LLM 评估#
“你无法优化你无法测量的东西”。
在LLMs的背景下尤其如此,由于其在广泛任务上的出色表现,它们变得越来越受欢迎。 评估LLMs及其应用在研究和生产中至关重要,以了解它们的能力和局限性。 总体而言,这种评估是一个复杂且多方面的过程。 下面,我们提供了一个评估LLMs及其应用的指南,结合了Chang等人概述的方面[1]以及更多用于RAG评估的内容。
评估内容: 大型语言模型(LLMs)被评估的任务和能力。
评估地点: 用于评估的数据集和基准。
如何评估: 用于评估的协议和指标。
任务和能力#
以下是一些在[1]中总结的LLMs常用评估任务和能力。
自然语言理解 (NLU) 任务,例如文本分类和情感分析,这些任务评估LLM理解自然语言的能力。
自然语言生成 (NLG) 任务,例如文本摘要、翻译和问答,这些任务评估LLM生成自然语言的能力。
推理任务,例如数学、逻辑和常识推理,这些任务评估LLM执行推理和推断以获得正确答案的能力。
鲁棒性,评估LLM对意外输入的泛化能力。
公平性,评估LLM做出无偏见决策的能力。
领域适应,评估LLM从通用语言适应到特定新领域的能力,例如医学或法律文本、编码等。
代理应用程序,评估LLM使用外部工具和API执行任务的能力,例如网络搜索。
有关LLMs评估任务和能力的更详细和全面的描述,请参阅Chang等人的综述论文[1]和Guo等人的综述论文[2]。 RRAG [21]的评估有所不同,因为它在流程中引入了检索组件,我们将在下一节中讨论这一点。
数据集和基准#
数据集和基准的选择[19]非常重要,因为它决定了评估的质量和相关性。
为了全面评估LLMs的能力,研究人员通常使用涵盖广泛任务的基准和数据集。例如,在GPT-4技术报告[3]中,作者使用了各种通用语言基准,如MMLU [4],以及学术考试,如SAT、GRE和AP课程,来评估GPT-4的多样化能力。以下是一些常用的用于评估LLMs的数据集和基准。
MMLU [4],它评估了LLM在执行广泛语言理解任务方面的能力。
HumanEval [5],用于衡量LLM编写Python代码的能力。
HELM,它评估LLMs在语言理解、生成、常识推理和领域适应等多个方面的表现。
Chatbot Arena,这是一个通过人类投票来评估LLMs的开放平台。
API-Bank,它评估了LLMs使用外部工具和API执行任务的能力。
请参考综述论文(Chang 等人 [1]、Guo 等人 [2] 和 Liu 等人 [6])以获取关于 LLM 评估中使用的数据集和基准的更全面概述。此外,许多数据集可以通过 Hugging Face Datasets 库轻松访问。例如,可以使用以下代码片段从 Hub 轻松加载 MMLU 数据集。
1from datasets import load_dataset
2dataset = load_dataset(path="cais/mmlu", name='abstract_algebra')
3print(dataset["test"])
输出将是一个包含MMLU数据集测试集的Dataset对象。
用于RAG评估的数据集
根据RAGEval [21],评估数据集可以分为两种类型:传统的开放域QA数据集和特定场景的RAG评估数据集。
传统的开放领域问答数据集包括:
HotPotQA: 一个用于多跳问答的数据集。
自然问题:一个用于开放领域问答的数据集。
MS MARCO: 一个用于段落检索和问答的数据集。
2WikiMultiHopQA: 一个用于多跳问答的数据集。
KILT: 知识密集型语言任务的基准。
特定场景的RAG评估数据集,
RGB:评估LLMs利用检索信息的能力,重点关注噪声鲁棒性和信息整合。
CRAG:增加领域覆盖范围并引入模拟API以模拟现实世界的检索场景。
评估指标#
评估方法可以分为自动评估和人工评估(Chang等人 [1] 和 Liu等人 [6])。
自动化评估通常涉及使用诸如准确性和BERTScore等指标,或采用LLM作为评判者,以定量评估LLM在特定任务上的表现。 另一方面,人工评估则涉及人类参与循环,以评估生成文本的质量或LLM的表现。
在这里,我们将自动化评估方法分类如下:
对于经典的NLU任务,如文本分类和情感分析,您可以使用诸如准确率、F1分数和ROC-AUC等指标来评估LLM响应的性能,就像您使用非生成式AI模型一样。您可以查看TorchMetrics。
对于NLG任务,如文本摘要、翻译和问答:(1) 你可以使用诸如ROUGE、BLEU、METEOR和BERTScore、困惑度、
LLMasJudge等指标来评估生成文本相对于参考文本的质量。 或者使用GEvalLLMJudge来评估生成文本,即使没有参考文本。对于RAG(检索增强生成)管道,您可以使用诸如
RetrieverRecall、AnswerMatchAcc和LLMasJudge等指标来评估检索到的上下文和生成答案的质量。
你也可以查看由Hugging Face Metrics、RAGAS、TorchMetrics、ARES、SemScore、RGB等提供的指标。
自然语言生成评估#
经典字符串度量#
最简单的指标是EM AnswerMatchAcc:通过将生成的答案与真实答案进行比较,计算生成答案的精确匹配准确率或模糊匹配准确率。
