (GH 10604)在使用 python
datetime.date和 numpydatetime64设置时间戳列的向量化设置中的错误 (GH 10408, GH 10412)Index.take中的错误可能会添加不必要的freq属性 (GH 10791)在
merge中使用空的DataFrame可能会引发IndexError(GH 10824)to_latex中的错误,对某些已记录的参数出现意外的关键字参数 (GH 10888)当文件仅包含标题行时,使用
nrows或chunksize参数在read_csv中存在错误 (GH 9535)在存在替代编码的情况下,HDF5 中
category类型的序列化存在错误。(GH 10366)在
pd.DataFrame中构造一个带有字符串数据类型的空 DataFrame 时出现的错误 (GH 9428)当 DataFrame 未合并时,
pd.DataFrame.diff中的错误 (GH 10907)在
datetime64或timedelta64数据类型的数组中,pd.unique存在一个错误,这意味着返回的是一个对象数据类型的数组,而不是原始数据类型 (GH 9431)。Timedelta从 0s 切片时引发错误的错误 (GH 10583)DatetimeIndex.take和TimedeltaIndex.take中的错误可能不会对无效索引引发IndexError(GH 10295)Series([np.nan]).astype('M8[ms]')中的错误,现在返回Series([pd.NaT])(GH 10747)PeriodIndex.order重置频率中的错误 (GH 10295)当
freq以纳秒划分end时date_range中的 Bug (GH 10885)iloc中的一个错误,允许使用负整数访问 Series 边界外的内存 (GH 10779)read_msgpack中编码未被尊重的错误 (GH 10581)TimedeltaIndex格式化器中的错误导致在尝试使用to_csv保存带有TimedeltaIndex的DataFrame时出错 (GH 10833)当 Bigquery 返回零行时
pd.read_gbq抛出ValueError的错误 (GH 10273)to_json中的一个错误,在序列化 0 秩 ndarray 时导致段错误 (GH 9576)绘图函数中的错误在
GridSpec上绘制时可能会引发IndexError(GH 10819)绘图结果中的错误可能会显示不必要的次要刻度标签 (GH 10657)
groupby中的错误:在包含NaT的DataFrame上进行聚合计算不正确(例如first,last,min)。(GH 10590, GH 11010)在构建
DataFrame时,传递仅包含标量值的字典并指定列时未引发错误 (GH 10856).var()中的错误导致高度相似值的舍入误差 (GH 10242)DataFrame.plot(subplots=True)中重复列的错误输出不正确的结果 (GH 10962)Index算术中的错误可能导致不正确的类 (GH 10638)date_range中的错误导致如果 freq 是负的年、季度和月,结果为空 (GH 11018)DatetimeIndex中的错误无法推断负频率 (GH 11018)移除一些已弃用的 numpy 比较操作的使用,主要在测试中。(GH 10569)
Indexdtype 中的错误可能未正确应用 (GH 11017)在测试最低 google api 客户端版本时
io.gbq中的错误 (GH 10652)从嵌套
dict构造DataFrame时,timedelta键的错误 (GH 11129)当数据包含datetime类型时,
.fillna中的错误可能会引发TypeError(GH 7095, GH 11153)当分组的键数与索引长度相同时,
.groupby中的错误 (GH 11185)convert_objects中的错误,如果在所有值都为空且coerce的情况下可能不会返回转换后的值 (GH 9589)convert_objects中的错误,其中copy关键字未被尊重 (GH 9589)
贡献者#
总共有 112 人为此版本贡献了补丁。名字后面带有 “+” 的人首次贡献了补丁。
Alex Rothberg
Andrea Bedini +
Andrew Rosenfeld
Andy Hayden
Andy Li +
Anthonios Partheniou +
Artemy Kolchinsky
Bernard Willers
Charlie Clark +
Chris +
Chris Whelan
Christoph Gohlke +
Christopher Whelan
Clark Fitzgerald
Clearfield Christopher +
Dan Ringwalt +
Daniel Ni +
Data & Code Expert Experimenting with Code on Data +
David Cottrell
David John Gagne +
David Kelly +
ETF +
Eduardo Schettino +
Egor +
Egor Panfilov +
Evan Wright
Frank Pinter +
Gabriel Araujo +
Garrett-R
Gianluca Rossi +
Guillaume Gay
Guillaume Poulin
Harsh Nisar +
Ian Henriksen +
Ian Hoegen +
Jaidev Deshpande +
Jan Rudolph +
Jan Schulz
Jason Swails +
Jeff Reback
Jonas Buyl +
Joris Van den Bossche
Joris Vankerschaver +
Josh Levy-Kramer +
Julien Danjou
Ka Wo Chen
Karrie Kehoe +
Kelsey Jordahl
Kerby Shedden
Kevin Sheppard
Lars Buitinck
Leif Johnson +
Luis Ortiz +
Mac +
Matt Gambogi +
Matt Savoie +
Matthew Gilbert +
Maximilian Roos +
Michelangelo D’Agostino +
Mortada Mehyar
Nick Eubank
Nipun Batra
Ondřej Čertík
Phillip Cloud
Pratap Vardhan +
Rafal Skolasinski +
Richard Lewis +
Rinoc Johnson +
Rob Levy
Robert Gieseke
Safia Abdalla +
Samuel Denny +
Saumitra Shahapure +
Sebastian Pölsterl +
Sebastian Rubbert +
Sheppard, Kevin +
Sinhrks
Siu Kwan Lam +
Skipper Seabold
Spencer Carrucciu +
Stephan Hoyer
Stephen Hoover +
Stephen Pascoe +
Terry Santegoeds +
Thomas Grainger
Tjerk Santegoeds +
Tom Augspurger
Vincent Davis +
Winterflower +
Yaroslav Halchenko
Yuan Tang (Terry) +
agijsberts
ajcr +
behzad nouri
cel4
chris-b1 +
cyrusmaher +
davidovitch +
ganego +
jreback
juricast +
larvian +
maximilianr +
msund +
rekcahpassyla
robertzk +
scls19fr
seth-p
sinhrks
springcoil +
terrytangyuan +
tzinckgraf +