%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2TSMixer
时间序列混合器(
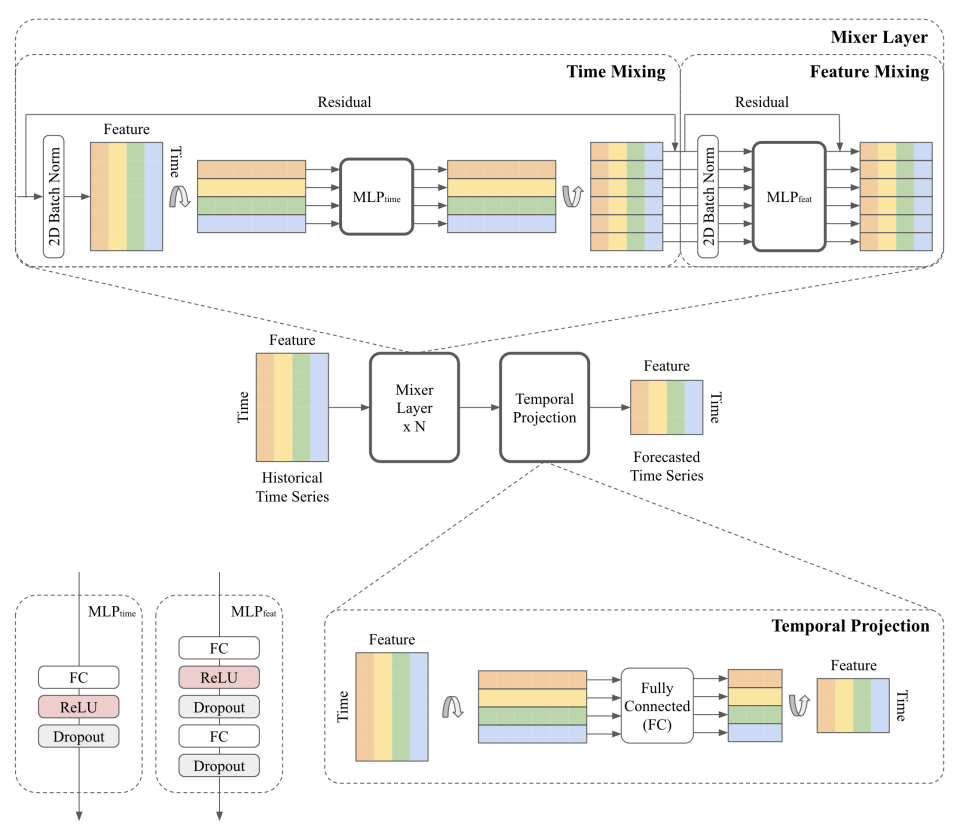
TSMixer)是一种基于多层感知器(MLP)的多变量时间序列预测模型。TSMixer通过使用堆叠混合层反复结合时间和特征信息,联合学习时间序列的时间和横截面表示。混合层由一个顺序的时间和特征多层感知器(MLP)组成。注意:该模型无法处理外生输入。如果您想使用额外的外生输入,请使用TSMixerx。
from fastcore.test import test_eq
from nbdev.showdoc import show_docimport torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
from neuralforecast.common._base_multivariate import BaseMultivariate1. 辅助函数
1.1 混合层
混合层由一个顺序的时间和特征多层感知器(MLP)组成。
class 时间混合(nn.Module):
"""
时间混合
"""
def __init__(self, n_series, input_size, dropout):
super().__init__()
self.temporal_norm = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=n_series * input_size, eps=0.001, momentum=0.01)
self.temporal_lin = nn.Linear(input_size, input_size)
self.temporal_drop = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, input):
# 获取形状
batch_size = input.shape[0]
input_size = input.shape[1]
n_series = input.shape[2]
# 时间多层感知器
x = input.permute(0, 2, 1) # [B, L, N] -> [B, N, L]
x = x.reshape(batch_size, -1) # [B, N, L] -> [B, N * L]
x = self.temporal_norm(x) # [B, N * L] -> [B, N * L]
x = x.reshape(batch_size, n_series, input_size) # [B, N * L] -> [B, N, L]
x = F.relu(self.temporal_lin(x)) # [B, N, L] -> [B, N, L]
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) # [B, N, L] -> [B, L, N]
x = self.temporal_drop(x) # [批次, 长度, 嵌入维度] -> [批次, 长度, 嵌入维度]
return x + input
class 特征混合(nn.Module):
"""
特征混合
"""
def __init__(self, n_series, input_size, dropout, ff_dim):
super().__init__()
self.feature_norm = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=n_series * input_size, eps=0.001, momentum=0.01)
self.feature_lin_1 = nn.Linear(n_series, ff_dim)
self.feature_lin_2 = nn.Linear(ff_dim, n_series)
self.feature_drop_1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.feature_drop_2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, input):
# 获取形状
batch_size = input.shape[0]
input_size = input.shape[1]
n_series = input.shape[2]
# 特征多层感知器
x = input.reshape(batch_size, -1) # [B, L, N] -> [B, L * N]
x = self.feature_norm(x) # [B, L * N] -> [B, L * N]
x = x.reshape(batch_size, input_size, n_series) # [B, L * N] -> [B, L, N]
x = F.relu(self.feature_lin_1(x)) # [B, L, N] -> [B, L, ff_dim]
x = self.feature_drop_1(x) # [批次大小, 序列长度, 前馈维度] -> [批次大小, 序列长度, 前馈维度]
x = self.feature_lin_2(x) # [B, L, ff_dim] -> [B, L, N]
x = self.feature_drop_2(x) # [批次, 长度, 嵌入维度] -> [批次, 长度, 嵌入维度]
return x + input
class 混合层(nn.Module):
"""
混合层
"""
def __init__(self, n_series, input_size, dropout, ff_dim):
super().__init__()
# 混合层由时间混合器和特征混合器组成。
self.temporal_mixer = 时间混合(n_series, input_size, dropout)
self.feature_mixer = 特征混合(n_series, input_size, dropout, ff_dim)
def forward(self, input):
x = self.temporal_mixer(input)
x = self.feature_mixer(x)
return x1.2 可逆的实例归一化
一个可逆的实例归一化层,基于 这个参考实现。
class 可逆实例归一化1维(nn.Module):
"""
可逆实例归一化1维
"""
def __init__(self, n_series, eps=1e-5):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones((1, 1, n_series)))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, 1, n_series)))
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
# 批量统计
self.batch_mean = torch.mean(x, axis=1, keepdim=True).detach()
self.batch_std = torch.sqrt(torch.var(x, axis=1, keepdim=True, unbiased=False) + self.eps).detach()
# 实例归一化
x = x - self.batch_mean
x = x / self.batch_std
x = x * self.weight
x = x + self.bias
return x
def reverse(self, x):
# 逆转正常化
x = x - self.bias
x = x / self.weight
x = x * self.batch_std
x = x + self.batch_mean
return x2. 模型
class TSMixer(BaseMultivariate):
""" TSMixer
