版本 0.20.1 (2017年5月5日)#
这是从 0.19.2 版本以来的一个重大发布,包括许多 API 变更、弃用、新功能、增强功能和性能改进,以及大量错误修复。我们建议所有用户升级到此版本。
亮点包括:
新的
.agg()API 用于 Series/DataFrame,类似于 groupby-rolling-resample API,请参见 这里与
feather-format的集成,包括一个新的顶级pd.read_feather()和DataFrame.to_feather()方法,参见 这里。.ix索引器已被弃用,请参见 这里Panel已被弃用,请参见 这里添加了
IntervalIndex和Interval标量类型,请参见 这里在
.groupby()中按索引级别分组时改进了用户API,请参见 这里改进了对
UInt64dtypes 的支持,请参见 这里一种新的 JSON 序列化方向,
orient='table',使用 Table Schema 规范,并提供了在 Jupyter Notebook 中更交互式的 repr 的可能性,请参见 这里实验性支持将样式化的 DataFrame (
DataFrame.style) 导出到 Excel,请参见 这里窗口二进制相关/协方差操作现在返回一个多索引的
DataFrame而不是一个Panel,因为Panel现在已被弃用,请参见 这里对 S3 处理的支持现在使用
s3fs,请参见 这里Google BigQuery 支持现在使用
pandas-gbq库,请参见 这里
警告
pandas 已经改变了代码库的内部结构和布局。这可能会影响不是从顶层 pandas.* 命名空间导入的情况,请查看更改 这里。
备注
这是 0.20.0 和 0.20.1 的联合发布。版本 0.20.1 包含一个额外的更改,以向后兼容使用 pandas 的 utils 例程的下游项目。(GH 16250)
v0.20.0 中的新功能
新功能#
DataFrame/Series 的 agg 方法 API#
Series 和 DataFrame 已经增强以支持聚合 API。这是一个从 groupby、窗口操作和重采样中熟悉的 API。这允许通过使用 agg() 和 transform() 以简洁的方式进行聚合操作。完整的文档在 这里 (GH 1623)。
这是一个示例
In [1]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 3), columns=['A', 'B', 'C'],
...: index=pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=10))
...:
In [2]: df.iloc[3:7] = np.nan
In [3]: df
Out[3]:
A B C
2000-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059
2000-01-02 -1.135632 1.212112 -0.173215
2000-01-03 0.119209 -1.044236 -0.861849
2000-01-04 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-05 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-06 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-07 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-08 0.113648 -1.478427 0.524988
2000-01-09 0.404705 0.577046 -1.715002
2000-01-10 -1.039268 -0.370647 -1.157892
[10 rows x 3 columns]
可以使用字符串函数名、可调用对象、列表或这些对象的字典进行操作。
使用单个函数等同于 .apply。
In [4]: df.agg('sum')
Out[4]:
A -1.068226
B -1.387015
C -4.892029
Length: 3, dtype: float64
使用函数列表进行多重聚合。
In [5]: df.agg(['sum', 'min'])
Out[5]:
A B C
sum -1.068226 -1.387015 -4.892029
min -1.135632 -1.478427 -1.715002
[2 rows x 3 columns]
使用字典提供了按列应用特定聚合的能力。您将获得类似矩阵的输出,包含所有聚合器。输出有一列对应每个唯一的函数。这些函数应用于特定列的结果将是 NaN:
In [6]: df.agg({'A': ['sum', 'min'], 'B': ['min', 'max']})
Out[6]:
A B
sum -1.068226 NaN
min -1.135632 -1.478427
max NaN 1.212112
[3 rows x 2 columns]
API 还支持用于广播结果的 .transform() 函数。
In [7]: df.transform(['abs', lambda x: x - x.min()])
Out[7]:
A B C
abs <lambda> abs <lambda> abs <lambda>
2000-01-01 0.469112 1.604745 0.282863 1.195563 1.509059 0.205944
2000-01-02 1.135632 0.000000 1.212112 2.690539 0.173215 1.541787
2000-01-03 0.119209 1.254841 1.044236 0.434191 0.861849 0.853153
2000-01-04 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-05 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-06 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-07 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-08 0.113648 1.249281 1.478427 0.000000 0.524988 2.239990
2000-01-09 0.404705 1.540338 0.577046 2.055473 1.715002 0.000000
2000-01-10 1.039268 0.096364 0.370647 1.107780 1.157892 0.557110
[10 rows x 6 columns]
当遇到无法聚合的混合数据类型时,.agg() 将只接受有效的聚合。这与 groupby .agg() 的工作方式类似。(GH 15015)
In [8]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3],
...: 'B': [1., 2., 3.],
...: 'C': ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'],
...: 'D': pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3)})
...:
In [9]: df.dtypes
Out[9]:
A int64
B float64
C object
D datetime64[ns]
Length: 4, dtype: object
In [10]: df.agg(['min', 'sum'])
Out[10]:
A B C D
min 1 1.0 bar 2013-01-01
sum 6 6.0 foobarbaz NaT
关键字参数 dtype 用于数据输入输出#
'python' 引擎用于 read_csv() ,以及用于解析固定宽度文本文件的 read_fwf() 函数和用于解析 Excel 文件的 read_excel() 函数,现在接受 dtype 关键字参数,用于指定特定列的类型 (GH 14295)。更多信息请参见 io 文档。
In [10]: data = "a b\n1 2\n3 4"
In [11]: pd.read_fwf(StringIO(data)).dtypes
Out[11]:
a int64
b int64
Length: 2, dtype: object
In [12]: pd.read_fwf(StringIO(data), dtype={'a': 'float64', 'b': 'object'}).dtypes
Out[12]:
a float64
b object
Length: 2, dtype: object
方法 .to_datetime() 增加了一个 origin 参数#
to_datetime() 增加了一个新参数 origin,用于定义一个参考日期,以便在解析具有指定 unit 的数值时计算结果时间戳。(GH 11276, GH 11745)
例如,以1960-01-01作为起始日期:
In [13]: pd.to_datetime([1, 2, 3], unit='D', origin=pd.Timestamp('1960-01-01'))
Out[13]: DatetimeIndex(['1960-01-02', '1960-01-03', '1960-01-04'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
默认设置为 origin='unix',默认值为 1970-01-01 00:00:00,这通常被称为 ‘unix 纪元’ 或 POSIX 时间。这是之前的默认值,因此这是一个向后兼容的更改。
In [14]: pd.to_datetime([1, 2, 3], unit='D')
Out[14]: DatetimeIndex(['1970-01-02', '1970-01-03', '1970-01-04'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
GroupBy 增强功能#
传递给 DataFrame.groupby() 作为 by 参数的字符串现在可以引用列名或索引级别名。以前,只能引用列名。这使得可以轻松地同时按列和索引级别进行分组。(GH 5677)
In [15]: arrays = [['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'qux', 'qux'],
....: ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two']]
....:
In [16]: index = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(arrays, names=['first', 'second'])
In [17]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3],
....: 'B': np.arange(8)},
....: index=index)
....:
In [18]: df
Out[18]:
A B
first second
bar one 1 0
two 1 1
baz one 1 2
two 1 3
foo one 2 4
two 2 5
qux one 3 6
two 3 7
[8 rows x 2 columns]
In [19]: df.groupby(['second', 'A']).sum()
Out[19]:
B
second A
one 1 2
2 4
3 6
two 1 4
2 5
3 7
[6 rows x 1 columns]
在 read_csv 中更好地支持压缩的URL#
压缩代码被重构(GH 12688)。结果,从 read_csv() 或 read_table() 中的 URL 读取数据帧现在支持额外的压缩方法:xz、bz2 和 zip``(:issue:`14570`)。之前,只支持 ``gzip 压缩。默认情况下,现在通过文件扩展名推断 URL 和路径的压缩。此外,python 2 C-engine 中的 bz2 压缩支持得到了改进(GH 14874)。
In [20]: url = ('https://github.com/{repo}/raw/{branch}/{path}'
....: .format(repo='pandas-dev/pandas',
....: branch='main',
....: path='pandas/tests/io/parser/data/salaries.csv.bz2'))
....:
# default, infer compression
In [21]: df = pd.read_csv(url, sep='\t', compression='infer')
# explicitly specify compression
In [22]: df = pd.read_csv(url, sep='\t', compression='bz2')
In [23]: df.head(2)
Out[23]:
S X E M
0 13876 1 1 1
1 11608 1 3 0
[2 rows x 4 columns]
Pickle 文件 IO 现在支持压缩#
read_pickle(), DataFrame.to_pickle() 和 Series.to_pickle() 现在可以从压缩的 pickle 文件读取和写入。压缩方法可以是一个显式参数,或者从文件扩展名推断。请参见 这里的文档。
In [24]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': np.random.randn(1000),
....: 'B': 'foo',
....: 'C': pd.date_range('20130101', periods=1000, freq='s')})
....:
使用显式的压缩类型
In [25]: df.to_pickle("data.pkl.compress", compression="gzip")
In [26]: rt = pd.read_pickle("data.pkl.compress", compression="gzip")
In [27]: rt.head()
Out[27]:
A B C
0 -1.344312 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:00
1 0.844885 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:01
2 1.075770 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:02
3 -0.109050 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:03
4 1.643563 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:04
[5 rows x 3 columns]
默认情况下,会从扩展名推断压缩类型(compression='infer'):
In [28]: df.to_pickle("data.pkl.gz")
In [29]: rt = pd.read_pickle("data.pkl.gz")
In [30]: rt.head()
Out[30]:
A B C
0 -1.344312 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:00
1 0.844885 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:01
2 1.075770 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:02
3 -0.109050 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:03
4 1.643563 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:04
[5 rows x 3 columns]
In [31]: df["A"].to_pickle("s1.pkl.bz2")
In [32]: rt = pd.read_pickle("s1.pkl.bz2")
In [33]: rt.head()
Out[33]:
0 -1.344312
1 0.844885
2 1.075770
3 -0.109050
4 1.643563
Name: A, Length: 5, dtype: float64
UInt64 支持改进#
pandas 显著改进了对涉及无符号或纯非负整数的操作的支持。以前,处理这些整数会导致不正确的舍入或数据类型转换,从而导致错误的结果。值得注意的是,创建了一个新的数值索引 UInt64Index (GH 14937)
In [1]: idx = pd.UInt64Index([1, 2, 3])
In [2]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', 'c']}, index=idx)
In [3]: df.index
Out[3]: UInt64Index([1, 2, 3], dtype='uint64')
分类上的GroupBy#
在之前的版本中,当对一个包含某些未出现在数据中的类别的分类系列进行分组时,.groupby(..., sort=False) 会失败并抛出一个 ValueError。(GH 13179)
In [34]: chromosomes = np.r_[np.arange(1, 23).astype(str), ['X', 'Y']]
In [35]: df = pd.DataFrame({
....: 'A': np.random.randint(100),
....: 'B': np.random.randint(100),
....: 'C': np.random.randint(100),
....: 'chromosomes': pd.Categorical(np.random.choice(chromosomes, 100),
....: categories=chromosomes,
....: ordered=True)})
....:
In [36]: df
Out[36]:
A B C chromosomes
0 87 22 81 4
1 87 22 81 13
2 87 22 81 22
3 87 22 81 2
4 87 22 81 6
.. .. .. .. ...
