坐标系¶
限定名称: manim.mobject.graphing.coordinate\_systems.CoordinateSystem
- class CoordinateSystem(x_range=None, y_range=None, x_length=None, y_length=None, dimension=2)[source]¶
基础:
objectAxes 和 NumberPlane 的抽象基类。
示例
示例:CoordSysExample ¶
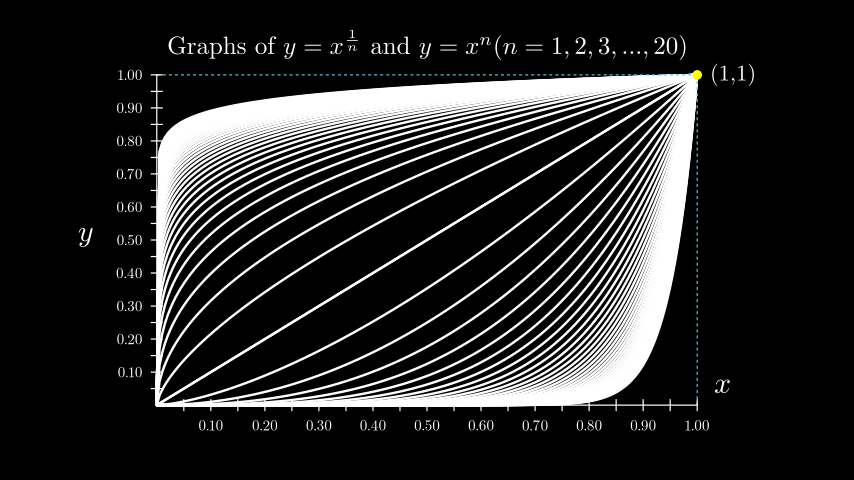
from manim import * class CoordSysExample(Scene): def construct(self): # the location of the ticks depends on the x_range and y_range. grid = Axes( x_range=[0, 1, 0.05], # step size determines num_decimal_places. y_range=[0, 1, 0.05], x_length=9, y_length=5.5, axis_config={ "numbers_to_include": np.arange(0, 1 + 0.1, 0.1), "font_size": 24, }, tips=False, ) # Labels for the x-axis and y-axis. y_label = grid.get_y_axis_label("y", edge=LEFT, direction=LEFT, buff=0.4) x_label = grid.get_x_axis_label("x") grid_labels = VGroup(x_label, y_label) graphs = VGroup() for n in np.arange(1, 20 + 0.5, 0.5): graphs += grid.plot(lambda x: x ** n, color=WHITE) graphs += grid.plot( lambda x: x ** (1 / n), color=WHITE, use_smoothing=False ) # Extra lines and labels for point (1,1) graphs += grid.get_horizontal_line(grid.c2p(1, 1, 0), color=BLUE) graphs += grid.get_vertical_line(grid.c2p(1, 1, 0), color=BLUE) graphs += Dot(point=grid.c2p(1, 1, 0), color=YELLOW) graphs += Tex("(1,1)").scale(0.75).next_to(grid.c2p(1, 1, 0)) title = Title( # spaces between braces to prevent SyntaxError r"Graphs of $y=x^{ {1}\over{n} }$ and $y=x^n (n=1,2,3,...,20)$", include_underline=False, font_size=40, ) self.add(title, graphs, grid, grid_labels)
class CoordSysExample(Scene): def construct(self): # the location of the ticks depends on the x_range and y_range. grid = Axes( x_range=[0, 1, 0.05], # step size determines num_decimal_places. y_range=[0, 1, 0.05], x_length=9, y_length=5.5, axis_config={ "numbers_to_include": np.arange(0, 1 + 0.1, 0.1), "font_size": 24, }, tips=False, ) # Labels for the x-axis and y-axis. y_label = grid.get_y_axis_label("y", edge=LEFT, direction=LEFT, buff=0.4) x_label = grid.get_x_axis_label("x") grid_labels = VGroup(x_label, y_label) graphs = VGroup() for n in np.arange(1, 20 + 0.5, 0.5): graphs += grid.plot(lambda x: x ** n, color=WHITE) graphs += grid.plot( lambda x: x ** (1 / n), color=WHITE, use_smoothing=False ) # Extra lines and labels for point (1,1) graphs += grid.get_horizontal_line(grid.c2p(1, 1, 0), color=BLUE) graphs += grid.get_vertical_line(grid.c2p(1, 1, 0), color=BLUE) graphs += Dot(point=grid.c2p(1, 1, 0), color=YELLOW) graphs += Tex("(1,1)").scale(0.75).next_to(grid.c2p(1, 1, 0)) title = Title( # spaces between braces to prevent SyntaxError r"Graphs of $y=x^{ {1}\over{n} }$ and $y=x^n (n=1,2,3,...,20)$", include_underline=False, font_size=40, ) self.add(title, graphs, grid, grid_labels)方法
