操作指南系列
通过API端点桥接访问远程资产#
预计阅读时间:20分钟
简介:访问远程资产#
欢迎阅读我们关于通过API端点桥接访问远程资产的指南。
如果您的数据存储在云端或具有公开API的内部平台上,在将数据迁移或复制到PySyft Datasite时可能会遇到挑战和效率低下的问题。
本教程将演示如何利用存储在外部数据仓库或平台(如各种云服务提供的)中的数据集,通过PySyft为外部研究人员提供便捷访问。我们将展示如何通过API端点桥接实现更可控、高效的信息流动,这比直接API访问更具优势。
这种方法不仅简化了数据访问流程,还增强了数据安全性并确保合规性。
它是如何工作的?#
首先,PySyft如何与远程资产协同工作?
PySyft 允许管理员定义自定义API端点,这些端点可以扩展其PySyft数据站点的功能,研究人员可以通过Python syft客户端无缝使用这些功能。
这些端点充当连接外部服务的桥梁,例如存储数据的云平台,只要它们暴露了我们的服务器可以与之通信的API接口。
定义这样的端点可以按如下方式进行:
MY_API_KEY="*****"
@sy.api_endpoint(
path="my_org.query",
description="This is an example endpoint.",
settings={"key": MY_API_KEY}
)
def execute_query(
context,
query: str,
) -> Any:
aws_client = ...
result = aws_client(query)
... # apply post-processing, error handling
return processed_result
这意味着研究人员可以通过他们的客户端访问此端点,甚至将其作为syft函数的一部分使用:
ds_client.api.services.my_org.execute_query(query="SELECT * from table limit 10")
此类API桥接使研究人员能够通过PySyft访问数据所属组织的外部API
"但现在呢?",你可能会问。
如何实现对这类外部API的负责任访问?
在之前的教程中,我们学习了模拟和私有数据的概念:它们是sy.Asset的核心组件,能够访问托管在PySyft数据站点上的数据。
关于模拟数据和私有数据的提醒
一个模拟数据集可以以开放访问的方式分发,因为它是虚构的,不包含任何关于个人的私人信息,也不包含任何我们不想发布的数据。它帮助研究人员了解他们可以开展的项目,并提供一个用于编码和测试的沙盒环境。相比之下,私有数据绝不允许外部研究人员直接访问,只能通过明确批准后才能发布。
使用远程资产的方式出奇地相似!这可以通过TwinAPIEndpoint实现,它需要定义两个独立的API端点:
Mock: 一个与外部API通信的端点,该API托管了与真实数据具有相同模式和相似字段的模拟数据
私有: 一个与外部API通信的端点,该API托管实际的私有数据。
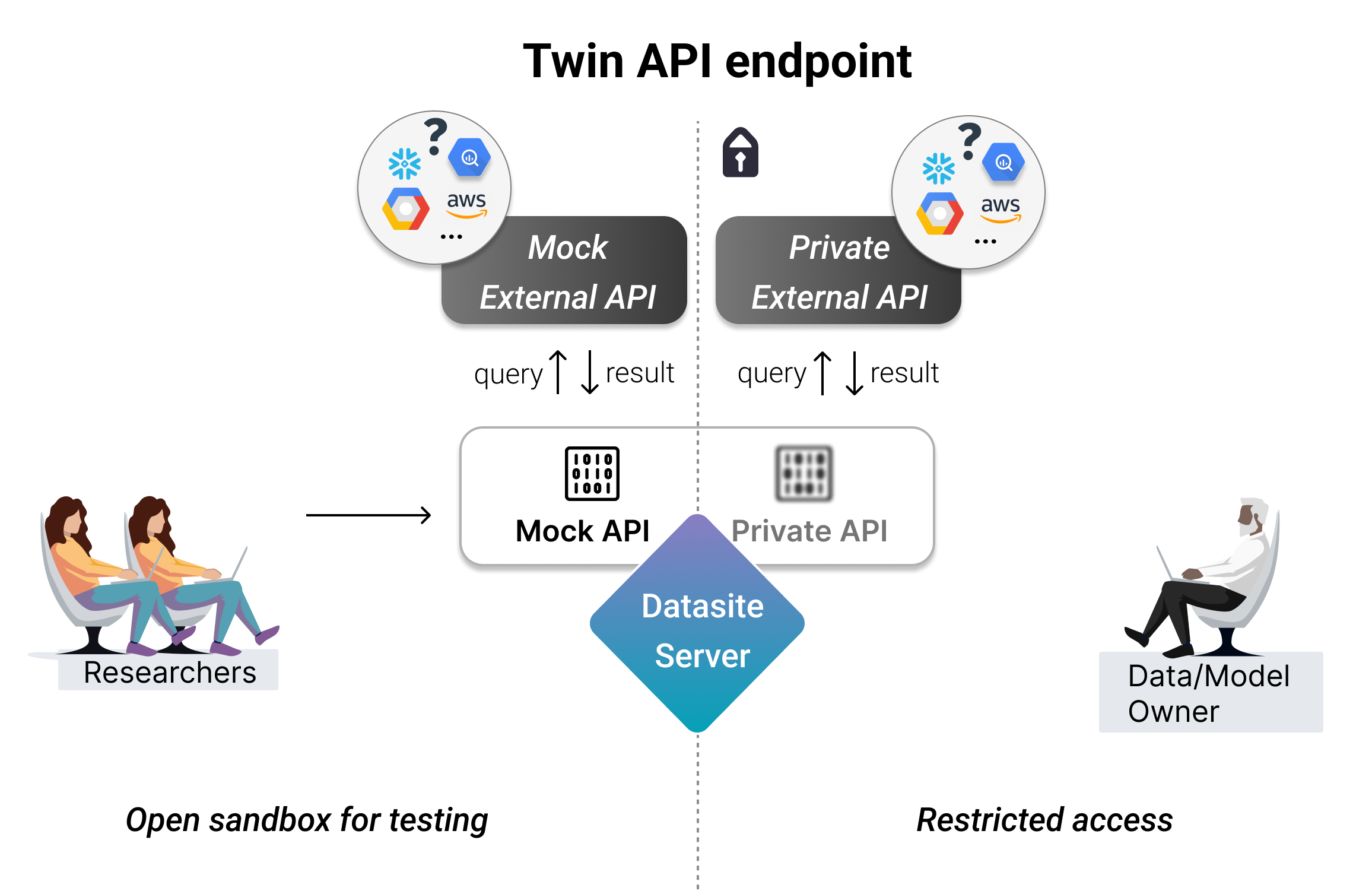
以下是可以通过TwinAPIEndpoint连接的一些服务示例:
Google BigQuery/BigTable
亚马逊Redshift
Microsoft Azure SQL 数据库
今天我们将模拟一个虚构场景。假设有一个名为Nimbus的云平台,它提供了一个全托管的SQL数据库NimbusDB来存储我们的数据。此外,我们假设该平台还提供了一个现成的Python客户端,下面是我们模拟的版本:
class NimbusDBClient:
def __init__(self, api_key, endpoint):
self.api_key = api_key
self.endpoint = endpoint
