注意
点击 这里 下载完整的示例代码
ONNX简介 || 将PyTorch模型导出为ONNX || 扩展ONNX注册表
扩展ONNX注册表¶
创建于:2023年10月06日 | 最后更新:2024年7月22日 | 最后验证:2024年11月05日
作者: Ti-Tai Wang (titaiwang@microsoft.com)
概述¶
本教程是对ONNX注册表的介绍,它使用户能够实现新的ONNX操作符,甚至可以用新的实现替换现有的操作符。
在将模型导出到ONNX期间,PyTorch模型被降低为由ATen运算符组成的中间表示。 虽然ATen运算符由PyTorch核心团队维护,但ONNX导出团队有责任通过ONNX Script独立实现每个运算符到ONNX的转换。 用户还可以替换ONNX导出团队实现的行为,使用自己的实现来修复错误或提高特定ONNX运行时的性能。
ONNX 注册表管理 PyTorch 运算符与 ONNX 运算符之间的映射,并提供扩展注册表的 API。
在本教程中,我们将介绍三种需要扩展ONNX注册表以添加自定义操作符的场景:
不支持的ATen运算符
具有现有ONNX Runtime支持的自定义操作符
没有ONNX Runtime支持的自定义操作符
不支持的ATen运算符¶
尽管ONNX导出团队尽力支持所有ATen操作符,但其中一些可能尚未得到支持。在本节中,我们将演示如何将不受支持的ATen操作符添加到ONNX注册表中。
注意
实现不支持的ATen运算符的步骤与用自定义实现替换现有ATen运算符的实现相同。
因为我们实际上没有在本教程中使用不支持的ATen运算符,所以我们将利用这一点,并用自定义实现替换aten::add.Tensor的实现,就像该运算符不在ONNX注册表中一样。
当模型由于不支持的运算符而无法导出到ONNX时,ONNX导出器将显示类似于以下的错误消息:
RuntimeErrorWithDiagnostic: Unsupported FX nodes: {'call_function': ['aten.add.Tensor']}.
错误信息表明不支持的ATen运算符的完全限定名称是aten::add.Tensor。
运算符的完全限定名称由命名空间、运算符名称和重载组成,遵循格式namespace::operator_name.overload。
要为不支持的ATen操作符添加支持或替换现有操作符的实现,我们需要:
ATen 操作符的完全限定名称(例如
aten::add.Tensor)。 此信息始终存在于如上所示的错误消息中。使用ONNX Script实现操作符。 ONNX Script 是本教程的先决条件。请确保您已经阅读了 ONNX Script 教程 再继续。
因为aten::add.Tensor已经被ONNX注册表支持,我们将演示如何用自定义实现替换它,但请记住,同样的步骤适用于支持新的不受支持的ATen操作符。
这是可能的,因为OnnxRegistry允许用户覆盖操作符注册。我们将用我们的自定义实现覆盖aten::add.Tensor的注册,并验证其存在。
import torch
import onnxruntime
import onnxscript
from onnxscript import opset18 # opset 18 is the latest (and only) supported version for now
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, input_x, input_y):
return torch.ops.aten.add(input_x, input_y) # generates a aten::add.Tensor node
input_add_x = torch.randn(3, 4)
input_add_y = torch.randn(3, 4)
aten_add_model = Model()
# Now we create a ONNX Script function that implements ``aten::add.Tensor``.
# The function name (e.g. ``custom_aten_add``) is displayed in the ONNX graph, so we recommend to use intuitive names.
custom_aten = onnxscript.values.Opset(domain="custom.aten", version=1)
# NOTE: The function signature must match the signature of the unsupported ATen operator.
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/aten/src/ATen/native/native_functions.yaml
# NOTE: All attributes must be annotated with type hints.
@onnxscript.script(custom_aten)
def custom_aten_add(input_x, input_y, alpha: float = 1.0):
input_y = opset18.Mul(input_y, alpha)
return opset18.Add(input_x, input_y)
# Now we have everything we need to support unsupported ATen operators.
# Let's register the ``custom_aten_add`` function to ONNX registry, and export the model to ONNX again.
onnx_registry = torch.onnx.OnnxRegistry()
onnx_registry.register_op(
namespace="aten", op_name="add", overload="Tensor", function=custom_aten_add
)
print(f"aten::add.Tensor is supported by ONNX registry: \
{onnx_registry.is_registered_op(namespace='aten', op_name='add', overload='Tensor')}"
)
export_options = torch.onnx.ExportOptions(onnx_registry=onnx_registry)
onnx_program = torch.onnx.dynamo_export(
aten_add_model, input_add_x, input_add_y, export_options=export_options
)
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/onnxscript/converter.py:820: FutureWarning:
'onnxscript.values.Op.param_schemas' is deprecated in version 0.1 and will be removed in the future. Please use '.op_signature' instead.
