数据类#
在LLM应用中,数据经常需要以字符串的形式通过提示与LLMs进行交互,并从LLMs的文本预测中解析回结构化数据。
DataClass 旨在通过提示(输入)简化与LLMs的数据交互,并解析文本预测(输出)。
与Parser一起使用,解析LLMs的输出更加方便。
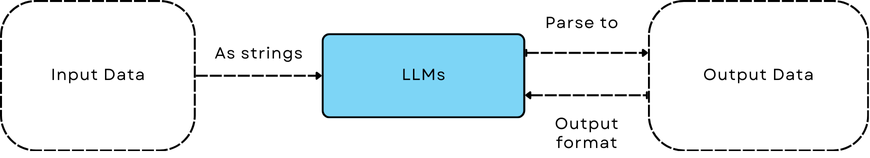
DataClass 旨在简化与LLMs的数据交互。#
设计#
在Python中,数据通常表示为具有属性的类。
为了与LLM交互,我们需要一种很好的方式来描述数据格式和数据实例给LLM,并能够从文本预测中转换回数据实例。
这与传统编程中的数据序列化和反序列化有重叠。
像Pydantic或Marshmallow这样的包可以涵盖序列化和反序列化,但最终会导致更多的复杂性和对用户的透明度降低。
众所周知,LLM提示是敏感的,数据格式的细节、可控性和透明度在这里至关重要。
我们最终创建了一个基类 DataClass 来处理将与LLMs交互的数据,它建立在Python的原生 dataclasses 模块之上。
以下是我们的理由:
dataclasses模块轻量、灵活,并且已经在 Python 中广泛用于数据类。在dataclasses中使用
field(metadata,default,default_factory)提供了更多描述数据的方式。asdict()来自 dataclasses 已经非常擅长将数据类实例转换为字典以便进行序列化。获取数据类的数据类模式是可行的。
以下是用户通常如何使用dataclasses模块的方式:
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
@dataclass
class TrecData:
question: str = field(
metadata={"desc": "The question asked by the user"}
) # Required field, you have to provide the question field at the instantiation
label: int = field(
metadata={"desc": "The label of the question"}, default=0
) # Optional field
DataClass 涵盖以下内容:
生成类
schema和signature(更简洁)以描述数据格式给LLMs。将数据实例转换为json或yaml字符串,以向LLMs展示数据示例。
从json或yaml字符串加载数据实例,以便将数据实例返回到程序中进行处理。
我们还努力提供了更多的控制:
保持数据字段的顺序。 我们提供了
required_field与default_factory,以将字段标记为必需,即使它在可选字段之后。我们还必须进行自定义,以在转换为字典、json和yaml字符串时保持它们的顺序。标记输出/输入字段。 我们允许您使用
__output_fields__和__input_fields__来明确标记输出和输入字段。(1) 它可以是数据类中字段的子集。(2) 您可以在 __output_fields__ 中指定顺序。从输出中排除某些字段。 所有序列化方法都支持 exclude 参数,即使对于嵌套的数据类也可以排除某些字段。
允许嵌套的数据类、列表和字典。 所有方法都支持嵌套的数据类、列表和字典。
易于与输出解析器一起使用。 它与
JsonOutputParser、YamlOutputParser和DataClassParser等输出解析器配合良好。您可以参考 :doc:`Parser`了解更多详情。
描述数据格式(数据类)#
名称 |
描述 |
|---|---|
|
输入字段的列表。 |
|
比 |
|
生成一个比签名更详细的JSON模式。 |
|
生成一个比签名更详细的JSON模式字符串。 |
|
从元数据中的描述生成类的YAML签名。 |
|
从元数据中的描述生成类的JSON签名(JSON字符串)。 |
|
生成数据格式字符串,包括 |
处理数据实例#
名称 |
描述 |
|---|---|
|
从字典创建数据类实例。支持嵌套的数据类、列表和字典。 |
|
将数据类对象转换为字典。支持嵌套的数据类、列表和字典。允许排除特定字段。 |
|
将数据类实例转换为JSON对象,保持字段的顺序。 |
|
将数据类实例转换为JSON字符串,保持字段的顺序。 |
|
将数据类实例转换为YAML对象,保持字段的顺序。 |
|
将数据类实例转换为YAML字符串,保持字段的顺序。 |
|
从JSON字符串创建数据类实例。 |
|
从YAML字符串创建数据类实例。 |
|
生成数据示例字符串,涵盖 |
我们有DataclassFormatType来指定数据格式方法的格式类型。
注意
要使用DataClass,你必须用dataclasses模块中的dataclass装饰器来装饰你的类。
实战中的DataClass#
假设你有几个如下结构的TrecData,你想与LLMs进行交互:
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
@dataclass
class Question:
question: str = field(
metadata={"desc": "The question asked by the user"}
)
metadata: dict = field(
metadata={"desc": "The metadata of the question"}, default_factory=dict
)
@dataclass
class TrecData:
question: Question = field(
metadata={"desc": "The question asked by the user"}
) # Required field, you have to provide the question field at the instantiation
label: int = field(
metadata={"desc": "The label of the question"}, default=0
) # Optional field
向LLMs描述数据格式#
我们将创建一个从DataClass派生的TrecData2类。
你决定向TrecData类添加一个metadata字段来存储问题的元数据。
出于你自己的原因,你希望metadata成为一个必填字段,并且希望在转换为字符串时保持字段的顺序。
DataClass将通过字段的default_factory上的required_field帮助你实现这一点。
通常情况下,使用原生的dataclasses模块这是不可能的,因为如果你将一个必填字段放在可选字段之后,它会引发错误。
注意
字段的顺序很重要,因为在典型的思维链中,我们希望推理/思维字段在输出中位于答案之前。
from adalflow.core import DataClass, required_field
@dataclass
class TrecData2(DataClass):
question: Question = field(
metadata={"desc": "The question asked by the user"}
) # Required field, you have to provide the question field at the instantiation
