模型客户端#
ModelClient 是所有模型推理SDK(无论是通过API还是本地)与AdalFlow内部组件通信的标准化协议和基类。
因此,通过替换Generator、Embedder或Retriever(这些组件使用模型)中的ModelClient,您可以使这些功能组件与模型无关。
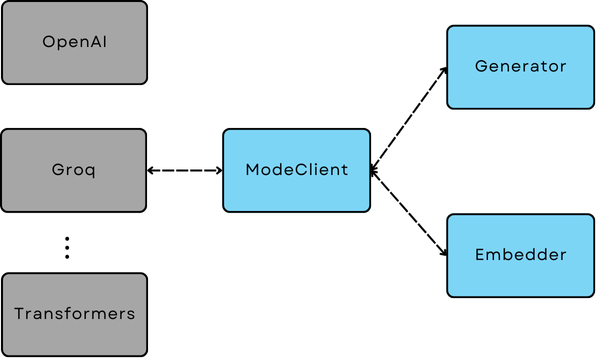
AdalFlow中所有模型推理SDK与内部组件之间的桥梁#
注意
鼓励所有用户在需要时自定义自己的ModelClient。您可以参考我们在components.model_client目录中的代码。
模型推理SDKs#
使用像OpenAI、Groq和Anthropic这样的云API提供商时,通常通过他们的SDK提供同步和异步客户端。 例如:
from openai import OpenAI, AsyncOpenAI
sync_client = OpenAI()
async_client = AsyncOpenAI()
# sync call using APIs
response = sync_client.chat.completions.create(...)
对于本地模型,例如使用huggingface transformers,你需要自己创建这些模型推理SDK。
你如何做到这一点非常灵活。
这里有一个使用本地嵌入模型(例如,thenlper/gte-base)作为模型的示例(详情请参阅TransformerEmbedder)。
它实际上只是普通的模型推理代码。
模型客户端协议#
模型客户端可用于管理不同类型的模型,我们定义了一个ModelType来对模型类型进行分类。
class ModelType(Enum):
EMBEDDER = auto()
LLM = auto()
RERANKER = auto()
UNDEFINED = auto()
我们在ModelClient类中设计了6个抽象方法,这些方法可以由子类实现,以与不同的模型推理SDK集成。
我们将使用OpenAIClient作为云API示例,并使用TransformersClient以及本地推理代码TransformerEmbedder作为本地模型客户端的示例。
首先,我们提供了两种方法,init_async_client 和 init_sync_client,供子类初始化SDK客户端。
你可以参考OpenAIClient来查看这些方法以及__init__方法的实现方式:
这是TransformerClient如何做同样的事情:
class TransformersClient(ModelClient):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.sync_client = self.init_sync_client()
self.async_client = None
support_model_list = {
"thenlper/gte-base": {
"type": ModelType.EMBEDDER,
}
}
def init_sync_client(self):
return TransformerEmbedder()
其次,我们使用convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs将AdalFlow输入转换为api_kwargs(SDK参数)。
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self,
input: Optional[Any] = None,
model_kwargs: Dict = {},
model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED,
) -> Dict:
raise NotImplementedError(
f"{type(self).__name__} must implement _combine_input_and_model_kwargs method"
)
这是OpenAIClient实现此方法的方式:
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self,
input: Optional[Any] = None,
model_kwargs: Dict = {},
model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED,
) -> Dict:
final_model_kwargs = model_kwargs.copy()
if model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER:
if isinstance(input, str):
input = [input]
# convert input to input
assert isinstance(input, Sequence), "input must be a sequence of text"
final_model_kwargs["input"] = input
elif model_type == ModelType.LLM:
messages: List[Dict[str, str]] = []
if input is not None and input != "":
messages.append({"role": "system", "content": input})
assert isinstance(
messages, Sequence
), "input must be a sequence of messages"
final_model_kwargs["messages"] = messages
else:
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
return final_model_kwargs
对于嵌入,由于Embedder接受str和List[str]作为输入,我们需要将输入转换为SDK可接受的字符串列表。
对于LLM,由于Generator将接受一个prompt_kwargs`(dict)并将其转换为单个字符串,因此我们需要将输入转换为消息列表。
对于Rerankers,您可以参考:class:`CohereAPIClient
这是TransformerClient如何做同样的事情:
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self,
input: Any,
model_kwargs: dict = {},
model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED,
) -> dict:
final_model_kwargs = model_kwargs.copy()
if model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER:
final_model_kwargs["input"] = input
return final_model_kwargs
else:
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
此外,您可以添加任何将SDK特定输出解析为与AdalFlow组件兼容的格式的方法。
通常,LLM需要使用parse_chat_completion将完成解析为文本,并使用parse_embedding_response将嵌入响应解析为AdalFlow组件可以理解的结构。
您可以参考OpenAIClient进行API嵌入模型集成,并参考TransformersClient进行本地嵌入模型集成。
最后,call 和 acall 方法用于通过它们自己的参数调用模型推理。 我们鼓励子类在这些方法中提供错误处理和重试机制。
OpenAIClient 示例:
def call(self, api_kwargs: Dict = {}, model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED):
if model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER:
return self.sync_client.embeddings.create(**api_kwargs)
elif model_type == ModelType.LLM:
return self.sync_client.chat.completions.create(**api_kwargs)
else:
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
TransformerClient 示例:
def call(self, api_kwargs: Dict = {}, model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED):
return self.sync_client(**api_kwargs)
我们的库目前集成了六个提供商:OpenAI、Groq、Anthropic、Huggingface、Google 和 Cohere。 请查看 ModelClient Integration。
直接使用ModelClient#
虽然ModelClient通常在Generator、Embedder或Retriever组件中管理,但如果你计划编写自己的组件,可以直接使用它。
这里有一个直接使用OpenAIClient的示例,首先是在LLM模型上:
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
setup_env()
openai_client = OpenAIClient()
query = "What is the capital of France?"