更高级的传统指标,如F1、BLEU [8]、ROUGE [9]、[20]和METEOR [12],可能无法捕捉参考文本和生成文本之间的语义相似性,导致与人类判断的相关性较低。
你可以使用TorchMetrics [10] 或 Hugging Face Metrics 来计算这些指标。例如,
gt = "Brazil has won 5 FIFA World Cup titles"
pred = "Brazil is the five-time champion of the FIFA WorldCup."
def compute_rouge(gt, pred):
from torchmetrics.text.rouge import ROUGEScore
rouge = ROUGEScore()
return rouge(pred, gt)
def compute_bleu(gt, pred):
from torchmetrics.text.bleu import BLEUScore
bleu = BLEUScore()
return bleu([pred], [[gt]])
输出的Rouge分数是:
{'rouge1_fmeasure': tensor(0.2222), 'rouge1_precision': tensor(0.2000), 'rouge1_recall': tensor(0.2500), 'rouge2_fmeasure': tensor(0.), 'rouge2_precision': tensor(0.), 'rouge2_recall': tensor(0.), 'rougeL_fmeasure': tensor(0.2222), 'rougeL_precision': tensor(0.2000), 'rougeL_recall': tensor(0.2500), 'rougeLsum_fmeasure': tensor(0.2222), 'rougeLsum_precision': tensor(0.2000), 'rougeLsum_recall': tensor(0.2500)}
输出的BLEU分数是:0.0
这两句话的意思完全相同,但在BLEU和ROUGE评分中得分较低。
基于嵌入的指标#
为了弥补这一点,创建了基于嵌入的度量或神经评估器,如BERTScore。 你可以在Hugging Face Metrics和TorchMetrics中找到BERTScore。 BERTScore使用BERT的预训练上下文嵌入,并通过余弦相似度匹配生成文本和参考文本中的单词。
def compute_bertscore(gt, pred):
r"""
https://lightning.ai/docs/torchmetrics/stable/text/bert_score.html
"""
from torchmetrics.text.bert import BERTScore
bertscore = BERTScore()
return bertscore([pred], [gt])
输出的BERT分数是:
{'precision': tensor(0.9752), 'recall': tensor(0.9827), 'f1': tensor(0.9789)}
这个分数几乎完美地反映了两句话之间的语义相似性。 然而,上述所有指标的缺点是,你需要有一个参考文本来进行比较。 在许多自然语言生成任务中,如摘要生成,创建参考文本等标注工作可能非常具有挑战性。
LLM 作为评判者#
正如LLM如何使AI任务变得更容易一样,它也使得AI任务的评估变得更加容易。
使用LLM作为评判的真正力量在于:
与上述所有指标相比,它的适应性,可以即插即用地适应任何任务。
其灵活性和鲁棒性在测量方面。对于许多自然语言生成任务,可能只有多个参考甚至无数个正确的响应。使用传统指标可能会非常有限。
更少的训练数据。使用(问题、真实答案、生成文本、真实分数)元组来对齐LLM裁判到你的任务,比微调像BERTScore这样的模型需要的数据更少。
使用LLM作为评判者来评估LLM应用程序类似于构建LLM任务管道。 开发人员需要理解LLM评判者使用的基础提示,以确定默认评判者是否足够,或者是否需要定制。
在审查了研究论文和现有库之后,我们发现没有解决方案能够在不要求开发者安装大量额外依赖的情况下,为这些评估器提供完全的清晰度。 考虑到这一点,AdalFlow决定提供一套全面的LLM评估器,而不是将我们的开发者引导到外部的评估包。
无论是否有参考文本,您都可以使用LLM作为评判者。 关键是要用文本明确定义度量标准。
我们正在开发LLM评判系统以取代人工标注员,提高效率并降低财务成本。
最直接的LLM判断器根据生成的文本与参考文本之间的比较,预测一个是/否答案或一个在[0, 1]范围内的浮点分数,以应对给定的判断查询。
这是AdalFlow的默认判断查询:
DEFAULT_JUDGEMENT_QUERY = "Does the predicted answer contain the ground truth answer? Say True if yes, False if no."
AdalFlow 提供了一个高度可定制的 LLM 评判器,可以通过以下三种方式使用:
带有问题、真实答案和生成的文本
毫无疑问,使用真实数据和生成的文本,主要是匹配真实数据和生成的文本
有问题,没有真实答案,有生成的文本,主要是问题和生成的文本之间的匹配
你可以根据你的使用场景自定义judgement_query,甚至可以自定义整个llm模板。
AdalFlow LLM 判断返回 LLMJudgeEvalResult,它有三个字段: 1. avg_score: 生成文本的平均分数 2. judgement_score_list: 每个生成文本的分数列表 3. confidence_interval: 分数的95%置信区间的元组
DefaultLLMJudge 是一个LLM任务管道,它接受一个问题(可选)、真实答案(可选)和生成的文本,并返回范围在[0,1]内的浮点分数。
你可以将其用作AdalFlow Trainer的eval_fn。
LLMAsJudge 是一个评估器,它接收一系列输入并返回一系列 LLMJudgeEvalResult。 除了分数外,它还计算分数的置信区间。
案例1:带有参考文献
现在,您可以使用以下代码根据判断查询计算最终分数:
def compute_llm_as_judge():
import adalflow as adal
from adalflow.eval.llm_as_judge import LLMasJudge, DefaultLLMJudge
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
adal.setup_env()
questions = [
"Is Beijing in China?",
"Is Apple founded before Google?",
"Is earth flat?",
]
pred_answers = ["Yes", "Yes, Appled is founded before Google", "Yes"]
gt_answers = ["Yes", "Yes", "No"]
llm_judge = DefaultLLMJudge(
model_client=OpenAIClient(),
model_kwargs={
"model": "gpt-4o",
"temperature": 1.0,
"max_tokens": 10,
},
)
llm_evaluator = LLMasJudge(llm_judge=llm_judge)
print(llm_judge)
eval_rslt = llm_evaluator.compute(
questions=questions, gt_answers=gt_answers, pred_answers=pred_answers
)
print(eval_rslt)
为了确保更加严谨,你可以计算判断分数的95%置信区间。当评估数据集较小时,置信区间可能会有较大的范围,这表明判断分数不太可靠。
输出将是:
LLMJudgeEvalResult(avg_score=0.6666666666666666, judgement_score_list=[1, 1, 0], confidence_interval=(0.013333333333333197, 1))
这种类型的LLM判断在文本梯度[17]中可见。 你可以通过简单地使用print(llm_judge)来查看我们使用的提示:
DefaultLLMJudge(
judgement_query= Does the predicted answer contain the ground truth answer? Say True if yes, False if no.,
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
(llm_evaluator): Generator(
model_kwargs={'model': 'gpt-4o', 'temperature': 1.0, 'max_tokens': 10}, trainable_prompt_kwargs=['task_desc_str', 'examples_str']
(prompt): Prompt(
template: <START_OF_SYSTEM_PROMPT>
{# task desc #}
{{task_desc_str}}
{# examples #}
{% if examples_str %}
{{examples_str}}
{% endif %}
<END_OF_SYSTEM_PROMPT>
---------------------
<START_OF_USER>
{# question #}
{% if question_str is defined %}
Question: {{question_str}}
{% endif %}
{# ground truth answer #}
{% if gt_answer_str is defined %}
Ground truth answer: {{gt_answer_str}}
{% endif %}
{# predicted answer #}
Predicted answer: {{pred_answer_str}}