label: int = field(
metadata={"desc": "The label of the question"}, default=0
) # Optional field
metadata: dict = field(
metadata={"desc": "The metadata of the question"}, default_factory=required_field()
) # required field
模式
现在,让我们看看TrecData2类的结构:
print(TrecData2.to_schema())
输出将是:
{
"type": "TrecData2",
"properties": {
"question": {
"type": "{'type': 'Question', 'properties': {'question': {'type': 'str', 'desc': 'The question asked by the user'}, 'metadata': {'type': 'dict', 'desc': 'The metadata of the question'}}, 'required': ['question']}",
"desc": "The question asked by the user",
},
"label": {"type": "int", "desc": "The label of the question"},
"metadata": {"type": "dict", "desc": "The metadata of the question"},
},
"required": ["question", "metadata"],
}
如你所见,它正确地处理了嵌套的数据类 Question 和必填字段 metadata。
注意
Optional 类型提示不会影响字段的必填状态。我们建议您不要在 dataclasses 模块中使用它,尤其是在嵌套多层数据类时。这可能会导致 LLMs 混淆。
签名
由于模式可能相当冗长,有时更简洁地模仿你想要的输出数据结构效果更好。
比如说,你希望LLM生成一个yaml或json字符串,之后你可以将其转换回字典甚至你的数据实例。
我们可以使用以下签名来实现:
print(TrecData2.to_json_signature())
json签名输出将是:
{
"question": "The question asked by the user ({'type': 'Question', 'properties': {'question': {'type': 'str', 'desc': 'The question asked by the user'}, 'metadata': {'type': 'dict', 'desc': 'The metadata of the question'}}, 'required': ['question']}) (required)",
"label": "The label of the question (int) (optional)",
"metadata": "The metadata of the question (dict) (required)"
}
转换为yaml签名:
question: The question asked by the user ({'type': 'Question', 'properties': {'question': {'type': 'str', 'desc': 'The question asked by the user'}, 'metadata': {'type': 'dict', 'desc': 'The metadata of the question'}}, 'required': ['question']}) (required)
label: The label of the question (int) (optional)
metadata: The metadata of the question (dict) (required)
注意
如果你使用schema(json字符串)来指示LLMs输出yaml数据,LLMs可能会感到困惑,并可能输出json数据。
排除
现在,如果你决定不在输出中显示某些字段,你可以在方法中使用exclude参数。
让我们从类TrecData2和类Question中排除metadata:
json_signature_exclude = TrecData2.to_json_signature(exclude={"TrecData2": ["metadata"], "Question": ["metadata"]})
print(json_signature_exclude)
输出将是:
{
"question": "The question asked by the user ({'type': 'Question', 'properties': {'question': {'type': 'str', 'desc': 'The question asked by the user'}}, 'required': ['question']}) (required)",
"label": "The label of the question (int) (optional)"
}
如果你只想从类 metadata 中排除 TrecData2 - 外部类,你可以简单地传递一个字符串列表:
json_signature_exclude = TrecData2.to_json_signature(exclude=["metadata"])
print(json_signature_exclude)
输出将是:
{
"question": "The question asked by the user ({'type': 'Question', 'properties': {'question': {'type': 'str', 'desc': 'The question asked by the user'}, 'metadata': {'type': 'dict', 'desc': 'The metadata of the question'}}, 'required': ['question']}) (required)",
"label": "The label of the question (int) (optional)"
}
exclude 参数在所有方法中的工作方式相同。
数据类格式类型
对于数据类格式,我们有DataClassFormatType以及format_class_str方法来指定数据格式方法的格式类型。
from adalflow.core import DataClassFormatType
json_signature = TrecData2.format_class_str(DataClassFormatType.SIGNATURE_JSON)
print(json_signature)
yaml_signature = TrecData2.format_class_str(DataClassFormatType.SIGNATURE_YAML)
print(yaml_signature)