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/torch/onnx/_internal/_exporter_legacy.py:116: UserWarning:
torch.onnx.dynamo_export only implements opset version 18 for now. If you need to use a different opset version, please register them with register_custom_op.
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/onnxscript/converter.py:820: FutureWarning:
'onnxscript.values.OnnxFunction.param_schemas' is deprecated in version 0.1 and will be removed in the future. Please use '.op_signature' instead.
aten::add.Tensor is supported by ONNX registry: True
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/torch/onnx/_internal/fx/onnxfunction_dispatcher.py:503: FutureWarning:
'onnxscript.values.TracedOnnxFunction.param_schemas' is deprecated in version 0.1 and will be removed in the future. Please use '.op_signature' instead.
现在让我们检查模型并验证模型是否有一个custom_aten_add而不是aten::add.Tensor。
图中有一个custom_aten_add的图节点,其中包含四个函数节点,每个操作符一个,还有一个用于常量属性。
# graph node domain is the custom domain we registered
assert onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node[0].domain == "custom.aten"
assert len(onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node) == 1
# graph node name is the function name
assert onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node[0].op_type == "custom_aten_add"
# function node domain is empty because we use standard ONNX operators
assert {node.domain for node in onnx_program.model_proto.functions[0].node} == {""}
# function node name is the standard ONNX operator name
assert {node.op_type for node in onnx_program.model_proto.functions[0].node} == {"Add", "Mul", "Constant"}
这是使用Netron查看ONNX图中custom_aten_add_model的样子:
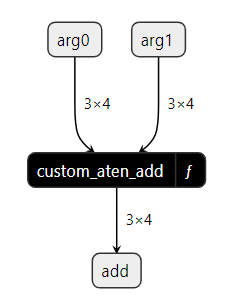
在custom_aten_add函数内部,我们可以看到我们在函数中使用的三个ONNX节点(CastLike、Add和Mul),以及一个Constant属性:

这就是我们需要将新的ATen操作符注册到ONNX注册表中的全部内容。 作为额外的步骤,我们可以使用ONNX Runtime来运行模型,并将结果与PyTorch进行比较。
# Use ONNX Runtime to run the model, and compare the results with PyTorch
onnx_program.save("./custom_add_model.onnx")
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
"./custom_add_model.onnx", providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
def to_numpy(tensor):
return tensor.detach().cpu().numpy() if tensor.requires_grad else tensor.cpu().numpy()
onnx_input = onnx_program.adapt_torch_inputs_to_onnx(input_add_x, input_add_y)
onnxruntime_input = {k.name: to_numpy(v) for k, v in zip(ort_session.get_inputs(), onnx_input)}
onnxruntime_outputs = ort_session.run(None, onnxruntime_input)
torch_outputs = aten_add_model(input_add_x, input_add_y)
torch_outputs = onnx_program.adapt_torch_outputs_to_onnx(torch_outputs)
assert len(torch_outputs) == len(onnxruntime_outputs)
for torch_output, onnxruntime_output in zip(torch_outputs, onnxruntime_outputs):
torch.testing.assert_close(torch_output, torch.tensor(onnxruntime_output))
支持现有ONNX运行时的自定义操作符¶
在这种情况下,用户使用标准的PyTorch操作符创建了一个模型,但ONNX运行时(例如Microsoft的ONNX运行时)可以为该内核提供自定义实现,从而有效地替换ONNX注册表中的现有实现。另一个用例是当用户希望使用现有ONNX操作符的自定义实现来修复错误或提高特定操作符的性能。为了实现这一点,我们只需要使用现有的ATen完全限定名称注册新的实现。
在以下示例中,我们使用了来自ONNX Runtime的com.microsoft.Gelu,
这与来自ONNX规范的Gelu不同。因此,我们使用命名空间com.microsoft和操作符名称Gelu注册了Gelu。
在我们开始之前,让我们检查一下aten::gelu.default是否真的被ONNX注册表支持。
onnx_registry = torch.onnx.OnnxRegistry()
print(f"aten::gelu.default is supported by ONNX registry: \
{onnx_registry.is_registered_op(namespace='aten', op_name='gelu', overload='default')}")
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/torch/onnx/_internal/_exporter_legacy.py:116: UserWarning:
torch.onnx.dynamo_export only implements opset version 18 for now. If you need to use a different opset version, please register them with register_custom_op.