<END_OF_USER>
, prompt_kwargs: {'task_desc_str': 'You are an evaluator. Given the question(optional), ground truth answer(optional), and predicted answer, Does the predicted answer contain the ground truth answer? Say True if yes, False if no.', 'examples_str': None}, prompt_variables: ['task_desc_str', 'examples_str', 'pred_answer_str', 'question_str', 'gt_answer_str']
)
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
)
)
案例2:无问题
def compute_llm_as_judge_wo_questions():
from adalflow.eval.llm_as_judge import LLMasJudge, DefaultLLMJudge
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
llm_judge = DefaultLLMJudge(
model_client=OpenAIClient(),
model_kwargs={
"model": "gpt-4o",
"temperature": 1.0,
"max_tokens": 10,
},
jugement_query="Does the predicted answer means the same as the ground truth answer? Say True if yes, False if no.",
)
llm_evaluator = LLMasJudge(llm_judge=llm_judge)
print(llm_judge)
eval_rslt = llm_evaluator.compute(gt_answers=[gt], pred_answers=[pred])
print(eval_rslt)
输出将是:
LLMJudgeEvalResult(avg_score=1.0, judgement_score_list=[1], confidence_interval=(0, 1))
G_Eval#
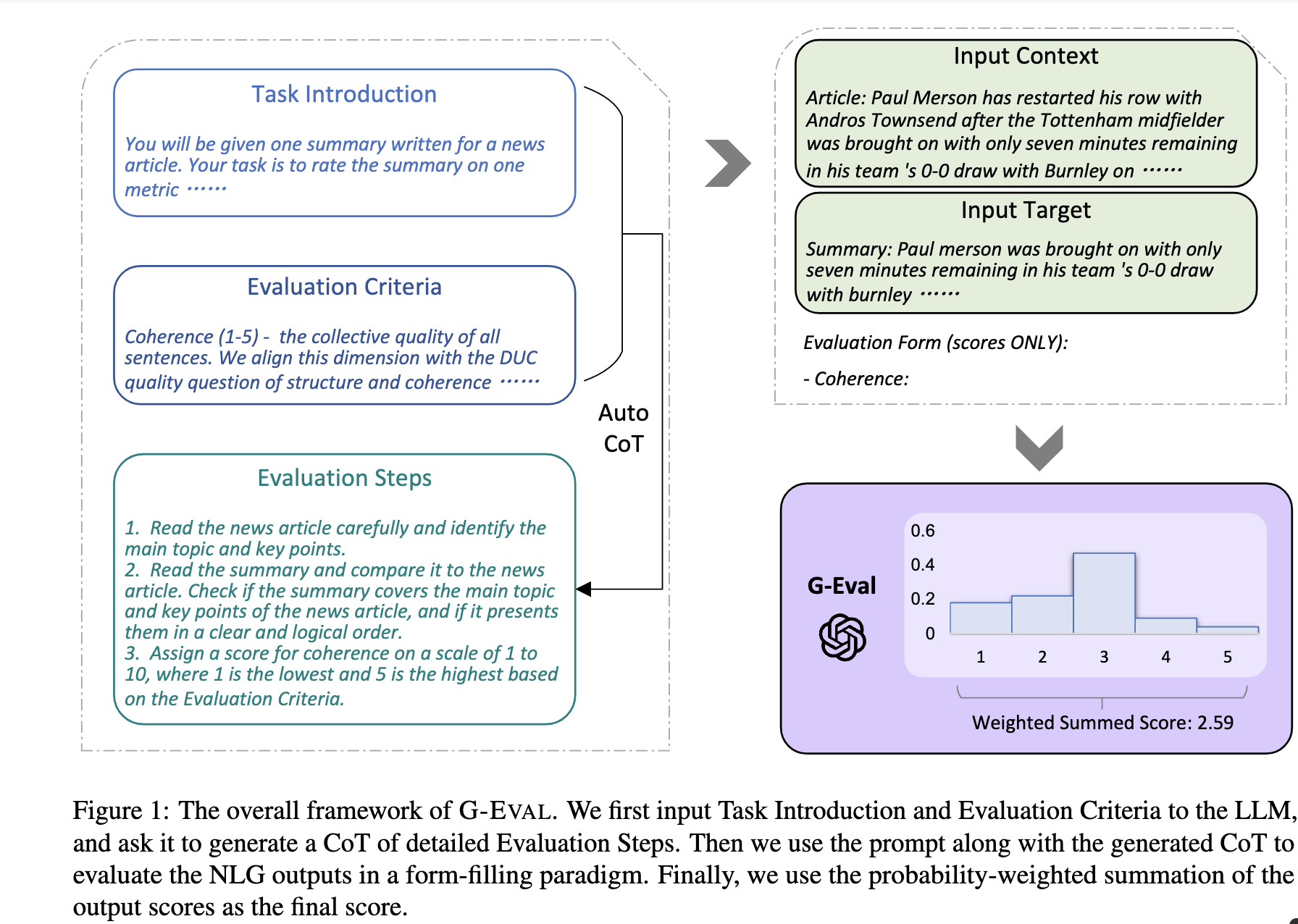
G-eval 框架结构#
如果你没有参考文本,你也可以使用G-eval [11] 来即时评估生成的文本。 G-eval 提供了一种评估方法:
relevance: 评估摘要文本与源文本的相关性。
fluency: 摘要的质量,包括语法、拼写、标点、词汇选择和句子结构。
一致性: 评估所有句子的整体质量。
coherence: 评估摘要与被摘要源之间的事实一致性。
在我们的库中,我们默认提供了Summarization和Chatbot任务的提示。 为了方便优化,我们还将分数映射到[0, 1]的范围。
以下是计算G-eval分数的代码片段:
def compute_g_eval_summarization():
from adalflow.eval.g_eval import GEvalLLMJudge, GEvalJudgeEvaluator, NLGTask
model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-4o",
"n": 20,
"top_p": 1,
"max_tokens": 5,
"temperature": 1,
}
g_eval = GEvalLLMJudge(
default_task=NLGTask.SUMMARIZATION, model_kwargs=model_kwargs
)
print(g_eval)
input_template = """Source Document: {source}
Summary: {summary}
"""
input_str = input_template.format(
source="Paul Merson has restarted his row with Andros Townsend after the Tottenham midfielder was brought on with only seven minutes remaining in his team 's 0-0 draw with Burnley on Sunday . 