注意
This page was generated from 画廊/使用Folium进行绘图.ipynb.
使用Folium绘图#
什么是Folium?
Folium 建立在 Python 生态系统的数据处理优势和 leaflet.js 库的映射优势之上。这使您能够在 Geopandas 中处理数据,并通过 Folium 以 Leaflet 地图的形式进行可视化。
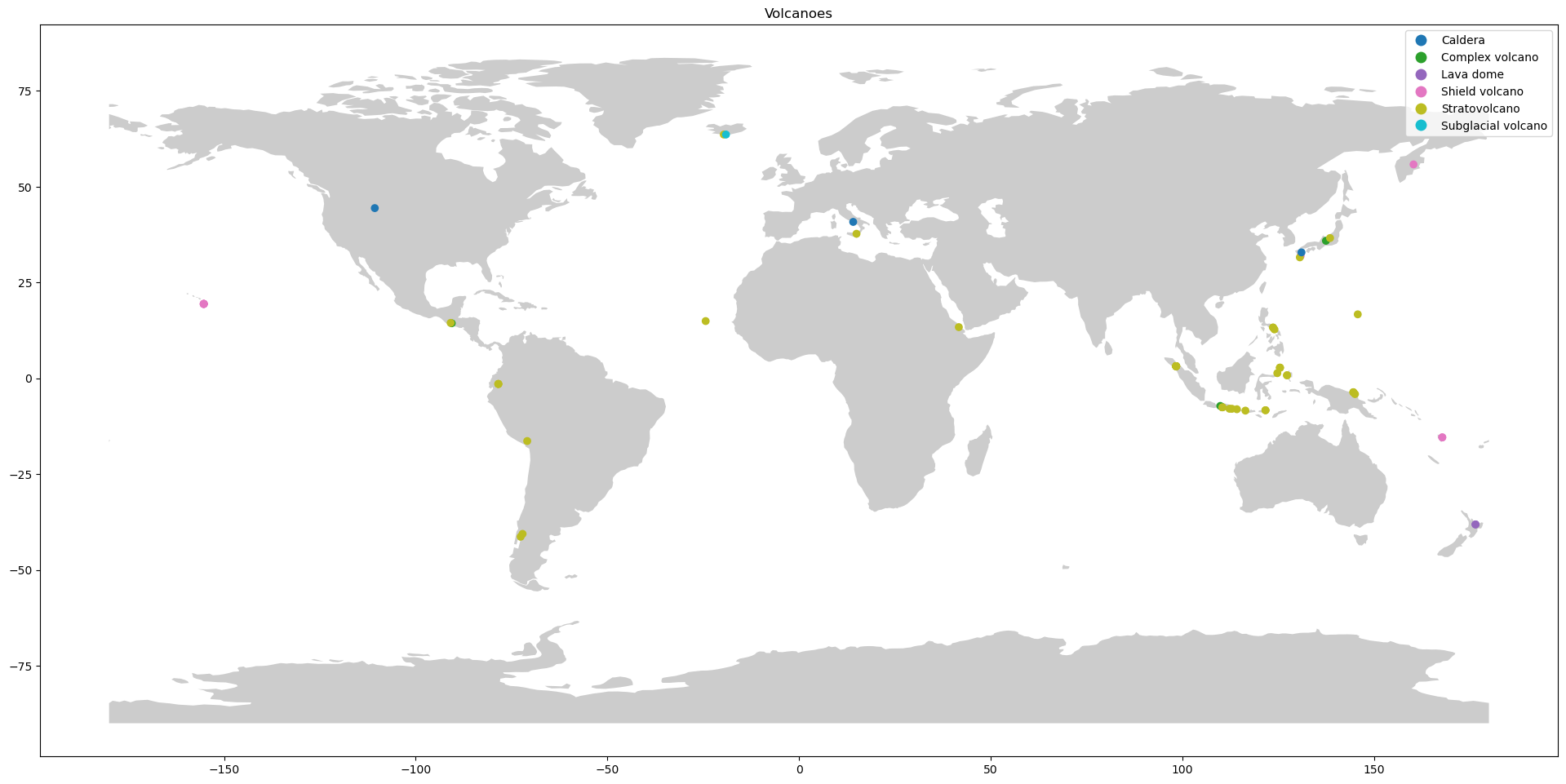
在这个例子中,我们将首先使用 Geopandas 加载几何图形(火山点数据),然后创建一个 Folium 地图,标记表示不同类型的火山。
加载几何#
这个例子使用了一个可自由获取的 火山数据集。我们将使用pandas读取csv文件,然后将pandas DataFrame 转换为Geopandas GeoDataFrame。
[1]:
# Import Libraries
import pandas as pd
import geopandas
import folium
import geodatasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[2]:
df1 = pd.read_csv("volcano_data_2010.csv")
# Keep only relevant columns
df = df1.loc[:, ("Year", "Name", "Country", "Latitude", "Longitude", "Type")]
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 63 entries, 0 to 62
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Year 63 non-null int64
1 Name 63 non-null object
2 Country 63 non-null object
3 Latitude 63 non-null float64
4 Longitude 63 non-null float64
5 Type 63 non-null object
dtypes: float64(2), int64(1), object(3)
memory usage: 3.1+ KB
[3]:
# Create point geometries
geometry = geopandas.points_from_xy(df.Longitude, df.Latitude)
geo_df = geopandas.GeoDataFrame(
df[["Year", "Name", "Country", "Latitude", "Longitude", "Type"]], geometry=geometry
)
geo_df.head()
[3]:
| 年份 | 名称 | 国家 | 纬度 | 经度 | 类型 | 几何 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2010 | 通古鲁阿省 | 厄瓜多尔 | -1.467 | -78.442 | 层状火山 | POINT (-78.442 -1.467) |
| 1 | 2010 | Eyjafjallajokull | 冰岛 | 63.630 | -19.620 | 层状火山 | POINT (-19.62 63.63) |
| 2 | 2010 | 帕卡亚 | 危地马拉 | 14.381 | -90.601 | 复合火山 | POINT (-90.601 14.381) |
| 3 | 2010 | Sarigan | 美国 | 16.708 | 145.780 | 层状火山 | POINT (145.78 16.708) |
| 4 | 2010 | Karangetang [Api Siau] | 印度尼西亚 | 2.780 | 125.480 | 层状火山 | POINT (125.48 2.78) |
[4]:
world = geopandas.read_file(geodatasets.get_path("naturalearth.land"))
df.Type.unique()
[4]:
array(['Stratovolcano', 'Complex volcano', 'Shield volcano',
'Subglacial volcano', 'Lava dome', 'Caldera'], dtype=object)
[5]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(24, 18))
world.plot(ax=ax, alpha=0.4, color="grey")
geo_df.plot(column="Type", ax=ax, legend=True)
