%set_env PYTORCH_ENABLE_MPS_FALLBACK=1KAN
%load_ext autoreload
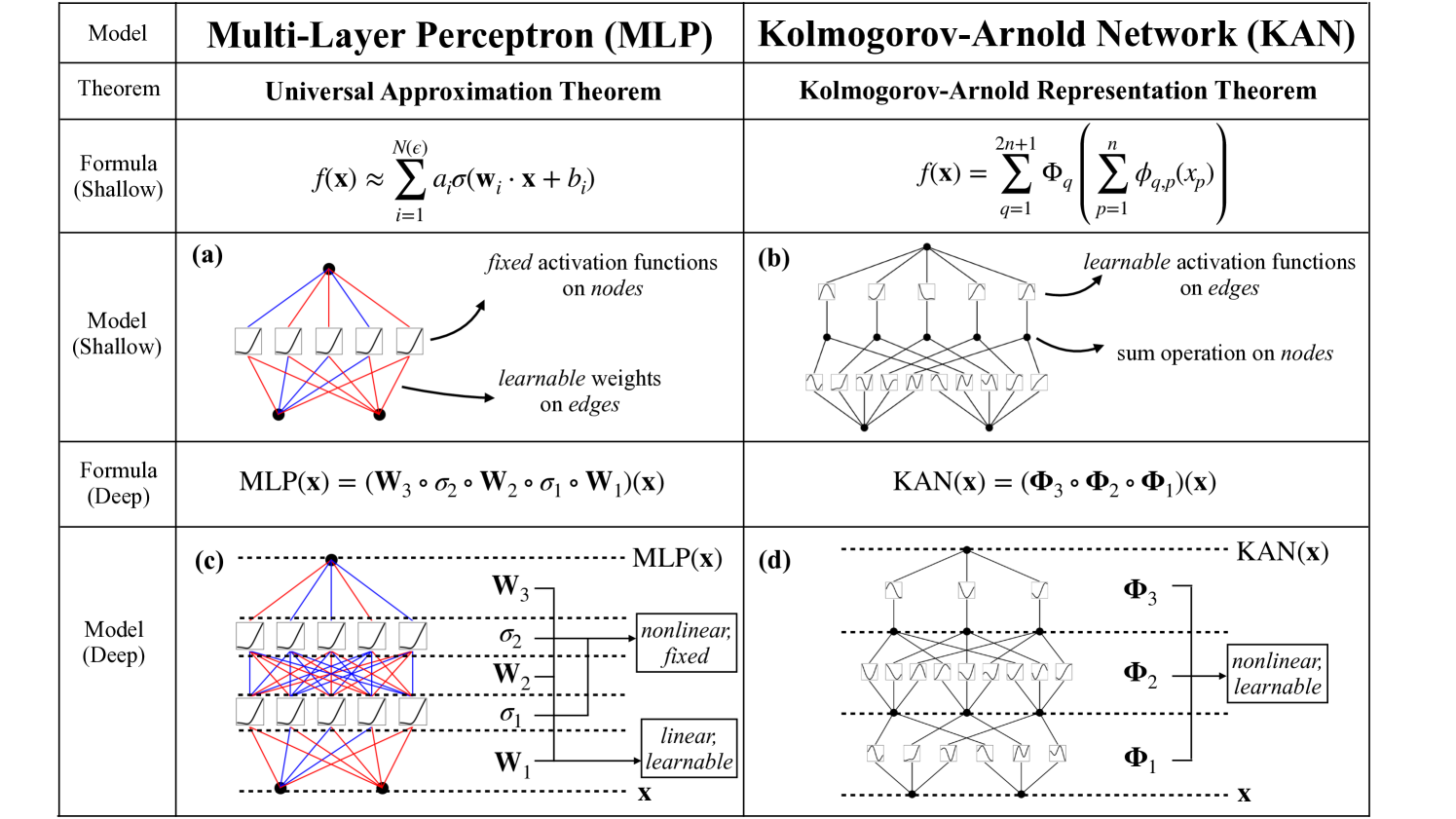
%autoreload 2Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)是多层感知器(MLPs)的替代方案。该模型以与我们的MLP模型类似的方式使用KANs。
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_docfrom typing import Optional, Union
import math
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_windows import BaseWindowsclass KANLinear(torch.nn.Module):
"""
KANLinear
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_features,
out_features,
grid_size=5,
spline_order=3,
scale_noise=0.1,
scale_base=1.0,
scale_spline=1.0,
enable_standalone_scale_spline=True,
base_activation=torch.nn.SiLU,
grid_eps=0.02,
grid_range=[-1, 1],
):
super(KANLinear, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.grid_size = grid_size
self.spline_order = spline_order
h = (grid_range[1] - grid_range[0]) / grid_size
grid = (
(
torch.arange(-spline_order, grid_size + spline_order + 1) * h
+ grid_range[0]
)
.expand(in_features, -1)
.contiguous()
)
self.register_buffer("grid", grid)
self.base_weight = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features))
self.spline_weight = torch.nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features, grid_size + spline_order)
)
if enable_standalone_scale_spline:
self.spline_scaler = torch.nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features)
)
self.scale_noise = scale_noise
self.scale_base = scale_base
self.scale_spline = scale_spline
self.enable_standalone_scale_spline = enable_standalone_scale_spline
self.base_activation = base_activation()
self.grid_eps = grid_eps
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.base_weight, a=math.sqrt(5) * self.scale_base)
with torch.no_grad():
noise = (
(
torch.rand(self.grid_size + 1, self.in_features, self.out_features)