'Just been watching the game , did you miss the coach ? # RubberDub # 7minutes , ' Merson put on Twitter . Merson initially angered Townsend for writing in his Sky Sports column that 'if Andros Townsend can get in ( the England team ) then it opens it up to anybody . ' Paul Merson had another dig at Andros Townsend after his appearance for Tottenham against Burnley Townsend was brought on in the 83rd minute for Tottenham as they drew 0-0 against Burnley Andros Townsend scores England 's equaliser in their 1-1 friendly draw with Italy in Turin on Tuesday night The former Arsenal man was proven wrong when Townsend hit a stunning equaliser for England against Italy and he duly admitted his mistake . 'It 's not as though I was watching hoping he would n't score for England , I 'm genuinely pleased for him and fair play to him \u00e2\u20ac\u201c it was a great goal , ' Merson said . 'It 's just a matter of opinion , and my opinion was that he got pulled off after half an hour at Manchester United in front of Roy Hodgson , so he should n't have been in the squad . 'When I 'm wrong , I hold my hands up . I do n't have a problem with doing that - I 'll always be the first to admit when I 'm wrong . ' Townsend hit back at Merson on Twitter after scoring for England against Italy Sky Sports pundit Merson ( centre ) criticised Townsend 's call-up to the England squad last week Townsend hit back at Merson after netting for England in Turin on Wednesday , saying 'Not bad for a player that should be 'nowhere near the squad ' ay @ PaulMerse ? ' Any bad feeling between the pair seemed to have passed but Merson was unable to resist having another dig at Townsend after Tottenham drew at Turf Moor .",
summary="Paul merson was brought on with only seven minutes remaining in his team 's 0-0 draw with burnley . Andros townsend scored the tottenham midfielder in the 89th minute . Paul merson had another dig at andros townsend after his appearance . The midfielder had been brought on to the england squad last week . Click here for all the latest arsenal news news .",
)
g_evaluator = GEvalJudgeEvaluator(llm_judge=g_eval)
response = g_evaluator(input_strs=[input_str])
print(f"response: {response}")
输出将是:
response: ({'Relevance': 0.4, 'Fluency': 0.3333333333333333, 'Consistency': 0.2, 'Coherence': 0.4, 'overall': 0.33333333333333337}, [{'Relevance': 0.4, 'Fluency': 0.3333333333333333, 'Consistency': 0.2, 'Coherence': 0.4, 'overall': 0.33333333333333337}])
