检索器#
LLMs 会产生幻觉并且有知识截止点。
需要外部和相关上下文来增加 LLM 答案的事实性、相关性和新鲜度。
由于 LLM 的上下文窗口限制(它一次只能处理一定数量的标记),lost-in-the-middle 问题 [6],以及使用大上下文在速度和资源上的高成本,
使用检索器检索最相关的信息以获得最佳性能是实际可行的。检索增强生成(RAG)[7] 应用已成为 LLMs 中的主要应用之一。
什么是检索器?
尽管定义很简单——“从给定数据库中检索给定查询的相关信息”——检索器的范围可以扩展到整个搜索和信息检索领域。 在向量/语义搜索和重排序模型出现之前,已经存在许多搜索技术,例如关键字搜索、模糊搜索、邻近搜索、短语搜索、布尔搜索、分面搜索、全文搜索。 这些技术可以应用于各种数据类型,包括文本、时间敏感数据、位置、传感器数据、图像、视频和音频。 此外,它们可以存储在各种类型的数据库中,例如关系数据库、NoSQL数据库、向量数据库和图数据库。
生产中的检索
在实际生产中,检索通常是一个多阶段的过程,从最便宜到最昂贵和准确的方法逐步推进,从数百万候选者缩小到几百甚至更少。 例如,当你想从存储在Postgres等关系数据库中的个人资料池中搜索候选者时,可以从简单的关键字搜索或检查名称是否等于查询开始。 你可能还想按职业进行搜索,这些职业已经通过模型或人工标注进行了分类,使其成为过滤搜索。 如果搜索查询需要更多的语义理解,我们将利用嵌入模型进行语义搜索。 如果我们希望它更加准确,我们可以转向更昂贵和准确的方法,如重新排序模型和基于LLM的检索方法。
设计#
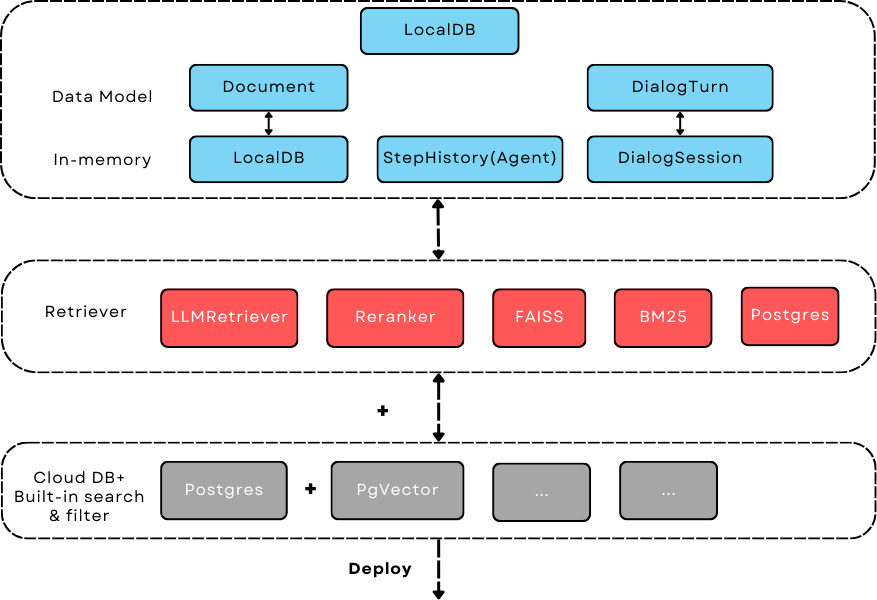
AdalFlow 检索器涵盖了 (1) 高精度检索方法,并使它们能够在本地和内存中工作,以及 (2) 如何与云数据库一起处理大规模数据,利用其内置的搜索和过滤方法。#
范围和设计目标#
AdalFlow 库不优先考虑集成覆盖的原因如下:
字面上来说,要涵盖所有内容范围太广。
RAG 应用程序的挑战更多在于评估和优化,因为有许多不同的移动部件和许多超参数,而在实现或集成第三方检索器方面则较少。
相反,我们的设计目标是:
涵盖具有代表性和价值的检索方法:
高精度检索方法,并使它们能够在本地和内存中工作,以便研究人员和开发人员能够更高效地构建和测试。
展示如何使用云数据库处理大规模数据,利用其内置的搜索和过滤方法。
提供一个清晰的设计模式,以便用户可以:
轻松集成他们自己的检索器,并使其与LLM任务管道的其余部分无缝协作。
轻松组合不同的检索器方法,形成一个多阶段的检索管道。
以下是当前检索器方法的覆盖范围:
LLMAsRetriever
重新排序器(交叉编码器)
语义搜索(双编码器)
BM25
数据库的内置搜索功能,如全文搜索/基于SQL的搜索使用Postgres,以及语义搜索使用
PgVector。
使用数据库#
检索器将与database紧密合作。
我们将提供一个LocalDB和一个基于云的SQL数据库(使用SQLAlchemy),它可以与任何数据类/模型一起工作,特别是与Document用于数据处理和DialogTurn用于对话数据。
Document与文本分割器和嵌入模型结合将提供RAG中的context。
与DialogTurn合作可以帮助管理conversation_history,特别是对于聊天机器人的终身记忆。
检索器数据类型#
查询
在大多数情况下,查询是字符串。但在某些情况下,我们可能需要文本和图像作为查询,例如“找到一件看起来像这样的衣服”。 我们定义了查询类型RetrieverQueriesType,以便我们所有的检索器都能同时处理单个查询和多个查询。 对于基于文本的检索器,我们将RetrieverStrQueriesType定义为字符串或字符串序列。
RetrieverQueryType = TypeVar("RetrieverQueryType", contravariant=True)
