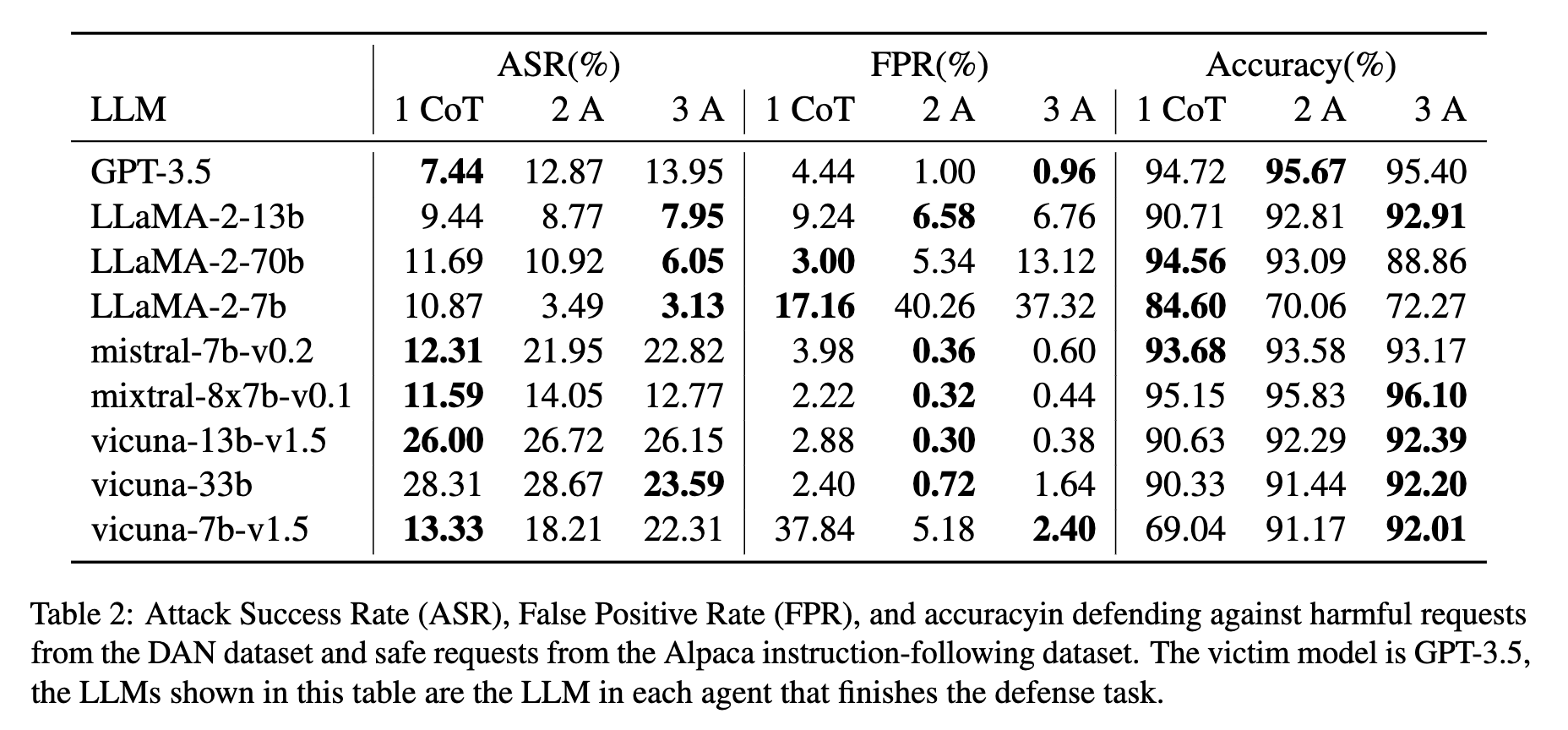
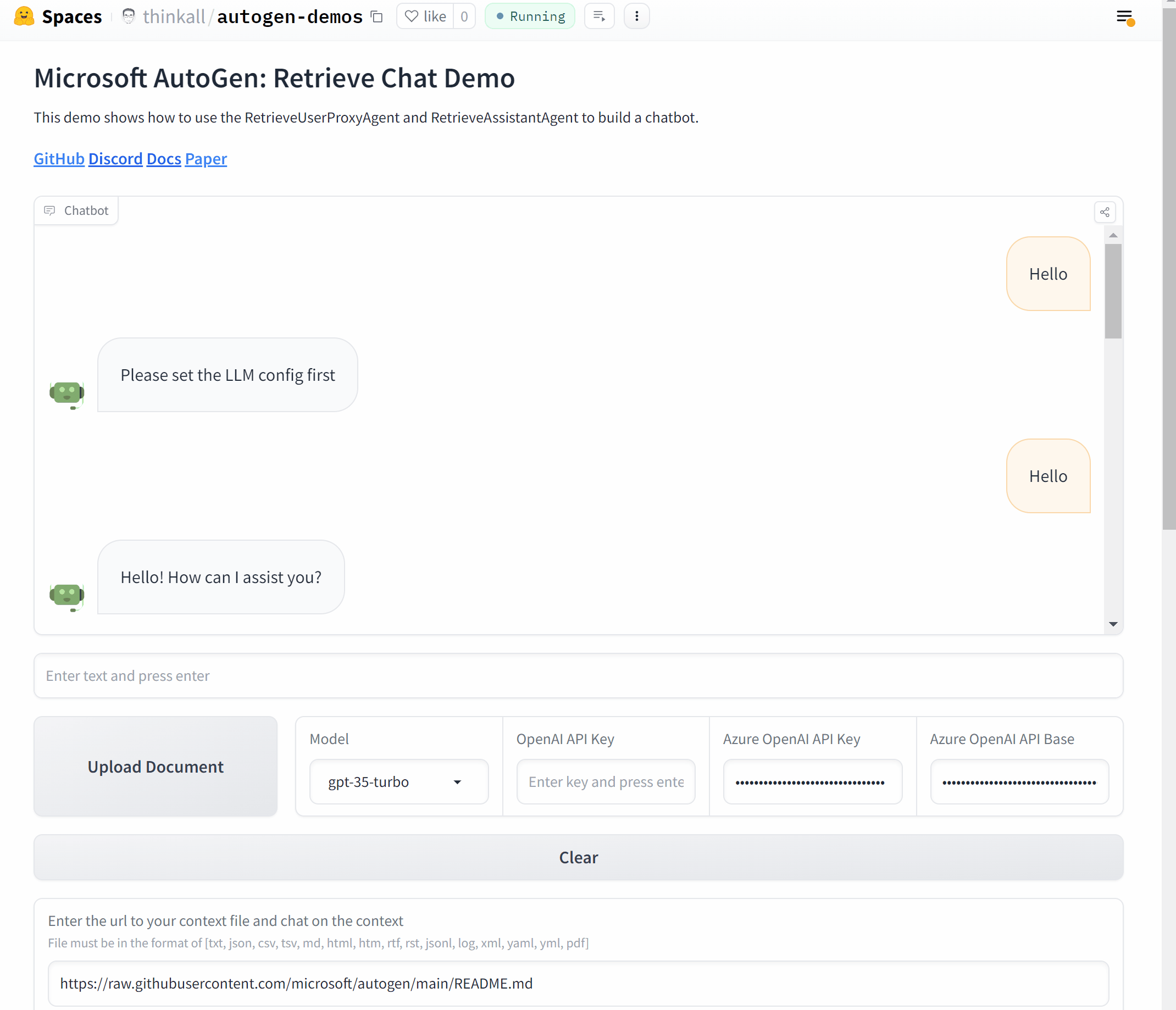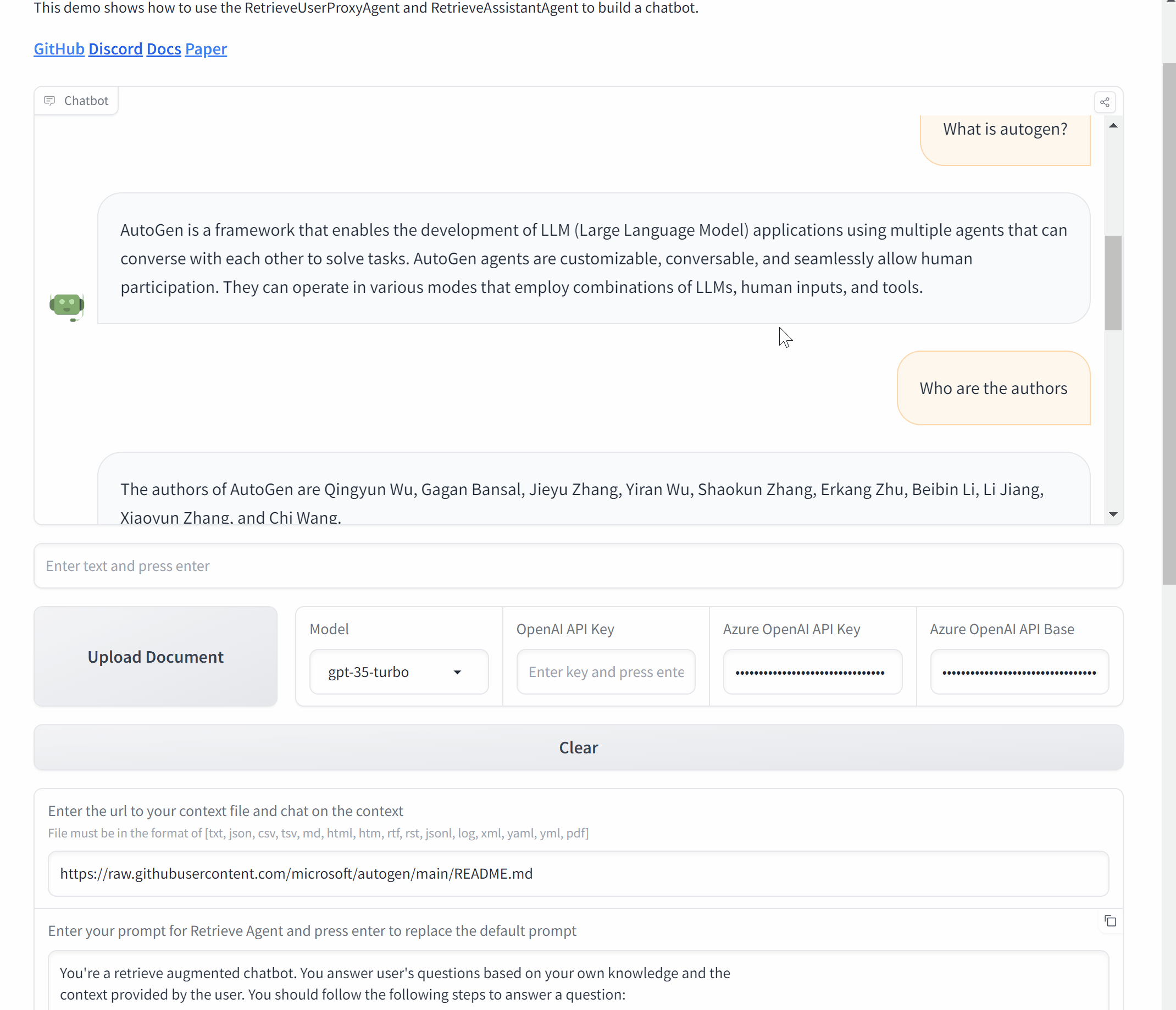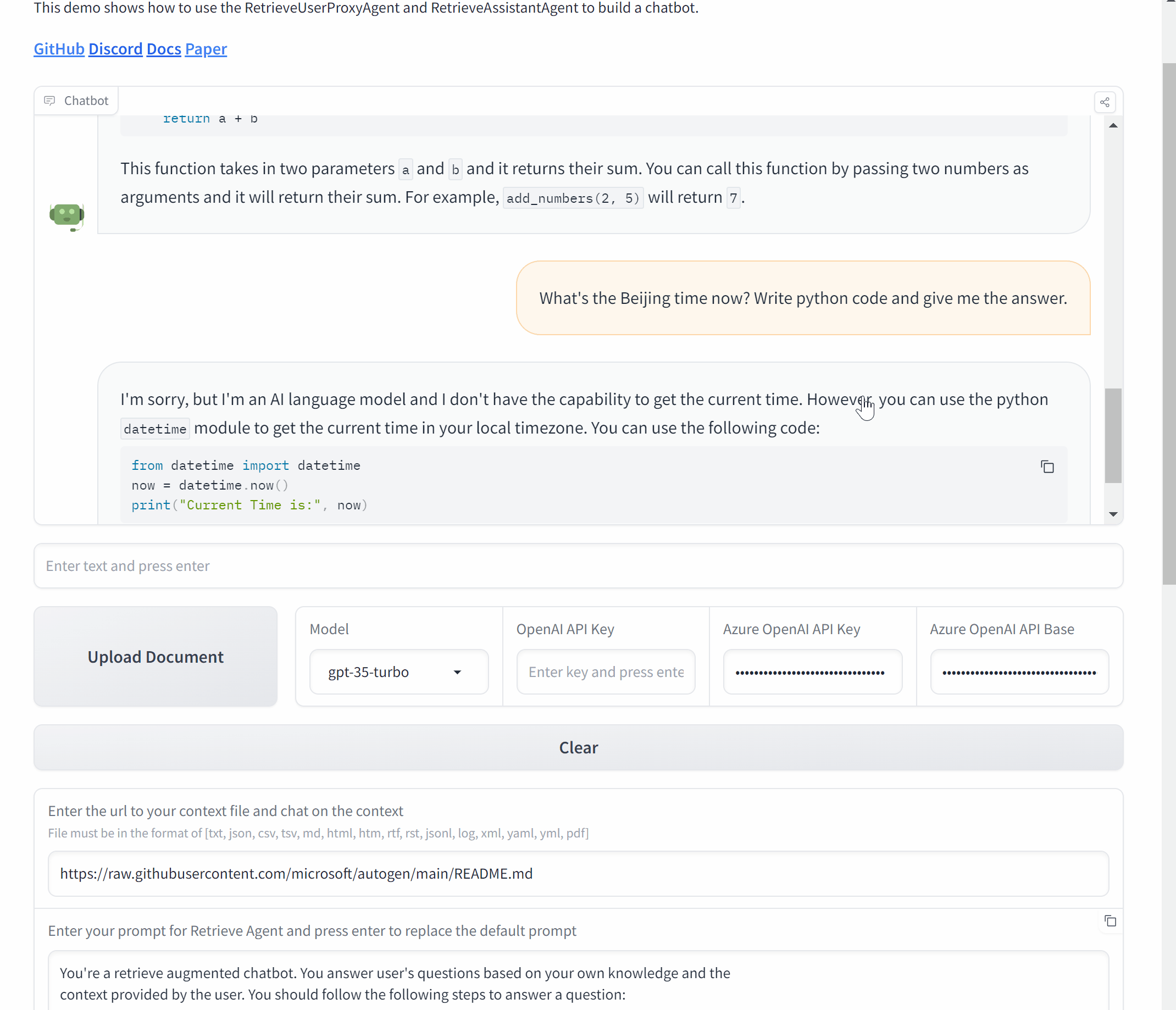