print(g_eval) 将会是:
GEvalLLMJudge(
default_task= NLGTask.SUMMARIZATION, prompt_kwargs={'Relevance': {'task_desc_str': 'You will be given a summary of a text. Please evaluate the summary based on the following criteria:', 'evaluation_criteria_str': 'Relevance (1-5) - selection of important content from the source.\n The summary should include only important information from the source document.\n Annotators were instructed to penalize summaries which contained redundancies and excess information.', 'evaluation_steps_str': '1. Read the summary and the source document carefully.\n 2. Compare the summary to the source document and identify the main points of the article.\n 3. Assess how well the summary covers the main points of the article, and how much irrelevant or redundant information it contains.\n 4. Assign a relevance score from 1 to 5.', 'metric_name': 'Relevance'}, 'Fluency': {'task_desc_str': 'You will be given a summary of a text. Please evaluate the summary based on the following criteria:', 'evaluation_criteria_str': 'Fluency (1-3): the quality of the summary in terms of grammar, spelling, punctuation, word choice, and sentence structure.\n - 1: Poor. The summary has many errors that make it hard to understand or sound unnatural.\n - 2: Fair. The summary has some errors that affect the clarity or smoothness of the text, but the main points are still comprehensible.\n - 3: Good. The summary has few or no errors and is easy to read and follow.\n ', 'evaluation_steps_str': None, 'metric_name': 'Fluency'}, 'Consistency': {'task_desc_str': 'You will be given a summary of a text. Please evaluate the summary based on the following criteria:', 'evaluation_criteria_str': 'Consistency (1-5) - the factual alignment between the summary and the summarized source.\n A factually consistent summary contains only statements that are entailed by the source document.\n Annotators were also asked to penalize summaries that contained hallucinated facts. ', 'evaluation_steps_str': '1. Read the summary and the source document carefully.\n 2. Identify the main facts and details it presents.\n 3. Read the summary and compare it to the source document to identify any inconsistencies or factual errors that are not supported by the source.