# print(f"Initialized NimbusDBClient with endpoint {self.endpoint}")
def connect(self):
""" Simulate connecting to NimbusDB """
# Simulate a connection setup
self.connection_status = "Connected"
def execute_query(self, query):
""" Simulate executing a SQL query """
if self.connection_status == "Connected":
print(f"Executing query: {query}")
# Mock result based on query
if "SELECT" in query:
return [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bob'}]
elif "UPDATE" in query or "INSERT" in query:
return "Error: Query executed successfully."
else:
return "Error: Unsupported query type."
else:
return "Error: Not connected to database."
def get_schema(self, table=""):
""" Simulate fetching the schema of the SQL table."""
if self.connection_status == "Connected":
import pandas as pd
print(f"Fetching table metadata: {table}")
return pd.DataFrame.from_dict({
'field_name': ['id', 'session_id', 'name', '...'],
'field_type': ['int', 'int', 'str', '...']
})
else:
return "Error: Not connected to database."
# Usage
api_key = "your_api_key_here"
endpoint = "https://api.nimbusdb.com"
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(api_key, endpoint)
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute a query
result = client.execute_query("SELECT * FROM users")
print("Query Result:", result)
# Execute a query
result = client.get_schema(table="users")
print("Table Scehma Result:", result)
Executing query: SELECT * FROM users
Query Result: [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bob'}]
Fetching table metadata: users
Table Scehma Result: field_name field_type
0 id int
1 session_id int
2 name str
3 ... ...