# try LLM model
model_type = ModelType.LLM
prompt = f"User: {query}\n"
model_kwargs = {"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(input=prompt,
model_kwargs=model_kwargs,
model_type=model_type)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
response = openai_client.call(api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
response_text = openai_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
print(f"response_text: {response_text}")
输出将是:
api_kwargs: {'model': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'temperature': 0.5, 'max_tokens': 100, 'messages': [{'role': 'system', 'content': 'User: What is the capital of France?\n'}]}
response_text: The capital of France is Paris.
然后在嵌入模型上:
# try embedding model
model_type = ModelType.EMBEDDER
# do batch embedding
input = [query] * 2
model_kwargs = {"model": "text-embedding-3-small", "dimensions": 8, "encoding_format": "float"}
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(input=input, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
response = openai_client.call(api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
reponse_embedder_output = openai_client.parse_embedding_response(response)
print(f"reponse_embedder_output: {reponse_embedder_output}")
输出将是:
api_kwargs: {'model': 'text-embedding-3-small', 'dimensions': 8, 'encoding_format': 'float', 'input': ['What is the capital of France?', 'What is the capital of France?']}
reponse_embedder_output: EmbedderOutput(data=[Embedding(embedding=[0.6175549, 0.24047995, 0.4509756, 0.37041178, -0.33437008, -0.050995983, -0.24366009, 0.21549304], index=0), Embedding(embedding=[0.6175549, 0.24047995, 0.4509756, 0.37041178, -0.33437008, -0.050995983, -0.24366009, 0.21549304], index=1)], model='text-embedding-3-small', usage=Usage(prompt_tokens=14, total_tokens=14), error=None, raw_response=None)
OPENAI EMBEDDER - 嵌入处理示例#
在这个例子中,我们使用一组嵌入来展示不同的功能,例如计算语义相似性、查找最近邻和平均嵌入。以下是用于实现这些任务的Python代码:
from typing import List
import numpy as np
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType, EmbedderOutput
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
from numpy.linalg import norm
数据类
我们使用两种数据类类型来构建收集和使用数据的结构:
EmbeddingCollection: 存储单个嵌入集合及其对应的索引。 用法: 跟踪令牌使用情况,例如prompt_tokens和total_tokens。
@dataclass
class EmbeddingCollection:
collection: List[float]
cindex: int
@dataclass
class Usage:
prompt_tokens: int
total_tokens: int
以下函数 get_openai_embedding 向 OpenAI API 发送请求以获取给定文本的嵌入。它将模型类型设置为 EMBEDDER,准备所需的模型特定参数,并处理响应:
openai_client = OpenAIClient()
def get_openai_embedding(text):
# Set model type to EMBEDDER for embedding functionality
model_type = ModelType.EMBEDDER
# Prepare input and model-specific parameters
input = text
model_kwargs = {
"model": "text-embedding-3-small",
"dimensions": 8,
"encoding_format": "float",
}
# Convert inputs to the required API format
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=input, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=model_type
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Debug output to verify API arguments
# Call OpenAI API and parse response for embeddings
response = openai_client.call(api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
reponse_embedder_output = openai_client.parse_embedding_response(response)
print(
f"reponse_embedder_output: {reponse_embedder_output}"
) # Debug output to verify embeddings
return reponse_embedder_output
嵌入处理
函数 process_embeddings 接收一组嵌入,并提供计算相似性、平均嵌入和查找最近邻的工具:
相似度:测量两个嵌入之间的余弦相似度。 平均嵌入:计算一组嵌入的平均嵌入。 最近邻:基于余弦相似度识别前k个最近邻。
def process_embeddings(embeddings_collection):
# Extract embedding data for each item in the collection
embeddingOutput = [emb.collection for emb in embeddings_collection]
embeddingDataList = [each_emb_out.data for each_emb_out in embeddingOutput]
embeddingList = [
each_item.embedding
for each_emb_data in embeddingDataList
for each_item in each_emb_data
]
# Convert to numpy array for easier manipulation and calculations
embeddings_array = np.array(embeddingList)
def calculate_similarity(emb1, emb2):
