用户给定的有向无环图的伪造#
本笔记本演示了一个工具,用于使用观测数据伪造用户给定的DAG。主要函数是falsify_graph(),它接受一个DAG和数据作为输入,并返回一个评估结果。有关此方法的更多详细信息,请阅读相关论文:
Eulig, E., Mastakouri, A. A., Blöbaum, P., Hardt, M., & Janzing, D. (2023). 使用基于排列的测试来伪造因果图。 https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.09565
[1]:
# Import the necessary libraries and functions for this demo
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import networkx as nx
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
from dowhy.gcm.falsify import FalsifyConst, falsify_graph, plot_local_insights, run_validations, apply_suggestions
from dowhy.gcm.independence_test.generalised_cov_measure import generalised_cov_based
from dowhy.gcm.util import plot
from dowhy.gcm.util.general import set_random_seed
from dowhy.gcm.ml import SklearnRegressionModel
from dowhy.gcm.util.general import set_random_seed
set_random_seed(0)
# Set random seed
set_random_seed(1332)
合成数据#
我们将首先在合成数据上演示该工具。为此,我们生成了一个包含5个节点的随机DAG falsify_g_true.gml 和一些来自具有非线性条件随机SCM的数据 (falsify_data_nonlinear.csv)。
[2]:
# Load example graph and data
g_true = nx.read_gml(f"falsify_g_true.gml")
data = pd.read_csv(f"falsify_data_nonlinear.csv")
# Plot true DAG
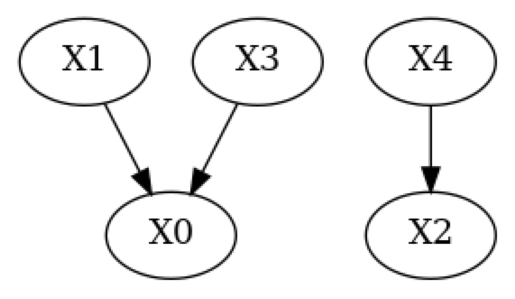
print("True DAG")
plot(g_true)
True DAG
首先让我们评估该数据上的真实DAG(以下单元格大约需要20秒运行)
[3]:
result = falsify_graph(g_true, data, plot_histogram=True)
# Summarize the result
print(result)
Test permutations of given graph: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:16<00:00, 1.24it/s]
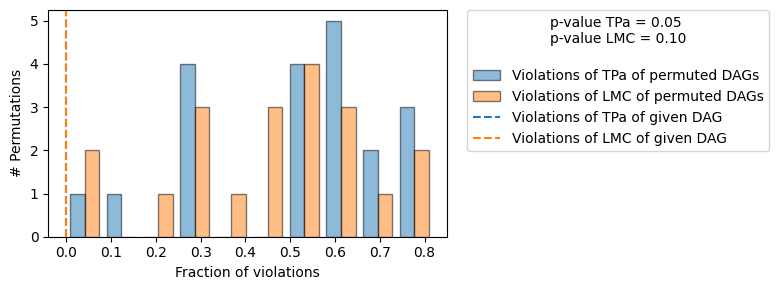
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Falsification Summary |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| The given DAG is informative because 1 / 20 of the permutations lie in the Markov |
| equivalence class of the given DAG (p-value: 0.05). |
| The given DAG violates 0/11 LMCs and is better than 90.0% of the permuted DAGs (p-value: 0.10). |
| Based on the provided significance level (0.05) and because the DAG is informative, |
| we do not reject the DAG. |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
正如预期的那样,我们没有拒绝真实的DAG。让我们理解falsify_graph()具体做了什么:当我们提供一个给定的DAG给falsify_graph()时,我们通过运行条件独立性测试(CIs)来测试局部马尔可夫条件(LMC)的违反情况。也就是说,对于图中的每个节点,我们测试是否
然后我们随机排列给定DAG的节点,并再次测试LMC的违反情况。我们可以对固定数量的排列或所有\(n!,n:\)(给定DAG中的节点数)进行此操作。然后,我们可以使用随机节点排列(零假设)具有与给定DAG(测试统计量)相同或更少的违反概率作为验证给定DAG的度量(图中右上角报告的p值)。
同样,我们可以针对给定的DAG运行一个oracle测试,即如果给定的DAG是真实的DAG,我们预计某些排列会有多少违反LMCs的情况。注意,询问违反零个LMCs的排列数量等同于询问有多少DAG与给定的DAG位于相同的马尔可夫等价类(MEC)中。在我们的方法中,我们使用与给定DAG位于相同MEC的排列DAG数量(具有0个tPA违反)作为衡量给定DAG信息量的指标。只有当少数排列位于相同的MEC时,给定DAG所蕴含的独立性才是“特征性”的,即通过测试隐含的CIs可以证伪给定的DAG。
在上面的图表中,我们看到了排列DAG的LMC违规(蓝色)和d-分离(oracle,橙色)违规的直方图。橙色和蓝色的虚线表示给定DAG的LMC(蓝色)/d-分离(橙色)违规的数量。正如对真实DAG所预期的那样,两个直方图大致重叠(除了CI测试中的统计误差)。