aten::gelu.default is supported by ONNX registry: True
在我们的示例中,aten::gelu.default 操作符由 ONNX 注册表支持,
因此 onnx_registry.is_registered_op() 返回 True。
class CustomGelu(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, input_x):
return torch.ops.aten.gelu(input_x)
# com.microsoft is an official ONNX Runtime namspace
custom_ort = onnxscript.values.Opset(domain="com.microsoft", version=1)
# NOTE: The function signature must match the signature of the unsupported ATen operator.
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/aten/src/ATen/native/native_functions.yaml
# NOTE: All attributes must be annotated with type hints.
@onnxscript.script(custom_ort)
def custom_aten_gelu(input_x, approximate: str = "none"):
# We know com.microsoft::Gelu is supported by ONNX Runtime
# It's only not supported by ONNX
return custom_ort.Gelu(input_x)
onnx_registry = torch.onnx.OnnxRegistry()
onnx_registry.register_op(
namespace="aten", op_name="gelu", overload="default", function=custom_aten_gelu)
export_options = torch.onnx.ExportOptions(onnx_registry=onnx_registry)
aten_gelu_model = CustomGelu()
input_gelu_x = torch.randn(3, 3)
onnx_program = torch.onnx.dynamo_export(
aten_gelu_model, input_gelu_x, export_options=export_options
)
'Gelu' is not a known op in 'com.microsoft'
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/torch/onnx/_internal/_exporter_legacy.py:116: UserWarning:
torch.onnx.dynamo_export only implements opset version 18 for now. If you need to use a different opset version, please register them with register_custom_op.
让我们检查模型并验证模型是否使用了来自命名空间 com.microsoft 的 op_type Gelu。
注意
custom_aten_gelu() 不存在于图中,因为少于三个操作符的函数会自动内联。
# graph node domain is the custom domain we registered
assert onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node[0].domain == "com.microsoft"
# graph node name is the function name
assert onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node[0].op_type == "Gelu"
下图展示了使用Netron查看的custom_aten_gelu_model ONNX图,我们可以看到函数中使用的来自模块com.microsoft的Gelu节点:
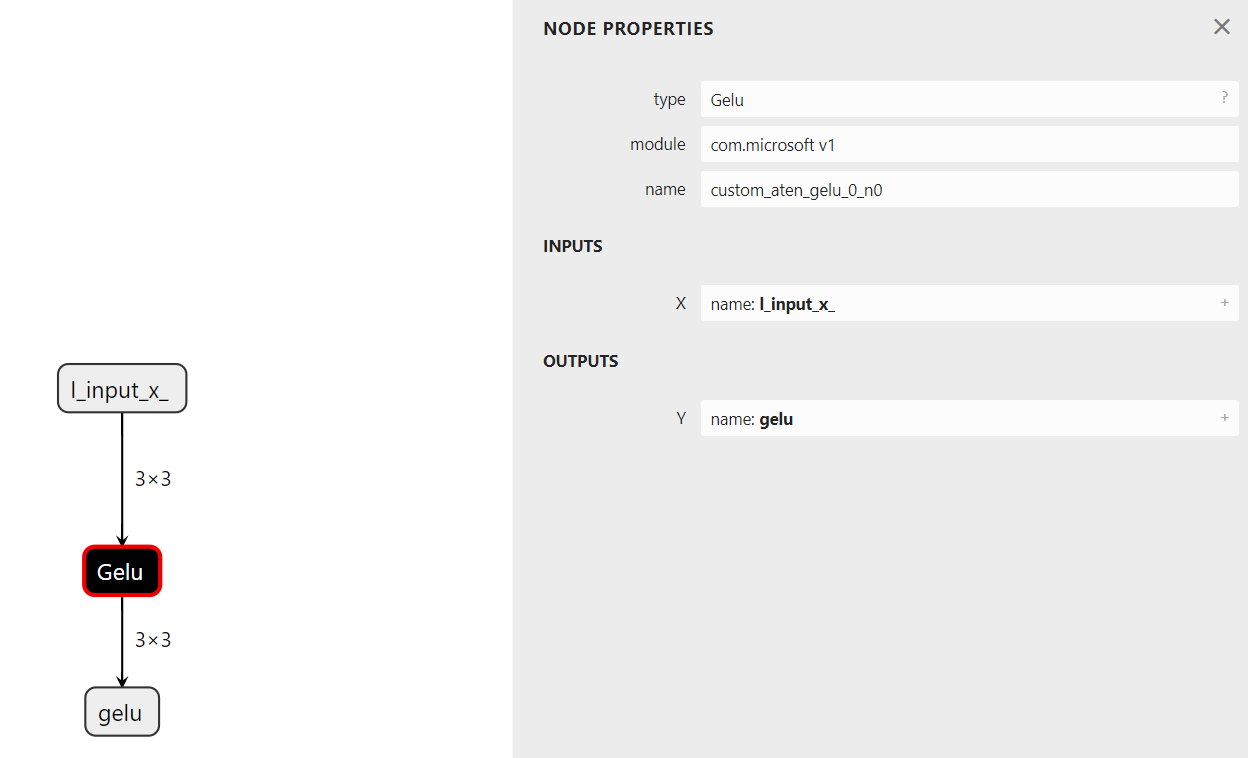
这就是我们需要做的全部。作为额外的步骤,我们可以使用ONNX Runtime来运行模型,并将结果与PyTorch进行比较。