95 87 22 81 8
96 87 22 81 11
97 87 22 81 X
98 87 22 81 1
99 87 22 81 19
[100 rows x 4 columns]
之前的行为:
In [3]: df[df.chromosomes != '1'].groupby('chromosomes', observed=False, sort=False).sum()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError: items in new_categories are not the same as in old categories
新行为:
In [37]: df[df.chromosomes != '1'].groupby('chromosomes', observed=False, sort=False).sum()
Out[37]:
A B C
chromosomes
4 348 88 324
13 261 66 243
22 348 88 324
2 348 88 324
6 174 44 162
... ... .. ...
3 348 88 324
11 348 88 324
19 174 44 162
1 0 0 0
21 0 0 0
[24 rows x 3 columns]
表模式输出#
对于 DataFrame.to_json() 的新方向 'table' 将生成与 Table Schema 兼容的数据字符串表示。
In [38]: df = pd.DataFrame(
....: {'A': [1, 2, 3],
....: 'B': ['a', 'b', 'c'],
....: 'C': pd.date_range('2016-01-01', freq='d', periods=3)},
....: index=pd.Index(range(3), name='idx'))
In [39]: df
Out[39]:
A B C
idx
0 1 a 2016-01-01
1 2 b 2016-01-02
2 3 c 2016-01-03
[3 rows x 3 columns]
In [40]: df.to_json(orient='table')
Out[40]:
'{"schema":{"fields":[{"name":"idx","type":"integer"},{"name":"A","type":"integer"},{"name":"B","type":"string"},{"name":"C","type":"datetime"}],"primaryKey":["idx"],"pandas_version":"1.4.0"},"data":[{"idx":0,"A":1,"B":"a","C":"2016-01-01T00:00:00.000"},{"idx":1,"A":2,"B":"b","C":"2016-01-02T00:00:00.000"},{"idx":2,"A":3,"B":"c","C":"2016-01-03T00:00:00.000"}]}'
请参阅 IO: 表模式以获取更多信息。
此外,如果使用 IPython(或其他使用 Jupyter 消息协议的前端,如 nteract),DataFrame 和 Series 的 repr 现在可以发布此 JSON 表模式表示的 Series 或 DataFrame。这使得像 Jupyter notebook 和 nteract 这样的前端在如何显示 pandas 对象方面更加灵活,因为它们有更多关于数据的信息。您必须通过将 display.html.table_schema 选项设置为 True 来启用此功能。
从/到 SparseDataFrame 的 SciPy 稀疏矩阵#
pandas 现在支持直接从 scipy.sparse.spmatrix 实例创建稀疏数据帧。更多信息请参见 文档。 (GH 4343)
所有稀疏格式都支持,但不在 COOrdinate 格式中的矩阵将被转换,必要时复制数据。
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.random.random(size=(1000, 5))
arr[arr < .9] = 0
sp_arr = csr_matrix(arr)
sp_arr
sdf = pd.SparseDataFrame(sp_arr)
sdf
要将 SparseDataFrame 转换回 COO 格式的稀疏 SciPy 矩阵,可以使用:
sdf.to_coo()
样式化的 DataFrame 的 Excel 输出#
已添加实验性支持,可以使用 openpyxl 引擎将 DataFrame.style 格式导出到 Excel。(GH 15530)
例如,运行以下内容后,styled.xlsx 呈现如下:
In [38]: np.random.seed(24)
In [39]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': np.linspace(1, 10, 10)})
In [40]: df = pd.concat([df, pd.DataFrame(np.random.RandomState(24).randn(10, 4),
....: columns=list('BCDE'))],
....: axis=1)
....:
In [41]: df.iloc[0, 2] = np.nan
In [42]: df
Out[42]:
A B C D E
0 1.0 1.329212 NaN -0.316280 -0.990810
1 2.0 -1.070816 -1.438713 0.564417 0.295722
2 3.0 -1.626404 0.219565 0.678805 1.889273
3 4.0 0.961538 0.104011 -0.481165 0.850229
4 5.0 1.453425 1.057737 0.165562 0.515018
5 6.0 -1.336936 0.562861 1.392855 -0.063328
6 7.0 0.121668 1.207603 -0.002040 1.627796
7 8.0 0.354493 1.037528 -0.385684 0.519818
8 9.0 1.686583 -1.325963 1.428984 -2.089354
9 10.0 -0.129820 0.631523 -0.586538 0.290720
[10 rows x 5 columns]
In [43]: styled = (df.style
....: .map(lambda val: 'color:red;' if val < 0 else 'color:black;')
....: .highlight_max())
....:
In [44]: styled.to_excel('styled.xlsx', engine='openpyxl')
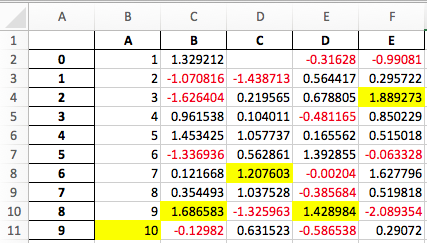
查看 样式文档 获取更多细节。
IntervalIndex#
pandas 获得了一个 IntervalIndex,它有自己的数据类型 interval 以及 Interval 标量类型。这些允许对区间表示法提供一流的支持,特别是作为 cut() 和 qcut() 中类别的返回类型。IntervalIndex 允许一些独特的索引,请参阅 文档。(GH 7640, GH 8625)
警告
IntervalIndex 的这些索引行为是暂定的,可能会在未来的 pandas 版本中更改。欢迎提供使用反馈。
之前的行为:
返回的类别是字符串,表示区间
In [1]: c = pd.cut(range(4), bins=2)
In [2]: c
Out[2]:
[(-0.003, 1.5], (-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3], (1.5, 3]]
Categories (2, object): [(-0.003, 1.5] < (1.5, 3]]
In [3]: c.categories
Out[3]: Index(['(-0.003, 1.5]', '(1.5, 3]'], dtype='object')
新行为:
In [45]: c = pd.cut(range(4), bins=2)
In [46]: c
Out[46]:
[(-0.003, 1.5], (-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3.0], (1.5, 3.0]]
Categories (2, interval[float64, right]): [(-0.003, 1.5] < (1.5, 3.0]]
In [47]: c.categories
Out[47]: IntervalIndex([(-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3.0]], dtype='interval[float64, right]')
此外,这允许将 其他 数据与这些相同的箱子一起分箱,其中 NaN 表示类似于其他数据类型的缺失值。
In [48]: pd.cut([0, 3, 5, 1], bins=c.categories)
Out[48]:
[(-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3.0], NaN, (-0.003, 1.5]]
Categories (2, interval[float64, right]): [(-0.003, 1.5] < (1.5, 3.0]]
IntervalIndex 也可以在 Series 和 DataFrame 中用作索引。
In [49]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': range(4),
....: 'B': pd.cut([0, 3, 1, 1], bins=c.categories)
....: }).set_index('B')
....:
In [50]: df
Out[50]:
A
B
(-0.003, 1.5] 0
(1.5, 3.0] 1
(-0.003, 1.5] 2
(-0.003, 1.5] 3
[4 rows x 1 columns]
通过特定间隔进行选择:
In [51]: df.loc[pd.Interval(1.5, 3.0)]
Out[51]:
A 1
Name: (1.5, 3.0], Length: 1, dtype: int64
通过包含在区间内的标量值进行选择。
In [52]: df.loc[0]
Out[52]:
A
B
(-0.003, 1.5] 0
(-0.003, 1.5] 2
(-0.003, 1.5] 3
[3 rows x 1 columns]
其他增强功能#
DataFrame.rolling()现在接受参数closed='right'|'left'|'both'|'neither'来选择滚动窗口端点的闭合性。请参阅 文档 (GH 13965)与
feather-format的集成,包括一个新的顶级pd.read_feather()和DataFrame.to_feather()方法,参见 这里。Series.str.replace()现在接受一个可调用对象作为替换,该对象传递给re.sub(GH 15055)Series.str.replace()现在接受一个编译的正则表达式作为模式 (GH 15446)Series.sort_index接受参数kind和na_position(GH 13589, GH 14444)DataFrame和DataFrame.groupby()获得了一个nunique()方法,用于计算一个轴上的不同值的数量 (GH 14336, GH 15197)。DataFrame获得了一个melt()方法,相当于pd.melt(),用于从宽格式转换为长格式 (GH 12640)。pd.read_excel()现在在使用sheetname=None时保留工作表顺序 (GH 9930)现在支持带有小数点的多个偏移别名(例如
0.5min被解析为30s)(GH 8419).isnull()和.notnull()已被添加到Index对象中,以使它们与SeriesAPI 更加一致 (GH 15300)新的
UnsortedIndexError``(``KeyError的子类)在索引/切片未排序的 MultiIndex 时引发(GH 11897)。这允许区分由于缺乏排序或错误键导致的错误。请参见 这里MultiIndex获得了一个.to_frame()方法,用于转换为DataFrame(GH 12397)pd.cut和pd.qcut现在支持 datetime64 和 timedelta64 dtypes (GH 14714, GH 14798)pd.qcut增加了duplicates='raise'|'drop'选项来控制是否在重复边缘时引发 (GH 7751)Series提供了一个to_excel方法来输出 Excel 文件 (GH 8825)pd.read_csv()中的usecols参数现在接受一个可调用函数作为值 (GH 14154)pd.read_csv()中的skiprows参数现在接受一个可调用函数作为值 (GH 10882)在
pd.read_csv()中的nrows和chunksize参数如果同时传递是被支持的 (GH 6774, GH 15755)如果