向坐标轴添加标签。
返回在特定x值处绘制曲线的切线与x轴的角度。
coords_to_point()的缩写coords_to_point创建一个带有标签的三角形标记,并在给定的x值处从x轴到曲线绘制一条垂直线。
返回一个
Polygon,表示传递的图形下的区域。get_axesget_axisget_axis_labels为传递的图形创建一个正确定位的标签,带有可选的点。
从y轴到场景中给定点的水平线。
返回从给定轴到场景中某一点的直线。
从轴到一个点生成水平和垂直线。
获取
Axes的原点。为给定曲线生成一个
VGroup的黎曼矩形。创建两条线表示dx和df,dx和df的标签,以及
从x轴到场景中给定点的垂直线。
从x轴到曲线获取多行。
get_x_axis生成一个x轴标签。
get_x_unit_sizeget_y_axis生成一个y轴标签。
get_y_unit_sizeget_z_axis返回基于给定x值的图表上点的轴相对坐标的元组。
返回对应于
x值的graph上的点的坐标。point_to_coords()的缩写基于函数生成曲线。
绘制一个反导数图。
返回传递图形的导数曲线。
创建一个隐式函数的曲线。
参数曲线。
一个极坐标图。
基于函数生成一个表面。
point_to_coords从点获取极坐标。
从极坐标获取一个点。
返回在特定x值处绘制曲线的切线的斜率。
- Parameters:
x_range (序列[浮点数] | 无)
y_range (序列[浮点数] | 无)
x_length (浮点数 | 无)
y_length (float | None)
维度 (整数)
- add_coordinates(*axes_numbers, **kwargs)[source]¶
向坐标轴添加标签。使用
Axes.coordinate_labels来在创建后访问坐标。- Parameters:
axes_numbers (Iterable[float] | None | dict[float, str | float | Mobject]) – 要添加到轴上的数字。使用
None表示带有默认标签的轴。kwargs (任意)
- Return type:
自我
示例
ax = ThreeDAxes() x_labels = range(-4, 5) z_labels = range(-4, 4, 2) ax.add_coordinates(x_labels, None, z_labels) # default y labels, custom x & z labels ax.add_coordinates(x_labels) # only x labels
您还可以使用字典专门控制标签的位置和值。
ax = Axes(x_range=[0, 7]) x_pos = [x for x in range(1, 8)] # strings are automatically converted into a Tex mobject. x_vals = ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"] x_dict = dict(zip(x_pos, x_vals)) ax.add_coordinates(x_dict)
- angle_of_tangent(x, graph, dx=1e-08)[source]¶
返回在特定x值处绘制曲线的切线与x轴的角度。
- Parameters:
x (float) – 切线与曲线接触的x值。
graph (ParametricFunction) – 用于计算切线的
ParametricFunction。dx (float) – 用于确定曲线切线角度的x的变化量。
- Returns:
曲线切线的角度。
- Return type:
float
示例
ax = Axes() curve = ax.plot(lambda x: x**2) ax.angle_of_tangent(x=3, graph=curve) # 1.4056476493802699
- c2p(*coords)[source]¶
coords_to_point()的缩写- Parameters:
coords (float | Sequence[float] | Sequence[Sequence[float]] | ndarray)
- Return type:
ndarray
- get_T_label(x_val, graph, label=None, label_color=None, triangle_size=0.25, triangle_color=ManimColor('#FFFFFF'), line_func=<class 'manim.mobject.geometry.line.Line'>, line_color=ManimColor('#FFFF00'))[source]¶
创建一个带有标签的三角形标记,并从x轴到给定x值的曲线绘制一条垂直线。
- Parameters:
x_val (float) – 沿着曲线的位置,标签、线和三角形将在此位置构建。
graph (ParametricFunction) – 用于构建标签的