Time-Series Mixer (`TSMixer`) is a MLP-based multivariate time-series forecasting model. `TSMixer` jointly learns temporal and cross-sectional representations of the time-series by repeatedly combining time- and feature information using stacked mixing layers. A mixing layer consists of a sequential time- and feature Multi Layer Perceptron (`MLP`).
**Parameters:**<br>
`h`: int, forecast horizon.<br>
`input_size`: int, considered autorregresive inputs (lags), y=[1,2,3,4] input_size=2 -> lags=[1,2].<br>
`n_series`: int, number of time-series.<br>
`futr_exog_list`: str list, future exogenous columns.<br>
`hist_exog_list`: str list, historic exogenous columns.<br>
`stat_exog_list`: str list, static exogenous columns.<br>
`n_block`: int=2, number of mixing layers in the model.<br>
`ff_dim`: int=64, number of units for the second feed-forward layer in the feature MLP.<br>
`dropout`: float=0.9, dropout rate between (0, 1) .<br>
`revin`: bool=True, if True uses Reverse Instance Normalization to process inputs and outputs.<br>
`loss`: PyTorch module, instantiated train loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`valid_loss`: PyTorch module=`loss`, instantiated valid loss class from [losses collection](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/losses.pytorch.html).<br>
`max_steps`: int=1000, maximum number of training steps.<br>
`learning_rate`: float=1e-3, Learning rate between (0, 1).<br>
`num_lr_decays`: int=-1, Number of learning rate decays, evenly distributed across max_steps.<br>
`early_stop_patience_steps`: int=-1, Number of validation iterations before early stopping.<br>
`val_check_steps`: int=100, Number of training steps between every validation loss check.<br>
`batch_size`: int=32, number of different series in each batch.<br>
`step_size`: int=1, step size between each window of temporal data.<br>
`scaler_type`: str='identity', type of scaler for temporal inputs normalization see [temporal scalers](https://nixtla.github.io/neuralforecast/common.scalers.html).<br>
`random_seed`: int=1, random_seed for pytorch initializer and numpy generators.<br>
`num_workers_loader`: int=os.cpu_count(), workers to be used by `TimeSeriesDataLoader`.<br>
`drop_last_loader`: bool=False, if True `TimeSeriesDataLoader` drops last non-full batch.<br>
`alias`: str, optional, Custom name of the model.<br>
`optimizer`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.Optimizer', optional, user specified optimizer instead of the default choice (Adam).<br>
`optimizer_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `optimizer`.<br>
`lr_scheduler`: Subclass of 'torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LRScheduler', optional, user specified lr_scheduler instead of the default choice (StepLR).<br>
`lr_scheduler_kwargs`: dict, optional, list of parameters used by the user specified `lr_scheduler`.<br>
`**trainer_kwargs`: int, keyword trainer arguments inherited from [PyTorch Lighning's trainer](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer.html?highlight=trainer).<br>
**References:**<br>
- [Chen, Si-An, Chun-Liang Li, Nate Yoder, Sercan O. Arik, and Tomas Pfister (2023). "TSMixer: An All-MLP Architecture for Time Series Forecasting."](http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.06053)
"""
# Class attributes
SAMPLING_TYPE = 'multivariate'
EXOGENOUS_FUTR = False
EXOGENOUS_HIST = False
EXOGENOUS_STAT = False
def __init__(self,
h,
input_size,
n_series,
futr_exog_list = None,
hist_exog_list = None,
stat_exog_list = None,
n_block = 2,
ff_dim = 64,
dropout = 0.9,
revin = True,
loss = MAE(),
valid_loss = None,
max_steps: int = 1000,
learning_rate: float = 1e-3,
num_lr_decays: int = -1,
early_stop_patience_steps: int =-1,