suplots=True并且title是一个字符串列表,DataFrame.plot现在会在每个子图上方打印一个标题 (GH 14753)DataFrame.plot可以将 matplotlib 2.0 默认颜色循环作为单个字符串作为颜色参数传递,参见 这里。 (GH 15516)Series.interpolate()现在支持使用method='time'时将 timedelta 作为索引类型 (GH 6424)在
DataFrame/Series.rename中添加level关键字,以重命名 MultiIndex 中指定级别的标签 (GH 4160)。DataFrame.reset_index()现在会将元组index.name解释为跨越columns级别的键,如果这是一个MultiIndex(GH 16164)Timedelta.isoformat方法添加用于将 Timedeltas 格式化为 ISO 8601 持续时间。请参阅 Timedelta 文档 (GH 15136).select_dtypes()现在允许字符串datetimetz来通用选择带时区的日期时间 (GH 14910).to_latex()方法现在接受multicolumn和multirow参数,以使用配套的 LaTeX 增强功能pd.merge_asof()获得了direction='backward'|'forward'|'nearest'选项 (GH 14887)Series/DataFrame.asfreq()获得了一个fill_value参数,用于填充缺失值 (GH 3715)。Series/DataFrame.resample.asfreq获得了一个fill_value参数,用于在重采样期间填充缺失值 (GH 3715)。pandas.util.hash_pandas_object()已经获得了对MultiIndex进行哈希的能力 (GH 15224)Series/DataFrame.squeeze()已获得axis参数。(GH 15339)DataFrame.to_excel()有一个新的freeze_panes参数,用于在导出到Excel时启用冻结窗格 (GH 15160)pd.read_html()将解析多个标题行,创建一个 MultiIndex 标题。(GH 13434)。HTML 表格输出会跳过
colspan或rowspan属性,如果它们的值等于 1。(GH 15403)pandas.io.formats.style.Styler模板现在有块,以便更容易扩展,请参见 示例笔记本 (GH 15649)Styler.render()现在接受**kwargs以允许在模板中使用用户定义的变量 (GH 15649)与 Jupyter notebook 5.0 的兼容性;MultiIndex 列标签左对齐,MultiIndex 行标签顶部对齐 (GH 15379)
TimedeltaIndex现在有一个专门为纳秒级精度设计的自定义日期刻度格式化器 (GH 8711)pd.api.types.union_categoricals获得了ignore_ordered参数,以允许忽略联合分类的顺序属性 (GH 13410)。更多信息请参见 分类联合文档。DataFrame.to_latex()和DataFrame.to_string()现在允许可选的表头别名。(GH 15536)重新启用
pd.read_excel()的parse_dates关键字,以将字符串列解析为日期 (GH 14326)在
Index的子类中添加了.empty属性。(GH 15270)为
Timedelta和TimedeltaIndex启用整除 (GH 15828)pandas.io.json.json_normalize()获得了errors='ignore'|'raise'选项;默认是errors='raise',这是向后兼容的。 (GH 14583)pandas.io.json.json_normalize()使用一个空的list将返回一个空的DataFrame(GH 15534)pandas.io.json.json_normalize()增加了一个sep选项,该选项接受str来分隔连接的字段;默认值是 “.”,这是向后兼容的。(GH 14883)MultiIndex.remove_unused_levels()已被添加,以方便 移除未使用的层级。 (GH 15694)pd.read_csv()现在将在任何解析错误发生时引发ParserError错误 (GH 15913, GH 15925)pd.read_csv()现在支持 Python 解析器的error_bad_lines和warn_bad_lines参数 (GH 15925)display.show_dimensions选项现在也可以用来指定是否在Series的 repr 中显示其长度 (GH 7117)。parallel_coordinates()增加了一个sort_labels关键字参数,用于对类别标签及其分配的颜色进行排序 (GH 15908)DataFrame.style.bar()现在接受两个额外的选项来进一步自定义条形图。条形对齐方式通过align='left'|'mid'|'zero'设置,默认是 ‘left’,这是向后兼容的;你现在可以传递一个color=[color_negative, color_positive]的列表。(GH 14757)
向后不兼容的 API 变化#
使用 pandas < 0.13.0 创建的 HDF5 格式可能存在不兼容性#
pd.TimeSeries 在 0.17.0 版本中正式弃用,尽管自 0.13.0 版本以来它已经是一个别名。它已被 pd.Series 取代。(GH 15098)。
这*可能*会导致在先前版本中创建的HDF5文件变得不可读,如果使用了``pd.TimeSeries``。这最有可能发生在pandas < 0.13.0。如果你发现自己处于这种情况,你可以使用一个较新的先前版本的pandas来读取你的HDF5文件,然后在应用以下步骤后再次写出来。
In [2]: s = pd.TimeSeries([1, 2, 3], index=pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3))
In [3]: s
Out[3]:
2013-01-01 1
2013-01-02 2
2013-01-03 3
Freq: D, dtype: int64
In [4]: type(s)
Out[4]: pandas.core.series.TimeSeries
In [5]: s = pd.Series(s)
In [6]: s
Out[6]:
2013-01-01 1
2013-01-02 2
2013-01-03 3
Freq: D, dtype: int64
In [7]: type(s)
Out[7]: pandas.core.series.Series
索引类型的映射现在返回其他索引类型#
Index 上的 map 现在返回一个 Index ,而不是一个 numpy 数组 (GH 12766)
In [53]: idx = pd.Index([1, 2])
In [54]: idx
Out[54]: Index([1, 2], dtype='int64')
In [55]: mi = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([(1, 2), (2, 4)])
In [56]: mi
Out[56]:
MultiIndex([(1, 2),
(2, 4)],
)
之前的行为:
In [5]: idx.map(lambda x: x * 2)
Out[5]: array([2, 4])
In [6]: idx.map(lambda x: (x, x * 2))
Out[6]: array([(1, 2), (2, 4)], dtype=object)
In [7]: mi.map(lambda x: x)
Out[7]: array([(1, 2), (2, 4)], dtype=object)
In [8]: mi.map(lambda x: x[0])
Out[8]: array([1, 2])
新行为:
In [57]: idx.map(lambda x: x * 2)
Out[57]: Index([2, 4], dtype='int64')
In [58]: idx.map(lambda x: (x, x * 2))
Out[58]:
MultiIndex([(1, 2),
(2, 4)],
)
In [59]: mi.map(lambda x: x)
Out[59]:
MultiIndex([(1, 2),
(2, 4)],
)
In [60]: mi.map(lambda x: x[0])
Out[60]: Index([1, 2], dtype='int64')
在具有 datetime64 值的 Series 上使用 map 可能会返回 int64 数据类型,而不是 int32
In [64]: s = pd.Series(pd.date_range('2011-01-02T00:00', '2011-01-02T02:00', freq='H')
....: .tz_localize('Asia/Tokyo'))
....:
In [65]: s
Out[65]:
0 2011-01-02 00:00:00+09:00
1 2011-01-02 01:00:00+09:00
2 2011-01-02 02:00:00+09:00
Length: 3, dtype: datetime64[ns, Asia/Tokyo]
之前的行为:
In [9]: s.map(lambda x: x.hour)
Out[9]:
0 0
1 1
2 2
dtype: int32
新行为:
In [66]: s.map(lambda x: x.hour)
Out[66]:
0 0
1 1
2 2
Length: 3, dtype: int64
访问 Index 的 datetime 字段现在返回 Index#
与日期时间相关的属性(概述见 这里)``DatetimeIndex``、PeriodIndex 和 TimedeltaIndex 之前返回的是 numpy 数组。现在它们将返回一个新的 Index 对象,除非在布尔字段的情况下,结果仍然是一个布尔 ndarray。(GH 15022)
之前的行为:
In [1]: idx = pd.date_range("2015-01-01", periods=5, freq='10H')
In [2]: idx.hour
Out[2]: array([ 0, 10, 20, 6, 16], dtype=int32)
新行为:
In [67]: idx = pd.date_range("2015-01-01", periods=5, freq='10H')
In [68]: idx.hour
Out[68]: Index([0, 10, 20, 6, 16], dtype='int32')
这有一个优点,即特定的 Index 方法在结果上仍然可用。另一方面,这可能会有向后不兼容的问题:例如,与 numpy 数组相比,Index 对象是不可变的。要获取原始的 ndarray,您可以始终使用 np.asarray(idx.hour) 显式转换。
pd.unique 现在将与扩展类型保持一致#
在之前的版本中,对 Categorical 和 tz-aware 数据类型使用 Series.unique() 和 pandas.unique() 会返回不同的类型。现在这些已经保持一致。(GH 15903)
Datetime tz-aware
之前的行为:
# Series In [5]: pd.Series([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]).unique() Out[5]: array([Timestamp('2016-01-01 00:00:00-0500', tz='US/Eastern')], dtype=object) In [6]: pd.unique(pd.Series([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')])) Out[6]: array(['2016-01-01T05:00:00.000000000'], dtype='datetime64[ns]') # Index In [7]: pd.Index([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]).unique() Out[7]: DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]', freq=None) In [8]: pd.unique([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]) Out[8]: array(['2016-01-01T05:00:00.000000000'], dtype='datetime64[ns]')
新行为:
