Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
SVM 边界示例#
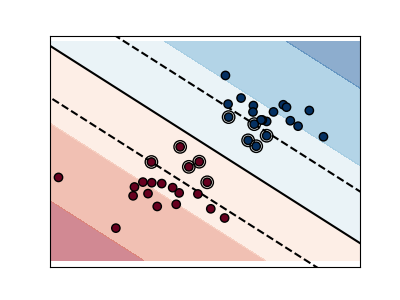
下图说明了参数 C 对分隔线的影响。 C 的值较大时,基本上告诉我们的模型我们对数据的分布没有太多信心,只会考虑靠近分隔线的点。
C的值较小时,会包含更多/所有的观测值,允许使用该区域内的所有数据来计算边界。
# 代码来源:Gaël Varoquaux
# 由Jaques Grobler修改用于文档
# SPDX许可证标识符:BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
# 我们创建了40个可分离点
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(20, 2) - [2, 2], np.random.randn(20, 2) + [2, 2]]
Y = [0] * 20 + [1] * 20
# 图号
fignum = 1
# 拟合模型
for name, penalty in (("unreg", 1), ("reg", 0.05)):
clf = svm.SVC(kernel="linear", C=penalty)
clf.fit(X, Y)
# 获取分离超平面
w = clf.coef_[0]
a = -w[0] / w[1]
xx = np.linspace(-5, 5)
yy = a * xx - (clf.intercept_[0]) / w[1]
# 绘制通过支持向量的平行于分离超平面的直线(在垂直于超平面的方向上距离超平面一个边距)。在二维中,这个距离是垂直方向上的 sqrt(1+a^2)。
margin = 1 / np.sqrt(np.sum(clf.coef_**2))
yy_down = yy - np.sqrt(1 + a**2) * margin
yy_up = yy + np.sqrt(1 + a**2) * margin
# 绘制直线、点和最近的向量到平面
plt.figure(fignum, figsize=(4, 3))
plt.clf()
plt.plot(xx, yy, "k-")
plt.plot(xx, yy_down, "k--")
plt.plot(xx, yy_up, "k--")
plt.scatter(
clf.support_vectors_[:, 0],
clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=80,
facecolors="none",
zorder=10,
edgecolors="k",
)
plt.scatter(
X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, zorder=10, cmap=plt.get_cmap("RdBu"), edgecolors="k"
)
plt.axis("tight")
x_min = -4.8
x_max = 4.2
y_min = -6
y_max = 6
YY, XX = np.meshgrid(yy, xx)
xy = np.vstack([XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()]).T
Z = clf.decision_function(xy).reshape(XX.shape)
# 将结果放入轮廓图中
plt.contourf(XX, YY, Z, cmap=plt.get_cmap("RdBu"), alpha=0.5, linestyles=["-"])
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
fignum = fignum + 1
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.033 seconds)
Related examples
sphx_glr_auto_examples_exercises_plot_iris_exercise.py
SVM 练习