Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
绘制随机生成的多标签数据集#
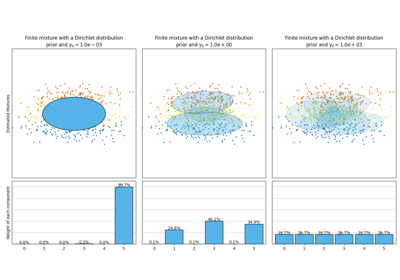
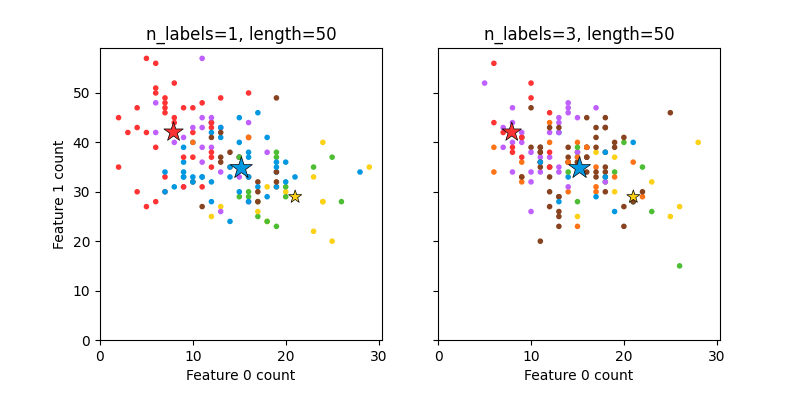
这展示了 make_multilabel_classification 数据集生成器。每个样本由两个特征的计数(最多50个)组成,这些特征在两个类别中有不同的分布。
点的标签如下,其中 Y 表示类别存在:
1
2
3
颜色
Y
N
N
红色
N
Y
N
蓝色
N
N
Y
黄色
Y
Y
N
紫色
Y
N
Y
橙色
Y
Y
N
绿色
Y
Y
Y
棕色
星号标记了每个类别的预期样本;其大小反映了选择该类别标签的概率。
左右两个示例突出了 n_labels 参数:右图中的更多样本具有2或3个标签。
请注意,这个二维示例非常退化:通常特征的数量会远大于“文档长度”,而在这里我们有比词汇量大得多的文档。同样,当 n_classes > n_features 时,某个特征区分特定类别的可能性要小得多。
The data was generated from (random_state=669):
Class P(C) P(w0|C) P(w1|C)
red 0.36 0.16 0.84
blue 0.41 0.30 0.70
yellow 0.23 0.42 0.58
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_multilabel_classification as make_ml_clf
COLORS = np.array(
[
"!",
"#FF3333", # red
"#0198E1", # blue
"#BF5FFF", # purple
"#FCD116", # yellow
"#FF7216", # orange
"#4DBD33", # green
"#87421F", # brown
]
)
# 使用相同的随机种子多次调用 make_multilabel_classification 以确保相同的分布
RANDOM_SEED = np.random.randint(2**10)
def plot_2d(ax, n_labels=1, n_classes=3, length=50):
X, Y, p_c, p_w_c = make_ml_clf(
n_samples=150,
n_features=2,
n_classes=n_classes,
n_labels=n_labels,
length=length,
allow_unlabeled=False,
return_distributions=True,
random_state=RANDOM_SEED,
)
ax.scatter(
X[:, 0], X[:, 1], color=COLORS.take((Y * [1, 2, 4]).sum(axis=1)), marker="."
)
ax.scatter(
p_w_c[0] * length,
p_w_c[1] * length,
marker="*",
linewidth=0.5,
edgecolor="black",
s=20 + 1500 * p_c**2,
color=COLORS.take([1, 2, 4]),
)
ax.set_xlabel("Feature 0 count")
return p_c, p_w_c
_, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex="row", sharey="row", figsize=(8, 4))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15)
p_c, p_w_c = plot_2d(ax1, n_labels=1)
ax1.set_title("n_labels=1, length=50")
ax1.set_ylabel("Feature 1 count")
plot_2d(ax2, n_labels=3)
ax2.set_title("n_labels=3, length=50")
ax2.set_xlim(left=0, auto=True)
ax2.set_ylim(bottom=0, auto=True)
plt.show()
print("The data was generated from (random_state=%d):" % RANDOM_SEED)
print("Class", "P(C)", "P(w0|C)", "P(w1|C)", sep="\t")
for k, p, p_w in zip(["red", "blue", "yellow"], p_c, p_w_c.T):
print("%s\t%0.2f\t%0.2f\t%0.2f" % (k, p, p_w[0], p_w[1]))
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.057 seconds)
Related examples