\n 4. Assign a score for consistency based on the Evaluation Criteria.', 'metric_name': 'Consistency'}, 'Coherence': {'task_desc_str': 'You will be given a summary of a text. Please evaluate the summary based on the following criteria:', 'evaluation_criteria_str': 'Coherence (1-5) - the collective quality of all sentences.\n We align this dimension with the DUC quality question of structure and coherence whereby "the summary should be well-structured and well-organized.\n The summary should not just be a heap of related information, but should build from sentence to a coherent body of information about a topic.', 'evaluation_steps_str': '1. Read the input text carefully and identify the main topic and key points.\n 2. Read the summary and assess how well it captures the main topic and key points. And if it presents them in a clear and logical order.\n 3. Assign a score for coherence on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 is the lowest and 5 is the highest based on the Evaluation Criteria.', 'metric_name': 'Coherence'}}
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
(llm_evaluator): Generator(
model_kwargs={'model': 'gpt-4o', 'n': 20, 'top_p': 1, 'max_tokens': 5, 'temperature': 1}, trainable_prompt_kwargs=[]
(prompt): Prompt(
template:
<START_OF_SYSTEM_PROMPT>
{# task desc #}
{{task_desc_str}}
---------------------
{# evaluation criteria #}
Evaluation Criteria:
{{evaluation_criteria_str}}
---------------------
{# evaluation steps #}
{% if evaluation_steps_str %}
Evaluation Steps:
{{evaluation_steps_str}}
---------------------
{% endif %}
{{input_str}}
{ # evaluation form #}
Evaluation Form (scores ONLY):
- {{metric_name}}:
Output the score only.
<END_OF_SYSTEM_PROMPT>
, prompt_variables: ['input_str', 'task_desc_str', 'evaluation_criteria_str', 'evaluation_steps_str', 'metric_name']
)
(model_client): OpenAIClient()
(output_processors): FloatParser()
)
)
训练/对齐LLM法官#
我们应该更好地将LLM评判器与包含(生成文本、真实文本、分数)三元组的人类偏好数据集对齐。
这个过程与优化任务管道相同,您可以创建一个AdalComponent并调用我们的Trainer来进行上下文学习。
从打印输出中,您可以观察到DefaultLLMJudge中的两个trainable_prompt_kwargs。
在这种情况下,我们可能想要计算人类评委和LLM评委之间的相关性评分。 你有多种选择,例如:
皮尔逊相关系数
来自ARES的Kendall秩相关系数 [14],特别适用于排名系统(检索)。
RAG评估#
RAG(检索增强生成)管道是检索器和生成器的组合。 检索器从大型语料库中检索相关上下文,生成器根据检索到的上下文生成最终答案。 当检索器未能检索到相关上下文时,生成器可能会失败。 因此,除了使用NLG指标整体评估RAG管道外,评估检索器并优化两个阶段的评估指标以最大程度地提高最终性能也很重要。