ParametricFunction。标签 (浮点数 | 字符串 | Mobject | 无) – 垂直线和三角形的标签。
label_color (ParsableManimColor | None) – 标签的颜色。
triangle_size (float) – 三角形的大小。
triangle_color (ParsableManimColor | None) – 三角形的颜色。
line_func (type[Line]) – 用于构造垂直线的函数。
line_color (ParsableManimColor) – 垂直线的颜色。
- Returns:
标签、三角形和垂直线mobjects的
VGroup。- Return type:
示例
示例:TLabelExample ¶
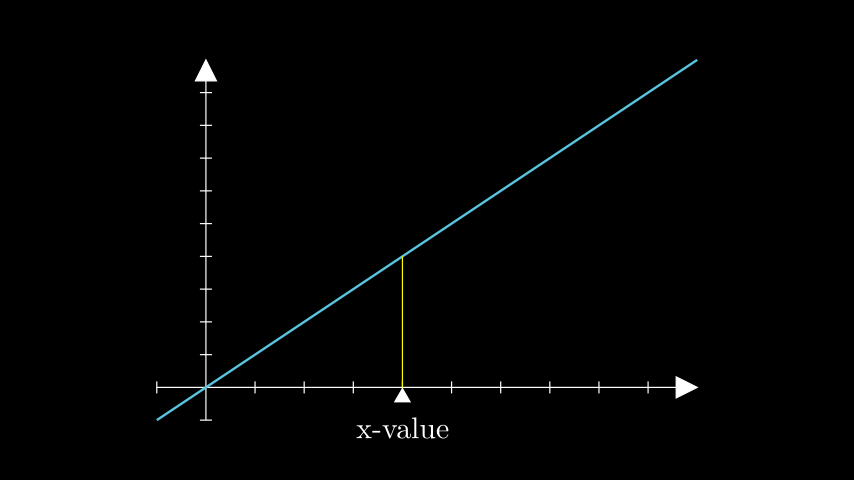
from manim import * class TLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): # defines the axes and linear function axes = Axes(x_range=[-1, 10], y_range=[-1, 10], x_length=9, y_length=6) func = axes.plot(lambda x: x, color=BLUE) # creates the T_label t_label = axes.get_T_label(x_val=4, graph=func, label=Tex("x-value")) self.add(axes, func, t_label)
class TLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): # defines the axes and linear function axes = Axes(x_range=[-1, 10], y_range=[-1, 10], x_length=9, y_length=6) func = axes.plot(lambda x: x, color=BLUE) # creates the T_label t_label = axes.get_T_label(x_val=4, graph=func, label=Tex("x-value")) self.add(axes, func, t_label)
- get_area(graph, x_range=None, color=(ManimColor('#58C4DD'), ManimColor('#83C167')), opacity=0.3, bounded_graph=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
返回一个
Polygon,表示传递的图形下的区域。- Parameters:
graph (ParametricFunction) – 需要获取面积的图形/曲线。
x_range (tuple[float, float] | None) – 区域的最小和最大x值的范围。
x_range = [x_min, x_max].颜色 (ParsableManimColor | Iterable[ParsableManimColor]) – 区域的颜色。如果提供颜色列表,则创建渐变。
opacity (float) – 区域的不透明度。
bounded_graph (ParametricFunction) – 如果指定了第二个
graph,则包围两条曲线之间的区域。kwargs (Any) – 传递给
Polygon的附加参数。
- Returns:
表示区域的
Polygon。- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – 当x_ranges不匹配时(无论是区域的x_range、图形的x_range还是有界图形的x_range)。
示例
示例:GetAreaExample ¶
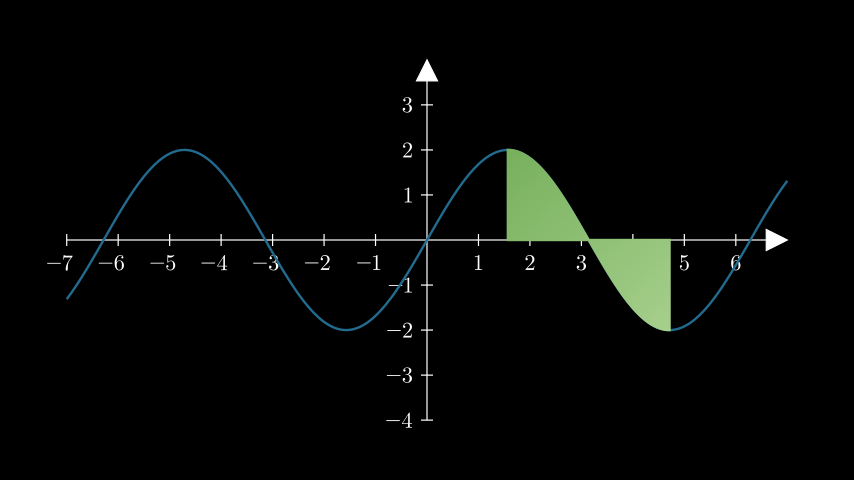
from manim import * class GetAreaExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() curve = ax.plot(lambda x: 2 * np.sin(x), color=DARK_BLUE) area = ax.get_area( curve, x_range=(PI / 2, 3 * PI / 2), color=(GREEN_B, GREEN_D), opacity=1, ) self.add(ax, curve, area)
class GetAreaExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() curve = ax.plot(lambda x: 2 * np.sin(x), color=DARK_BLUE) area = ax.get_area( curve, x_range=(PI / 2, 3 * PI / 2), color=(GREEN_B, GREEN_D), opacity=1, ) self.add(ax, curve, area)
- get_graph_label(graph, label='f(x)', x_val=None, direction=array([1., 0., 0.]), buff=0.25, color=None, dot=False, dot_config=None)[来源]¶