# Series, returns an array of Timestamp tz-aware In [61]: pd.Series([pd.Timestamp(r'20160101', tz=r'US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp(r'20160101', tz=r'US/Eastern')]).unique() ....: Out[61]: <DatetimeArray> ['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'] Length: 1, dtype: datetime64[s, US/Eastern] In [62]: pd.unique(pd.Series([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')])) ....: Out[62]: <DatetimeArray> ['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'] Length: 1, dtype: datetime64[s, US/Eastern] # Index, returns a DatetimeIndex In [63]: pd.Index([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]).unique() ....: Out[63]: DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[s, US/Eastern]', freq=None) In [64]: pd.unique(pd.Index([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')])) ....: Out[64]: DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[s, US/Eastern]', freq=None)
分类数据
之前的行为:
In [1]: pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category').unique() Out[1]: [b, a, c] Categories (3, object): [b, a, c] In [2]: pd.unique(pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category')) Out[2]: array(['b', 'a', 'c'], dtype=object)
新行为:
# returns a Categorical In [65]: pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category').unique() Out[65]: ['b', 'a', 'c'] Categories (3, object): ['a', 'b', 'c'] In [66]: pd.unique(pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category')) Out[66]: ['b', 'a', 'c'] Categories (3, object): ['a', 'b', 'c']
S3 文件处理#
pandas 现在使用 s3fs 来处理 S3 连接。这不应破坏任何代码。然而,由于 s3fs 不是必需的依赖项,你需要单独安装它,就像在 pandas 的早期版本中安装 boto 一样。(GH 11915)。
部分字符串索引更改#
DatetimeIndex 部分字符串索引 现在作为精确匹配工作,前提是字符串解析与索引解析一致,包括当两者都是秒时 (GH 14826)。详情请参见 切片与精确匹配。
In [67]: df = pd.DataFrame({'a': [1, 2, 3]}, pd.DatetimeIndex(['2011-12-31 23:59:59',
....: '2012-01-01 00:00:00',
....: '2012-01-01 00:00:01']))
....:
之前的行为:
In [4]: df['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
Out[4]:
a
2011-12-31 23:59:59 1
In [5]: df['a']['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
Out[5]:
2011-12-31 23:59:59 1
Name: a, dtype: int64
新行为:
In [4]: df['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
KeyError: '2011-12-31 23:59:59'
In [5]: df['a']['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
Out[5]: 1
不同浮点数据类型的连接不会自动向上转换#
之前,具有不同 float 数据类型的多个对象的 concat 会自动将结果向上转换为 float64 数据类型。现在将使用最小可接受的数据类型 (GH 13247)
In [68]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.array([1.0], dtype=np.float32, ndmin=2))
In [69]: df1.dtypes
Out[69]:
0 float32
Length: 1, dtype: object
In [70]: df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.array([np.nan], dtype=np.float32, ndmin=2))
In [71]: df2.dtypes
Out[71]:
0 float32
Length: 1, dtype: object
之前的行为:
In [7]: pd.concat([df1, df2]).dtypes
Out[7]:
0 float64
dtype: object
新行为:
In [72]: pd.concat([df1, df2]).dtypes
Out[72]:
0 float32
Length: 1, dtype: object
pandas 的 Google BigQuery 支持已迁移#
pandas 已将 Google BigQuery 支持分离到一个单独的包 pandas-gbq。你可以 conda install pandas-gbq -c conda-forge 或 pip install pandas-gbq 来获取它。read_gbq() 和 DataFrame.to_gbq() 的功能在当前发布的 pandas-gbq=0.1.4 版本中保持不变。文档现在托管在 这里 (GH 15347)
索引的内存使用更准确#
在以前的版本中,在具有索引的 pandas 结构上显示 .memory_usage(),只会包括实际的索引值,而不包括促进快速索引的结构。对于 Index 和 MultiIndex 来说,这通常会有所不同,而对于其他索引类型则不太明显。(GH 15237)
之前的行为:
In [8]: index = pd.Index(['foo', 'bar', 'baz'])
In [9]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[9]: 180
In [10]: index.get_loc('foo')
Out[10]: 0
In [11]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[11]: 180
新行为:
In [8]: index = pd.Index(['foo', 'bar', 'baz'])
In [9]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[9]: 180
In [10]: index.get_loc('foo')
Out[10]: 0
In [11]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[11]: 260
DataFrame.sort_index 更改#
在某些情况下,在 MultiIndexed DataFrame 上调用 .sort_index() 会返回 相同 的 DataFrame,而看似没有排序。这会发生在 lexsorted 但非单调级别的情况下。(GH 15622, GH 15687, GH 14015, GH 13431, GH 15797)
这与之前的版本 不变 ,但为了说明目的而展示:
In [81]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(6), columns=['value'],
....: index=pd.MultiIndex.from_product([list('BA'), range(3)]))
....:
In [82]: df
Out[82]:
value
B 0 0
1 1
2 2
A 0 3
1 4
2 5
[6 rows x 1 columns]
In [87]: df.index.is_lexsorted()
Out[87]: False
In [88]: df.index.is_monotonic
Out[88]: False
排序按预期工作
In [73]: df.sort_index()
Out[73]:
a
2011-12-31 23:59:59 1
2012-01-01 00:00:00 2
2012-01-01 00:00:01 3
[3 rows x 1 columns]
In [90]: df.sort_index().index.is_lexsorted()
Out[90]: True
In [91]: df.sort_index().index.is_monotonic
Out[91]: True
然而,这个例子具有非单调的第二级,其行为并不如预期。
In [74]: df = pd.DataFrame({'value': [1, 2, 3, 4]},
....: index=pd.MultiIndex([['a', 'b'], ['bb', 'aa']],
....: [[0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 1]]))
....:
In [75]: df
Out[75]:
value
a bb 1
aa 2
b bb 3
aa 4
[4 rows x 1 columns]
之前的行为:
In [11]: df.sort_index()
Out[11]:
value
a bb 1
aa 2
b bb 3
aa 4
In [14]: df.sort_index().index.is_lexsorted()
Out[14]: True
In [15]: df.sort_index().index.is_monotonic
Out[15]: False
新行为:
In [94]: df.sort_index()
Out[94]:
value
a aa 2
bb 1
b aa 4
bb 3
[4 rows x 1 columns]
In [95]: df.sort_index().index.is_lexsorted()
Out[95]: True
In [96]: df.sort_index().index.is_monotonic
Out[96]: True
GroupBy 描述格式化#
groupby.describe() 的输出格式现在在列中标记 describe() 指标,而不是在索引中。这种格式与 groupby.agg() 在同时应用多个函数时一致。(GH 4792)
之前的行为:
In [1]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 2, 2], 'B': [1, 2, 3, 4]})
In [2]: df.groupby('A').describe()
Out[2]:
B
A
1 count 2.000000
mean 1.500000
std 0.707107
min 1.000000
25% 1.250000
50% 1.500000
75% 1.750000
max 2.000000
2 count 2.000000
mean 3.500000
std 0.707107
min 3.000000
25% 3.250000
50% 3.500000
75% 3.750000
max 4.000000
In [3]: df.groupby('A').agg(["mean", "std", "min", "max"])
Out[3]:
B
mean std amin amax
A
1 1.5 0.707107 1 2
2 3.5 0.707107 3 4
新行为:
In [76]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 2, 2], 'B': [1, 2, 3, 4]})
In [77]: df.groupby('A').describe()
Out[77]:
B
count mean std min 25% 50% 75% max
A
1 2.0 1.5 0.707107 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.75 2.0
2 2.0 3.5 0.707107 3.0 3.25 3.5 3.75 4.0
[2 rows x 8 columns]
In [78]: df.groupby('A').agg(["mean", "std", "min", "max"])
Out[78]:
B
mean std min max
A
1 1.5 0.707107 1 2
2 3.5 0.707107 3 4
[2 rows x 4 columns]
窗口二进制相关/协方差操作返回一个多索引 DataFrame#
