注意
Go to the end 下载完整示例代码。
拓扑排序
这个例子演示了如何获取有向无环图(DAG)的拓扑排序。有向图的拓扑排序是基于有向边所隐含的优先级的线性排序。当且仅当图中没有任何循环时,拓扑排序才存在。在igraph中,我们可以使用igraph.GraphBase.topological_sorting()来获取顶点的拓扑排序。
import igraph as ig
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
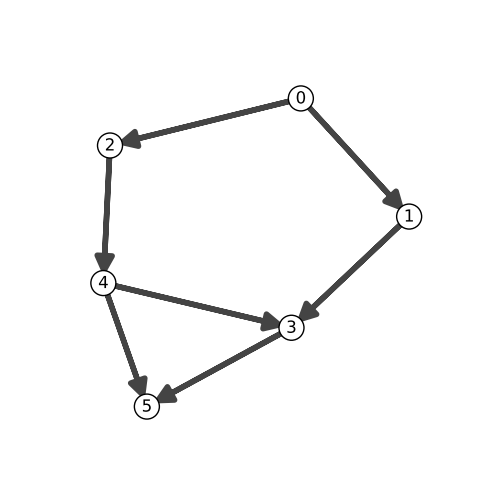
首先,我们生成一个有向无环图(DAG):
g = ig.Graph(
edges=[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (4, 3), (3, 5), (4, 5)],
directed=True,
)
我们可以立即验证这实际上是一个DAG:
assert g.is_dag
通过调用igraph.GraphBase.topological_sorting()可以很容易地计算出一个拓扑排序,该函数返回一个顶点ID的列表。如果给定的图不是有向无环图(DAG),将会发生错误。
results = g.topological_sorting(mode='out')
print('Topological sort of g (out):', *results)
Topological sort of g (out): 0 1 2 4 3 5
实际上,igraph.GraphBase.topological_sorting() 有两种模式,
'out' 和 'in'。'out' 是默认模式,从入度为0的节点开始。
相反,'in' 从出度为0的节点开始。要调用另一种模式,我们可以简单地使用:
results = g.topological_sorting(mode='in')
print('Topological sort of g (in):', *results)
Topological sort of g (in): 5 3 1 4 2 0
我们可以使用 igraph.Vertex.indegree() 来查找节点的入度。
for i in range(g.vcount()):
print('degree of {}: {}'.format(i, g.vs[i].indegree()))
# %
# Finally, we can plot the graph to make the situation a little clearer.
# Just to change things up a bit, we use the matplotlib visualization mode
# inspired by `xkcd <https://xkcd.com/>_:
with plt.xkcd():
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
ig.plot(
g,
target=ax,
layout='kk',
vertex_size=25,
edge_width=4,
vertex_label=range(g.vcount()),
vertex_color="white",
)
degree of 0: 0
degree of 1: 1
degree of 2: 1
degree of 3: 2
degree of 4: 1
degree of 5: 2
脚本的总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.313 秒)