RetrieverStrQueryType = str
RetrieverQueriesType = Union[RetrieverQueryType, Sequence[RetrieverQueryType]]
RetrieverStrQueriesType = Union[str, Sequence[RetrieverStrQueryType]]
文档
文档是任何类型的文档序列,稍后将由子类指定:
RetrieverDocumentType = TypeVar("RetrieverDocumentType", contravariant=True) # a single document
RetrieverDocumentsType = Sequence[RetrieverDocumentType] # The final documents types retriever can use
输出
我们进一步定义了统一的输出数据结构 RetrieverOutput,以便在我们的任务管道中轻松切换不同的检索器。
检索器应返回一个 RetrieverOutput 列表,以支持同时处理多个查询。这对于以下情况很有帮助:
批处理:特别是对于语义搜索,多个查询可以表示为numpy数组并一次性计算,提供比逐个处理每个查询更快的速度。
查询扩展:为了提高召回率,用户通常从原始查询生成多个查询。
@dataclass
class RetrieverOutput(DataClass):
doc_indices: List[int] = field(metadata={"desc": "List of document indices"})
doc_scores: Optional[List[float]] = field(
default=None, metadata={"desc": "List of document scores"}
)
query: Optional[RetrieverQueryType] = field(
default=None, metadata={"desc": "The query used to retrieve the documents"}
)
documents: Optional[List[RetrieverDocumentType]] = field(
default=None, metadata={"desc": "List of retrieved documents"}
)
RetrieverOutputType = List[RetrieverOutput] # so to support multiple queries at once
文档和文本分割器
如果你的文档(文本格式)太大,通常的做法是首先使用TextSplitter将文本分割成较小的块。
请参考Text Splitter教程了解如何使用它。
检索器基类#
从功能上讲,基础检索器 Retriever 定义了另一个必需的方法 build_index_from_documents,子类将在此方法中为实际的检索调用准备检索器。
可选地,子类可以实现 save_to_file 和 load_from_file 来将检索器保存到磁盘或从磁盘加载。
由于检索器是组件的一个子类,你已经继承了强大的序列化和反序列化方法,如 to_dict、from_dict 和 from_config,这些方法有助于保存和加载过程。至于辅助属性,我们有 indexed 和 index_keys 来区分检索器是否准备好进行检索,以及哪些属性是恢复检索器功能/状态的关键。
由子类决定如何决定索引的存储方式,可以是内存、本地磁盘或云存储,或者保存为 json 或 pickle 文件,甚至是一个数据库表。
例如,BM25Retriever 有以下关键属性用于索引。
class Retriever(Component, Generic[RetrieverDocumentType, RetrieverQueryType]):
...