一个二进制窗口操作,如 .corr() 或 .cov(),当在 .rolling(..)、.expanding(..) 或 .ewm(..) 对象上操作时,现在将返回一个 2 级 MultiIndexed DataFrame 而不是一个 Panel,因为 Panel 现在已被弃用,请参见 这里。这些在功能上是等价的,但 MultiIndexed DataFrame 在 pandas 中得到更多支持。有关更多信息,请参见 窗口二进制操作 部分。(GH 15677)
In [79]: np.random.seed(1234)
In [80]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(100, 2),
....: columns=pd.Index(['A', 'B'], name='bar'),
....: index=pd.date_range('20160101',
....: periods=100, freq='D', name='foo'))
....:
In [81]: df.tail()
Out[81]:
bar A B
foo
2016-04-05 0.640880 0.126205
2016-04-06 0.171465 0.737086
2016-04-07 0.127029 0.369650
2016-04-08 0.604334 0.103104
2016-04-09 0.802374 0.945553
[5 rows x 2 columns]
之前的行为:
In [2]: df.rolling(12).corr()
Out[2]:
<class 'pandas.core.panel.Panel'>
Dimensions: 100 (items) x 2 (major_axis) x 2 (minor_axis)
Items axis: 2016-01-01 00:00:00 to 2016-04-09 00:00:00
Major_axis axis: A to B
Minor_axis axis: A to B
新行为:
In [82]: res = df.rolling(12).corr()
In [83]: res.tail()
Out[83]:
bar A B
foo bar
2016-04-07 B -0.132090 1.000000
2016-04-08 A 1.000000 -0.145775
B -0.145775 1.000000
2016-04-09 A 1.000000 0.119645
B 0.119645 1.000000
[5 rows x 2 columns]
获取一个横截面的相关矩阵
In [84]: df.rolling(12).corr().loc['2016-04-07']
Out[84]:
bar A B
bar
A 1.00000 -0.13209
B -0.13209 1.00000
[2 rows x 2 columns]
HDFStore 字符串比较#
在以前的版本中,大多数类型可以与 HDFStore 中的字符串列进行比较,通常会导致无效的比较,返回一个空的结果帧。现在这些比较将引发一个 TypeError (GH 15492)
In [85]: df = pd.DataFrame({'unparsed_date': ['2014-01-01', '2014-01-01']})
In [86]: df.to_hdf('store.h5', key='key', format='table', data_columns=True)
In [87]: df.dtypes
Out[87]:
unparsed_date object
Length: 1, dtype: object
之前的行为:
In [4]: pd.read_hdf('store.h5', 'key', where='unparsed_date > ts')
File "<string>", line 1
(unparsed_date > 1970-01-01 00:00:01.388552400)
^
SyntaxError: invalid token
新行为:
In [18]: ts = pd.Timestamp('2014-01-01')
In [19]: pd.read_hdf('store.h5', 'key', where='unparsed_date > ts')
TypeError: Cannot compare 2014-01-01 00:00:00 of
type <class 'pandas.tslib.Timestamp'> to string column
Index.intersection 和 inner join 现在保留左边 Index 的顺序#
Index.intersection() 现在保留调用 Index``(左侧)的顺序,而不是另一个 ``Index``(右侧)的顺序(:issue:`15582`)。这影响内连接、:meth:`DataFrame.join` 和 :func:`merge`,以及 ``.align 方法。
Index.intersectionIn [88]: left = pd.Index([2, 1, 0]) In [89]: left Out[89]: Index([2, 1, 0], dtype='int64') In [90]: right = pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) In [91]: right Out[91]: Index([1, 2, 3], dtype='int64')
之前的行为:
In [4]: left.intersection(right) Out[4]: Int64Index([1, 2], dtype='int64')
新行为:
In [92]: left.intersection(right) Out[92]: Index([2, 1], dtype='int64')
DataFrame.join和pd.mergeIn [93]: left = pd.DataFrame({'a': [20, 10, 0]}, index=[2, 1, 0]) In [94]: left Out[94]: a 2 20 1 10 0 0 [3 rows x 1 columns] In [95]: right = pd.DataFrame({'b': [100, 200, 300]}, index=[1, 2, 3]) In [96]: right Out[96]: b 1 100 2 200 3 300 [3 rows x 1 columns]
之前的行为:
In [4]: left.join(right, how='inner') Out[4]: a b 1 10 100 2 20 200
新行为:
In [97]: left.join(right, how='inner') Out[97]: a b 2 20 200 1 10 100 [2 rows x 2 columns]
数据透视表总是返回一个 DataFrame#
pivot_table() 的文档指出,总是返回一个 DataFrame。这里修复了一个允许在某些情况下返回 Series 的错误。(GH 4386)
In [98]: df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': [3, 4, 5],
....: 'col2': ['C', 'D', 'E'],
....: 'col3': [1, 3, 9]})
....:
In [99]: df
Out[99]:
col1 col2 col3
0 3 C 1
1 4 D 3
2 5 E 9
[3 rows x 3 columns]
之前的行为:
In [2]: df.pivot_table('col1', index=['col3', 'col2'], aggfunc="sum")
Out[2]:
col3 col2
1 C 3
3 D 4
9 E 5
Name: col1, dtype: int64
新行为:
In [100]: df.pivot_table('col1', index=['col3', 'col2'], aggfunc="sum")
Out[100]:
col1
col3 col2
1 C 3
3 D 4
9 E 5
[3 rows x 1 columns]
其他 API 更改#
numexpr版本现在要求 >= 2.4.6,如果这个要求不满足,它将完全不被使用 (GH 15213)。CParserError在pd.read_csv()中已重命名为ParserError,并将在未来被移除 (GH 12665)SparseArray.cumsum()和SparseSeries.cumsum()现在将始终分别返回SparseArray和SparseSeries(GH 12855)DataFrame.applymap()在一个空的DataFrame上将返回一个空的DataFrame的副本,而不是一个Series(GH 8222)Series.map()现在尊重具有__missing__方法的字典子类的默认值,例如collections.Counter(GH 15999).loc与.ix兼容,接受迭代器和命名元组 (GH 15120)如果
limit关键字参数不大于 0,interpolate()和fillna()将引发ValueError。(GH 9217)pd.read_csv()现在会在dialect参数和用户提供的值之间存在冲突时发出ParserWarning(GH 14898)pd.read_csv()现在会为 C 引擎在引号字符大于一个字节时引发一个ValueError(GH 11592)inplace参数现在需要一个布尔值,否则会抛出ValueError(GH 14189)pandas.api.types.is_datetime64_ns_dtype现在会在 tz-aware dtype 上报告True,类似于pandas.api.types.is_datetime64_any_dtypeDataFrame.asof()如果在未找到匹配项时将返回一个填充了 null 的Series而不是标量NaN(GH 15118)对 NDFrame 对象上的
copy.copy()和copy.deepcopy()函数的特定支持 (GH 15444)Series.sort_values()接受一个布尔值列表,以与DataFrame.sort_values()的行为保持一致 (GH 15604).merge()和.join()在category数据类型列上现在会在可能的情况下保留 category 数据类型 (GH 10409)SparseDataFrame.default_fill_value将是 0,之前在pd.get_dummies(..., sparse=True)的返回中是nan(GH 15594)Series.str.match的默认行为已从提取组变为匹配模式。提取行为自 pandas 版本 0.13.0 起已被弃用,可以使用Series.str.extract方法完成(GH 5224)。因此,as_indexer关键字被忽略(不再需要指定新行为)并已弃用。NaT现在会为类似is_month_start的日期时间布尔操作正确报告False(GH 15781)NaT现在会为Timedelta和Period访问器(如days和quarter)正确返回np.nan(GH 15782)NaT现在对tz_localize和tz_convert方法返回NaT(GH 15830)如果使用标量输入而不是轴调用,
DataFrame和Panel构造函数现在会引发ValueError而不是PandasError(GH 15541)如果使用标量输入而不是轴调用
DataFrame和Panel构造函数,现在会引发ValueError而不是pandas.core.common.PandasError;异常PandasError也被移除了。(GH 15541)异常
pandas.core.common.AmbiguousIndexError已被移除,因为它没有被引用 (GH 15541)
图书馆的重组:隐私变化#
模块隐私已更改#
一些以前公开的 python/c/c++/cython 扩展模块已经被移动和/或重命名。这些都已从公共 API 中移除。此外,pandas.core、pandas.compat 和 pandas.util 顶级模块现在被认为是私有的。如果指示,如果您引用这些模块,将会发出弃用警告。(GH 12588)
上一个位置 |
新位置 |
弃用 |
|---|---|---|
pandas.lib |
pandas._libs.lib |
X |
pandas.tslib |
pandas._libs.tslib |
X |
pandas.computation |
pandas.core.computation |
X |
pandas.msgpack |
pandas.io.msgpack |
|
pandas.index |
pandas._libs.index |
|
pandas.algos |
pandas._libs.algos |
|
pandas.hashtable |
pandas._libs.hashtable |
|
pandas.indexes |
pandas.core.indexes |
|
pandas.json |
pandas._libs.json / pandas.io.json |
X |
pandas.解析器 |
pandas._libs.parsers |
X |
pandas.formats |
pandas.io.formats |
|
pandas.sparse |
pandas.core.sparse |
|
pandas.工具 |
pandas.core.reshape |
X |
pandas.types |
pandas.core.dtypes |
X |
pandas.io.sas.saslib |