schema = TrecData2.format_class_str(DataClassFormatType.SCHEMA)
print(schema)
显示数据示例 & 将字符串解析为数据实例#
我们在数据实例上的功能将帮助您向LLMs展示数据示例。
这主要通过to_dict方法完成,您可以进一步将其转换为json或yaml字符串。
为了将原始字符串转换回数据实例,无论是从json还是yaml字符串,我们利用类方法from_dict。
因此,对于DataClass来说,确保重建的数据实例与原始数据实例相同是非常重要的。
以下是如何使用DataClass子类来实现这一点:
example = TrecData2(Question("What is the capital of France?"), 1, {"key": "value"})
print(example)
dict_example = example.to_dict()
print(dict_example)
reconstructed = TrecData2.from_dict(dict_example)
print(reconstructed)
print(reconstructed == example)
输出将是:
TrecData2(question=Question(question='What is the capital of France?', metadata={}), label=1, metadata={'key': 'value'})
{'question': {'question': 'What is the capital of France?', 'metadata': {}}, 'label': 1, 'metadata': {'key': 'value'}}
TrecData2(question=Question(question='What is the capital of France?', metadata={}), label=1, metadata={'key': 'value'})
True
除了from_dict和to_dict之外,我们还确保您可以直接使用:
from_yaml(从 yaml 字符串重建实例) 和to_yaml(一个 yaml 字符串)from_json(从json字符串重建实例)和to_json(一个json字符串)
以下是它与DataClass子类的工作方式:
json_str = example.to_json()
print(json_str)
yaml_str = example.to_yaml(example)
print(yaml_str)
reconstructed_from_json = TrecData2.from_json(json_str)
print(reconstructed_from_json)
print(reconstructed_from_json == example)
reconstructed_from_yaml = TrecData2.from_yaml(yaml_str)
print(reconstructed_from_yaml)
print(reconstructed_from_yaml == example)
输出将是:
{
"question": {
"question": "What is the capital of France?",
"metadata": {}
},
"label": 1,
"metadata": {
"key": "value"
}
}
question:
question: What is the capital of France?
metadata: {}
label: 1
metadata:
key: value
TrecData2(question=Question(question='What is the capital of France?', metadata={}), label=1, metadata={'key': 'value'})
True
TrecData2(question=Question(question='What is the capital of France?', metadata={}), label=1, metadata={'key': 'value'})
True
同样地,(1) 所有的 to_dict、to_json 和 to_yaml 都可以使用 exclude 参数来从输出中排除某些字段,
(2) 你可以使用 DataClassFormatType 和 format_example_str 方法来为数据示例方法指定格式类型。
from adalflow.core import DataClassFormatType
example_str = example.format_example_str(DataClassFormatType.EXAMPLE_JSON)
print(example_str)
example_str = example.format_example_str(DataClassFormatType.EXAMPLE_YAML)
print(example_str)
从数据集中加载数据作为示例#
由于我们需要从数据集中加载或创建一个实例,这通常来自Pytorch数据集或huggingface数据集,每个数据点都以字典的形式存在。
您希望如何向LLMs描述您的数据格式可能与现有数据集的键和字段名称不匹配。 您可以简单地做一些定制,将数据集的键映射到您的数据类中的字段名称。
@dataclass
class OutputFormat(DataClass):
thought: str = field(
metadata={
"desc": "Your reasoning to classify the question to class_name",
}
)
class_name: str = field(metadata={"desc": "class_name"})
class_index: int = field(metadata={"desc": "class_index in range[0, 5]"})
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, data: Dict[str, object]):
_COARSE_LABELS_DESC = [
"Abbreviation",
"Entity",
"Description and abstract concept",
"Human being",
"Location",
"Numeric value",
]
data = {
"thought": None,
"class_index": data["coarse_label"],
"class_name": _COARSE_LABELS_DESC[data["coarse_label"]],
}
return super().from_dict(data)
注意
如果您正在寻找我们过去支持的每个组件或任何其他类(如Optimizer)的数据类型,您可以查看core.types文件。
关于 __output_fields__#
虽然你可以在JsonOutputParser中使用exclude来排除输出中的某些字段,但这不如直接在数据类中使用__output_fields__来标记输出字段并直接使用DataClassParser来得可读和方便。