onnx_program.save("./custom_gelu_model.onnx")
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
"./custom_gelu_model.onnx", providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
def to_numpy(tensor):
return tensor.detach().cpu().numpy() if tensor.requires_grad else tensor.cpu().numpy()
onnx_input = onnx_program.adapt_torch_inputs_to_onnx(input_gelu_x)
onnxruntime_input = {k.name: to_numpy(v) for k, v in zip(ort_session.get_inputs(), onnx_input)}
onnxruntime_outputs = ort_session.run(None, onnxruntime_input)
torch_outputs = aten_gelu_model(input_gelu_x)
torch_outputs = onnx_program.adapt_torch_outputs_to_onnx(torch_outputs)
assert len(torch_outputs) == len(onnxruntime_outputs)
for torch_output, onnxruntime_output in zip(torch_outputs, onnxruntime_outputs):
torch.testing.assert_close(torch_output, torch.tensor(onnxruntime_output))
不支持ONNX Runtime的自定义操作符¶
在这种情况下,该运算符不受任何ONNX运行时的支持,但我们希望在ONNX图中将其用作自定义运算符。因此,我们需要在三个地方实现该运算符:
PyTorch FX 图
ONNX 注册表
ONNX 运行时
在以下示例中,我们希望使用一个自定义运算符,该运算符接受一个张量输入,并返回一个输出。该运算符将输入与自身相加,并返回四舍五入后的结果。
在PyTorch FX图中注册自定义操作(测试版)¶
首先,我们需要在PyTorch FX图中实现操作符。
这可以通过使用torch._custom_op来完成。
# NOTE: This is a beta feature in PyTorch, and is subject to change.
from torch._custom_op import impl as custom_op
@custom_op.custom_op("mylibrary::addandround_op")
def addandround_op(tensor_x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
...
@addandround_op.impl_abstract()
def addandround_op_impl_abstract(tensor_x):
return torch.empty_like(tensor_x)
@addandround_op.impl("cpu")
def addandround_op_impl(tensor_x):
return torch.round(tensor_x + tensor_x) # add x to itself, and round the result
torch._dynamo.allow_in_graph(addandround_op)
class CustomFoo(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, tensor_x):
return addandround_op(tensor_x)
input_addandround_x = torch.randn(3)
custom_addandround_model = CustomFoo()
在ONNX注册表中注册自定义操作¶
对于步骤2和3,我们需要在ONNX注册表中实现操作符。
在这个例子中,我们将在ONNX注册表中实现操作符,
使用命名空间test.customop和操作符名称CustomOpOne,
以及CustomOpTwo。这两个操作符在
cpu_ops.cc中注册和构建。
custom_opset = onnxscript.values.Opset(domain="test.customop", version=1)