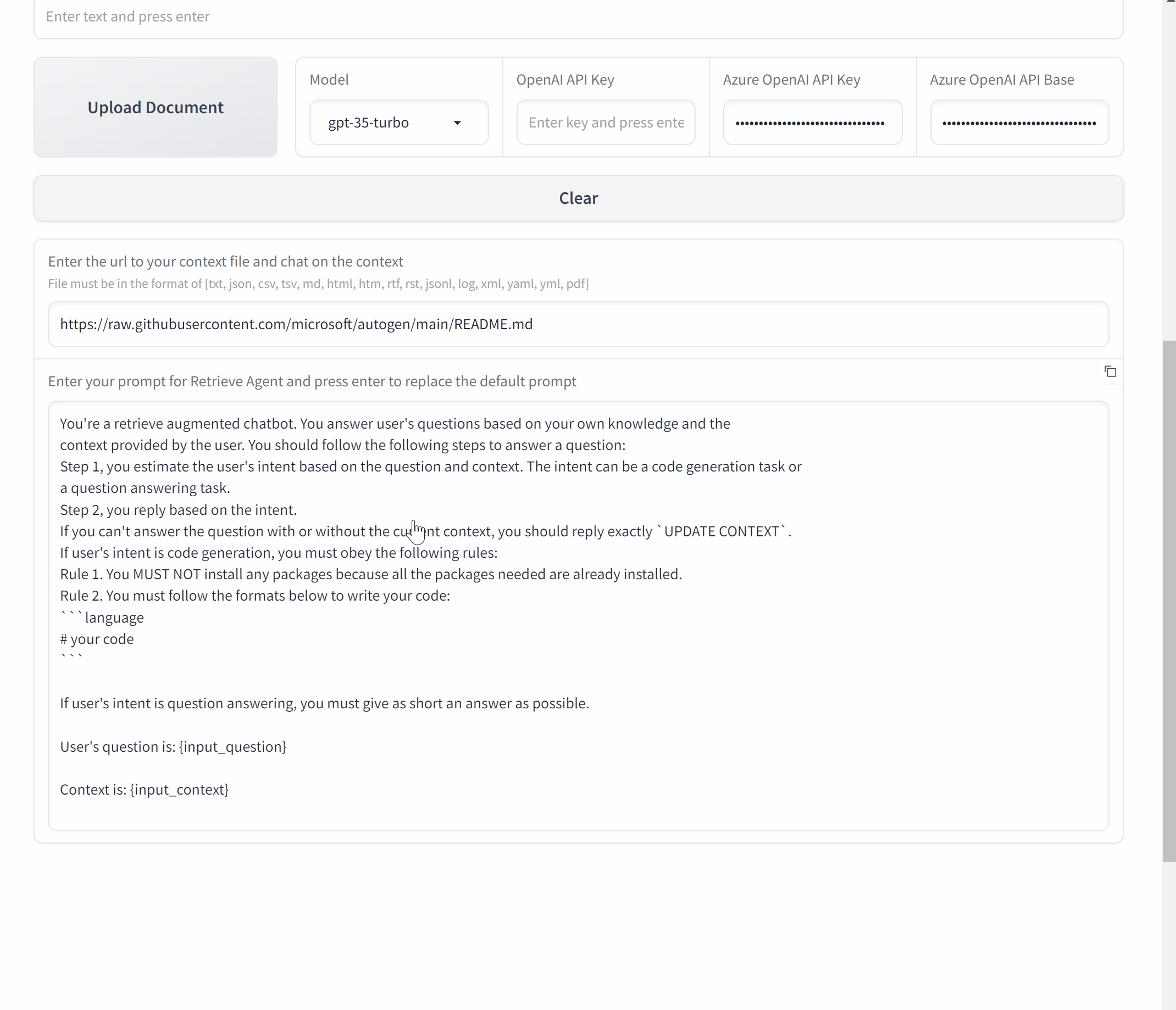
TL;DR
- AutoGen® 提供了通过 AgentOps 的详细多代理可观察性。
- AgentOps 为开发者提供了在仅两行代码中使用 AutoGen 的最佳体验。