# Compute cosine similarity between two embeddings
return np.dot(emb1, emb2) / (norm(emb1) * norm(emb2))
def get_average_embedding(embeddings_list):
# Calculate the mean embedding across a list of embeddings
return np.mean(embeddings_list, axis=0)
def find_nearest_neighbors(
query_index: int, embedding_list: List[List[float]], k: int = 5
):
# Find top-k most similar embeddings to a query embedding, based on cosine similarity
query_embedding = embedding_list[query_index]
similarities = [
(i, calculate_similarity(query_embedding, emb))
for i, emb in enumerate(embedding_list)
if i != query_index
]
return sorted(similarities, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:k]
# Return dictionary of functions and processed data for further use
return {
"embeddings_array": embeddings_array,
"calculate_similarity": calculate_similarity,
"average_embedding": get_average_embedding,
"find_nearest_neighbors": find_nearest_neighbors,
}
函数 demonstrate_embeddings_usage 展示了如何分析语义相似性、查找最近邻以及计算样本文本的平均嵌入。它选择随机文本,比较它们的相似性,查找特定查询的最近邻,并比较包含“Paris”的文本的平均嵌入。
# Demonstrate embeddings usage with sample data
def demonstrate_embeddings_usage(sample_embeddings, input_text_list):
# Initialize processor and retrieve embeddings array
processor = process_embeddings(sample_embeddings)
embeddings = processor["embeddings_array"]
print("1. Analyzing Semantic Similarities:")
print("-" * 50)
# Select a few random indices for similarity testing
num_indices = 5
assert len(input_text_list) == len(embeddings)
indices = np.random.choice(len(input_text_list), num_indices, replace=False)
selected_text = np.array(input_text_list)[indices]
selected_embeddings = np.array(embeddings)[indices]
# Display selected texts and their embeddings
print("Selected indices:", indices)
print("Selected elements from array1:", selected_text)
print("Selected elements from array2:", selected_embeddings)
# Calculate similarity between each pair of selected texts
for i in range(len(selected_text)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(selected_text)):
similarity = processor["calculate_similarity"](
selected_embeddings[i], selected_embeddings[j]
)
print(f"\nComparing:\n'{selected_text[i]}' \nwith:\n'{selected_text[j]}'")
print(f"Similarity score: {similarity:.4f}")
print("\n2. Finding Nearest Neighbors:")
print("-" * 50)
# Find and display the 3 nearest neighbors for the first text
query_idx = 0
neighbors = processor["find_nearest_neighbors"](query_idx, embeddings, k=3)
print(f"\nQuery text: '{input_text_list[query_idx]}'")
print("\nNearest neighbors:")
for idx, similarity in neighbors:
print(f"- '{input_text_list[idx]}' (similarity: {similarity:.4f})")
print("\n3. Using Average Embeddings:")
print("-" * 50)
# Calculate and compare the average embedding for texts containing "Paris"
paris_indices = [i for i, text in enumerate(input_text_list) if "Paris" in text]
paris_embeddings = embeddings[paris_indices]
avg_paris_embedding = processor["average_embedding"](paris_embeddings)
print("\nComparing average 'Paris' embedding with all texts:")
for i, text in enumerate(input_text_list):
similarity = processor["calculate_similarity"](
avg_paris_embedding, embeddings[i]
)
print(f"- '{text}' (similarity: {similarity:.4f})")
运行模型客户端
最后,我们通过初始化一组样本文本、生成它们的嵌入,并使用嵌入处理函数来分析相似性和邻居来运行模型客户端。
def run_model_client_embedding_usage():
# Define a set of sample texts to test embedding and similarity functionalities
sample_texts = [
"What is the capital of France?",
"Paris is the capital of France.",
"What is the population of France?",
"How big is Paris?",
"What is the weather like in Paris?",
]
# Duplicate each sample text to form an input list with repeated entries (for embedding testing)
input_text_list = [text for text in sample_texts for _ in range(2)]
# Generate embeddings for each text in the input list, and store them in an EmbeddingCollection
embeddings_collection = [
EmbeddingCollection(collection=get_openai_embedding(text), cindex=i)
for i, text in enumerate(input_text_list)
]