- 1 / 2
)
* self.scale_noise
/ self.grid_size
)
self.spline_weight.data.copy_(
(self.scale_spline if not self.enable_standalone_scale_spline else 1.0)
* self.curve2coeff(
self.grid.T[self.spline_order : -self.spline_order],
noise,
)
)
if self.enable_standalone_scale_spline:
# torch.nn.init.constant_(self.spline_scaler, self.scale_spline)
torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.spline_scaler, a=math.sqrt(5) * self.scale_spline)
def b_splines(self, x: torch.Tensor):
"""
Compute the B-spline bases for the given input tensor.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Input tensor of shape (batch_size, in_features).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: B-spline bases tensor of shape (batch_size, in_features, grid_size + spline_order).
"""
assert x.dim() == 2 and x.size(1) == self.in_features
grid: torch.Tensor = (
self.grid
) # (in_features, 网格大小 + 2 * 样条阶数 + 1)
x = x.unsqueeze(-1)
bases = ((x >= grid[:, :-1]) & (x < grid[:, 1:])).to(x.dtype)
for k in range(1, self.spline_order + 1):
bases = (
(x - grid[:, : -(k + 1)])
/ (grid[:, k:-1] - grid[:, : -(k + 1)])
* bases[:, :, :-1]
) + (
(grid[:, k + 1 :] - x)
/ (grid[:, k + 1 :] - grid[:, 1:(-k)])
* bases[:, :, 1:]
)
assert bases.size() == (
x.size(0),
self.in_features,
self.grid_size + self.spline_order,
)
return bases.contiguous()
def curve2coeff(self, x: torch.Tensor, y: torch.Tensor):
"""
Compute the coefficients of the curve that interpolates the given points.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Input tensor of shape (batch_size, in_features).
y (torch.Tensor): Output tensor of shape (batch_size, in_features, out_features).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Coefficients tensor of shape (out_features, in_features, grid_size + spline_order).