为传递的图形创建一个正确定位的标签,带有可选的点。
- Parameters:
graph (ParametricFunction) – 曲线。
标签 (浮点数 | 字符串 | Mobject) – 函数曲线的标签。默认为
MathTex用于字符串和浮点数输入。x_val (float | None) – 沿着曲线定位标签的x值。
方向 (序列[浮点数]) – 标签相对于曲线的笛卡尔位置 –>
LEFT,RIGHT.buff (float) – 曲线与标签之间的距离。
color (ParsableManimColor | None) – 标签的颜色。默认为曲线的颜色。
dot (bool) – 是否在图表上的点添加一个点。
dot_config (dict[str, Any] | None) – 传递给
Dot的额外参数。
- Returns:
定位的标签和
Dot,如果适用的话。- Return type:
Mobject
示例
示例:GetGraphLabelExample ¶

from manim import * class GetGraphLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() sin = ax.plot(lambda x: np.sin(x), color=PURPLE_B) label = ax.get_graph_label( graph=sin, label= MathTex(r"\frac{\pi}{2}"), x_val=PI / 2, dot=True, direction=UR, ) self.add(ax, sin, label)
class GetGraphLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() sin = ax.plot(lambda x: np.sin(x), color=PURPLE_B) label = ax.get_graph_label( graph=sin, label= MathTex(r"\frac{\pi}{2}"), x_val=PI / 2, dot=True, direction=UR, ) self.add(ax, sin, label)
- get_horizontal_line(point, **kwargs)[来源]¶
从y轴到场景中给定点的水平线。
- Parameters:
point (Sequence[float]) – 水平线将绘制到的点。
kwargs – 传递给
get_line_from_axis_to_point的额外参数。
- Returns:
从y轴到该点的水平线。
- Return type:
Line
示例
示例:GetHorizontalLineExample ¶
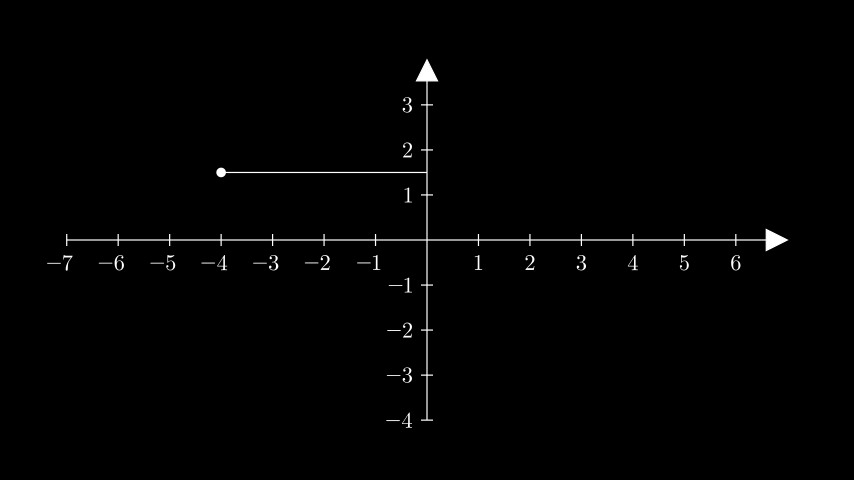
from manim import * class GetHorizontalLineExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() point = ax.c2p(-4, 1.5) dot = Dot(point) line = ax.get_horizontal_line(point, line_func=Line) self.add(ax, line, dot)
class GetHorizontalLineExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() point = ax.c2p(-4, 1.5) dot = Dot(point) line = ax.get_horizontal_line(point, line_func=Line) self.add(ax, line, dot)
- get_line_from_axis_to_point(index: int, point: Sequence[float], line_config: dict | None = None, color: ParsableManimColor | None = None, stroke_width: float = 2) DashedLine[来源]¶
- get_line_from_axis_to_point(index: int, point: Sequence[float], line_func: type[LineType], line_config: dict | None = None, color: ParsableManimColor | None = None, stroke_width: float = 2) LineType
返回从给定轴到场景中某一点的直线。
- get_lines_to_point(point, **kwargs)[source]¶
从轴到一个点生成水平和垂直线。
- Parameters:
点 (序列[浮点数]) – 场景中的一个点。
kwargs – 传递给
get_line_from_axis_to_point()的额外参数
- Returns:
一组水平和垂直线的
VGroup。- Return type:
示例
示例:GetLinesToPointExample ¶
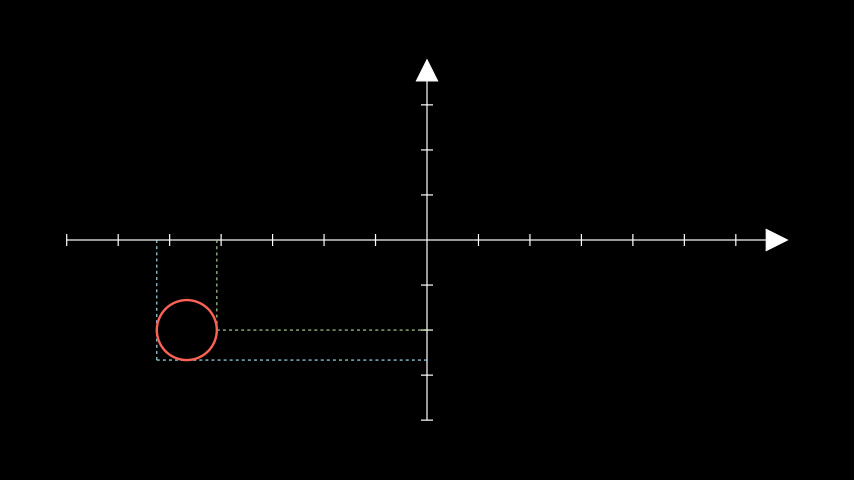