使用GT进行检索#
对于检索器来说,使用的指标并不新鲜,而是来自标准的信息检索/排名文献。 通常,我们有
Recall@k: 检索到的相关文档占所有相关文档总数的比例。
平均倒数排名(MRR@k), 命中率@k, 等。
NDCG@k
Precision@k, MAP@k 等。
有关这些指标的详细信息,请参阅[18]。 所有这些指标,您也可以在TorchMetrics中找到。
例如,如果提供了真实上下文,您可以使用以下代码片段来计算RAG管道检索器组件的recall@k,针对单个查询。 在此示例中,检索到的上下文是检索到的上下文块的连接字符串,而gt_contexts是每个查询的真实上下文块列表。
from adalflow.eval import RetrieverRecall, RetrieverRelevance
retrieved_contexts = [
"Apple is founded before Google.",
"Feburary has 28 days in common years. Feburary has 29 days in leap years. Feburary is the second month of the year.",
]
gt_contexts = [
[
"Apple is founded in 1976.",
"Google is founded in 1998.",
"Apple is founded before Google.",
],
["Feburary has 28 days in common years", "Feburary has 29 days in leap years"],
]
retriever_recall = RetrieverRecall()
avg_recall, recall_list = retriever_recall.compute(retrieved_contexts, gt_contexts) # Compute the recall of the retriever
print(f"Recall: {avg_recall}, Recall List: {recall_list}")
输出将是:
对于第一个查询,只有三个相关文档中的一个被检索到,导致召回率为0.33。 对于第二个查询,所有相关文档都被检索到,导致召回率为1.0。
没有gt_contexts#
RAGAS#
理想情况下,对于每个查询,我们将检索前k个(@k)块,并且为了获得上述分数,我们期望每个查询、检索到的块对都带有真实标签。 但这在语料库很大的情况下尤其不现实。 如果我们有100个测试查询,并且语料库包含1000个块,那么我们需要注释的对数是10^5。 有不同的策略来处理这个问题,但我们无法在这里深入探讨所有策略。
有一种新的方法是间接使用生成器的真实答案来评估检索器。 RAGAS 框架提供了一种实现这一目标的方法。
召回率 = [可归因于检索到的上下文的GT语句] / [GT语句]
在RAGAS中还有上下文相关性和上下文精确度指标。
基于LLM或模型的检索器召回判断#
使用上下文提示的LLM判断
LLM 判断直接以直观的方式即时评估前 k 个分数。
我们可以创建一个查询、检索块对的子集并手动标记它们,然后我们训练一个LLM判断器来预测分数。 如果判断器能够达到高准确率,那么我们就能够根据查询和检索到的块对来注释检索器中的任何指标。
使用合成数据微调分类器的ARES
ARES [14] 提出从领域内语料库中创建合成数据集。 生成的数据代表了查询-段落-答案三元组的正例和负例(例如,相关/不相关的段落和正确/错误的答案)。
合成数据集用于训练一个由嵌入和分类头组成的分类器。 它声称能够适应分类器未训练过的其他领域。 这种方法的成本相当低,因为你可以为每个查询和语料库中的每个块只计算一次嵌入。
用于垂直领域评估的RAGEval
RAGEVal [21] 提出了一个框架来合成垂直领域的评估数据集,如金融、医疗、法律等,由于隐私问题,创建大规模的真实世界数据集具有挑战性。
更多
查看数据集上的评估,请访问评估RAG管道。
此外,还有更多关于RAG评估的研究,例如SemScore [13]、ARES [14]、RGB [15]等。
注意
新加坡政府科技局提供了一个详细解释的评估指南[22],该指南与我们的指南一致,但在某些指标上提供了更多的理论解释。
贡献者指南#
AdalFlow 库中涵盖了太多的指标和评估方法。 我们鼓励从事评估研究和生产的贡献者构建与 AdalFlow 兼容的评估器。 这意味着:
评估器可能会输出一个在范围 [0, 1] 内的单一浮点分数,以便 AdalFlow Trainer 可以使用它来优化管道。
为了使用LLM作为评判者,评判者应该类似于DefaultLLMJudge构建,以便有trainable_prompt_kwargs,用户可以进一步将评判者与人类偏好数据集对齐。
例如,对于我们这里列出的研究论文,拥有一个与AdalFlow轻松兼容的版本将是非常好的。
参考文献#
AdalFlow Eval API 参考