print(
embeddings_collection
) # Debugging output to verify embeddings collection content
# Demonstrate the usage of embeddings by analyzing similarities, finding neighbors, etc.
demonstrate_embeddings_usage(embeddings_collection, input_text_list)
要执行完整的示例,只需调用run_model_client_embedding_usage()函数:
run_model_client_embedding_usage()
这将触发嵌入检索和处理功能,您将看到打印出的结果,展示如何使用嵌入进行相似性分析、邻居查找和平均。
OPENAI LLM 聊天 - 多聊天使用#
此示例演示了如何使用OpenAI的LLM与adalflow创建一个多聊天系统,其中助手的响应依赖于整个对话历史。这使得对话流程更加动态和上下文感知。
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
from typing import List, Dict
聊天对话类
在这里,我们定义了一个ChatConversation类来管理对话历史并向OpenAI模型进行API调用。助手的响应是基于整个对话历史生成的。
class ChatConversation:
def __init__(self):
# Initialize the OpenAI client for managing API calls
self.openai_client = OpenAIClient()
# Initialize an empty conversation history to store chat messages
self.conversation_history: str = ""
# Model parameters to customize the API call
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"temperature": 0.5, # Controls randomness; 0.5 for balanced responses
"max_tokens": 100, # Limits the response length
}
def add_user_message(self, message: str):
"""Add a user message to the conversation history"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<USER> {message} </USER>" # Format for user message
)
def add_assistant_message(self, message: str):
"""Add an assistant message to the conversation history"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<ASSISTANT> {message} </ASSISTANT>" # Format for assistant message
)
def get_response(self) -> str:
"""Get response from the model based on conversation history"""
# Convert the conversation history and model parameters into API arguments
api_kwargs = self.openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=self.conversation_history,
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs,
model_type=ModelType.LLM,
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Debugging output to verify API parameters
# Call the API with the generated arguments to get a response
response = self.openai_client.call(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.LLM
)
print("response: ", response) # Debugging output for raw API response
# Extract and parse the text response from the API output
response_text = self.openai_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
# Update conversation history with the assistant's response
self.add_assistant_message(response_text)
return response_text # Return the assistant's response to the caller
模拟多轮对话
在check_chat_conversation()函数中,我们通过遍历用户问题列表来模拟多轮对话。每个问题都会被添加到对话历史中,助手会根据累积的对话上下文进行响应。
def check_chat_conversation():
# Initialize a new chat conversation
chat = ChatConversation()
# Example list of user questions to simulate a multi-turn conversation
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?",
"What is its population?",
"Tell me about its famous landmarks",
]
# Iterate through each question in the list
for question in questions:
print(f"\nUser: {question}") # Display the user's question
chat.add_user_message(
question
) # Add the user question to the conversation history
response = (
chat.get_response()
) # Get assistant's response based on conversation history
print(f"Assistant: {response}") # Display the assistant's response
# Display the full conversation history after all exchanges
print("\nFull Conversation History:")
print(chat.conversation_history) # Print the accumulated conversation history
关键点 你可以观察到每个问题都依赖于前一个问题,聊天以适当的方式回应 check_chat_conversation()
OPENAI LLM 聊天 - 多聊天使用 - 异步#
此示例演示了如何使用adalflow与OpenAI的LLM创建一个异步多聊天系统。异步方法允许并行处理多个问题,使得在处理不相关的查询时交互更加高效。
import asyncio
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from typing import List
ChatConversationAsync 类
ChatConversationAsync 类旨在处理对 OpenAI 模型的异步 API 调用。它支持并发请求,从而在同时与多个问题交互时提高性能。
class ChatConversationAsync:
def __init__(self):
# Initialize with an asynchronous OpenAI client
self.openai_client = OpenAIClient()
# Default model parameters for the chat
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Model used for chat
"temperature": 0.5, # Controls randomness in response
"max_tokens": 100, # Maximum tokens in the generated response
}
async def get_response(self, message: str) -> str:
"""Asynchronously get a response from the model for a given user message"""
# Convert input message and model parameters into the format expected by the API
api_kwargs = self.openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=message, # User's message input
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs, # Model-specific settings
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type as a language model (LLM)
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Log the API arguments for debugging
# Make an asynchronous API call to OpenAI's model
response = await self.openai_client.acall(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Pass the prepared arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type again
)
print("response: ", response) # Print the raw response from the API
# Parse the API response to extract the assistant's reply (chat completion)
response_text = self.openai_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
return response_text # Return the parsed response text
运行多个异步聊天会话
在check_chat_conversations_async()函数中,我们同时处理一系列不相关的用户问题。这是通过创建一系列异步任务并收集它们的响应来完成的。
async def check_chat_conversations_async():
# Create an instance of ChatConversationAsync to handle asynchronous operations
chat = ChatConversationAsync()
# List of unrelated questions that will be handled in parallel
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?", # Question 1
"Is dog a wild animal?", # Question 2
"Tell me about amazon forest", # Question 3
]
# Create a list of asynchronous tasks, one for each question
# Each task calls the get_response method asynchronously for a question
tasks = [chat.get_response(question) for question in questions]
# Gather the results of all asynchronous tasks concurrently
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Print the responses from the assistant along with the respective user questions
for question, response in zip(questions, responses):
print(f"\nUser: {question}")
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
运行异步函数
要执行异步函数,您可以根据您的环境使用以下方法:
# Run the asynchronous function if in a file
# asyncio.run(check_chat_conversations_async())
# in jupyter notebook
await check_chat_conversations_async()
这种方法允许您同时处理多个独立的对话,从而提高系统的性能和响应能力。
OPENAI LLM 聊天 - 多聊天使用 - 基准测试 sync() 对比 async()#
本节比较了同步(call())与异步(acall())API调用OpenAI语言模型的性能,使用示例提示进行基准测试,以确定哪种方法在处理多个API请求时更高效。
import asyncio
import time
from adalflow.components.model_client import (
OpenAIClient,
) # Assuming OpenAIClient with .call() and .acall() is available
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
基准测试设置
我们初始化OpenAI客户端并设置一个示例提示来测试同步和异步API调用。
# Initialize the OpenAI client
openai_client = OpenAIClient()
# Sample prompt for testing
prompt = "Tell me a joke."
model_kwargs = {"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
同步基准测试
benchmark_sync_call 函数多次运行同步的 .call() 方法,并测量所有请求所花费的总时间。
# Synchronous function for benchmarking .call()
def benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs, runs=10):
"""
Benchmark the synchronous .call() method by running it multiple times.