val_check_steps: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 32,
step_size: int = 1,
scaler_type: str = 'identity',
random_seed: int = 1,
num_workers_loader: int = 0,
drop_last_loader: bool = False,
optimizer = None,
optimizer_kwargs = None,
lr_scheduler = None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs = None,
**trainer_kwargs):
# Inherit BaseMultivariate class
super(TSMixer, self).__init__(h=h,
input_size=input_size,
n_series=n_series,
futr_exog_list=futr_exog_list,
hist_exog_list=hist_exog_list,
stat_exog_list=stat_exog_list,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
max_steps=max_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
num_lr_decays=num_lr_decays,
early_stop_patience_steps=early_stop_patience_steps,
val_check_steps=val_check_steps,
batch_size=batch_size,
step_size=step_size,
scaler_type=scaler_type,
random_seed=random_seed,
num_workers_loader=num_workers_loader,
drop_last_loader=drop_last_loader,
optimizer=optimizer,
optimizer_kwargs=optimizer_kwargs,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
lr_scheduler_kwargs=lr_scheduler_kwargs,
**trainer_kwargs)
# Reversible InstanceNormalization layer
self.revin = revin
if self.revin:
self.norm = ReversibleInstanceNorm1d(n_series = n_series)
# Mixing layers
mixing_layers = [MixingLayer(n_series=n_series,
input_size=input_size,
dropout=dropout,
ff_dim=ff_dim)
for _ in range(n_block)]
self.mixing_layers = nn.Sequential(*mixing_layers)
# Linear output with Loss dependent dimensions
self.out = nn.Linear(in_features=input_size,
out_features=h * self.loss.outputsize_multiplier)
def forward(self, windows_batch):
# Parse batch
x = windows_batch['insample_y'] # x: [批次大小, 输入维度, 序列数量]
batch_size = x.shape[0]
# TSMixer:实例归一化 + 混合层 + 密集输出层 + 反向实例归一化
if self.revin:
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.mixing_layers(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1)
x = self.out(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1)
if self.revin:
x = self.norm.reverse(x)
x = x.reshape(batch_size, self.h, self.loss.outputsize_multiplier * self.n_series)
forecast = self.loss.domain_map(x)
# 在 n_series == 1 的情况下,domain_map 可能已经压缩了最后一个维度。
# 请注意,在元组损失的情况下,此方法会失败,但Multivariate目前尚不支持元组损失。
if forecast.ndim == 2:
return forecast.unsqueeze(-1)
else:
return forecastshow_doc(TSMixer)show_doc(TSMixer.fit, name='TSMixer.fit')show_doc(TSMixer.predict, name='TSMixer.predict')import logging
import warnings
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE, MSE, RMSE, MAPE, SMAPE, MASE, relMSE, QuantileLoss, MQLoss, DistributionLoss,PMM, GMM, NBMM, HuberLoss, TukeyLoss, HuberQLoss, HuberMQLoss# 测试损失
logging.getLogger("pytorch_lightning").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
AirPassengersStatic_single = AirPassengersStatic[AirPassengersStatic["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
Y_train_df_single = Y_train_df[Y_train_df["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
Y_test_df_single = Y_test_df[Y_test_df["unique_id"] == 'Airline1']
losses = [MAE(), MSE(), RMSE(), MAPE(), SMAPE(), MASE(seasonality=12), relMSE(y_train=Y_train_df), QuantileLoss(q=0.5), MQLoss(), DistributionLoss(distribution='Bernoulli'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Poisson'), DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT'), DistributionLoss(distribution='NegativeBinomial'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Tweedie'), PMM(), GMM(), NBMM(), HuberLoss(), TukeyLoss(), HuberQLoss(q=0.5), HuberMQLoss()]