# NOTE: The function signature must match the signature of the unsupported ATen operator.
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/aten/src/ATen/native/native_functions.yaml
# NOTE: All attributes must be annotated with type hints.
@onnxscript.script(custom_opset)
def custom_addandround(input_x):
# The same as opset18.Add(x, x)
add_x = custom_opset.CustomOpOne(input_x, input_x)
# The same as opset18.Round(x, x)
round_x = custom_opset.CustomOpTwo(add_x)
# Cast to FLOAT to match the ONNX type
return opset18.Cast(round_x, to=1)
onnx_registry = torch.onnx.OnnxRegistry()
onnx_registry.register_op(
namespace="mylibrary", op_name="addandround_op", overload="default", function=custom_addandround
)
export_options = torch.onnx.ExportOptions(onnx_registry=onnx_registry)
onnx_program = torch.onnx.dynamo_export(
custom_addandround_model, input_addandround_x, export_options=export_options
)
onnx_program.save("./custom_addandround_model.onnx")
'CustomOpOne' is not a known op in 'test.customop'
'CustomOpTwo' is not a known op in 'test.customop'
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/torch/onnx/_internal/_exporter_legacy.py:116: UserWarning:
torch.onnx.dynamo_export only implements opset version 18 for now. If you need to use a different opset version, please register them with register_custom_op.
onnx_program 通过 onnx_program.model_proto 将导出的模型作为 protobuf 暴露出来。
该图有一个用于 custom_addandround 的图节点,在 custom_addandround 内部,
有两个函数节点,每个操作符一个。
assert onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node[0].domain == "test.customop"
assert onnx_program.model_proto.graph.node[0].op_type == "custom_addandround"
assert onnx_program.model_proto.functions[0].node[0].domain == "test.customop"
assert onnx_program.model_proto.functions[0].node[0].op_type == "CustomOpOne"
assert onnx_program.model_proto.functions[0].node[1].domain == "test.customop"
assert onnx_program.model_proto.functions[0].node[1].op_type == "CustomOpTwo"