如果您是一名试图使用此类系统的数据科学家,可以深入阅读此组件指南了解如何访问自定义API端点并使用它们,或者直接跳转到下文的数据科学家部分查看示例。
 1. 数据所有者:定义API端点#
1. 数据所有者:定义API端点#
有两种类型的API端点,可能适合不同的需求:
双端点 - 用于处理私有资产,需要同时具备模拟和私有对应部分
Public Endpoint - 用于处理无需审批的信息 - 例如元数据
为了说明如何定义每个部分,我们将首先设置一个内存节点。
Show code cell source
import syft as sy
datasite = sy.orchestra.launch(
name="test-datasite",
dev_mode=False,
create_producer=True,
n_consumers=1,
reset=True,
port="auto",
)
client = datasite.login(email="[email protected]", password="changethis")
client.register(
email="[email protected]",
password="verysecurepassword",
password_verify="verysecurepassword",
name="New User",
)
ds_client = datasite.login(email="[email protected]", password="verysecurepassword")
Show code cell output
Starting test-datasite server on 0.0.0.0:54055
Waiting for server to start Done.
You have launched a development server at http://0.0.0.0:54055.It is intended only for local use.
Logged into <test-datasite: High side Datasite> as <[email protected]>
You are using a default password. Please change the password using `[your_client].account.set_password([new_password])`.
Logged into <test-datasite: High side Datasite> as <[email protected]>
公共API端点#
公共API端点无需管理员/数据所有者批准即可自由访问。在与远程资产协作时,一个典型应用场景是从平台获取有用的元数据(例如表结构信息)。
为此,我们依赖context.settings对象将相关信息(如API密钥)传递给端点,同时避免其暴露。
import pandas as pd
from syft import SyftError
MY_API_KEY = "*****"
ENDPOINT = "https://api.nimbusdb.com"
# Define a single, public API Endpoint
@sy.api_endpoint(
path="nimbusdb.schema",
description="""
## Description
Allows to get the schema of a table to NimbusDB, a fully managed SQL db in Nimbus.
## Available tables
- users
- sessions
- content
- ...
## How to use
Run `<client>.api.services.nimbusdb.schema(table="users")`
""",
settings={"key": MY_API_KEY, "endpoint": ENDPOINT}
)
def get_schema(
context,
table: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute the query
result = client.get_schema(table=table)
if not isinstance(result, pd.DataFrame):
return SyftError(message=result)
elif "Error: " in result:
return SyftError(message="An error occured. Please check your query and contact the admin if it persists.")
return pd.DataFrame(result)
# Add it to the node
response = client.custom_api.add(endpoint=get_schema)
response
Endpoint successfully created.
警告
使用第三方库: 设置API端点桥接可能需要使用第三方Python包。在这种情况下,管理员有责任定义一个包含这些依赖项的自定义Docker镜像,并启动运行该镜像的工作池。完成后,您可以将端点绑定到自定义工作池。
# We check the list of custom API endpoints.
client.custom_api.api_endpoints()
TwinAPI端点视图列表
总计: 0
client.api.services.nimbusdb.schema
API: nimbusdb.schema
描述:
## Description
Allows to get the schema of a table to NimbusDB, a fully managed SQL db in Nimbus.
## Available tables
- users
- sessions
- content
- ...
## How to use
Run `.api.services.nimbusdb.schema(table="users")`
</span><br>
私有代码:
N / A
公开代码:
def get_schema(
context,
table: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute the query
result = client.get_schema(table=table)
if not isinstance(result, pd.DataFrame):
return SyftError(message=result)
elif "Error: " in result:
return SyftError(message="An error occured. Please check your query and contact the admin if it persists.")