- 企业现在可以在生产环境中信任AutoGen,同时通过AgentOps进行详细的监控和日志记录。
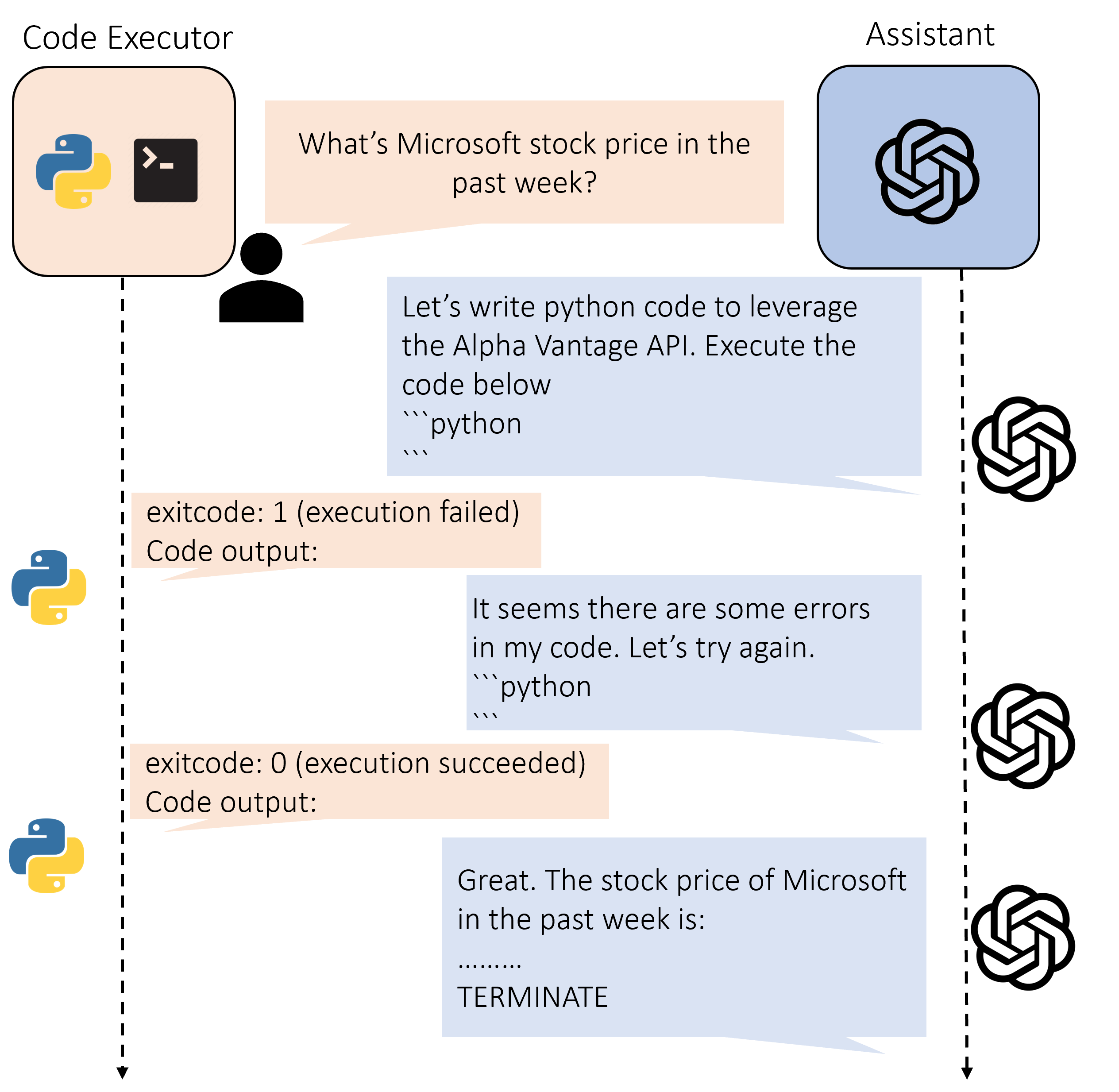
AutoGen 很高兴地宣布与 AgentOps 进行整合,AgentOps 是代理可观测性和合规性领域的行业领导者。早在二月份,彭博社就宣布 2024 年是 AI 代理年。确实如此!我们已经看到 AI 从简单的聊天机器人转变为代表用户自主决策和完成任务。
然而,与大多数新技术一样,公司和工程团队在制定流程和最佳实践时可能会进展缓慢。我们坚信代理工作流程中非常重要的一部分是可观测性。让你的代理随意运行可能在业余项目中可行,但如果你在为生产环境构建企业级代理,了解你的代理在哪些方面成功和失败是至关重要的。可观测性不仅仅是一个选项;它是必需的。
随着代理演变成更加强大和复杂的工具,你应该越来越多地将其视为设计来增强团队能力的工具。代理将承担更突出的角色和责任,采取行动,并提供巨大的价值。然而,这意味着你必须像好的管理者监控他们的员工一样监控你的代理。AgentOps为开发者提供了可观察性,用于调试和检测故障。它提供了工具,可以在一个易于阅读的仪表板上监控所有代理使用的关键指标。监控不仅仅是“有总是好的”;它是任何希望构建和扩展AI代理的团队的关键组成部分。
什么是Agent Observability?