Parameters:
- api_kwargs: The arguments to be passed to the API call
- runs: The number of times to run the call (default is 10)
"""
# List to store responses
responses = []
# Record the start time of the benchmark
start_time = time.time()
# Perform synchronous API calls for the specified number of runs
responses = [
openai_client.call(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Model type (e.g., LLM for language models)
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat 'runs' times
]
# Record the end time after all calls are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Output the results of each synchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"sync call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for all synchronous calls
print(f"\nSynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
# Asynchronous function for benchmarking .acall()
async def benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs, runs=10):
"""
Benchmark the asynchronous .acall() method by running it multiple times concurrently.
Parameters:
- api_kwargs: The arguments to be passed to the API call
- runs: The number of times to run the asynchronous call (default is 10)
"""
# Record the start time of the benchmark
start_time = time.time()
# Create a list of asynchronous tasks for the specified number of runs
tasks = [
openai_client.acall(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Model type (e.g., LLM for language models)
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat 'runs' times
]
# Execute all tasks concurrently and wait for them to finish
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Record the end time after all tasks are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Output the results of each asynchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"Async call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for all asynchronous calls
print(f"\nAsynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=prompt, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.LLM
)
# Run both benchmarks
print("Starting synchronous benchmark...\n")
benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs)
# Run the asynchronous function if in a file
# asyncio.run(benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs))
print("\nStarting asynchronous benchmark...\n")
await benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs)
OPENAI LLM 聊天 - 附加工具#
本节展示了如何使用OpenAI语言模型客户端的额外实用函数。包含以下实用函数:
get_first_message_content()get_all_messages_content()get_probabilities()
这些实用程序可以用于以各种方式与OpenAI模型进行交互,例如提取第一条消息内容、从多聊天场景中检索所有消息内容以及计算标记的概率。
代码设置
首先,我们导入必要的组件以利用OpenAI客户端和adalflow库中的实用工具。
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
from adalflow.components.model_client.openai_client import (
get_first_message_content,
get_all_messages_content,
get_probabilities,
)
from adalflow.core import Generator
函数: check_openai_additional_utils
此函数展示了如何根据给定的查询和实用函数,使用OpenAI客户端以及自定义实用函数从模型生成响应。
def check_openai_additional_utils(func, model_kwargs):
"""
This function demonstrates the usage of the OpenAI client and a custom utility function
for generating responses from the LLM model, based on the given query in openai client.
Parameters:
- func: A function that will be used to parse the chat completion (for custom parsing).
- model_kwargs: The additional model parameters (e.g., temperature, max_tokens) to be used in the model.
Returns:
- output: The generated response from the model based on the query.
"""
# Initialize the OpenAI client with a custom chat completion parser
openai_client = OpenAIClient(chat_completion_parser=func)
# Define a sample query (user question)
query = "What is the capital of France?"
# Set the model type to LLM (Large Language Model)
model_type = ModelType.LLM
# Create the prompt by formatting the user query as a conversation
prompt = f"User: {query}\n"
# Define any additional parameters needed for the model (e.g., the input string)
prompt_kwargs = {
"input_str": "What is the capital of France?",
}
# Initialize the Generator with the OpenAI client and model parameters
generator = Generator(model_client=openai_client, model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
# Execute the generator to get a response for the prompt (using the defined prompt_kwargs)
output = generator(prompt_kwargs=prompt_kwargs)
# Return the generated output (response from the LLM)
return output
函数: run_utils_functions
此函数使用不同的模型配置运行一系列实用函数以生成响应。它展示了如何使用各种实用函数检查OpenAI模型的输出。
def run_utils_functions():
"""
This function runs a series of utility functions using different model
configurations for generating responses. It demonstrates how to check
OpenAI model outputs using various utility functions.