def call(
self,
input: RetrieverQueriesType,
top_k: Optional[int] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> RetrieverOutputType:
raise NotImplementedError(f"retrieve is not implemented")
async def acall(
self,
input: RetrieverQueriesType,
top_k: Optional[int] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> RetrieverOutputType:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Async retrieve is not implemented")
self.index_keys = ["nd", "t2d", "idf","doc_len","avgdl","total_documents","top_k","k1","b","epsilon","indexed"]
实验数据#
在本笔记中,我们将使用以下文档和查询进行演示:
query_1 = "What are the benefits of renewable energy?" # gt is [0, 3]
query_2 = "How do solar panels impact the environment?" # gt is [1, 2]
documents =[
{
"title": "The Impact of Renewable Energy on the Economy",
"content": "Renewable energy technologies not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute significantly to the economy by creating jobs in the manufacturing and installation sectors. The growth in renewable energy usage boosts local economies through increased investment in technology and infrastructure."
},
{
"title": "Understanding Solar Panels",
"content": "Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity by allowing photons, or light particles, to knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity. Solar panels are a type of renewable energy technology that has been found to have a significant positive effect on the environment by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels."
},
{
"title": "Pros and Cons of Solar Energy",
"content": "While solar energy offers substantial environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon footprints and pollution, it also has downsides. The production of solar panels can lead to hazardous waste, and large solar farms require significant land, which can disrupt local ecosystems."
},
{
"title": "Renewable Energy and Its Effects",
"content": "Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro power play a crucial role in combating climate change. They do not produce greenhouse gases during operation, making them essential for sustainable development. However, the initial setup and material sourcing for these technologies can still have environmental impacts."
}
]
第一个查询应检索第一个和最后一个文档,第二个查询应检索第二个和第三个文档。
文档过滤#
在使用更高级的检索方法之前,通常首先对文档进行过滤。 文档过滤取决于您的数据存储方式,无论是在内存中、本地磁盘上还是云数据库中。 对于云数据库,它高度依赖于数据库的搜索和过滤方法。基于SQL的搜索是常见、可扩展且高效的。
如果您正在使用LocalDB和Document作为数据项,您可以使用filter方法来过滤文档。
在将文档或处理后的文档块和嵌入传递给检索器之前,您可以先过滤文档。
from adalflow.core.db import LocalDB
from adalflow.core.types import Document
db = LocalDB()
db.connect()
# Add the documents to the database
for doc in documents:
db.add_item(Document(**doc))
# Filter the documents
filtered_documents = db.filter(Document, title="Solar Panels")
print(filtered_documents)
检索器在行动中#
我们所有的检索器都是从基础检索器派生的子类,它们位于components.retriever模块中。
你可以在这里浏览它们的实现:retriever。
目前只有BM25Retriever需要有自己的save_to_file和load_from_file以避免重新计算。
FAISSRetriever将与数据库一起工作以存储嵌入,这减轻了检索器处理状态保存的需求。
FAISS检索器#
首先,让我们进行语义搜索,这里我们将使用内存中的FAISSRetriever。
FAISS检索器接受嵌入,可以是List[float]或np.ndarray,并使用FAISS库构建索引。
查询可以接受嵌入和字符串格式。
注意
faiss 包在我们的库中是可选的。当你想使用它时,请确保你的环境中已经安装了它。
我们将使用content字段快速准备上述文档的嵌入。
from adalflow.core.embedder import Embedder
from adalflow.core.types import ModelClientType
model_kwargs = {
"model": "text-embedding-3-small",
"dimensions": 256,
"encoding_format": "float",
}
embedder = Embedder(model_client =ModelClientType.OPENAI(), model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
output = embedder(input=[doc["content"] for doc in documents])
documents_embeddings = [x.embedding for x in output.data]
对于初始化,检索器可以接受其所需的文档以及包括top_k在内的超参数。
documents字段是可选的。让我们首先从__init__传递所有内容:
from adalflow.components.retriever import FAISSRetriever
retriever = FAISSRetriever(top_k=2, embedder=embedder, documents=documents_embeddings)
print(retriever)
打印输出:
FAISSRetriever(
top_k=2, metric=prob, dimensions=256, total_documents=4
(embedder): Embedder(