plt.title("Volcanoes")
[5]:
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Volcanoes')
创建 Folium 地图#
Folium 有来自 OpenStreetMap、Mapbox 和 CartoDB 的多个内置图层。例如:
[6]:
# CartoDB Positron
map = folium.Map(location=[13.406, 80.110], tiles="CartoDB Positron", zoom_start=9)
map
[6]:
Make this Notebook Trusted to load map: File -> Trust Notebook
[7]:
# OpenStreetMap
map = folium.Map(location=[13.406, 80.110], tiles="OpenStreetMap", zoom_start=9)
map
[7]:
Make this Notebook Trusted to load map: File -> Trust Notebook
添加标记#
要表示不同类型的火山,您可以创建Folium标记并将它们添加到您的地图中。
[8]:
# Create a geometry list from the GeoDataFrame
geo_df_list = [[point.xy[1][0], point.xy[0][0]] for point in geo_df.geometry]
# Iterate through list and add a marker for each volcano, color-coded by its type.
i = 0
for coordinates in geo_df_list:
# assign a color marker for the type of volcano, Strato being the most common
if geo_df.Type[i] == "Stratovolcano":
type_color = "green"
elif geo_df.Type[i] == "Complex volcano":
type_color = "blue"
elif geo_df.Type[i] == "Shield volcano":
type_color = "orange"
elif geo_df.Type[i] == "Lava dome":
type_color = "pink"
else:
type_color = "purple"
# Place the markers with the popup labels and data
map.add_child(
folium.Marker(
location=coordinates,
popup="Year: "
+ str(geo_df.Year[i])
+ "<br>"
+ "Name: "
+ str(geo_df.Name[i])
+ "<br>"
+ "Country: "
+ str(geo_df.Country[i])
+ "<br>"
+ "Type: "
+ str(geo_df.Type[i])
+ "<br>"
+ "Coordinates: "
+ str(geo_df_list[i]),
icon=folium.Icon(color="%s" % type_color),
)
)
i = i + 1
[9]:
map
[9]:
Make this Notebook Trusted to load map: File -> Trust Notebook
Folium 热力图#
Folium 以其热图而闻名,热图创建一个热图层。要在 Folium 中绘制热图,您需要一个纬度和经度的列表。
[10]:
# This example uses heatmaps to visualize the density of volcanoes
# which is more in some parts of the world compared to others.
from folium import plugins
map = folium.Map(location=[15, 30], tiles="Cartodb dark_matter", zoom_start=2)
heat_data = [[point.xy[1][0], point.xy[0][0]] for point in geo_df.geometry]
heat_data
plugins.HeatMap(heat_data).add_to(map)
map
[10]:
Make this Notebook Trusted to load map: File -> Trust Notebook