"""
# Define the model arguments for the probability-based function (with logprobs)
probability_model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Specify the model version
"logprobs": True, # Enable logprobs to get probability distributions for tokens
"n": 2, # Request 2 different completions for each query
}
# Define general model arguments for most other functions
model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Specify the model version
"temperature": 0.5, # Control the randomness of responses (0 is deterministic)
"max_tokens": 100, # Set the maximum number of tokens (words) in the response
}
# List of functions to run with corresponding model arguments
func_list = [
[
get_probabilities,
probability_model_kwargs,
], # Function to get probabilities with specific kwargs
[
get_first_message_content,
model_kwargs,
], # Function to get first message content
[
get_all_messages_content,
model_kwargs,
], # Function to get all messages content in multi-chat scenarios
]
# Loop through each function and its corresponding arguments
for each_func in func_list:
# Check the function output using the specified arguments
result = check_openai_additional_utils(each_func[0], each_func[1])
# Print the function and result for debugging purposes
print(f"Function: {each_func[0].__name__}, Model Args: {each_func[1]}")
print(f"Result: {result}")
运行实用函数
要执行实用函数,我们调用run_utils_functions()方法,该方法运行定义的函数并打印它们的结果。
run_utils_functions()
目的和用途
这些实用工具(get_first_message_content, get_all_messages_content, 和 get_probabilities)允许用户从OpenAI LLM的响应中提取特定信息,例如聊天中的单个消息内容或令牌上的概率分布。
Groq LLM 聊天 - 多聊天使用#
注意:Groq没有像openai那样的嵌入方法来获取嵌入
以下示例演示了如何使用GroqAPIClient设置与Groq LLM的多轮对话。
from adalflow.components.model_client import GroqAPIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
from typing import List, Dict
聊天对话类
该类通过与Groq模型交互来处理对话流程,跟踪对话历史记录,并生成响应。
class ChatConversation:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize a new ChatConversation object.
- GroqAPIClient is used to interact with the Groq model.
- conversation_history keeps track of the conversation between the user and assistant.
- model_kwargs contains the model parameters like temperature and max tokens.
"""
self.groq_client = (
GroqAPIClient()
) # Initialize GroqAPIClient for model interaction
self.conversation_history: str = (
"" # Initialize conversation history as an empty string
)
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "llama3-8b-8192", # Specify the model to use
"temperature": 0.5, # Set the temperature for response variability
"max_tokens": 100, # Limit the number of tokens in the response
}
def add_user_message(self, message: str):
"""
Add a user message to the conversation history in the required format.
The message is wrapped with <USER> tags for better processing by the assistant.
"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<USER> {message} </USER>" # Append user message to history
)
def add_assistant_message(self, message: str):
"""
Add an assistant message to the conversation history in the required format.
The message is wrapped with <ASSISTANT> tags for better processing.
"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<ASSISTANT> {message} </ASSISTANT>" # Append assistant message to history
)
def get_response(self) -> str:
"""
Generate a response from the assistant based on the conversation history.
- Converts the conversation history and model kwargs into the format required by the Groq API.
- Calls the API to get the response.
- Parses and adds the assistant's reply to the conversation history.
"""
# Prepare the request for the Groq API, converting the inputs into the correct format
api_kwargs = self.groq_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=self.conversation_history, # Use the conversation history as input
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs, # Include model-specific parameters
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type (Large Language Model)
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Log the API request parameters
# Call the Groq model API to get the response
response = self.groq_client.call(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs,
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type again for clarity
)
print("response: ", response) # Log the API response
# Parse the response to extract the assistant's reply
response_text = self.groq_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
# Add the assistant's message to the conversation history
self.add_assistant_message(response_text)
# Return the assistant's response text
return response_text
示例多轮对话
以下函数模拟了一个多轮对话,用户提出一系列问题,助手进行回应。它展示了如何处理用户输入,并在保持对话历史的同时生成响应。
def check_chat_conversation():
"""
This function simulates a multi-turn conversation between a user and an assistant.
It demonstrates how user inputs are processed, and the assistant generates responses,
while maintaining the conversation history for each query.
"""
# Initialize the ChatConversation object
chat = ChatConversation() # This creates an instance of the ChatConversation class
# Define a list of user questions for a multi-turn conversation
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?", # First user question
"What is its population?", # Second user question
"Tell me about its famous landmarks", # Third user question
]
# Loop through each question and get the assistant's response
for question in questions:
# Print the current question from the user
print(f"\nUser: {question}")
# Add the user's message to the conversation history
chat.add_user_message(question)
# Get the assistant's response based on the conversation history
response = chat.get_response()
# Print the assistant's response
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
# After the conversation, print the full conversation history
print("\nFull Conversation History:")
print(
chat.conversation_history
) # This will print all messages (user and assistant) in the conversation history
运行以下内容以使用 groq_client 的多聊天功能
check_chat_conversation()
Groq LLM 聊天 - 多聊天使用 - 异步#
这个示例演示了如何使用异步调用来与Groq LLM进行多轮对话。它使用Python的asyncio来同时处理多个独立的请求。
import asyncio
from adalflow.components.model_client import GroqAPIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from typing import List
聊天对话类
该类允许您与Groq模型进行异步交互。get_response方法从模型中异步获取单个用户输入的响应。
class ChatConversation:
def __init__(self):
# Using an asynchronous client for communication with GroqAPI
self.groq_client = GroqAPIClient() # Create an instance of GroqAPIClient
# Model configuration parameters (e.g., Llama model with 8b parameters and 8192 context length)
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "llama3-8b-8192", # Llama model with specific size