model_kwargs={'model': 'text-embedding-3-small', 'dimensions': 256, 'encoding_format': 'float'},
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
)
)
我们也可以在初始化后使用build_index_from_documents方法传递文档。
这在你的检索器每次需要处理不同的文档池时非常有用。
retriever_1 = FAISSRetriever(top_k=2, embedder=embedder)
retriever_1.build_index_from_documents(documents=documents_embeddings)
现在,我们将进行检索器的操作,输入可以是一个单独的查询或一个查询列表:
output_1 = retriever(input=query_1)
output_2 = retriever(input=query_2)
output_3 = retriever(input = [query_1, query_2])
print(output_1)
print(output_2)
print(output_3)
打印输出为:
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=[0.8119999766349792, 0.7749999761581421], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[2, 1], doc_scores=[0.8169999718666077, 0.8109999895095825], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=[0.8119999766349792, 0.7749999761581421], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None), RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[2, 1], doc_scores=[0.8169999718666077, 0.8109999895095825], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
默认情况下,分数是使用余弦相似度模拟的概率,范围在[0, 1]之间。分数越高,文档与查询的相关性越高。
您可以查看检索器以获取更多类型的分数。
LanceDBRetriever#
要使用LanceDB执行语义搜索,我们将使用LanceDBRetriever。
LanceDBRetriever专为与LanceDB进行高效的基于向量的检索而设计,利用可以是List[float]或np.ndarray的嵌入。
LanceDB支持内存和基于磁盘的配置,并且可以处理大规模数据,具有高检索速度。
注意
lancedb 包是可选的。请确保在您的环境中安装了它,以便使用 LanceDBRetriever。
我们将使用content字段准备文档嵌入。
from adalflow.core.embedder import Embedder
from adalflow.core.types import ModelClientType
model_kwargs = {
"model": "text-embedding-3-small",
"dimensions": 256,
"encoding_format": "float",
}
embedder = Embedder(model_client=ModelClientType.OPENAI(), model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
output = embedder(input=[doc["content"] for doc in documents])
documents_embeddings = [x.embedding for x in output.data]
初始化LanceDB检索器后,我们可以添加文档并执行检索。检索器可以在初始化时设置其top-k超参数。
from adalflow.components.retriever import LanceDBRetriever
retriever = LanceDBRetriever(embedder=embedder, dimensions=256, db_uri="/tmp/lancedb", top_k=2)
print(retriever)
打印输出:
LanceDBRetriever(
top_k=2, dimensions=256, total_documents=0
(embedder): Embedder(
model_kwargs={'model': 'text-embedding-3-small', 'dimensions': 256, 'encoding_format': 'float'},
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
)
)
我们可以将文档添加到LanceDB,并使用检索器进行基于查询的搜索。
documents = [
{
"title": "The Impact of Renewable Energy on the Economy",
"content": "Renewable energy technologies not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute significantly to the economy by creating jobs."
},
{
"title": "Understanding Solar Panels",
"content": "Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity by allowing photons, or light particles, to knock electrons free from atoms."
},
{
"title": "Pros and Cons of Solar Energy",
"content": "While solar energy offers substantial environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon footprints and pollution, it also has downsides."
},
{
"title": "Renewable Energy and Its Effects",
"content": "Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro power play a crucial role in combating climate change."
}
]
# Add documents to LanceDB
retriever.add_documents(documents)
# Perform retrieval queries
output_1 = retriever.retrieve(query="What are the benefits of renewable energy?")
output_2 = retriever.retrieve(query="How do solar panels impact the environment?")
print("Query 1 Results:", output_1)
print("Query 2 Results:", output_2)
此设置允许LanceDBRetriever作为一个高效的工具,用于在LanceDB中进行大规模的、基于嵌入的文档检索。
BM25检索器#
所以语义搜索效果相当不错。我们将看看BM25Retriever相比如何工作。
我们重新实现了[9]中的代码,并做了一个改进:我们使用分词器来分割文本,而不是使用text.split(" ")。以下是它们的不同之处:
from adalflow.components.retriever.bm25_retriever import split_text_by_word_fn_then_lower_tokenized, split_text_by_word_fn
query_1_words = split_text_by_word_fn(query_1)
query_1_tokens = split_text_by_word_fn_then_lower_tokenized(query_1)
输出:
['what', 'are', 'the', 'benefits', 'of', 'renewable', 'energy?']