这是使用Netron查看custom_addandround_model ONNX图的方式:
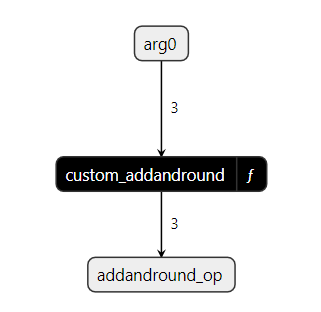
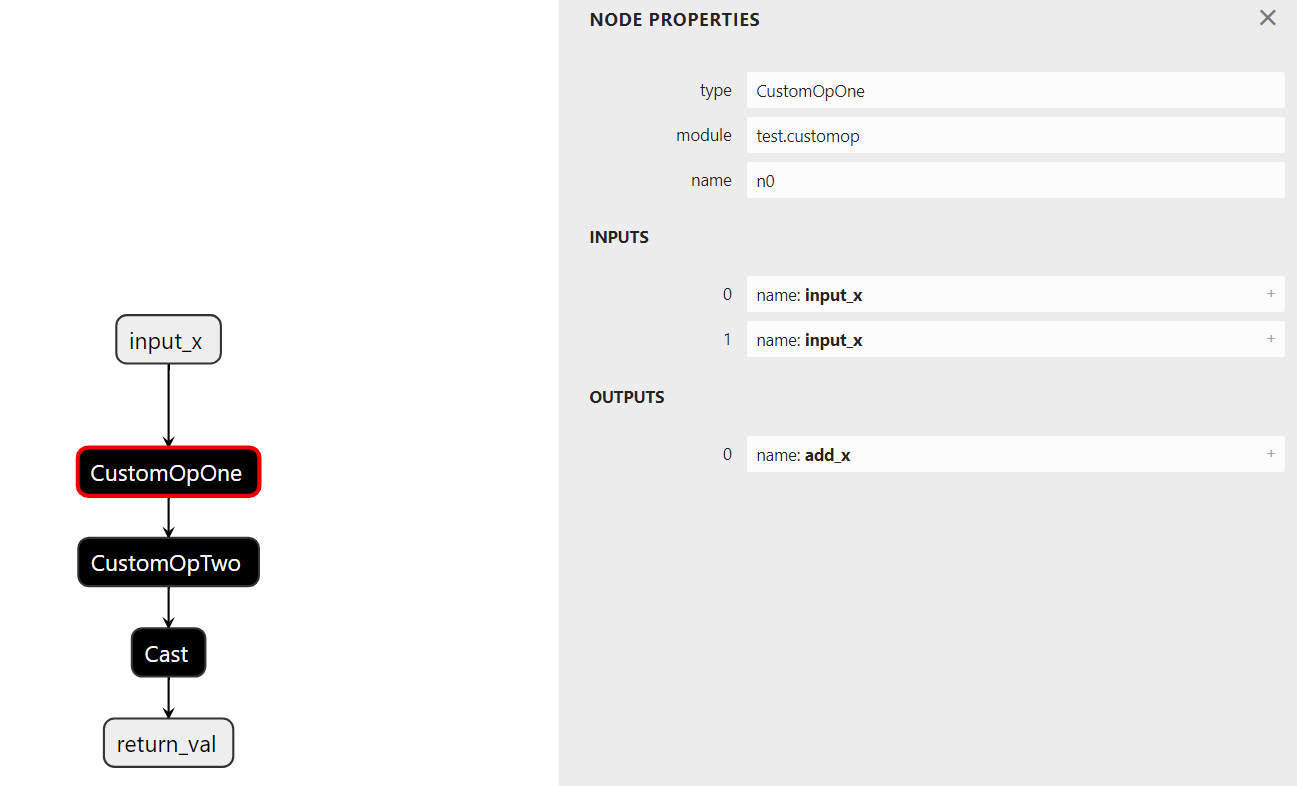
在custom_addandround函数内部,我们可以看到我们在函数中使用的两个自定义操作符(CustomOpOne和CustomOpTwo),它们来自模块test.customop:
在ONNX Runtime中注册自定义操作¶
要将您的自定义操作库链接到ONNX Runtime,您需要将您的C++代码编译成一个共享库并将其链接到ONNX Runtime。请按照以下说明操作:
按照ONNX Runtime 说明在 C++ 中实现您的自定义操作。
从ONNX Runtime 发布页面下载 ONNX Runtime 源代码分发版。
将您的自定义操作库编译并链接到ONNX Runtime,例如:
$ gcc -shared -o libcustom_op_library.so custom_op_library.cc -L /path/to/downloaded/ort/lib/ -lonnxruntime -fPIC
使用ONNX Runtime Python API运行模型,并将结果与PyTorch进行比较。
ort_session_options = onnxruntime.SessionOptions()
# NOTE: Link the custom op library to ONNX Runtime and replace the path
# with the path to your custom op library
ort_session_options.register_custom_ops_library(
"/path/to/libcustom_op_library.so"
)
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
"./custom_addandround_model.onnx", providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'], sess_options=ort_session_options)
def to_numpy(tensor):
return tensor.detach().cpu().numpy() if tensor.requires_grad else tensor.cpu().numpy()
onnx_input = onnx_program.adapt_torch_inputs_to_onnx(input_addandround_x)
onnxruntime_input = {k.name: to_numpy(v) for k, v in zip(ort_session.get_inputs(), onnx_input)}
onnxruntime_outputs = ort_session.run(None, onnxruntime_input)
torch_outputs = custom_addandround_model(input_addandround_x)
torch_outputs = onnx_program.adapt_torch_outputs_to_onnx(torch_outputs)
assert len(torch_outputs) == len(onnxruntime_outputs)
for torch_output, onnxruntime_output in zip(torch_outputs, onnxruntime_outputs):
torch.testing.assert_close(torch_output, torch.tensor(onnxruntime_output))
结论¶
恭喜!在本教程中,我们探索了ONNXRegistry API,并发现了如何使用ONNX Script为不支持或现有的ATen操作符创建自定义实现。最后,我们利用ONNX Runtime执行模型,并将结果与PyTorch进行比较,从而全面了解了在ONNX生态系统中处理不支持的操作符的方法。
进一步阅读¶
下面的列表涵盖了从基础示例到高级场景的教程,不一定按照列出的顺序排列。请随意直接跳转到您感兴趣的特定主题,或者坐下来,享受学习有关ONNX导出器的所有内容。
脚本总运行时间: ( 0 分钟 3.094 秒)