"temperature": 0.5, # Degree of randomness in the model's responses
"max_tokens": 100, # Maximum number of tokens in the response
}
async def get_response(self, message: str) -> str:
"""Get response from the model for a single message asynchronously"""
# Convert the user input message to the appropriate format for the Groq API
api_kwargs = self.groq_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=message, # User's input message
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs, # Model parameters
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Model type for large language models (LLM)
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Print the API arguments for debugging
# Asynchronously call the Groq API with the provided API arguments
response = await self.groq_client.acall(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Pass the API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type
)
print("response: ", response) # Print the API response for debugging
# Parse the response to extract the assistant's reply from the API response
response_text = self.groq_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
return response_text # Return the assistant's response text
异步多轮对话示例
以下函数展示了如何处理多个独立问题的异步操作。每个问题都是并发处理的,并使用asyncio.gather收集它们的响应。
async def check_chat_conversations():
# Create an instance of ChatConversation
chat = ChatConversation()
# List of unrelated questions for independent async calls
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?",
"Is dog a wild animal ?",
"Tell me about amazon forest",
]
# Run each question as an independent asynchronous task
tasks = [chat.get_response(question) for question in questions]
# Gather all the responses concurrently
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Display each response alongside the question
for question, response in zip(questions, responses):
print(f"\nUser: {question}")
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
要执行该函数,请运行以下内容:
# Run the asynchronous function if in a file
# asyncio.run(check_chat_conversations())
await check_chat_conversations()
Groq LLM 聊天 - 多聊天使用 - 基准测试 sync() 与 async()#
此示例演示了如何使用Groq对同步.call()方法与异步.acall()方法进行基准测试,以比较同步和异步执行多个API请求所需的时间。
import asyncio
import time
from adalflow.components.model_client import (
GroqAPIClient,
) # Assuming GroqAPI with .call() and .acall() is available
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
初始化
以下代码初始化了Groq客户端,并设置了用于测试的示例提示和模型参数。
# Initialize the Groq client
groq_client = GroqAPIClient()
# Sample prompt for testing
prompt = "Tell me a joke."
model_kwargs = {"model": "llama3-8b-8192", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
基准测试同步 .call() 方法
此函数通过多次同步调用Groq API来对同步.call()方法进行基准测试。
# Synchronous function for benchmarking .call()
def benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs, runs=10):
# List to store responses from each synchronous call
responses = []
# Record the start time for benchmarking
start_time = time.time()
# Perform synchronous API calls in a loop
responses = [
groq_client.call( # Calling the API synchronously
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Passing the API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Defining the model type
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat the call 'runs' times
]
# Record the end time after all calls are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Print out the response from each synchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"sync call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for the synchronous benchmark
print(f"\nSynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
基准测试异步 .acall() 方法
这个异步函数通过使用asyncio.gather()多次异步调用Groq API来对.acall()方法进行基准测试,以并发执行任务。
# Asynchronous function for benchmarking .acall()
async def benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs, runs=10):
# Record the start time for benchmarking
start_time = time.time()
# Create a list of tasks for asynchronous API calls
tasks = [
groq_client.acall( # Calling the API asynchronously
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Passing the API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Defining the model type
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat the call 'runs' times
]
# Await the completion of all tasks concurrently
responses = await asyncio.gather(
*tasks
) # Gather all the responses from asynchronous calls
# Record the end time after all asynchronous calls are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Print out the response from each asynchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"Async call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for the asynchronous benchmark
print(f"\nAsynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
运行基准测试
以下代码设置了API参数并运行了同步和异步基准测试。
api_kwargs = groq_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=prompt, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.LLM
)
# Run both benchmarks
print("Starting synchronous benchmark...\n")
benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs)
print("\nStarting asynchronous benchmark...\n")
await benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs)
构建自定义模型客户端#
构建一个同步API调用
注意:我正在使用openai api作为示例来在adalflow中构建自定义模型客户端。尽管adalflow仓库中已经存在,下面的代码绝对会成为任何想要构建自定义模型客户端的人的入门代码。
# Building simple custom third party model client and using it
# I have modified convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs() to make sure it follows the prompt of openai and i have used appropiate
# openai api call in __call__()
import openai
from adalflow.core.model_client import ModelClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType, GeneratorOutput, EmbedderOutput
from openai.types import (
CreateEmbeddingResponse,
)
from adalflow.components.model_client.utils import parse_embedding_response
此类定义了自定义模型客户端。构造函数通过调用父类的初始化器(ModelClient)来初始化客户端,这对于Adalflow框架的设置至关重要。
class SimpleCustomModelClient(ModelClient):
# Initialize the custom model client
def __init__(self):
# Call the parent class's initializer
super().__init__()
pass # Placeholder for any initialization logic if needed in the future
# Method to convert input into API parameters for different model types (LLM or Embedder)
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self, input=None, model_kwargs={}, model_type=ModelType.UNDEFINED
):
"""
Convert the inputs into API arguments based on the model type.
Args:
input (str): The input text to be processed.
model_kwargs (dict): Additional model parameters like temperature, max_tokens, etc.
model_type (ModelType): The type of model to use (LLM or Embedder).
Returns:
dict: API arguments formatted for the specified model type.