['what', 'are', 'the', 'benef', 'its', 'of', 're', 'new', 'able', 'energy', '?']
我们准备检索器:
from adalflow.components.retriever import BM25Retriever
document_map_func = lambda x: x["content"]
bm25_retriever = BM25Retriever(top_k=2, documents=documents, document_map_func=document_map_func)
print(bm25_retriever)
它需要document_map_func将文档映射为检索器可以处理的文本格式。
输出为:
BM25Retriever(top_k=2, k1=1.5, b=0.75, epsilon=0.25, use_tokenizer=True, total_documents=4)
现在我们以与FAISS检索器完全相同的方式调用检索器:
output_1 = bm25_retriever(input=query_1)
output_2 = bm25_retriever(input=query_2)
output_3 = bm25_retriever(input = [query_1, query_2])
print(output_1)
print(output_2)
print(output_3)
打印输出为:
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[2, 1], doc_scores=[2.151683837681807, 1.6294762236217233], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[3, 2], doc_scores=[1.5166601493236314, 0.7790170272403408], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[2, 1], doc_scores=[2.151683837681807, 1.6294762236217233], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None), RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[3, 2], doc_scores=[1.5166601493236314, 0.7790170272403408], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
在这里,我们看到第一个查询返回了[2, 1],而实际值是[0, 3]。第二个查询返回了[3, 2],而实际值是[1, 2]。
性能相当令人失望。BM25 以缺乏语义理解和不考虑上下文而闻名。
我们在较短且几乎像关键词版本的查询上进行了测试,并同时使用了title和content,使用分词拆分后它给出了正确的响应。
query_1_short = "renewable energy?" # gt is [0, 3]
query_2_short = "solar panels?" # gt is [1, 2]
document_map_func = lambda x: x["title"] + " " + x["content"]
bm25_retriever.build_index_from_documents(documents=documents, document_map_func=document_map_func)
这次检索给了我们正确的答案。
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=[0.9498793313012154, 0.8031794089550072], query='renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[2, 1], doc_scores=[0.5343238380789569, 0.4568096570283078], query='solar panels?', documents=None)]
重新排序器作为检索器#
语义搜索效果良好,而基于cross-encoder模型的重新排序器预计效果会更好。
我们集成了两个重新排序器:BAAI/bge-reranker-base [10]托管在transformers上,以及由Cohere [11]提供的重新排序器。
这些模型遵循ModelClient协议,并可以直接作为检索器从RerankerRetriever访问。
重排序模型客户端集成
重新排序器将使用ModelType.RERANKER,并且标准的AdalFlow库要求它在model_kwargs中有四个参数:
['model', 'top_k', 'documents', 'query']。这是在ModelClient中,它将AdalFlow的标准参数转换为模型的特定参数。
如果你想集成你的重新排序器,无论是本地还是使用API,请查看TransformersClient和
CohereAPIClient以了解如何操作。
要从RerankerRetriever中使用它,我们只需要传递model以及其他不需要在model_kwargs中转换的参数。以下是我们如何使用来自Cohere的模型rerank-english-v3.0(确保你已经安装了cohere sdk并准备好了api key):
from adalflow.components.retriever import RerankerRetriever
model_client = ModelClientType.COHERE()
model_kwargs = {"model": "rerank-english-v3.0"}
reranker = RerankerRetriever(
top_k=2, model_client=model_client, model_kwargs=model_kwargs
)
print(reranker)
打印输出:
RerankerRetriever(
top_k=2, model_kwargs={'model': 'rerank-english-v3.0'}, model_client=CohereAPIClient(), total_documents=0
(model_client): CohereAPIClient()
)
现在我们构建索引并进行检索:
document_map_func = lambda x: x["content"]
reranker.build_index_from_documents(documents=documents, document_map_func=document_map_func)
output_1 = reranker(input=query_1)
output_2 = reranker(input=query_2)
output_3 = reranker(input = [query_1, query_2])
从添加文档后的结构中,我们看到重新排序器已将文档传递给model_kwargs,以便它可以将其全部发送到ModelClient。
RerankerRetriever(
top_k=2, model_kwargs={'model': 'rerank-english-v3.0', 'documents': ['Renewable energy technologies not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute significantly to the economy by creating jobs in the manufacturing and installation sectors. The growth in renewable energy usage boosts local economies through increased investment in technology and infrastructure.', 'Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity by allowing photons, or light particles, to knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity. Solar panels are a type of renewable energy technology that has been found to have a significant positive effect on the environment by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.', 'While solar energy offers substantial environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon footprints and pollution, it also has downsides. The production of solar panels can lead to hazardous waste, and large solar farms require significant land, which can disrupt local ecosystems.', 'Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro power play a crucial role in combating climate change. They do not produce greenhouse gases during operation, making them essential for sustainable development. However, the initial setup and material sourcing for these technologies can still have environmental impacts.']}, model_client=CohereAPIClient(), total_documents=4
