通过命名空间复用流水线并分组节点¶
在本节中,我们将介绍命名空间(namespaces)——一种用于分组和隔离节点的强大工具。命名空间在以下两个关键场景中特别有用:
复用Kedro管道: 如果您需要复用某个管道但需调整输入、输出或参数,由于项目中所有节点名称必须唯一,Kedro不允许直接复制。通过使用命名空间可以隔离相同管道来解决此问题,同时还能增强Kedro-Viz中的可视化效果。
分组特定节点: 命名空间提供了一种简单的方式来分组选定的节点,使得在部署时可以一起执行它们,同时也能提升它们在Kedro-Viz中的可视化呈现。
如何复用您的管道¶
如果你想创建一个新管道,该管道使用与existing_pipeline不同的输入/输出/参数执行类似任务,可以按照如何构建管道创建中描述的相同pipeline()创建函数。此函数允许你覆盖输入、输出和参数。你的新管道创建代码应如下所示:
def create_pipeline(**kwargs) -> Pipeline:
return pipeline(
existing_pipeline, # Name of the existing Pipeline object
inputs = {"old_input_df_name" : "new_input_df_name"}, # Mapping existing Pipeline input to new input
outputs = {"old_output_df_name" : "new_output_df_name"}, # Mapping existing Pipeline output to new output
parameters = {"params: model_options": "params: new_model_options"}, # Updating parameters
)
这意味着您可以基于existing_pipeline管道创建多个流水线,以使用不同的输入数据集和模型训练参数测试各种方法。例如,对于来自我们Spaceflights教程的data_science流水线,您可以通过将data_science流水线创建代码分离到一个单独的base_data_science管道对象中,然后将其在create_pipeline()函数内部重用,来重构src/project_name/pipelines/data_science/pipeline.py文件:
#src/project_name/pipelines/data_science/pipeline.py
from kedro.pipeline import Pipeline, node, pipeline
from .nodes import evaluate_model, split_data, train_model
base_data_science = pipeline(
[
node(
func=split_data,
inputs=["model_input_table", "params:model_options"],
outputs=["X_train", "X_test", "y_train", "y_test"],
name="split_data_node",
),
node(
func=train_model,
inputs=["X_train", "y_train"],
outputs="regressor",
name="train_model_node",
),
node(
func=evaluate_model,
inputs=["regressor", "X_test", "y_test"],
outputs=None,
name="evaluate_model_node",
),
]
) # Creating a base data science pipeline that will be reused with different model training parameters
# data_science pipeline creation function
def create_pipeline(**kwargs) -> Pipeline:
return pipeline(
[base_data_science], # Creating a new data_science pipeline based on base_data_science pipeline
parameters={"params:model_options": "params:model_options_1"}, # Using a new set of parameters to train model
)
要使用一组新参数,您应该创建第二个参数文件来覆盖conf/base/parameters.yml中指定的参数。要覆盖参数model_options,请创建文件conf/base/parameters_data_science.yml并添加一个名为model_options_1的参数:
#conf/base/parameters.yml
model_options_1:
test_size: 0.15
random_state: 3
features:
- passenger_capacity
- crew
- d_check_complete
- moon_clearance_complete
- company_rating
注意
在Kedro中,无法运行具有相同节点名称的管道。在本示例中,两个管道都包含同名节点,因此无法同时执行它们。不过,base_data_science未被注册,不会通过kedro run命令执行。而data_science管道将在kedro run期间执行,因为它会被Kedro自动发现,该管道是在create_pipeline()函数内部创建的。
如果你想同时执行base_data_science和data_science流水线,或者需要多次复用base_data_science,就需要修改节点名称。最简单的方法是使用命名空间。
什么是命名空间¶
命名空间是一种隔离管道内节点、输入、输出和参数的方式。如果在pipeline()创建函数中添加namespace="namespace_name"属性,它会在新管道中的所有节点、输入、输出和参数前添加namespace_name.前缀。
注意