pandas.io.sas._sas |
|
pandas._join |
pandas._libs.join |
|
pandas._hash |
pandas._libs.hashing |
|
pandas._period |
pandas._libs.period |
|
pandas._sparse |
pandas._libs.sparse |
|
pandas._testing |
pandas._libs.testing |
|
pandas._窗口 |
pandas._libs.window |
一些新的子包被创建,它们具有公共功能,但这些功能并不直接暴露在顶层命名空间中:pandas.errors、pandas.plotting 和 pandas.testing``(更多详情如下)。与 ``pandas.api.types 和 pandas.io 及 pandas.tseries 子模块中的某些函数一起,这些现在都是公共子包。
进一步的更改:
函数
union_categoricals()现在可以从pandas.api.types导入,以前是从pandas.types.concat导入 (GH 15998)类型导入
pandas.tslib.NaTType已被弃用,可以使用type(pandas.NaT)替代 (GH 16146)pandas.tools.hashing中的公共函数已从该位置弃用,但现可从pandas.util导入 (GH 16223)pandas.util中的模块:decorators、print_versions、doctools、validators、depr_module现在是私有的。只有pandas.util本身暴露的函数是公开的 (GH 16223)
pandas.errors#
我们正在为所有 pandas 异常和警告添加一个标准的公共模块 pandas.errors。(GH 14800)。以前这些异常和警告可以从 pandas.core.common 或 pandas.io.common 导入。这些异常和警告将在未来的版本中从 *.common 位置移除。(GH 15541)
以下内容现在是此API的一部分:
['DtypeWarning',
'EmptyDataError',
'OutOfBoundsDatetime',
'ParserError',
'ParserWarning',
'PerformanceWarning',
'UnsortedIndexError',
'UnsupportedFunctionCall']
pandas.testing#
我们正在添加一个标准模块,该模块在 pandas.testing 中公开了公共测试函数(GH 9895)。在为使用 pandas 对象的功能编写测试时,可以使用这些函数。
以下测试函数现在是此API的一部分:
pandas.plotting#
一个新的公共 pandas.plotting 模块已被添加,该模块包含了之前在 pandas.tools.plotting 或顶层命名空间中的绘图功能。更多详情请参见 弃用部分。
其他开发变化#
弃用#
弃用 .ix#
.ix 索引器已被弃用,取而代之的是更严格的 .iloc 和 .loc 索引器。.ix 在推断用户想要做什么时提供了许多魔法。更具体地说,.ix 可以根据索引的数据类型决定按 位置 或按 标签 进行索引。这多年来引起了相当多的用户困惑。完整的索引文档在 这里。(GH 14218)
推荐的索引方法有:
.loc如果你想 标记 索引.iloc如果你想按 位置 索引。
使用 .ix 现在会显示一个 DeprecationWarning ,并附带一些如何转换代码的示例链接 在此。
In [101]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3],
.....: 'B': [4, 5, 6]},
.....: index=list('abc'))
.....:
In [102]: df
Out[102]:
A B
a 1 4
b 2 5
c 3 6
[3 rows x 2 columns]
之前的行为,你希望从’A’列的索引中获取第0个和第2个元素。
In [3]: df.ix[[0, 2], 'A']
Out[3]:
a 1
c 3
Name: A, dtype: int64
使用 .loc。在这里,我们将从索引中选择适当的索引,然后使用 标签 索引。
In [103]: df.loc[df.index[[0, 2]], 'A']
Out[103]:
a 1
c 3
Name: A, Length: 2, dtype: int64
使用 .iloc。这里我们将获取 ‘A’ 列的位置,然后使用 位置 索引来选择内容。
In [104]: df.iloc[[0, 2], df.columns.get_loc('A')]
Out[104]:
a 1
c 3
Name: A, Length: 2, dtype: int64
弃用 Panel#
Panel 已被弃用,并将在未来版本中移除。推荐表示 3-D 数据的方法是使用 DataFrame 上的 MultiIndex 通过 to_frame() 或者使用 xarray 包。pandas 提供了一个 to_xarray() 方法来自动化此转换 (GH 13563)。
In [133]: import pandas._testing as tm
In [134]: p = tm.makePanel()
In [135]: p
Out[135]:
<class 'pandas.core.panel.Panel'>
Dimensions: 3 (items) x 3 (major_axis) x 4 (minor_axis)
Items axis: ItemA to ItemC
Major_axis axis: 2000-01-03 00:00:00 to 2000-01-05 00:00:00
Minor_axis axis: A to D
转换为 MultiIndex DataFrame
In [136]: p.to_frame()
Out[136]:
ItemA ItemB ItemC
major minor
2000-01-03 A 0.628776 -1.409432 0.209395
B 0.988138 -1.347533 -0.896581
C -0.938153 1.272395 -0.161137
D -0.223019 -0.591863 -1.051539
2000-01-04 A 0.186494 1.422986 -0.592886
B -0.072608 0.363565 1.104352
C -1.239072 -1.449567 0.889157
D 2.123692 -0.414505 -0.319561
2000-01-05 A 0.952478 -2.147855 -1.473116
B -0.550603 -0.014752 -0.431550
C 0.139683 -1.195524 0.288377
D 0.122273 -1.425795 -0.619993
[12 rows x 3 columns]
转换为 xarray DataArray
In [137]: p.to_xarray()
Out[137]:
<xarray.DataArray (items: 3, major_axis: 3, minor_axis: 4)>
array([[[ 0.628776, 0.988138, -0.938153, -0.223019],
[ 0.186494, -0.072608, -1.239072, 2.123692],
[ 0.952478, -0.550603, 0.139683, 0.122273]],
[[-1.409432, -1.347533, 1.272395, -0.591863],
[ 1.422986, 0.363565, -1.449567, -0.414505],
[-2.147855, -0.014752, -1.195524, -1.425795]],
[[ 0.209395, -0.896581, -0.161137, -1.051539],
[-0.592886, 1.104352, 0.889157, -0.319561],
[-1.473116, -0.43155 , 0.288377, -0.619993]]])
Coordinates:
* items (items) object 'ItemA' 'ItemB' 'ItemC'
* major_axis (major_axis) datetime64[ns] 2000-01-03 2000-01-04 2000-01-05
* minor_axis (minor_axis) object 'A' 'B' 'C' 'D'
当重命名时弃用 groupby.agg() 使用字典#
.groupby(..).agg(..), .rolling(..).agg(..), 和 .resample(..).agg(..) 语法可以接受多种输入,包括标量、列表和列名到标量或列表的字典。这提供了一种有用的语法来构建多个(可能是不同的)聚合。
然而,.agg(..) 也可以接受一个字典,允许对结果列进行’重命名’。这是一个复杂且令人困惑的语法,并且在 Series 和 DataFrame 之间不一致。我们正在弃用这个’重命名’功能。
我们正在弃用将字典传递给分组/滚动/重采样的
Series。这允许对结果聚合进行rename,但这与将字典传递给分组DataFrame的含义完全不同,后者接受列到聚合的映射。我们正在弃用以类似方式将字典传递给分组/滚动/重采样的
DataFrame。
这是一个说明性的例子:
In [105]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 1, 2, 2],
.....: 'B': range(5),
.....: 'C': range(5)})
.....:
In [106]: df
Out[106]:
A B C
0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1
2 1 2 2
3 2 3 3
4 2 4 4
[5 rows x 3 columns]
这是一个用于计算不同列的不同聚合的典型有用语法。这是一种自然且有用的语法。我们通过获取指定列并应用函数列表从字典聚合到列表。这会返回列的 ``MultiIndex``(这 不 被弃用)。
In [107]: df.groupby('A').agg({'B': 'sum', 'C': 'min'})
Out[107]:
B C
A
1 3 0
2 7 3
[2 rows x 2 columns]
这里是一个第一个弃用的例子,将一个字典传递给一个分组的 Series 。这是一个组合聚合和重命名的操作:
In [6]: df.groupby('A').B.agg({'foo': 'count'})
FutureWarning: using a dict on a Series for aggregation
is deprecated and will be removed in a future version
Out[6]:
foo
A
1 3
2 2
你可以通过以下方式更习惯地完成相同的操作:
In [108]: df.groupby('A').B.agg(['count']).rename(columns={'count': 'foo'})
Out[108]:
foo
A
1 3
2 2
[2 rows x 1 columns]
这里是第二个弃用的示例,传递一个字典的字典给一个分组的 DataFrame:
In [23]: (df.groupby('A')
...: .agg({'B': {'foo': 'sum'}, 'C': {'bar': 'min'}})
...: )
FutureWarning: using a dict with renaming is deprecated and
will be removed in a future version
Out[23]:
B C
foo bar
A
1 3 0
2 7 3
你可以通过以下方式实现几乎相同的效果:
In [109]: (df.groupby('A')
.....: .agg({'B': 'sum', 'C': 'min'})
.....: .rename(columns={'B': 'foo', 'C': 'bar'})
.....: )
.....:
Out[109]:
foo bar
A
1 3 0
2 7 3
[2 rows x 2 columns]
弃用 .plotting#
pandas.tools.plotting 模块已被弃用,取而代之的是顶层 pandas.plotting 模块。所有公共绘图函数现在都可以从 pandas.plotting 中获得 (GH 12548)。
此外,顶层的 pandas.scatter_matrix 和 pandas.plot_params 已被弃用。用户也可以从 pandas.plotting 导入这些。
上一个脚本:
pd.tools.plotting.scatter_matrix(df)
pd.scatter_matrix(df)
应改为:
pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(df)
其他弃用#