return pd.DataFrame(result)
# Test the endpoint works
client.api.services.nimbusdb.schema(table="users")
Fetching table metadata: users
| 字段名称 | 字段类型 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | id | int |
| 1 | session_id | int |
| 2 | 名称 | 字符串 |
| 3 | ... | ... |
现在,让我们看看如何定义一个TwinAPIEndpoint。
双生API端点#
这些功能非常适合处理数据或模型资产,因为它们支持定义模拟行为和私有访问,从而让数据科学家无需接触任何私有信息即可进行通知、原型设计和提交分析,这与PySyft托管资产的使用方式类似。
现在,让我们定义一个TwinAPIEndpoint用于查询数据。这可以通过多种方式实现,例如:
选项1:模拟查询返回一个硬编码/编排好的答案
选项2:模拟查询从一个与私有设置完全相同的配置中提取数据,但包含的是模拟数据。
目前我们假设采用选项2,并设置了两个NimbusDB实例(一个模拟实例和一个私有实例),它们通过不同的终端节点访问,使用不同的访问密钥。
MY_MOCK_API_KEY = "*****"
MOCK_ENPOINT = "https://mock.api.nimbusdb.com"
# Define the mock counterpart
@sy.api_endpoint_method(
settings={"key": MY_MOCK_API_KEY,
"endpoint": MOCK_ENPOINT},
)
def public_endpoint_method(
context,
query: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute the query
result = client.execute_query(query)
if result == "Error: Unsupported query type.":
return SyftError(message=result)
elif "Error: " in result:
return SyftError(
message="An error occured. Please check your query and contact the admin if it persists."
)
return pd.DataFrame(result)
MY_API_KEY = "9fhe3ss..."
ENPOINT = "https://api.nimbusdb.com"
# Define the private counterpart
@sy.api_endpoint_method(
settings={"key": MY_API_KEY,
"endpoint": ENPOINT},
)
def private_endpoint_method(
context,
query: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute the query
result = client.execute_query(query)
if result == "Error: Unsupported query type.":
return SyftError(message=result)
elif "Error: " in result:
return SyftError(
message="An error occured. Please check your query and contact the admin if it persists."
)
return pd.DataFrame(result)
new_endpoint = sy.TwinAPIEndpoint(
path="nimbusdb.query",
mock_function=public_endpoint_method,
private_function=private_endpoint_method,
description="Allows to query to NimbusDB, a fully managed SQL db in Nimbus.",
)
# Add it to the node.
response = client.custom_api.add(endpoint=new_endpoint)
response
Endpoint successfully created.
此时,所有有权访问Datasite的用户都可以看到这些端点,甚至可以选择运行他们的模拟和私有版本,如下所示:
注意
访问私有版本 只有管理员和数据所有者可以在未经批准的情况下运行端点的私有版本。
让我们来测试一下!
client.api.services.nimbusdb.query.mock(query="SELECT 1")
Executing query: SELECT 1
| id | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Alice |
| 1 | 2 | Bob |
client.api.services.nimbusdb.query.private(query="WRONG 10")