"""
assert x.dim() == 2 and x.size(1) == self.in_features
assert y.size() == (x.size(0), self.in_features, self.out_features)
A = self.b_splines(x).transpose(
0, 1
) # (输入特征,批量大小,网格大小 + 样条阶数)
B = y.transpose(0, 1) # (输入特征数,批量大小,输出特征数)
solution = torch.linalg.lstsq(
A, B
).solution # (输入特征数, 网格大小 + 样条阶数, 输出特征数)
result = solution.permute(
2, 0, 1
) # (输出特征数, 输入特征数, 网格大小 + 样条阶数)
assert result.size() == (
self.out_features,
self.in_features,
self.grid_size + self.spline_order,
)
return result.contiguous()
@property
def scaled_spline_weight(self):
return self.spline_weight * (
self.spline_scaler.unsqueeze(-1)
if self.enable_standalone_scale_spline
else 1.0
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
assert x.dim() == 2 and x.size(1) == self.in_features
base_output = F.linear(self.base_activation(x), self.base_weight)
spline_output = F.linear(
self.b_splines(x).view(x.size(0), -1),
self.scaled_spline_weight.view(self.out_features, -1),
)
return base_output + spline_output
@torch.no_grad()
def update_grid(self, x: torch.Tensor, margin=0.01):
assert x.dim() == 2 and x.size(1) == self.in_features
batch = x.size(0)
splines = self.b_splines(x) # (批次,输入,系数)
splines = splines.permute(1, 0, 2) # (内,批量,系数)
orig_coeff = self.scaled_spline_weight # (出,入,系数)
orig_coeff = orig_coeff.permute(1, 2, 0) # (输入,系数,输出)
unreduced_spline_output = torch.bmm(splines, orig_coeff) # (输入,批处理,输出)
unreduced_spline_output = unreduced_spline_output.permute(
1, 0, 2
) # (批次,输入,输出)
# 分别对每个通道进行排序以收集数据分布
x_sorted = torch.sort(x, dim=0)[0]
grid_adaptive = x_sorted[
torch.linspace(
0, batch - 1, self.grid_size + 1, dtype=torch.int64, device=x.device
)
]
uniform_step = (x_sorted[-1] - x_sorted[0] + 2 * margin) / self.grid_size
grid_uniform = (
torch.arange(
self.grid_size + 1, dtype=torch.float32, device=x.device
).unsqueeze(1)
* uniform_step
+ x_sorted[0]
- margin
)
grid = self.grid_eps * grid_uniform + (1 - self.grid_eps) * grid_adaptive
grid = torch.concatenate(
[
grid[:1]
- uniform_step
* torch.arange(self.spline_order, 0, -1, device=x.device).unsqueeze(1),
grid,
grid[-1:]
+ uniform_step
* torch.arange(1, self.spline_order + 1, device=x.device).unsqueeze(1),
],
dim=0,
)
self.grid.copy_(grid.T)
self.spline_weight.data.copy_(self.curve2coeff(x, unreduced_spline_output))
def regularization_loss(self, regularize_activation=1.0, regularize_entropy=1.0):
l1_fake = self.spline_weight.abs().mean(-1)
regularization_loss_activation = l1_fake.sum()
p = l1_fake / regularization_loss_activation
regularization_loss_entropy = -torch.sum(p * p.log())
return (
regularize_activation * regularization_loss_activation
+ regularize_entropy * regularization_loss_entropy
)
class KAN(BaseWindows):
""" KAN
Simple Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN).
This network uses the Kolmogorov-Arnold approximation theorem, where splines
are learned to approximate more complex functions. Unlike the MLP, the
non-linear function are learned at the edges, and the nodes simply sum
the different learned functions.
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, forecast horizon.<br>
`input_size`: int, considered autorregresive inputs (lags), y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> lags=[1,2].<br>
`grid_size`: int, number of intervals used by the splines to approximate the function.<br>
`spline_order`: int, order of the B-splines.<br>
`scale_noise`: float, regularization coefficient for the splines.<br>
`scale_base`: float, scaling coefficient for the base function.<br>
`scale_spline`: float, scaling coefficient for the splines.<br>
`enable_standalone_scale_spline`: bool, whether each spline is scaled individually.<br>
`grid_eps`: float, used for numerical stability.<br>
`grid_range`: list, range of the grid used for spline approximation.<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`exclude_insample_y`: bool=False, the model skips the autoregressive features y[t-input_size:t] if True.<br>
`n_hidden_layers`: int, number of hidden layers for the KAN.<br>
`hidden_size`: int or list, number of units for each hidden layer of the KAN. If an integer, all hidden layers will have the same size. Use a list to specify the size of each hidden layer.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`valid_batch_size`: int=None, number of different series in each validation and test batch, if None uses batch_size.<br>
`windows_batch_size`: int=1024, number of windows to sample in each training batch, default uses all.<br>
`inference_windows_batch_size`: int=-1, number of windows to sample in each inference batch, -1 uses all.<br>
`start_padding_enabled`: bool=False, if True, the model will pad the time series with zeros at the beginning, by input size.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int=1, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
**References**<br>
- [Ziming Liu, Yixuan Wang, Sachin Vaidya, Fabian Ruehle, James Halverson, Marin Soljačić, Thomas Y. Hou, Max Tegmark. "KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756)