SparseArray.to_dense()已弃用fill参数,因为该参数未被尊重 (GH 14647)SparseSeries.to_dense()已弃用sparse_only参数 (GH 14647)Series.repeat()已经弃用了reps参数,改为使用repeats(GH 12662)Series构造函数和.astype方法已弃用接受没有频率的时间戳数据类型(例如np.datetime64)作为dtype参数 (GH 15524)Index.repeat()和MultiIndex.repeat()已经弃用了n参数,改为使用repeats(GH 12662)Categorical.searchsorted()和Series.searchsorted()已经弃用了v参数,改为使用value参数 (GH 12662)TimedeltaIndex.searchsorted()、DatetimeIndex.searchsorted()和PeriodIndex.searchsorted()已弃用key参数,改为使用value(GH 12662)DataFrame.astype()已弃用raise_on_error参数,改为使用errors(GH 14878)Series.sortlevel和DataFrame.sortlevel已被弃用,取而代之的是Series.sort_index和DataFrame.sort_index(GH 15099)从
pandas.tools.merge导入concat已被弃用,建议从pandas命名空间进行导入。这只会影响显式导入 (GH 15358)。Series/DataFrame/Panel.consolidate()作为公共方法已被弃用。(GH 15483)Series.str.match()的as_indexer关键字已被弃用(忽略的关键字)(GH 15257)。以下顶级 pandas 函数已被弃用,并将在未来版本中移除 (GH 13790, GH 15940)
pd.pnow(),已被Period.now()取代pd.Term已被移除,因为它不适用于用户代码。相反,在 HDFStore 中搜索时,请在 where 子句中使用内联字符串表达式。pd.Expr已被移除,因为它不适用于用户代码。pd.match()已被移除。pd.groupby(),通过直接在Series/DataFrame上使用.groupby()方法替代。pd.get_store(),已被直接调用pd.HDFStore(...)取代
is_any_int_dtype、is_floating_dtype和is_sequence已从pandas.api.types中弃用(GH 16042)
移除先前版本的弃用/更改#
pandas.io.ga模块与google-analytics接口已被移除(GH 11308)。类似的功能可以在 Google2Pandas 包中找到。pd.to_datetime和pd.to_timedelta已经取消了coerce参数,改为使用errors(GH 13602)pandas.stats.fama_macbeth,pandas.stats.ols,pandas.stats.plm和pandas.stats.var,以及顶层的pandas.fama_macbeth和pandas.ols例程已被移除。类似的功能可以在 statsmodels 包中找到。(GH 11898)TimeSeries和SparseTimeSeries类,Series和SparseSeries的别名,已被移除 (GH 10890, GH 15098)。Series.is_time_series被弃用,取而代之的是Series.index.is_all_dates(GH 15098)已弃用的
irow,icol,iget和iget_value方法已被移除,取而代之的是iloc和iat,如 这里 所述 (GH 10711)。已弃用的
DataFrame.iterkv()已被DataFrame.iteritems()取代 (GH 10711)Categorical构造函数已删除name参数 (GH 10632)Categorical已放弃对NaN类别的支持 (GH 10748)take_last参数已从duplicated(),drop_duplicates(),nlargest(), 和nsmallest()方法中移除 (GH 10236, GH 10792, GH 10920)Series、Index和DataFrame已经移除了sort和order方法 (GH 10726)在
pytables中的 where 子句只接受字符串和表达式类型,不接受其他数据类型 (GH 12027)DataFrame已经取消了combineAdd和combineMult方法,取而代之的是add和mul方法(GH 10735)
性能提升#
改进了
pd.wide_to_long()的性能 (GH 14779)通过在推断为字符串时使用
objectdtype 释放 GIL,改进了pd.factorize()的性能 (GH 14859, GH 16057)改进了使用不规则 DatetimeIndex(或使用
compat_x=True)的时间序列绘图性能 (GH 15073)。改进了
groupby().cummin()和groupby().cummax()的性能 (GH 15048, GH 15109, GH 15561, GH 15635)使用
MultiIndex进行索引时性能提升和内存减少 (GH 15245)在
read_sas()方法中读取缓冲区对象时,如果没有指定格式,则推断的是文件路径字符串而不是缓冲区对象。(GH 14947)改进了分类数据的
.rank()性能 (GH 15498)使用
.unstack()时的性能改进 (GH 15503)改进了
category列上的合并/连接性能 (GH 10409)改进了
bool列上的drop_duplicates()性能 (GH 12963)当应用的函数使用了分组 DataFrame 的
.name属性时,改进了pd.core.groupby.GroupBy.apply的性能 (GH 15062)。改进了使用列表或数组进行
iloc索引的性能 (GH 15504)。改进了
Series.sort_index()在单调索引下的性能 (GH 15694)在某些平台上通过缓冲读取提高了
pd.read_csv()的性能 (GH 16039)
错误修复#
转换#
在
Timestamp.replace中的错误现在会在给出错误的参数名称时引发TypeError;之前这是引发ValueError(GH 15240)。Timestamp.replace中处理传递长整数的兼容性问题 (GH 15030)在
TimedeltaIndex加法中存在一个错误,允许溢出而没有错误 (GH 14816)TimedeltaIndex在使用loc进行布尔索引时引发ValueError的错误 (GH 14946)在
Timestamp+Timedelta/Offset操作中捕获溢出的错误 (GH 15126)DatetimeIndex.round()和Timestamp.round()在按毫秒或更小单位舍入时浮点精度问题 (GH 14440, GH 15578)在
astype()中的一个错误,其中inf值被错误地转换为整数。现在在使用astype()时会引发错误,适用于 Series 和 DataFrames (GH 14265)当值为类型 decimal.Decimal 时,
DataFrame(..).apply(to_numeric)中的错误。(GH 14827)当传递一个不包含中位数的 numpy 数组到
percentiles关键字参数时,describe()中的错误 (GH 14908)清理了
PeriodIndex构造函数,包括更一致地对浮点数引发异常 (GH 13277)在空NDFrame对象上使用
__deepcopy__的错误 (GH 15370)Series.replace和DataFrame.replace中的错误,在空替换字典上失败 (GH 15289)Series.replace中的错误,将数字替换为字符串 (GH 15743)在指定整数数据类型时,
Index构建中存在NaN元素的错误 (GH 15187)在
Series构造中存在一个 datetimetz 的错误 (GH 14928)Series.dt.round()中的错误:在不同参数下对NaT的处理不一致 (GH 14940)当同时提供
copy=True和dtype参数时,Series构造函数中的错误 (GH 15125)比较方法(例如,
lt、gt等)对空DataFrame与常量进行比较时返回了不正确的 dtypedSeries(GH 15077)包含时区感知的日期时间的混合数据类型在
Series.ffill()中的错误。(GH 14956)DataFrame.fillna()中的一个错误,当 fillna 值为dict类型时,参数downcast被忽略 (GH 15277).asfreq()中的错误,其中频率未为空的Series设置 (GH 14320)在
DataFrame构造中存在一个错误,当列表中包含空值和日期时间时 (GH 15869)DataFrame.fillna()中带有 tz-aware 日期时间的错误 (GH 15855)在
is_string_dtype、is_timedelta64_ns_dtype和is_string_like_dtype中的错误,当传入None时会引发错误 (GH 15941)在
Categorical上使用pd.unique时返回类型的错误,返回的是一个 ndarray 而不是Categorical(GH 15903)Index.to_series()中的一个错误,其中索引未被复制(因此稍后突变会改变原始索引),(GH 15949)使用部分字符串索引与长度为1的DataFrame进行索引时出现错误 (GH 16071)
在
Series构造中,传递无效的 dtype 时未引发错误的错误。(GH 15520)
索引#
Index在反向操作数进行幂运算时存在错误 (GH 14973)在
DataFrame.sort_values()中按多列排序时,当其中一列是int64类型并包含NaT时的错误 (GH 14922)DataFrame.reindex()中的一个错误,当传递columns时method被忽略 (GH 14992)使用
Series索引器对MultiIndex进行索引时DataFrame.loc中的错误 (GH 14730, GH 15424)在
DataFrame.loc中使用 numpy 数组索引MultiIndex的错误 (GH 15434)Series.asof中的错误,如果序列包含所有np.nan则会引发 (GH 15713)在从 tz-aware 列中选择时
.at中的 Bug (GH 15822)Series.where()和DataFrame.where()中的错误,其中类似数组的条件被拒绝 (GH 15414)Series.where()中的一个错误,其中时区感知数据被转换为浮点表示 (GH 15701).loc中的一个错误,在访问标量时不会返回正确的 dtype 给 DataFrame (GH 11617)Categorical.searchsorted()中的一个错误,使用了字母顺序而不是提供的分类顺序 (GH 14522)在
Series.iloc中的一个错误,当输入类似列表的索引时返回了一个Categorical对象,而预期返回的是一个Series。 (GH 14580)DataFrame.isin中比较类似日期时间与空帧的错误 (GH 15473)当
MultiIndex的一个全NaN级别时,.reset_index()中的错误 (GH 6322)当在
MultiIndex列中已经存在索引名称时,在.reset_index()中引发错误的错误 (GH 16120)在用元组创建
MultiIndex时没有传递名称列表的错误;这将引发ValueError(GH 15110)在
MultiIndex和截断情况下的 HTML 显示问题 (GH 14882)在
.info()显示中的一个错误,其中限定符(+)总是会与仅包含非字符串的MultiIndex一起显示(GH 15245)pd.concat()中的一个错误,当输入的DataFrame的MultiIndex名称中出现None时,结果DataFrame的MultiIndex名称处理不正确 (GH 15787)DataFrame.sort_index()和Series.sort_index()中的错误,其中na_position在MultiIndex中不起作用 (GH 14784, GH 16604)当合并带有
CategoricalIndex的对象时,pd.concat()中的错误 (GH 16111)使用标量和
CategoricalIndex进行索引时的错误 (GH 16123)
IO#
pd.to_numeric()中的一个错误,其中浮点数和无符号整数元素被不当转换 (GH 14941, GH 15005)pd.read_fwf()中的一个错误,其中 skiprows 参数在推断列宽时未被遵守 (GH 11256)pd.read_csv()中的一个错误,在处理之前未验证dialect参数 (GH 14898)pd.read_csv()中的一个错误,在处理usecols时未能正确处理缺失数据 (GH 6710)pd.read_csv()中的一个错误,当文件包含一行有很多列,后面跟着行数较少的列时会导致崩溃 (GH 14125)在
pd.read_csv()的 C 引擎中,当usecols与parse_dates一起使用时,索引不正确的问题 (GH 14792)在使用
parse_dates时pd.read_csv()中的错误,当指定多行标题时 (GH 15376)在
pd.read_csv()中使用float_precision='round_trip'时出现的错误,当解析文本条目时会导致段错误 (GH 15140)当指定了索引且未指定空值时,
pd.read_csv()中的错误 (GH 15835)pd.read_csv()中的一个错误,其中某些无效的文件对象导致 Python 解释器崩溃 (GH 15337)pd.read_csv()中的一个错误,允许nrows和chunksize的无效值 (GH 15767)在Python引擎中,当解析错误发生时,