如果不想在使用命名空间时通过namespace_name.前缀更改输入、输出或参数的名称,您应该将这些对象列在pipeline()创建函数的相应参数中。例如:
pipeline(
[node(...), node(...), node(...)],
namespace="your_namespace_name",
inputs={"first_input_to_not_be_prefixed", "second_input_to_not_be_prefixed"},
outputs={"first_output_to_not_be_prefixed", "second_output_to_not_be_prefixed"},
parameters={"first_parameter_to_not_be_prefixed", "second_parameter_to_not_be_prefixed"},
)
让我们扩展之前的示例,尝试通过基于base_data_science管道创建另一个管道来再次复用该管道。首先,我们应该使用kedro pipeline create命令创建一个名为data_science_2的新空白管道:
kedro pipeline create data_science_2
接下来,我们需要修改src/project_name/pipelines/data_science_2/pipeline.py文件,按照与上述示例类似的方式创建管道。我们将从上面的代码中导入base_data_science,并使用命名空间来隔离我们的节点:
#src/project_name/pipelines/data_science_2/pipeline.py
from kedro.pipeline import Pipeline, pipeline
from ..data_science.pipeline import base_data_science # Import pipeline to create a new one based on it
def create_pipeline() -> Pipeline:
return pipeline(
base_data_science, # Creating a new data_science_2 pipeline based on base_data_science pipeline
namespace = "ds_2", # With that namespace, "ds_2." prefix will be added to inputs, outputs, params, and node names
parameters={"params:model_options": "params:model_options_2"}, # Using a new set of parameters to train model
inputs={"model_input_table"}, # Inputs remain the same, without namespace prefix
)
要使用一组新参数,请将model_options从conf/base/parameters_data_science.yml复制到conf/base/parameters_data_science_2.yml并稍作修改以尝试新的模型训练参数,例如测试大小和不同的特征集。将其命名为model_options_2:
#conf/base/parameters.yml
model_options_2:
test_size: 0.3
random_state: 3
features:
- d_check_complete
- moon_clearance_complete
- iata_approved
- company_rating
在这个示例中,data_science_2管道内的所有节点都将以ds_2作为前缀:ds_2.split_data、ds_2.train_model、ds_2.evaluate_model。参数将从model_options_2中获取,因为我们用它们覆盖了model_options。该管道的输入将保持为model_input_table(与之前相同),因为我们在inputs参数中指定了它(若不指定,输入将被修改为ds_2.model_input_table,但我们的管道中并不存在该表)。
由于节点名称现在是唯一的,我们可以通过以下方式运行项目:
kedro run
日志显示data_science和data_science_2管道已成功执行,但R2结果不同。现在,我们可以看到Kedro-viz如何在可折叠的"超级节点"中呈现命名空间管道:
kedro viz run
运行可视化后,我们可以看到两条相同的流水线:data_science 和 data_science_2:

我们可以通过一个特殊按钮折叠所有命名空间管道(在本例中只有data_science_2),并看到data_science_2管道被折叠成一个名为Ds 2的超级节点:
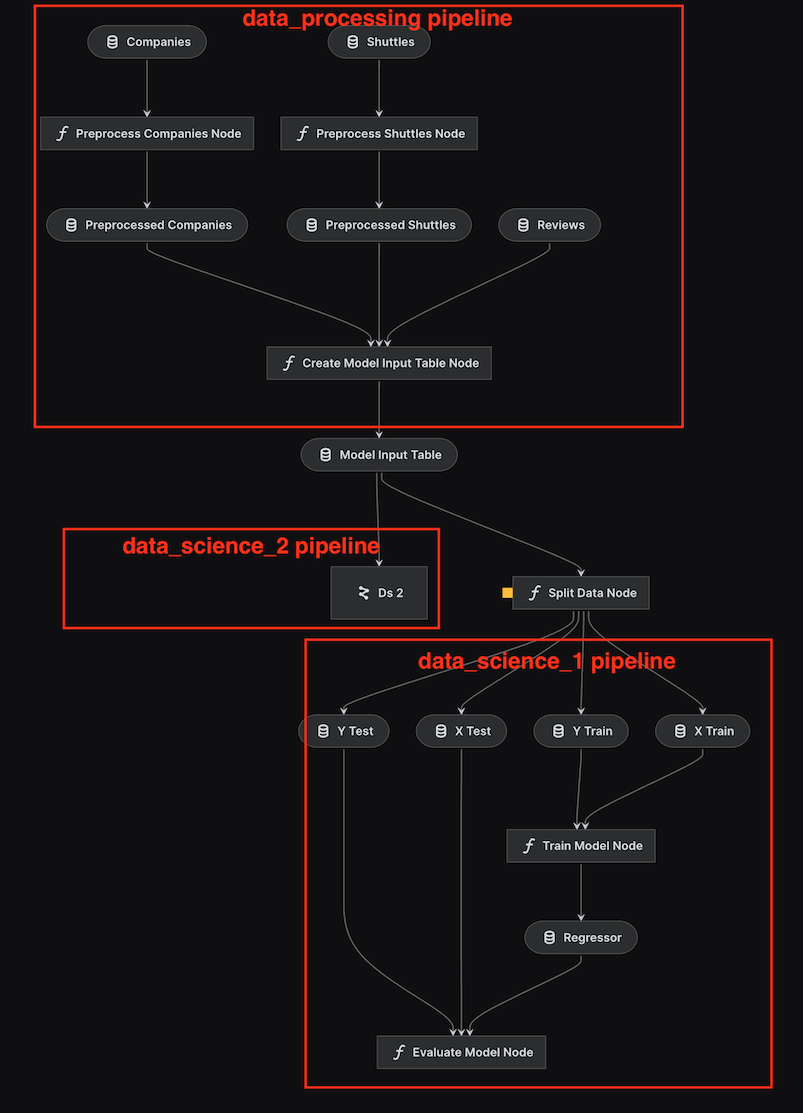
注意
你可以使用kedro run --namespace=namespace_name来仅运行特定的命名空间
如何为项目中的所有管道设置命名空间¶
如果我们想让这个示例中的所有管道完全命名空间化,我们应该:
修改data_processing流水线,通过在src/project_name/pipelines/data_processing/pipeline.py文件中向pipeline()创建函数添加以下代码:
namespace="data_processing",
inputs={"companies", "shuttles", "reviews"}, # Inputs remain the same, without namespace prefix
outputs={"model_input_table"}, # Outputs remain the same, without namespace prefix
按照data_science_2管道中的方式,通过添加命名空间和输入来修改data_science管道:
def create_pipeline(**kwargs) -> Pipeline:
return pipeline(
base_data_science,
namespace="ds_1",