valid_losses = [MAE(), MSE(), RMSE(), MAPE(), SMAPE(), MASE(seasonality=12), relMSE(y_train=Y_train_df), QuantileLoss(q=0.5), MQLoss(), DistributionLoss(distribution='Bernoulli'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Normal'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Poisson'), DistributionLoss(distribution='StudentT'), DistributionLoss(distribution='NegativeBinomial'), DistributionLoss(distribution='Tweedie'), PMM(), GMM(), NBMM(), HuberLoss(), TukeyLoss(), HuberQLoss(q=0.5), HuberMQLoss()]
for loss, valid_loss in zip(losses, valid_losses):
try:
model = TSMixer(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=2,
n_block=4,
ff_dim=4,
revin=True,
scaler_type='standard',
max_steps=2,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=loss,
valid_loss=valid_loss,
batch_size=32
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
except Exception as e:
assert str(e) == f"{loss} is not supported in a Multivariate model."
# 测试系列数 = 1
model = TSMixer(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=1,
n_block=4,
ff_dim=4,
revin=True,
scaler_type='standard',
max_steps=2,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=MAE(),
valid_loss=MAE(),
batch_size=32
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df_single, static_df=AirPassengersStatic_single, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df_single)3. 使用示例
训练模型并使用 predict 方法预测未来值。
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from neuralforecast import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import TSMixer
from neuralforecast.utils import AirPassengersPanel, AirPassengersStatic
from neuralforecast.losses.pytorch import MAE
Y_train_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds<AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 132次列车
Y_test_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel.ds>=AirPassengersPanel['ds'].values[-12]].reset_index(drop=True) # 12项测试
model = TSMixer(h=12,
input_size=24,
n_series=2,
n_block=4,
ff_dim=4,
dropout=0,
revin=True,
scaler_type='standard',
max_steps=500,
early_stop_patience_steps=-1,
val_check_steps=5,
learning_rate=1e-3,
loss=MAE(),
valid_loss=MAE(),
batch_size=32
)
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
fcst.fit(df=Y_train_df, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, val_size=12)
forecasts = fcst.predict(futr_df=Y_test_df)
# 情节预测
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (20, 7))
Y_hat_df = forecasts.reset_index(drop=False).drop(columns=['unique_id','ds'])
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_test_df, Y_hat_df], axis=1)
plot_df = pd.concat([Y_train_df, plot_df])
plot_df = plot_df[plot_df.unique_id=='Airline1'].drop('unique_id', axis=1)
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(plot_df['ds'], plot_df['TSMixer'], c='blue', label='Forecast')
ax.set_title('AirPassengers Forecast', fontsize=22)
ax.set_ylabel('Monthly Passengers', fontsize=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Year', fontsize=20)
ax.legend(prop={'size': 15})
ax.grid()使用cross_validation进行多个历史值的预测。
fcst = NeuralForecast(models=[model], freq='M')
forecasts = fcst.cross_validation(df=AirPassengersPanel, static_df=AirPassengersStatic, n_windows=2, step_size=12)
# 情节预测
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (20, 7))
Y_hat_df = forecasts.loc['Airline1']
Y_df = AirPassengersPanel[AirPassengersPanel['unique_id']=='Airline1']
plt.plot(Y_df['ds'], Y_df['y'], c='black', label='True')
plt.plot(Y_hat_df['ds'], Y_hat_df['TSMixer'], c='blue', label='Forecast')
ax.set_title('AirPassengers Forecast', fontsize=22)
ax.set_ylabel('Monthly Passengers', fontsize=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Year', fontsize=20)
ax.legend(prop={'size': 15})
ax.grid()Give us a ⭐ on Github