from manim import * class GetLinesToPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() circ = Circle(radius=0.5).move_to([-4, -1.5, 0]) lines_1 = ax.get_lines_to_point(circ.get_right(), color=GREEN_B) lines_2 = ax.get_lines_to_point(circ.get_corner(DL), color=BLUE_B) self.add(ax, lines_1, lines_2, circ)
class GetLinesToPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() circ = Circle(radius=0.5).move_to([-4, -1.5, 0]) lines_1 = ax.get_lines_to_point(circ.get_right(), color=GREEN_B) lines_2 = ax.get_lines_to_point(circ.get_corner(DL), color=BLUE_B) self.add(ax, lines_1, lines_2, circ)
- get_riemann_rectangles(graph, x_range=None, dx=0.1, input_sample_type='left', stroke_width=1, stroke_color=ManimColor('#000000'), fill_opacity=1, color=(ManimColor('#58C4DD'), ManimColor('#83C167')), show_signed_area=True, bounded_graph=None, blend=False, width_scale_factor=1.001)[source]¶
为给定曲线生成一个
VGroup的黎曼矩形。- Parameters:
graph (ParametricFunction) – 该图形的面积将通过黎曼矩形进行近似计算。
x_range (Sequence[float] | None) – 矩形的最小和最大x值。
x_range = [x_min, x_max].dx (float | None) – 分隔每个矩形的x值变化。
input_sample_type (str) – 可以是
"left","right"或"center"中的任意一个。指的是每个黎曼矩形的高度样本点将位于分区段内的位置。stroke_width (float) – 矩形边框的线条宽度。
stroke_color (ParsableManimColor) – 矩形边框的颜色。
fill_opacity (float) – 矩形的不透明度。
color (Iterable[ParsableManimColor] | ParsableManimColor) – 矩形的颜色。如果传递了多种颜色,则创建平衡的渐变。
show_signed_area (bool) – 当曲线在x轴下方时,通过反转其颜色来指示负面积。
blend (bool) – 将
stroke_color设置为fill_color,使矩形在没有清晰分隔的情况下混合。bounded_graph (ParametricFunction) – 如果指定了次要图形,则包围两条曲线之间的区域。
width_scale_factor (float) – 矩形宽度缩放的比例因子。
- Returns:
一个包含黎曼矩形的
VGroup。- Return type:
示例
示例:GetRiemannRectanglesExample ¶
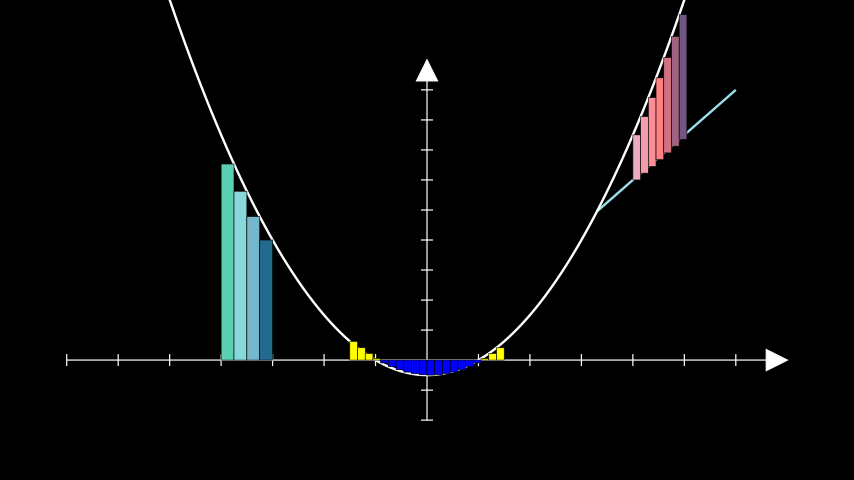
from manim import * class GetRiemannRectanglesExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(y_range=[-2, 10]) quadratic = ax.plot(lambda x: 0.5 * x ** 2 - 0.5) # the rectangles are constructed from their top right corner. # passing an iterable to `color` produces a gradient rects_right = ax.get_riemann_rectangles( quadratic, x_range=[-4, -3], dx=0.25, color=(TEAL, BLUE_B, DARK_BLUE), input_sample_type="right", ) # the colour of rectangles below the x-axis is inverted # due to show_signed_area rects_left = ax.get_riemann_rectangles( quadratic, x_range=[-1.5, 1.5], dx=0.15, color=YELLOW ) bounding_line = ax.plot( lambda x: 1.5 * x, color=BLUE_B, x_range=[3.3, 6] ) bounded_rects = ax.get_riemann_rectangles( bounding_line, bounded_graph=quadratic, dx=0.15, x_range=[4, 5], show_signed_area=False, color=(MAROON_A, RED_B, PURPLE_D), ) self.add( ax, bounding_line, quadratic, rects_right, rects_left, bounded_rects )
class GetRiemannRectanglesExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(y_range=[-2, 10]) quadratic = ax.plot(lambda x: 0.5 * x ** 2 - 0.5) # the rectangles are constructed from their top right corner. # passing an iterable to `color` produces a gradient rects_right = ax.get_riemann_rectangles( quadratic, x_range=[-4, -3], dx=0.25, color=(TEAL, BLUE_B, DARK_BLUE), input_sample_type="right", ) # the colour of rectangles below the x-axis is inverted # due to show_signed_area rects_left = ax.get_riemann_rectangles( quadratic, x_range=[-1.5, 1.5], dx=0.15, color=YELLOW ) bounding_line = ax.plot( lambda x: 1.5 * x, color=BLUE_B, x_range=[3.3, 6] ) bounded_rects = ax.get_riemann_rectangles( bounding_line, bounded_graph=quadratic, dx=0.15, x_range=[4, 5], show_signed_area=False, color=(MAROON_A, RED_B, PURPLE_D), ) self.add( ax, bounding_line, quadratic, rects_right, rects_left, bounded_rects )
- get_secant_slope_group(x, graph, dx=None, dx_line_color=ManimColor('#FFFF00'), dy_line_color=None, dx_label=None, dy_label=None, include_secant_line=True, secant_line_color=ManimColor('#83C167'), secant_line_length=10)[source]¶
- Creates two lines representing dx and df, the labels for dx and df, and
在特定x值处的曲线的割线。
- Parameters:
x (float) – 正割线第一次与图形相交时的x值。
graph (ParametricFunction) – 将找到其割线的曲线。
dx (float | None) – x 变化后割线退出的值。
dx_line_color (ParsableManimColor) – 表示x变化的线条的颜色。
dy_line_color (ParsableManimColor | None) – 表示y变化的线条颜色。默认为
graph的颜色。dx_label (float | str | None) – dx 线的标签。默认为
MathTex,适用于str和float输入。dy_label (float | str | None) – dy 线的标签。默认为
MathTex用于str和float输入。include_secant_line (bool) – 是否在图表中包含割线,或者仅包含df/dx线和标签。
secant_line_color (ParsableManimColor) – 割线的颜色。
secant_line_length (float) – 割线的长度。
- Returns:
一个包含以下元素的组:dx_line、df_line,如果适用还包括
dx_label、df_label、secant_line。- Return type:
示例
示例:GetSecantSlopeGroupExample ¶
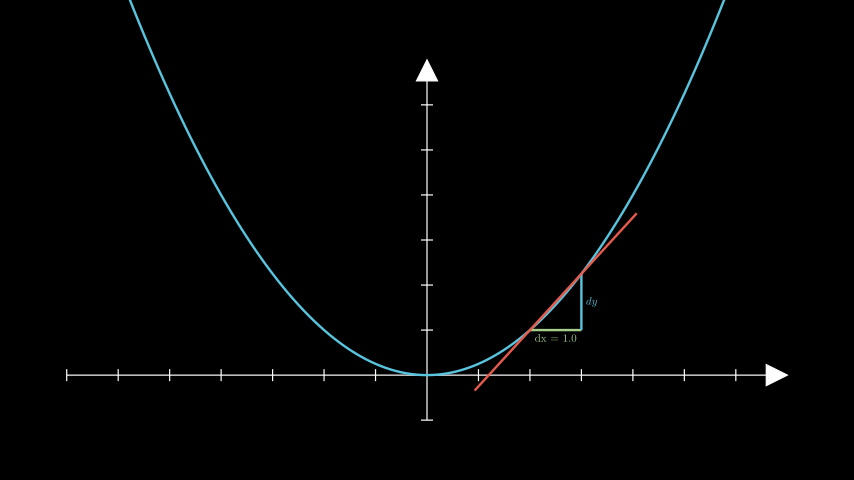
from manim import * class GetSecantSlopeGroupExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(y_range=[-1, 7]) graph = ax.plot(lambda x: 1 / 4 * x ** 2, color=BLUE) slopes = ax.get_secant_slope_group( x=2.0, graph=graph, dx=1.0, dx_label=Tex("dx = 1.0"), dy_label="dy", dx_line_color=GREEN_B, secant_line_length=4, secant_line_color=RED_D, ) self.add(ax, graph, slopes)
class GetSecantSlopeGroupExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(y_range=[-1, 7]) graph = ax.plot(lambda x: 1 / 4 * x ** 2, color=BLUE) slopes = ax.get_secant_slope_group( x=2.0, graph=graph, dx=1.0, dx_label=Tex("dx = 1.0"), dy_label="dy", dx_line_color=GREEN_B, secant_line_length=4, secant_line_color=RED_D, ) self.add(ax, graph, slopes)