Executing query: WRONG 10
SyftError: Error: Unsupported query type.
SyftError: Error: Unsupported query type.
SyftError: Error: Unsupported query type.
Error: Unsupported query type.
警告
如果我的API端点崩溃了怎么办? 当API端点的执行失败并导致异常时,数据科学家将无法查看输出。为了防止凭证或敏感数据的潜在泄露,建议他们联系管理员来调试问题。因此,我们强烈建议数据所有者主动测试预期的故障情况。
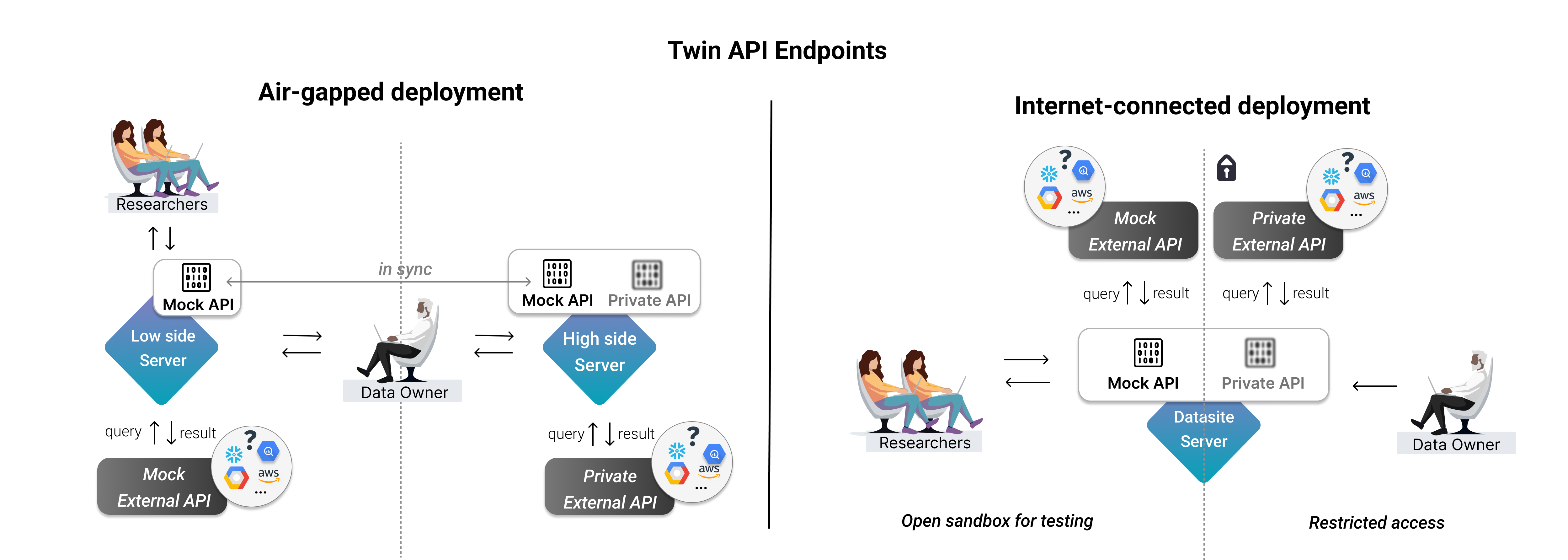
设置隔离环境部署#
上述设置可用作联网部署。不过,如果您更倾向于选择物理隔离部署,我们建议数据所有者:
如上定义高权限端服务器的TwinAPIEndpoint
通过我们的sync API将端点同步到低安全区服务器
这确保了API端点具有统一的定义,并且数据所有者可以直观地在两台服务器上执行任一版本。
 2. 数据所有者:自定义API端点#
2. 数据所有者:自定义API端点#
可以自定义API端点以更好地满足数据所有者的需求。例如,我们可以定义速率限制来约束研究人员允许调用的次数,以防止滥用。
让我们执行此操作并更新nimbusdb.query的当前公共版本。
使用上下文管理器#
为此,我们将使用context上下文管理器,除了之前介绍的设置外,它还提供了丰富的工具集和灵活性:
context.state: 为每位数据科学家维护跨端点调用的状态,并可在Python字典中存储信息contexg.user: 访问用户账户的元数据,例如他们的电子邮件context.code: 用于导入各种外部函数,帮助更好地管理我们API的实现代码context.user_client: 从调用此方法的用户视角访问状态和API
示例:速率限制#
我们将尝试利用所有这些功能来展示它们的用法——但数据所有者可以根据自身需求,自由发挥创意来自定义API端点。
我们将定义以下两条规则:
一名数据科学家每小时只能运行该端点5次
待处理请求超过5个的数据科学家无法运行此端点
def is_within_runs_rate_limit(state, email):
"""Rate limiter for custom API calls made by users."""
import datetime
CALLS_PER_MIN = 5
current_time = datetime.datetime.now()
calls_last_min = [1 if (current_time - call_time).seconds < 3600 else 0 for call_time in state[email]]
return sum(calls_last_min) < CALLS_PER_MIN
def is_under_pending_request_limit(user_client):
"""Fetch the number of pending requests from the user_client."""
PENDING_REQUESTS = 5
count = sum([1 for request in user_client.requests if str(request.status) == "RequestStatus.PENDING"])
return count < PENDING_REQUESTS
@sy.api_endpoint_method(
settings={"key": MY_MOCK_API_KEY,
"endpoint": "https://mock.api.nimbusdb.com"},
# Add the helper methods here
helper_functions=[is_within_runs_rate_limit, is_under_pending_request_limit]
)
def mock_endpoint_method( # Re-define the mock endpoint, since this one is user-facing
context,
query: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
import datetime
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Use the context.user to identify the user and store the state for that user
if context.user.email not in context.state.keys():
context.state[context.user.email] = []
# Check the runs limit agaisnt the stored state
if not context.code.is_within_runs_rate_limit(context.state, context.user.email):
return SyftError(message="Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.")