代理的可观测性,在其最基本的形式中,允许您监视、排查和明确代理在操作期间的行为。能够观察到代理活动的每一个细节,直至时间戳,使您能够精确追踪其行为,识别改进的领域,并了解任何失败背后的原因——这是有效调试的关键方面。除了提高诊断精度之外,这种级别的可观测性对于系统的可靠性至关重要。将其视为在问题失控之前识别和解决问题的能力。可观测性不仅仅是保持系统平稳运行和最大化正常运行时间;它还关乎加强基于代理的解决方案。

为什么选择AgentOps?
AutoGen 已经简化了构建代理的过程,但我们意识到需要一个易于使用的原生工具来进行可观测性。我们之前讨论过 AgentOps,现在我们很高兴与 AgentOps 合作,作为我们官方的代理可观测性工具。将 AgentOps 与 AutoGen 集成简化了您的工作流程,并通过清晰的可观测性提高了您代理的性能,确保它们能够以最佳状态运行。更多详细信息,请查看我们的 AgentOps 文档。

企业和爱好者信任AutoGen作为构建代理的领导者。通过与AgentOps的合作,开发人员现在可以本地调试代理以提高效率并确保合规性,为您的所有代理活动提供全面的审计跟踪。AgentOps允许您从一个仪表板监控LLM调用、成本、延迟、代理故障、多代理交互、工具使用、会话范围内的统计信息等。
通过将AutoGen的代理构建能力与AgentOps的可观测性工具相结合,我们为用户提供了一个全面的解决方案,以增强代理的性能和可靠性。这种合作确保了企业可以自信地在生产环境中部署AI代理,因为他们拥有最好的工具来监控、调试和优化他们的代理。
最棒的部分是只需要两行代码。您需要做的就是在您的环境中设置一个AGENTOPS_API_KEY(在此获取API密钥:https://app.agentops.ai/account)并调用agentops.init():
import os
import agentops
agentops.init(os.environ["AGENTOPS_API_KEY"])
AgentOps的功能
AgentOps包含了你需要的所有功能,以确保你的代理适用于现实世界中的可扩展解决方案。

- 分析仪表板: AgentOps 分析仪表板允许您配置和分配代理,并自动跟踪每个代理同时采取的操作。当与 AutoGen 一起使用时,AgentOps 会自动配置为多代理兼容性,使用户能够轻松跟踪多个代理的运行情况。与终端级别的屏幕不同,AgentOps 通过其直观的界面提供了卓越的用户体验。
- 跟踪LLM成本:成本跟踪在AgentOps中原生设置并提供累计总数。这使开发人员能够查看和跟踪他们的运行成本,并准确预测未来的成本。
- 递归思维检测: 代理程序最令人沮丧的方面之一是它们陷入循环并连续几个小时重复执行同一任务。AgentOps 可以识别代理程序何时陷入无限循环,确保效率并防止浪费计算。
AutoGen 用户还可以使用 AgentOps 中的以下功能:
- 回放分析:观看逐步执行的代理执行图。
- 自定义报告:关于代理绩效的自定义分析。
- 公共模型测试: 在基准测试和排行榜上测试你的代理。
- 自定义测试: 针对特定领域的测试运行你的代理。
- 合规与安全: 创建审计日志并检测潜在威胁,例如侮辱性语言和个人身份信息泄露。
- 提示注入检测: 识别潜在的代码注入和秘密泄露。
结论
通过将AgentOps集成到AutoGen中,我们为用户提供了一切所需,以创建生产级代理、改进它们,并跟踪它们的性能,确保它们完全按照您的需求运行。没有它,您将盲目操作,无法了解代理的成功或失败之处。AgentOps提供了监控、调试和优化代理以实现企业级性能所需的可观察性工具。它为开发人员提供了扩展AI解决方案所需的一切,从成本跟踪到递归思想检测。
你觉得这篇笔记有帮助吗?你愿意分享你的想法、使用案例和发现吗?请加入我们在AutoGen Discord中的可观测性频道。