Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
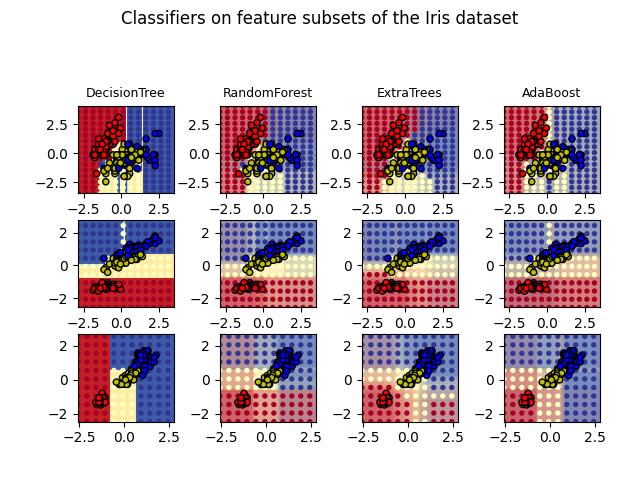
绘制鸢尾花数据集上树集成的决策边界#
绘制在鸢尾花数据集的特征对上训练的随机树森林的决策边界。
此图比较了决策树分类器(第一列)、随机森林分类器(第二列)、极端随机树分类器(第三列)和AdaBoost分类器(第四列)学习到的决策边界。
在第一行中,分类器仅使用花萼宽度和花萼长度特征构建;在第二行中,仅使用花瓣长度和花萼长度特征构建;在第三行中,仅使用花瓣宽度和花瓣长度特征构建。
按质量降序排列,当在所有4个特征上使用30个估计器进行训练并使用10折交叉验证评分时,我们看到:
ExtraTreesClassifier() # 0.95分 RandomForestClassifier() # 0.94分 AdaBoost(DecisionTree(max_depth=3)) # 0.94分 DecisionTree(max_depth=None) # 0.94分
增加AdaBoost的 max_depth 会降低分数的标准差(但平均分数不会提高)。
有关每个模型的更多详细信息,请参见控制台输出。
在此示例中,您可以尝试:
改变
DecisionTreeClassifier和AdaBoostClassifier的max_depth,例如尝试DecisionTreeClassifier的max_depth=3或AdaBoostClassifier的max_depth=None改变
n_estimators
值得注意的是,随机森林和极端随机树可以在多核上并行拟合,因为每棵树是独立构建的。AdaBoost的样本是顺序构建的,因此不使用多核。
DecisionTree with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.9266666666666666
RandomForest with 30 estimators with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.9266666666666666
ExtraTrees with 30 estimators with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.9266666666666666
AdaBoost with 30 estimators with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.82
DecisionTree with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
RandomForest with 30 estimators with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
ExtraTrees with 30 estimators with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
AdaBoost with 30 estimators with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
DecisionTree with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
RandomForest with 30 estimators with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
ExtraTrees with 30 estimators with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
AdaBoost with 30 estimators with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9866666666666667
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import (
AdaBoostClassifier,
ExtraTreesClassifier,
RandomForestClassifier,
)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# Parameters
n_classes = 3
n_estimators = 30
cmap = plt.cm.RdYlBu
plot_step = 0.02 # fine step width for decision surface contours
plot_step_coarser = 0.5 # step widths for coarse classifier guesses
RANDOM_SEED = 13 # fix the seed on each iteration
# Load data
iris = load_iris()
plot_idx = 1
models = [
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=None),
RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=n_estimators),
ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=n_estimators),
AdaBoostClassifier(
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3),
n_estimators=n_estimators,
algorithm="SAMME",
),
]
for pair in ([0, 1], [0, 2], [2, 3]):
for model in models:
# 我们只取两个对应的特征
X = iris.data[:, pair]
y = iris.target
# Shuffle
idx = np.arange(X.shape[0])
np.random.seed(RANDOM_SEED)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
X = X[idx]
y = y[idx]
# 标准化
mean = X.mean(axis=0)
std = X.std(axis=0)
X = (X - mean) / std
# Train
model.fit(X, y)
scores = model.score(X, y)
# 为每个列和控制台创建一个标题,使用 str() 并切掉字符串中无用的部分
model_title = str(type(model)).split(".")[-1][:-2][: -len("Classifier")]
model_details = model_title
if hasattr(model, "estimators_"):
model_details += " with {} estimators".format(len(model.estimators_))
print(model_details + " with features", pair, "has a score of", scores)
plt.subplot(3, 4, plot_idx)
if plot_idx <= len(models):
# 在每列的顶部添加一个标题
plt.title(model_title, fontsize=9)
# 现在使用细网格作为输入绘制决策边界,并生成填充轮廓图
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step), np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step)
)
# 绘制单个DecisionTreeClassifier或对分类器集成的决策边界进行alpha混合
if isinstance(model, DecisionTreeClassifier):
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap)
else:
# 选择 alpha 混合级别时要考虑正在使用的估计器数量(需要注意的是,如果 AdaBoost 提前达到了足够好的拟合效果,它可以使用比最大数量更少的估计器)。
estimator_alpha = 1.0 / len(model.estimators_)
for tree in model.estimators_:
Z = tree.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=estimator_alpha, cmap=cmap)
# 构建一个更粗略的网格来绘制一组集成分类,以展示这些分类与我们在决策边界中看到的有何不同。这些点是规则分布的,并且没有黑色轮廓。
xx_coarser, yy_coarser = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step_coarser),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step_coarser),
)
Z_points_coarser = model.predict(
np.c_[xx_coarser.ravel(), yy_coarser.ravel()]
).reshape(xx_coarser.shape)
cs_points = plt.scatter(
xx_coarser,
yy_coarser,
s=15,
c=Z_points_coarser,
cmap=cmap,
edgecolors="none",
)
# 绘制训练点,这些点聚集在一起并有黑色轮廓。
plt.scatter(
X[:, 0],
X[:, 1],
c=y,
cmap=ListedColormap(["r", "y", "b"]),
edgecolor="k",
s=20,
)
plot_idx += 1 # move on to the next plot in sequence
plt.suptitle("Classifiers on feature subsets of the Iris dataset", fontsize=12)
plt.axis("tight")
plt.tight_layout(h_pad=0.2, w_pad=0.2, pad=2.5)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.591 seconds)
Related examples
sphx_glr_auto_examples_exercises_plot_iris_exercise.py