# Check the pending requests limit using the user_client
if not context.code.is_under_pending_request_limit(context.user_client):
return SyftError(message="Number of max pending requests reached - no more calls are permitted for now.")
context.state[context.user.email].append(datetime.datetime.now())
# Execute the query
result = client.execute_query(query)
return pd.DataFrame(result)
现在,我们可以用新的定义更新现有的API端点。
client.custom_api.update(endpoint_path="nimbusdb.query", mock_function=mock_endpoint_method)
Endpoint successfully updated.
for _ in range(7):
client.api.services.nimbusdb.query.mock(query="SELECT 1")
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
SyftError: Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.
我们可以再次检查我们的端点以确保一切就绪。
client.api.services.nimbusdb.query
API: nimbusdb.query
描述:允许查询NimbusDB,这是Nimbus中一个完全托管的SQL数据库。
私有代码:
def private_endpoint_method(
context,
query: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute the query
result = client.execute_query(query)
if result == "Error: Unsupported query type.":
return SyftError(message=result)
elif "Error: " in result:
return SyftError(message="An error occured. Please check your query and contact the admin if it persists.")
return pd.DataFrame(result)
公开代码:
def mock_endpoint_method( # Re-define the mock endpoint, since this one is user-facing
context,
query: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
import datetime
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Use the context.user to identify the user and store the state for that user
if context.user.email not in context.state.keys():
context.state[context.user.email] = []
# Check the runs limit agaisnt the stored state
if not context.code.is_within_runs_rate_limit(context.state, context.user.email):
return SyftError(message="Rate limit of calls per minute has been reached.")
# Check the pending requests limit using the user_client
if not context.code.is_under_pending_request_limit(context.user_client):
return SyftError(message="Number of max pending requests reached - no more calls are permitted for now.")
context.state[context.user.email].append(datetime.datetime.now())
# Execute the query
result = client.execute_query(query)
return pd.DataFrame(result)
辅助函数:
def is_within_runs_rate_limit(state, email):
"""Rate limiter for custom API calls made by users."""
import datetime
CALLS_PER_MIN = 10
current_time = datetime.datetime.now()
calls_last_min = [1 if (current_time - call_time).seconds < 60 else 0 for call_time in state[email]]
return sum(calls_last_min) < CALLS_PER_MIN
def is_under_pending_request_limit(user_client):
"""Fetch the number of pending requests from the user_client."""
PENDING_REQUESTS = 5
count = sum([1 for request in user_client.requests if str(request.status) == "RequestStatus.PENDING"])
return count < PENDING_REQUESTS
默认情况下,私有API定义对研究人员是隐藏的。如果我们希望研究人员看不到模拟定义,可以按如下方式关闭:
client.custom_api.update(endpoint_path="nimbusdb.query", hide_mock_definition=True)
Endpoint successfully updated.
关于如何进一步自定义、更新或删除您的API的更多信息请点击此处。
 3. 数据科学家:探索API端点#
3. 数据科学家:探索API端点#
我们可以连接到客户端并检查可用的API端点。
ds_client
欢迎来到测试数据站点
Server Description: This is the default description for a Datasite Server.
Server Type: Datasite
Server Side Type:High Side
Syft Version: 0.9.1-beta.5
入门命令
.datasets - 列出数据集.code - 列出代码.projects - 列出项目
使用以下命令检查可用的API端点:
ds_client.custom_api.api_endpoints()
TwinAPI端点视图列表
总计: 0
数据科学家可以检查一个端点是否设计为公开的,或者是否符合mock/private范式,以及底层mock函数和工作池的名称。后者主要提供参考信息。
现在,我们可以进一步检查每个端点:
ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.query
API: nimbusdb.query
描述:允许查询NimbusDB,这是Nimbus中一个完全托管的SQL数据库。
私有代码:
N / A
公开代码:
N / A
ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.schema
API: nimbusdb.schema
描述:
## Description
Allows to get the schema of a table to NimbusDB, a fully managed SQL db in Nimbus.