如果我们对图表不感兴趣,只是想通过我们的测试知道某个给定的内容是否被伪造,我们可以使用falsify_graph()返回的EvaluationResult对象的falsified属性来代替。
[4]:
print(f"Graph is falsifiable: {result.falsifiable}, Graph is falsified: {result.falsified}")
Graph is falsifiable: True, Graph is falsified: False
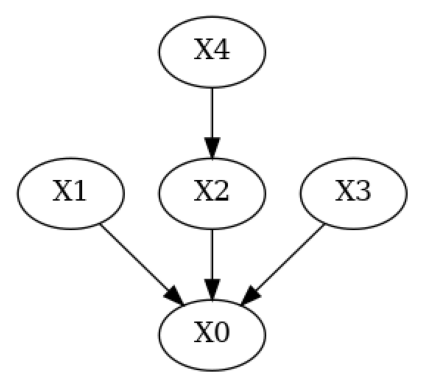
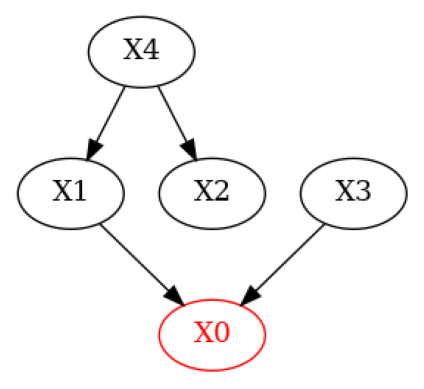
现在,让我们修改真实的DAG,以模拟一个领域专家知道一些边但移除了一条真实的边并引入了一条错误的边的情况。
[5]:
# Simulate a domain expert with knowledge over some of the edges in the system
g_given = g_true.copy()
g_given.add_edges_from(([('X4', 'X1')])) # Add wrong edge from X4 -> X1
g_given.remove_edge('X2', 'X0') # Remove true edge from X2 -> X0
plot(g_given)

[6]:
# Run evaluation and plot the result using `plot=True`
result = falsify_graph(g_given, data, plot_histogram=True)
# Summarize the result
print(result)
Test permutations of given graph: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:17<00:00, 1.13it/s]
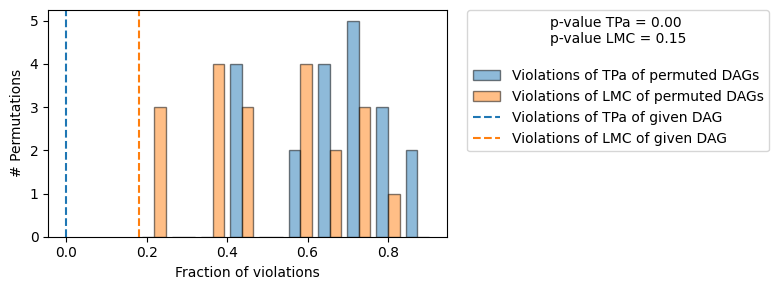
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Falsification Summary |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| The given DAG is informative because 0 / 20 of the permutations lie in the Markov |
| equivalence class of the given DAG (p-value: 0.00). |
| The given DAG violates 2/11 LMCs and is better than 85.0% of the permuted DAGs (p-value: 0.15). |
| Based on the provided significance level (0.05) and because the DAG is informative, |
| we reject the DAG. |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
在这里,我们观察到两件事。首先,给定的DAG比真实的DAG多违反了2个LMC。其次,有许多排列的DAG违反的LMC数量与给定的DAG相同或更少。这反映在p值LMC上,它比以前高得多。基于默认的显著性水平0.05,因此我们会拒绝给定的DAG。
我们可以通过突出显示在给定DAG中发生LMCs违规的节点来获得额外的见解。
[7]:
# Plot nodes for which violations of LMCs occured
print('Violations of LMCs')
plot_local_insights(g_given, result, method=FalsifyConst.VALIDATE_LMC)
Violations of LMCs
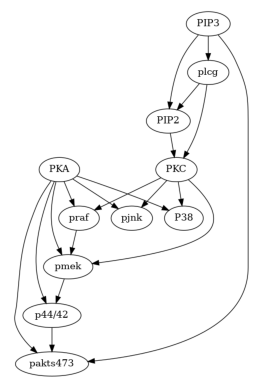
真实数据(Sachs等人,2005年的蛋白质网络数据集)#
[8]:
# Load the data and consensus DAG
data_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FenTechSolutions/CausalDiscoveryToolbox/master/cdt/data/resources/cyto_full_data.csv"
data_sachs = pd.read_csv(data_url)
g_sachs = nx.read_gml('falsify_sachs.gml')
[9]:
plot(g_sachs)
由于样本数量庞大,使用上述核测试进行评估在这个演示中耗时过长。因此,我们将改用基于广义协方差度量(GCM)的测试。我们将使用sklearn的梯度提升决策树作为回归器。
[10]:
# Define independence test based on the generalised covariance measure with gradient boosted decision trees as models
def create_gradient_boost_regressor(**kwargs) -> SklearnRegressionModel:
return SklearnRegressionModel(GradientBoostingRegressor(**kwargs))
def gcm(X, Y, Z=None):
return generalised_cov_based(X, Y, Z=Z, prediction_model_X=create_gradient_boost_regressor,
prediction_model_Y=create_gradient_boost_regressor)