pd.read_csv()会引发无用的错误信息 (GH 15910) 的Bugpd.read_csv()中的一个错误,其中skipfooter参数未被正确验证 (GH 15925)pd.to_csv()中的一个错误,当写入时间戳索引时发生数值溢出 (GH 15982)pd.util.hashing.hash_pandas_object()中的一个错误,其中分类数据的哈希依赖于分类的顺序,而不是仅仅依赖于它们的值。(GH 15143)在
.to_json()中的错误,当lines=True且内容(键或值)包含转义字符时 (GH 15096).to_json()中的错误导致单字节 ascii 字符扩展为四字节 unicode (GH 15344)在C引擎的``.to_json()``中,当frac为奇数且diff恰好为0.5时,滚动处理不正确的问题 (GH 15716, GH 15864)
在
pd.read_json()中,当lines=True且内容包含非 ASCII 的 Unicode 字符时,Python 2 的错误 (GH 15132)pd.read_msgpack()中的一个错误,其中Series分类数据被不当处理 (GH 14901)pd.read_msgpack()中的一个错误,不允许加载索引类型为CategoricalIndex的数据帧 (GH 15487)在反序列化
CategoricalIndex时pd.read_msgpack()中的错误 (GH 15487)在
DataFrame.to_records()中转换带有时区的DatetimeIndex的错误 (GH 13937)DataFrame.to_records()中的错误,当列名中包含unicode字符时会失败 (GH 11879)在写入带有数值索引名的 DataFrame 时,
.to_sql()中的 Bug (GH 15404)。在
DataFrame.to_html()中使用index=False和max_rows引发IndexError的错误 (GH 14998)pd.read_hdf()中将Timestamp传递给where参数与非日期列的错误 (GH 15492)DataFrame.to_stata()和StataWriter中的错误,导致某些地区格式不正确的文件生成 (GH 13856)StataReader和StataWriter中的错误允许无效的编码 (GH 15723)Seriesrepr 中的一个错误,当输出被截断时未显示长度 (GH 15962)。
绘图#
GroupBy/重采样/滚动#
当传递
on=kwarg 时,.groupby(..).resample()中的错误。(GH 15021)为
Groupby.*函数正确设置__name__和__qualname__(GH 14620)GroupBy.get_group()中的错误,当分组依据是分类变量时失败 (GH 15155)当指定
on并且使用DatetimeIndex时,.groupby(...).rolling(...)中的错误 (GH 15130, GH 13966)在使用
timedelta64进行 groupby 操作时,当传递numeric_only=False时的错误 (GH 5724)groupby.apply()中的错误,当不是所有值都是数值时,强制将object数据类型转换为数值类型 (GH 14423, GH 15421, GH 15670)resample中的一个错误,当loffset参数为非字符串时,在对时间序列进行重采样时不会应用该参数 (GH 13218)当按包含元组的
Index分组时,DataFrame.groupby().describe()中的错误 (GH 14848)在
groupby().nunique()中使用 datetimelike-grouper 时,分箱计数不正确 (GH 13453)groupby.transform()中的一个错误,会将结果的数据类型强制转换回原始类型 (GH 10972, GH 11444)groupby.agg()中的错误不正确地本地化datetime的时区 (GH 15426, GH 10668, GH 13046)在
.rolling/expanding()函数中的错误,其中count()没有计算np.Inf,也没有处理object数据类型 (GH 12541)在
.rolling()中的错误,其中pd.Timedelta或datetime.timedelta不被接受作为window参数 (GH 15440)Rolling.quantile函数中的一个错误,当使用范围 [0, 1] 之外的分位数值调用时会导致段错误 (GH 15463)如果存在重复的列名,
DataFrame.resample().median()中的错误 (GH 14233)
Sparse#
Reshaping#
pd.merge_asof()中的一个错误,当指定多个by时,left_index或right_index会导致失败 (GH 15676)pd.merge_asof()中的一个错误,当指定tolerance时,left_index/right_index一起使用会导致失败 (GH 15135)在
DataFrame.pivot_table()中的一个错误,当dropna=True时不会删除所有为NaN的列,当列是category数据类型时 (GH 15193)在
pd.melt()中的一个错误,当为value_vars传递一个元组值时会导致TypeError(GH 15348)pd.pivot_table()中的一个错误,当 values 参数不在 columns 中时没有引发错误 (GH 14938)在
pd.concat()中的一个错误,当使用join='inner'与一个空数据框连接时处理不当 (GH 15328)在
DataFrame.join和pd.merge中使用sort=True时出现的错误(GH 15582)DataFrame.nsmallest和DataFrame.nlargest中的错误,其中相同的值导致重复行 (GH 15297)pandas.pivot_table()中的一个错误,在为margins关键字传递 Unicode 输入时错误地引发UnicodeError(GH 13292)
Numeric#
.rank()中的错误,错误地对有序类别进行排名 (GH 15420).corr()和.cov()中的错误,其中列和索引是同一个对象 (GH 14617)在
.mode()中的一个错误,如果mode只是一个单一值,则不会返回 (GH 15714)在全是0的数组上使用
pd.cut()时只有一个bin的错误 (GH 15428)pd.qcut()在单个分位数和值相同的数组中存在错误 (GH 15431)在
pandas.tools.utils.cartesian_product()中,对于大输入在 Windows 上可能会导致溢出 (GH 15265).eval()中的一个错误,导致多行 eval 失败,因为本地变量不在第一行 (GH 15342)
其他#
贡献者#
总共有204人为此版本贡献了补丁。名字后面带有“+”的人是第一次贡献补丁。
Adam J. Stewart +
Adrian +
Ajay Saxena
Akash Tandon +
Albert Villanova del Moral +
Aleksey Bilogur +
Alexis Mignon +
Amol Kahat +
Andreas Winkler +
Andrew Kittredge +
Anthonios Partheniou
Arco Bast +
Ashish Singal +
Baurzhan Muftakhidinov +
Ben Kandel
Ben Thayer +
Ben Welsh +
Bill Chambers +
Brandon M. Burroughs
Brian +
Brian McFee +
Carlos Souza +
Chris
Chris Ham
Chris Warth
Christoph Gohlke
Christoph Paulik +
Christopher C. Aycock
Clemens Brunner +
D.S. McNeil +
DaanVanHauwermeiren +
Daniel Himmelstein
Dave Willmer
David Cook +
David Gwynne +
David Hoffman +
David Krych
Diego Fernandez +
Dimitris Spathis +
Dmitry L +
Dody Suria Wijaya +
Dominik Stanczak +
Dr-Irv
Dr. Irv +
Elliott Sales de Andrade +
Ennemoser Christoph +
Francesc Alted +
Fumito Hamamura +
Giacomo Ferroni
Graham R. Jeffries +
Greg Williams +
Guilherme Beltramini +
Guilherme Samora +
Hao Wu +
Harshit Patni +
Ilya V. Schurov +
Iván Vallés Pérez
Jackie Leng +
Jaehoon Hwang +
James Draper +
James Goppert +
James McBride +
James Santucci +
Jan Schulz
Jeff Carey
Jeff Reback
JennaVergeynst +
Jim +
Jim Crist
Joe Jevnik
Joel Nothman +
John +
John Tucker +
John W. O’Brien
John Zwinck
Jon M. Mease
Jon Mease
Jonathan Whitmore +
Jonathan de Bruin +
Joost Kranendonk +
Joris Van den Bossche
Joshua Bradt +
Julian Santander
Julien Marrec +
Jun Kim +
Justin Solinsky +
Kacawi +
Kamal Kamalaldin +
Kerby Shedden
Kernc
Keshav Ramaswamy
Kevin Sheppard
Kyle Kelley
Larry Ren
Leon Yin +
Line Pedersen +
Lorenzo Cestaro +
Luca Scarabello
Lukasz +
Mahmoud Lababidi
Mark Mandel +
Matt Roeschke
Matthew Brett
Matthew Roeschke +
Matti Picus
Maximilian Roos
Michael Charlton +
Michael Felt
Michael Lamparski +
Michiel Stock +
Mikolaj Chwalisz +
Min RK
Miroslav Šedivý +
Mykola Golubyev
Nate Yoder
Nathalie Rud +
Nicholas Ver Halen
Nick Chmura +
Nolan Nichols +
Pankaj Pandey +
Pawel Kordek
Pete Huang +
Peter +
Peter Csizsek +
Petio Petrov +
Phil Ruffwind +
Pietro Battiston
Piotr Chromiec
Prasanjit Prakash +
Rob Forgione +
Robert Bradshaw
Robin +
Rodolfo Fernandez
Roger Thomas
Rouz Azari +
Sahil Dua
Sam Foo +
Sami Salonen +
Sarah Bird +
Sarma Tangirala +
Scott Sanderson
Sebastian Bank
Sebastian Gsänger +
Shawn Heide
Shyam Saladi +
Sinhrks
Stephen Rauch +
Sébastien de Menten +
Tara Adiseshan
Thiago Serafim
Thoralf Gutierrez +
Thrasibule +
Tobias Gustafsson +
Tom Augspurger
Tong SHEN +
Tong Shen +
TrigonaMinima +
Uwe +
Wes Turner
Wiktor Tomczak +
WillAyd
Yaroslav Halchenko
Yimeng Zhang +
abaldenko +
adrian-stepien +
alexandercbooth +
atbd +
bastewart +
bmagnusson +
carlosdanielcsantos +
chaimdemulder +
chris-b1
dickreuter +
discort +
dr-leo +
dubourg
dwkenefick +
funnycrab +
gfyoung
goldenbull +
hesham.shabana@hotmail.com
jojomdt +
linebp +
manu +
manuels +
mattip +
maxalbert +
mcocdawc +
nuffe +
paul-mannino
pbreach +
sakkemo +
scls19fr
sinhrks
stijnvanhoey +
the-nose-knows +
themrmax +
tomrod +
tzinckgraf
wandersoncferreira
watercrossing +
wcwagner
xgdgsc +
yui-knk