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'windows'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = True
EXOGENOUS_HIST = True
EXOGENOUS_STAT = True
def __init__(self,
h,
input_size,
grid_size: int = 5,
spline_order: int = 3,
scale_noise: float = 0.1,
scale_base: float = 1.0,
scale_spline: float = 1.0,
enable_standalone_scale_spline: bool = True,
grid_eps: float = 0.02,
grid_range: list = [-1, 1],
n_hidden_layers: int = 1,
hidden_size: Union[int, list] = 512,
futr_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
stat_exog_list = None,
exclude_insample_y = False,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
valid_batch_size: Optional[int] = None,
windows_batch_size = 1024,
inference_windows_batch_size = -1,
start_padding_enabled = False,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
# 继承BaseWindows类
super(KAN, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
exclude_insample_y = exclude_insample_y,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
valid_batch_size=valid_batch_size,
windows_batch_size=windows_batch_size,
inference_windows_batch_size=inference_windows_batch_size,
start_padding_enabled=start_padding_enabled,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
random_seed=random_seed,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# 建筑学
self.n_hidden_layers = n_hidden_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
input_size_first_layer = input_size + self.hist_exog_size * input_size + \
self.futr_exog_size*(input_size + h) + self.stat_exog_size
if isinstance(self.hidden_size, int):
self.hidden_layers = [input_size_first_layer] + self.n_hidden_layers*[self.hidden_size] + [self.h * self.loss.outputsize_multiplier]
elif isinstance(self.hidden_size, list):
if len(self.hidden_size) != self.n_hidden_layers:
raise Exception("The number of elements in the list hidden_size must equal the number of n_hidden_layers")
self.hidden_layers = [input_size_first_layer] + self.hidden_size + [self.h * self.loss.outputsize_multiplier]
self.grid_size = grid_size
self.spline_order = spline_order
self.scale_noise = scale_noise
self.scale_base = scale_base
self.scale_spline = scale_spline
self.enable_standalone_scale_spline = enable_standalone_scale_spline
self.base_activation = torch.nn.SiLU
self.grid_eps = grid_eps
self.grid_range = grid_range
self.layers = torch.nn.ModuleList()
for in_features, out_features in zip(self.hidden_layers, self.hidden_layers[1:]):
self.layers.append(
KANLinear(
in_features,
out_features,
grid_size=grid_size,
spline_order=self.spline_order,
scale_noise=self.scale_noise,
scale_base=self.scale_base,
scale_spline=self.scale_spline,
base_activation=self.base_activation,
grid_eps=self.grid_eps,
grid_range=self.grid_range,
)
)
def regularization_loss(self, regularize_activation=1.0, regularize_entropy=1.0):
return sum(
layer.regularization_loss(regularize_activation, regularize_entropy)
for layer in self.layers
)
def forward(self, windows_batch, update_grid=False):
insample_y = windows_batch['insample_y']
futr_exog = windows_batch['futr_exog']
hist_exog = windows_batch['hist_exog']
stat_exog = windows_batch['stat_exog']
# 将 MLP 输入展平 [B, L+H, C] -> [B, (L+H)*C]
# 连接 [ Y_t, | X_{t-L},..., X_{t} | F_{t-L},..., F_{t+H} | S ]
batch_size = len(insample_y)
if self.hist_exog_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, hist_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
if self.futr_exog_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, futr_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
if self.stat_exog_size > 0:
insample_y = torch.cat(( insample_y, stat_exog.reshape(batch_size,-1) ), dim=1)
y_pred = insample_y.clone()
for layer in self.layers:
if update_grid:
layer.update_grid(y_pred)
y_pred = layer(y_pred)
y_pred = y_pred.reshape(batch_size, self.h,
self.loss.outputsize_multiplier)
y_pred = self.loss.domain_map(y_pred)
return y_pred
show_doc(KAN)show_doc(KAN.fit, name='KAN.fit')show_doc(KAN.predict, name='KAN.predict')用法示例
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import KAN
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import DistributionLoss
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]] # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
fcst = NeuralForecast(
models=[
KAN(h=12,
input_size=24,
loss = DistributionLoss(distribution="Normal"),
max_steps=100,
scaler_type='standard',
futr_exog_list=['y_[lag12]'],
hist_exog_list=None,
stat_exog_list=['airline1'],
),
],
freq='M'
)
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
# 绘制分位数预测图
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['KAN-median'], c='blue', label='median')
plt.fill_between(x=plot_df['ds'][-12:],
y1=plot_df['KAN-lo-90'][-12:].values,
y2=plot_df['KAN-hi-90'][-12:].values,
alpha=0.4, label='level 90')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()Give us a ⭐ on Github