在图的11个节点的所有排列上运行我们的基线是不可行的(也是不必要的)。因此,我们设置n_permutations=100来使用100个随机排列进行评估。为了使用上面定义的GCM测试,我们将使用参数independence_test=gcm(无条件独立性测试)和conditional_independence_test=gcm(条件独立性测试)。
以下单元格将需要大约3分钟来运行。
[11]:
# Run evaluation for consensus graph and data.
result_sachs = falsify_graph(g_sachs, data_sachs, n_permutations=100,
independence_test=gcm,
conditional_independence_test=gcm,
plot_histogram=True)
print(result_sachs)
Test permutations of given graph: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [11:57<00:00, 7.18s/it]

+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Falsification Summary |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| The given DAG is informative because 0 / 100 of the permutations lie in the Markov |
| equivalence class of the given DAG (p-value: 0.00). |
| The given DAG violates 21/49 LMCs and is better than 99.0% of the permuted DAGs (p-value: 0.01). |
| Based on the provided significance level (0.05) and because the DAG is informative, |
| we do not reject the DAG. |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
我们观察到,共识DAG既具有信息性(0/100排列位于相同的MEC中),并且在所涉及的CI方面显著优于随机。请注意,给定DAG的LMC违规数量远远超过了此处使用的默认显著性水平significance_ci=0.05的CI测试的预期类型I错误率。因此,拒绝具有超过5% LMC违规的DAG的简单方法会错误地拒绝这个DAG。
边缘建议#
除了上述展示的给定DAG的伪造之外,我们还可以使用suggestions=True运行额外的测试,并将这些结果反馈给用户。为了演示这一点,我们将使用之前的合成DAG和数据。
[12]:
result = falsify_graph(g_given, data, plot_histogram=True, suggestions=True)
print(result)
Test permutations of given graph: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:18<00:00, 1.07it/s]

+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Falsification Summary |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| The given DAG is informative because 0 / 20 of the permutations lie in the Markov |
| equivalence class of the given DAG (p-value: 0.00). |
| The given DAG violates 2/11 LMCs and is better than 100.0% of the permuted DAGs (p-value: 0.00). |
| Based on the provided significance level (0.05) and because the DAG is informative, |
| we do not reject the DAG. |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Suggestions |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Causal Minimality | - Remove edge X4 --> X1 |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
与上面的输出相比,我们现在在评估摘要的打印表示中看到了额外的行Suggestions。我们使用了因果最小性测试来向用户报告建议,并正确地建议移除由领域专家错误添加的边\(X4 \to X1\)。我们还可以使用plot_local_insights来绘制这些建议:
[13]:
# Plot suggestions
plot_local_insights(g_given, result, method=FalsifyConst.VALIDATE_CM)

我们可以使用apply_suggestions来应用这些建议。如果有一条我们不想移除的边,我们可以使用额外的参数edges_to_keep来指定我们不想移除的边。
[14]:
# Apply all suggestions (we could exclude suggestions via `edges_to_keep=[('X3', 'X4')])`)
g_given_pruned = apply_suggestions(g_given, result)
# Plot pruned DAG
plot(g_given_pruned)