(model_client): CohereAPIClient()
)
从结果中我们看到它得到了正确的答案,并且得分接近1。
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=[0.99520767, 0.9696708], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[1, 2], doc_scores=[0.98742366, 0.9701269], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=[0.99520767, 0.9696708], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None), RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[1, 2], doc_scores=[0.98742366, 0.9701269], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
现在让我们看看本地 transformers 模型中的 ``BAAI/bge-reranker-base` 是如何工作的:
model_client = ModelClientType.TRANSFORMERS()
model_kwargs = {"model": "BAAI/bge-reranker-base"}
reranker = RerankerRetriever(
top_k=2,
model_client=model_client,
model_kwargs=model_kwargs,
documents=documents,
document_map_func=document_map_func,
)
print(reranker)
打印输出:
RerankerRetriever(
top_k=2, model_kwargs={'model': 'BAAI/bge-reranker-base', 'documents': ['Renewable energy technologies not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute significantly to the economy by creating jobs in the manufacturing and installation sectors. The growth in renewable energy usage boosts local economies through increased investment in technology and infrastructure.', 'Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity by allowing photons, or light particles, to knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity. Solar panels are a type of renewable energy technology that has been found to have a significant positive effect on the environment by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.', 'While solar energy offers substantial environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon footprints and pollution, it also has downsides. The production of solar panels can lead to hazardous waste, and large solar farms require significant land, which can disrupt local ecosystems.', 'Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro power play a crucial role in combating climate change. They do not produce greenhouse gases during operation, making them essential for sustainable development. However, the initial setup and material sourcing for these technologies can still have environmental impacts.']}, model_client=TransformersClient(), total_documents=4
(model_client): TransformersClient()
)
以下是检索结果:
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=[0.9996004700660706, 0.9950029253959656], query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[2, 0], doc_scores=[0.9994490742683411, 0.9994476437568665], query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
它在第二个查询中漏掉了一个,但它在前三名中。 从语义上讲,这些文档可能很接近。 如果我们使用 top_k = 3,生成器可能能够过滤掉不相关的那个,并最终给出正确的最终响应。 此外,如果我们同时使用 title 和 content,它也会得到正确的响应。
LLM作为检索器#
使用LLM作为检索器有几种不同的方法:
直接显示所有文档和查询,并要求它返回前k个索引作为列表。
将查询和文档配对,并要求其进行是和否的判断。此外,我们可以使用是标记的logprobs来获得类似概率的分数。我们将在不久的将来实现这一点,目前,你可以参考[8]自行实现。
对于第一种情况,没有提示和零样本,gpt-3.5-turbo 的表现不如 gpt-4o,后者两个答案都答对了。 这是我们的代码:
from adalflow.components.retriever import LLMRetriever
model_client = ModelClientType.OPENAI()
model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-4o",
}
document_map_func = lambda x: x["content"]
llm_retriever = LLMRetriever(
top_k=2,
model_client=model_client,
model_kwargs=model_kwargs,
documents=documents,
document_map_func=document_map_func
)
print(llm_retriever)
打印输出:
LLMRetriever(
top_k=2, total_documents=4,
(generator): Generator(
model_kwargs={'model': 'gpt-4o'},
(prompt): Prompt(
template: <SYS>