## Available tables
- users
- sessions
- content
- ...
## How to use
Run `.api.services.nimbusdb.schema(table="users")`
</span><br>
私有代码:
N / A
公开代码:
def get_schema(
context,
table: str,
):
from external import NimbusDBClient
import pandas as pd
# Create a client instance
client = NimbusDBClient(context.settings["key"], context.settings["endpoint"])
# Connect to NimbusDB
client.connect()
# Execute the query
result = client.get_schema(table=table)
if not isinstance(result, pd.DataFrame):
return SyftError(message=result)
elif "Error: " in result:
return SyftError(message="An error occured. Please check your query and contact the admin if it persists.")
return pd.DataFrame(result)
理想情况下,该描述应包含足够信息,以便我们理解API格式或链接到外部托管的文档。让我们针对一些模拟/公共查询来测试我们的端点。
# Use a public endpoint
ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.schema(table="users")
Fetching table metadata: users
| 字段名称 | 字段类型 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | id | int |
| 1 | session_id | int |
| 2 | 名称 | 字符串 |
| 3 | ... | ... |
# Use the mock side of a private one
ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.query(query="SELECT 1")
Executing query: SELECT 1
| id | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Alice |
| 1 | 2 | 鲍勃 |
上述默认使用模拟执行。不允许执行私有版本。
ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.query.private(query="SELECT 1")
SyftError: You're not allowed to run this code.
SyftError: You're not allowed to run this code.
SyftError: You're not allowed to run this code.
You're not allowed to run this code.
现在,如果我们未经批准就无法执行私有对应部分,那么我们该如何从数据所有者那里获得批准呢?
 4. 数据科学家:使用自定义API端点时请求批准#
4. 数据科学家:使用自定义API端点时请求批准#
数据科学家可以像使用其他资产一样使用API端点,作为syft函数输入策略的一部分。
数据科学家可以轻松使用数据集资产的.mock端。然而,要在真实资产上运行任何计算,他们需要创建一个syft函数来展示其预期用途。基于该函数,数据所有者可以批准或拒绝请求,而数据科学家将获得执行权限或获取结果。
同样的概念在这里也适用。
@sy.syft_function_single_use(
endpoint=ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.query
)
def foo(endpoint):
query = "SELECT 1"
return endpoint(query=query)
Syft function 'foo' successfully created. To add a code request, please create a project using `project = syft.Project(...)`, then use command `project.create_code_request`.
ds_client.code.request_code_execution(foo)
请求
ID: d61ed95e50f944f5b9070e25419a10e8
请求时间:2024-08-24 20:13:58
状态:RequestStatus.PENDING
请求时间: 测试数据站点,类型为数据站点
请求者: 新用户 ([email protected])
变更内容: 请求将foo(池ID:default-pool)的权限状态更改为RequestStatus.APPROVED。无嵌套请求。
ds_client.code
用户代码列表
总计: 0
 5. 数据所有者:审批请求#
5. 数据所有者:审批请求#
这与我们之前看到的非常相似。
client.requests
请求列表
总计: 0
client.requests[0].code
用户代码
id: UID = 319de00ac6d2436fbf99dd7ac5e7e857
service_func_name: str = foo
股东: list = ['test-datasite']
状态: list = ['Server: test-datasite, Status: pending']
输入: dict =
{
"action_objects": {
"endpoint": "da8a798b313e43718750f1bc377488cf"
}
}
代码:
@sy.syft_function_single_use(
endpoint=ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.query
)
def foo(endpoint):
query = "SELECT 1"
return endpoint(query=query)
我们可以查看代码并检查它是否以我们认可的方式使用我们的API端点。
client.requests[0].approve()
Approving request on change foo for datasite test-datasite
Request d61ed95e50f944f5b9070e25419a10e8 changes applied
现在,数据科学家可以获取他们的计算结果:
# Won't work on the private endpoint
ds_client.code.foo(endpoint=ds_client.api.services.nimbusdb.query)
Executing query: SELECT 1
| id | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Alice |
| 1 | 2 | Bob |
成功!现在您已经了解PySyft如何促进对托管在外部数据仓库或平台上的数据进行负责任访问。