parameters={"params:model_options": "params:model_options_1"},
inputs={"model_input_table"},
)
执行完kedro run运行管道后,折叠状态下使用kedro viz run进行可视化的效果如下所示:

使用命名空间对节点进行分组¶
您可以在Kedro项目中使用命名空间,不仅是为了复用流水线,还能将节点分组以便在Kedro Viz中获得更好的高层可视化效果,同时也便于部署。在生产环境中,将每个节点映射到容器可能效率不高。通过将命名空间作为分组机制,您可以将每个带命名空间的流水线映射到部署环境中的容器或任务。
例如,在您的spaceflights项目中,您可以像这样为data_processing管道分配一个命名空间:
#src/project_name/pipelines/data_science/pipeline.py
from kedro.pipeline import Pipeline, node, pipeline
from .nodes import create_model_input_table, preprocess_companies, preprocess_shuttles
def create_pipeline(**kwargs) -> Pipeline:
return pipeline(
[
node(
func=preprocess_companies,
inputs="companies",
outputs="preprocessed_companies",
name="preprocess_companies_node",
),
node(
func=preprocess_shuttles,
inputs="shuttles",
outputs="preprocessed_shuttles",
name="preprocess_shuttles_node",
),
node(
func=create_model_input_table,
inputs=["preprocessed_shuttles", "preprocessed_companies", "reviews"],
outputs="model_input_table",
name="create_model_input_table_node",
),
],
namespace="data_processing",
)
流水线会期望输入和输出带有命名空间名称的前缀,即data_processing.。
注意
从Kedro 0.19.12版本开始,您可以使用Pipeline对象的grouped_nodes_by_namespace属性来获取按顶级命名空间分组的节点字典。我们鼓励插件开发者使用此属性来获取命名空间节点组与部署环境中容器或任务的映射关系。
您可以通过在节点层级使用node()函数的namespace参数来进一步嵌套命名空间。节点层级的命名空间仅应用于通过Kedro Viz创建可折叠的管道部分来增强可视化效果。在这种情况下,只有节点名称会以namespace_name为前缀,而输入、输出和参数将保持不变。此行为与管道层级的命名空间不同。
例如,如果你想将Spaceflights教程中data_processing管道的前两个节点分组到同一个可折叠命名空间以便可视化,可以像这样更新你的管道:
#src/project_name/pipelines/data_science/pipeline.py
from kedro.pipeline import Pipeline, node, pipeline
from .nodes import create_model_input_table, preprocess_companies, preprocess_shuttles
def create_pipeline(**kwargs) -> Pipeline:
return pipeline(
[
node(
func=preprocess_companies,
inputs="companies",
outputs="preprocessed_companies",
name="preprocess_companies_node",
namespace="preprocessing", # Assigning the node to the "preprocessing" nested namespace
),
node(
func=preprocess_shuttles,
inputs="shuttles",
outputs="preprocessed_shuttles",
name="preprocess_shuttles_node",
namespace="preprocessing", # Assigning the node to the "preprocessing" nested namespace
),
node(
func=create_model_input_table,
inputs=["preprocessed_shuttles", "preprocessed_companies", "reviews"],
outputs="model_input_table",
name="create_model_input_table_node",
),
],
namespace="data_processing",
)
如上例所示,整个流水线被命名为data_processing命名空间,而前两个节点还被命名为data_processing.preprocessing命名空间。这将允许您在Kedro-Viz中折叠嵌套的preprocessing命名空间以获得更好的可视化效果,但流水线的输入和输出仍将需要前缀data_processing.。
你可以执行整个命名空间管道:
kedro run --namespace=data_processing
或者,您可以通过以下方式运行前两个节点:
kedro run --namespace=data_processing.preprocessing
使用kedro viz run命令打开可视化界面,即可查看可折叠的流水线部分,您可以通过左侧面板上的"折叠流水线"按钮进行切换。

警告
不建议在节点级别使用namespace来对节点进行部署分组,因为这种行为与在pipeline()级别定义namespace不同。在节点级别定义命名空间时,其行为类似于标签,不能保证执行一致性。