"""
if (
model_type == ModelType.LLM
): # If the model type is a large language model (LLM)
return {
"model": model_kwargs[
"model"
], # Set the model to use (e.g., GPT-3, GPT-4)
"messages": input, # Provide the input as the message
"temperature": model_kwargs[
"temperature"
], # Set the temperature (creativity of the response)
"max_tokens": model_kwargs[
"max_tokens"
], # Max tokens to generate in the response
}
elif model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER: # If the model type is an embedder
return {
"model": model_kwargs["model"], # Model name for embedding
"input": [input], # Provide the input in a list format for embedding
}
else:
# Raise an error if the model type is unsupported
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
# Method to make the actual API call to OpenAI for either completions (LLM) or embeddings
def call(self, api_kwargs={}, model_type=ModelType.UNDEFINED):
"""
Call the appropriate OpenAI API method based on the model type (LLM or Embedder).
Args:
api_kwargs (dict): Arguments to be passed to the API call.
model_type (ModelType): The type of model (LLM or Embedder).
Returns:
Response: The API response from OpenAI.
"""
if model_type == ModelType.LLM: # If the model type is LLM (e.g., GPT-3, GPT-4)
return openai.chat.completions.create(
**api_kwargs
) # Call the chat API for completion
elif model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER: # If the model type is Embedder
return openai.embeddings.create(**api_kwargs) # Call the embedding API
else:
# Raise an error if an invalid model type is passed
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported model type: {model_type}")
# Method to parse the response from a chat completion API call
def parse_chat_completion(self, completion):
"""
Parse the response from a chat completion API call into a custom output format.
Args:
completion: The completion response from the OpenAI API.
Returns:
GeneratorOutput: A custom data structure containing the parsed response.
"""
# Note: GeneratorOutput is a adalflow dataclass that contains the parsed completion data
return GeneratorOutput(
data=completion, # Store the raw completion data
error=None, # No error in this case
raw_response=str(completion), # Store the raw response as a string
)
# Method to parse the response from an embedding API call
def parse_embedding_response(
self, response: CreateEmbeddingResponse
) -> EmbedderOutput:
"""
Parse the response from an embedding API call into a custom output format.
Args:
response (CreateEmbeddingResponse): The response from the embedding API.
Returns:
EmbedderOutput: A custom data structure containing the parsed embedding response.
"""
try:
# Attempt to parse the embedding response using a helper function
return parse_embedding_response(response)
except Exception as e:
# If parsing fails, return an error message with the raw response
return EmbedderOutput(data=[], error=str(e), raw_response=response)
在下面的代码块中,自定义模型客户端被实例化,并定义了一个查询,以便由LLM(如GPT-3.5)和Embedder模型处理。API参数被转换,并使用call()方法来获取响应。最后,两种类型的响应(LLM和Embedder)被解析并打印出来。
def build_custom_model_client():
# Instantiate the custom model client (SimpleCustomModelClient)
custom_client = SimpleCustomModelClient()
# Define the query for the model to process
query = "What is the capital of France?"
# Set the model type for a Large Language Model (LLM)
model_type = ModelType.LLM
# Prepare the message prompt as expected by the OpenAI chat API.
# This format is suitable for GPT-like models (e.g., gpt-3.5-turbo).
message_prompt = [
{
"role": "user", # Define the user role in the conversation
"content": [
{
"type": "text", # Specify that the input is a text type
"text": query, # The actual query to be processed by the model
}
],
}
]
# Print message indicating the usage of the LLM model type
print("ModelType LLM")
# Define additional model parameters like model name, temperature, and max tokens for LLM
model_kwargs = {"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
# Convert the input message and model kwargs into the required API parameters
api_kwargs = custom_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=message_prompt, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=model_type
)
# Print the API arguments that will be passed to the call method
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
# Call the LLM model using the prepared API arguments
result = custom_client.call(api_kwargs, ModelType.LLM)
# Print the result of the LLM model call (response from OpenAI)
print(result)
# Parse the chat completion response and output a more structured result
response_text = custom_client.parse_chat_completion(result)
# Print the structured response from the chat completion
print(f"response_text: {response_text}")
# Switch to using the Embedder model type
print("ModelType EMBEDDER")
# Define model-specific parameters for the embedding model
model_kwargs = {
"model": "text-embedding-3-small",
"dimensions": 8,
"encoding_format": "float",
}
# Convert the input query for the embedder model
api_kwargs = custom_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=query, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.EMBEDDER
)
# Print the API arguments that will be passed to the embedder model
print(f"embedder api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
# Call the Embedder model using the prepared API arguments
result = custom_client.call(api_kwargs, ModelType.EMBEDDER)
# Print the result of the Embedder model call (embedding response)
print(result)
# Parse the embedding response and output a more structured result
response_text = custom_client.parse_embedding_response(result)
# Print the structured response from the embedding model
print(f"response_text: {response_text}")
这是触发自定义模型客户端执行的函数调用,处理定义的查询并显示LLM和Embedder的结果。
build_custom_model_client()