You are a retriever. Given a list of documents, you will retrieve the top_k {{top_k}} most relevant documents and output the indices (int) as a list:
[<index of the most relevant with top_k options>]
<Documents>
{% for doc in documents %}
```Index {{ loop.index - 1 }}. {{ doc }}```
{% endfor %}
</Documents>
</SYS>
Query: {{ input_str }}
You:
, preset_prompt_kwargs: {'top_k': 2, 'documents': ['Renewable energy technologies not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute significantly to the economy by creating jobs in the manufacturing and installation sectors. The growth in renewable energy usage boosts local economies through increased investment in technology and infrastructure.', 'Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity by allowing photons, or light particles, to knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity. Solar panels are a type of renewable energy technology that has been found to have a significant positive effect on the environment by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.', 'While solar energy offers substantial environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon footprints and pollution, it also has downsides. The production of solar panels can lead to hazardous waste, and large solar farms require significant land, which can disrupt local ecosystems.', 'Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro power play a crucial role in combating climate change. They do not produce greenhouse gases during operation, making them essential for sustainable development. However, the initial setup and material sourcing for these technologies can still have environmental impacts.']}, prompt_variables: ['documents', 'top_k', 'input_str']
)
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
(output_processors): ListParser()
)
)
这是响应:
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 3], doc_scores=None, query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[1, 2], doc_scores=None, query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
我们可以在不重新初始化检索器的情况下使用不同的模型调用检索器。以下是我们如何使用gpt-3.5-turbo来实现这一点:
model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
}
output_1 = llm_retriever(model_kwargs=model_kwargs, input=query_1)
output_2 = llm_retriever(model_kwargs=model_kwargs, input=query_2)
响应是:
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[0, 1], doc_scores=None, query='What are the benefits of renewable energy?', documents=None)]
[RetrieverOutput(doc_indices=[1, 2], doc_scores=None, query='How do solar panels impact the environment?', documents=None)]
Qdrant 检索器#
您可以使用QdrantRetriever检索加载到Qdrant集合中的文档。
注意
在你的项目中安装qdrant-client包以使用此检索器。
检索器支持任何嵌入提供者。可以从Qdrant有效负载返回的字段可以与其他参数(如过滤器)一起配置。
from adalflow.components.retriever import QdrantRetriever
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
qdrant_retriever = QdrantRetriever(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
client=client,
embedder=embedder,
top_k=5,
text_key="content",
)
print(qdrant_retriever)
输出是:
QdrantRetriever(
(_embedder): Embedder(
model_kwargs={'model': 'text-embedding-3-small', 'dimensions': 256, 'encoding_format': 'float'},
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
)
)
我们可以像调用其他检索器一样调用Qdrant检索器:
output_1 = qdrant_retriever(input=query_1)
output_2 = qdrant_retriever(input=query_2)
output_3 = qdrant_retriever(input = [query_1, query_2])
在设置检索器时,您可以使用过滤器根据需求进一步优化搜索结果。
from qdrant_client import models
qdrant_retriever = QdrantRetriever(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
client=client,
embedder=embedder,
text_key="content",
filter=models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="category",
match=models.MatchValue(value="facts"),
),
models.FieldCondition(
key="weight",
range=models.Range(gte=0.98),
),
]
)
)
PostgresRetriever#
即将推出。
使用分数阈值代替top_k#
在某些情况下,当检索器有一个计算得分时,您可能更倾向于使用得分而不是top_k来过滤出相关文档。
为此,您可以将top_k设置为文档的完整大小,并使用后处理步骤或组件(与检索器链接)来过滤掉得分低于阈值的文档。
与数据库一起使用#
当数据规模较大时,我们将使用数据库来存储从文档中计算出的嵌入和索引。
使用LocalDB#
我们之前已经计算了嵌入,现在让我们使用LocalDB来帮助持久化。
(尽管你完全可以自己持久化它们,比如使用pickle)。
此外,LocalDB帮助我们跟踪我们的初始文档及其转换后的文档。
参考文献
API 参考