- get_vertical_line(point, **kwargs)[source]¶
从x轴到场景中给定点的垂直线。
- Parameters:
point (Sequence[float]) – 绘制垂直线的点。
kwargs (Any) – 传递给
get_line_from_axis_to_point的额外参数。
- Returns:
从x轴到该点的垂直线。
- Return type:
Line
示例
示例:GetVerticalLineExample ¶
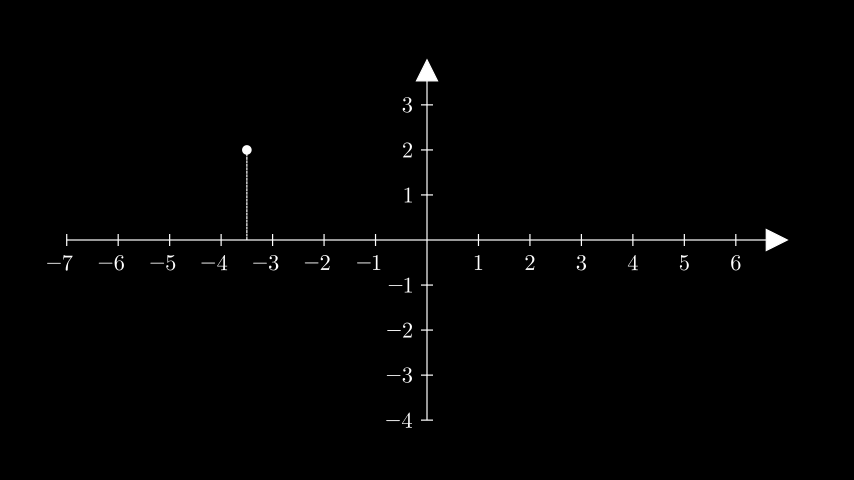
from manim import * class GetVerticalLineExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() point = ax.coords_to_point(-3.5, 2) dot = Dot(point) line = ax.get_vertical_line(point, line_config={"dashed_ratio": 0.85}) self.add(ax, line, dot)
class GetVerticalLineExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes().add_coordinates() point = ax.coords_to_point(-3.5, 2) dot = Dot(point) line = ax.get_vertical_line(point, line_config={"dashed_ratio": 0.85}) self.add(ax, line, dot)
- get_vertical_lines_to_graph(graph, x_range=None, num_lines=20, **kwargs)[来源]¶
从x轴到曲线获取多行。
- Parameters:
graph (ParametricFunction) – 线条所沿着的图形。
x_range (Sequence[float] | None) – 包含线条下限和上限的列表:
x_range = [x_min, x_max]。num_lines (int) – 均匀分布的线条数量。
kwargs (Any) – 传递给
get_vertical_line()的额外参数。
- Returns:
均匀间隔线的
VGroup。- Return type:
示例
示例:GetVerticalLinesToGraph ¶
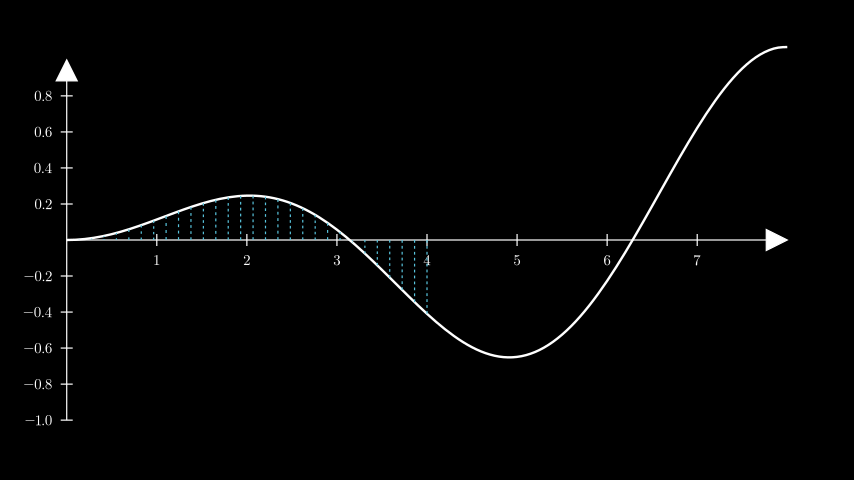
from manim import * class GetVerticalLinesToGraph(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes( x_range=[0, 8.0, 1], y_range=[-1, 1, 0.2], axis_config={"font_size": 24}, ).add_coordinates() curve = ax.plot(lambda x: np.sin(x) / np.e ** 2 * x) lines = ax.get_vertical_lines_to_graph( curve, x_range=[0, 4], num_lines=30, color=BLUE ) self.add(ax, curve, lines)
class GetVerticalLinesToGraph(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes( x_range=[0, 8.0, 1], y_range=[-1, 1, 0.2], axis_config={"font_size": 24}, ).add_coordinates() curve = ax.plot(lambda x: np.sin(x) / np.e ** 2 * x) lines = ax.get_vertical_lines_to_graph( curve, x_range=[0, 4], num_lines=30, color=BLUE ) self.add(ax, curve, lines)
- get_x_axis_label(label, edge=array([1., 1., 0.]), direction=array([1., 1., 0.]), buff=0.1, **kwargs)[source]¶
生成一个x轴标签。
- Parameters:
- Returns:
定位的标签。
- Return type:
示例
示例:GetXAxisLabelExample ¶
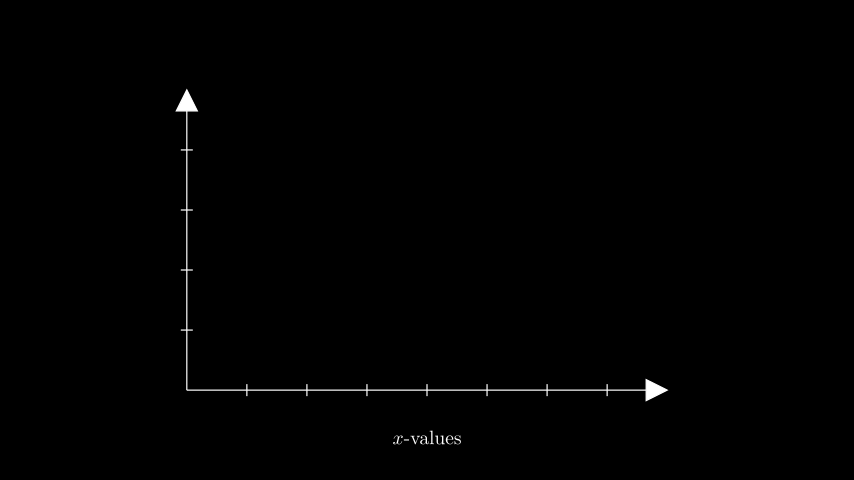
from manim import * class GetXAxisLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(x_range=(0, 8), y_range=(0, 5), x_length=8, y_length=5) x_label = ax.get_x_axis_label( Tex("$x$-values").scale(0.65), edge=DOWN, direction=DOWN, buff=0.5 ) self.add(ax, x_label)
class GetXAxisLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(x_range=(0, 8), y_range=(0, 5), x_length=8, y_length=5) x_label = ax.get_x_axis_label( Tex("$x$-values").scale(0.65), edge=DOWN, direction=DOWN, buff=0.5 ) self.add(ax, x_label)
- get_y_axis_label(label, edge=array([1., 1., 0.]), direction=array([1., 0.5, 0.]), buff=0.1, **kwargs)[source]¶
生成一个y轴标签。
- Parameters:
- Returns:
定位的标签。
- Return type:
示例
示例:GetYAxisLabelExample ¶
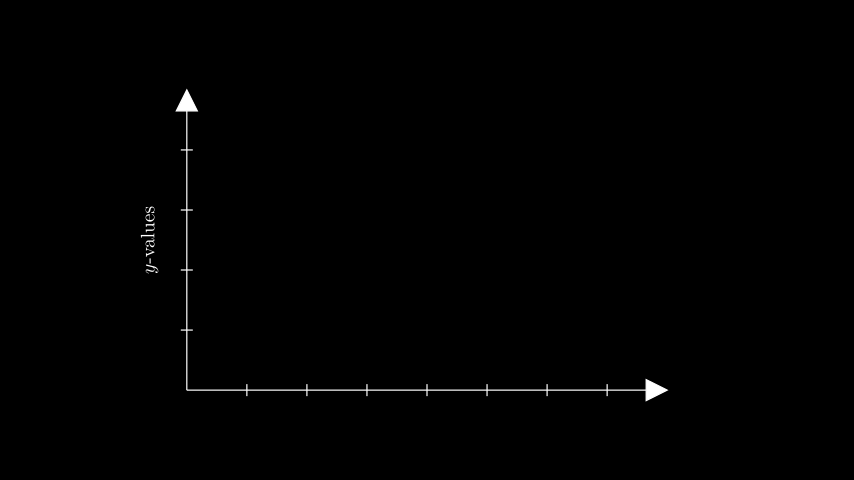
from manim import * class GetYAxisLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(x_range=(0, 8), y_range=(0, 5), x_length=8, y_length=5) y_label = ax.get_y_axis_label( Tex("$y$-values").scale(0.65).rotate(90 * DEGREES), edge=LEFT, direction=LEFT, buff=0.3, ) self.add(ax, y_label)
class GetYAxisLabelExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes(x_range=(0, 8), y_range=(0, 5), x_length=8, y_length=5) y_label = ax.get_y_axis_label( Tex("$y$-values").scale(0.65).rotate(90 * DEGREES), edge=LEFT, direction=LEFT, buff=0.3, ) self.add(ax, y_label)
- input_to_graph_coords(x, graph)[来源]¶
返回基于给定x值的点在图表上的轴相对坐标的元组。
示例
>>> from manim import Axes >>> ax = Axes() >>> parabola = ax.plot(lambda x: x**2) >>> ax.input_to_graph_coords(x=3, graph=parabola) (3, 9)
- Parameters:
x (浮点数)
图形 (参数函数)
- Return type:
元组[浮点数, 浮点数]
- input_to_graph_point(x, graph)[来源]¶
返回对应于
x值的graph上的点的坐标。- Parameters:
x (float) – 图表上某点的x值。
graph (ParametricFunction | VMobject) – 点所在的
ParametricFunction。
- Returns:
图表上对应于
x值的点的坐标。- Return type:
np.ndarray- Raises:
ValueError – 当目标x不在折线图的范围内时。
示例
示例:InputToGraphPointExample ¶
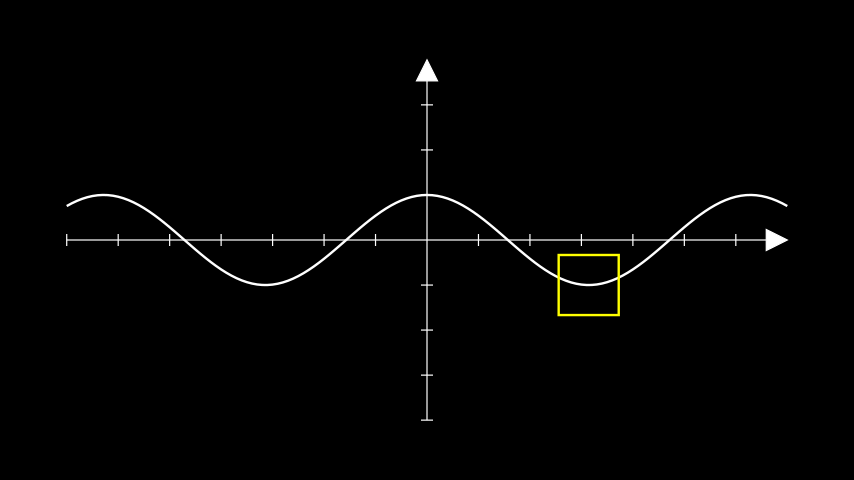
from manim import * class InputToGraphPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() curve = ax.plot(lambda x : np.cos(x)) # move a square to PI on the cosine curve. position = ax.input_to_graph_point(x=PI, graph=curve) sq = Square(side_length=1, color=YELLOW).move_to(position) self.add(ax, curve, sq)
class InputToGraphPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() curve = ax.plot(lambda x : np.cos(x)) # move a square to PI on the cosine curve. position = ax.input_to_graph_point(x=PI, graph=curve) sq = Square(side_length=1, color=YELLOW).move_to(position) self.add(ax, curve, sq)
- plot(function, x_range=None, use_vectorized=False, **kwargs)[来源]¶
基于函数生成曲线。
- Parameters:
function (Callable[[float], float]) – 用于构造
ParametricFunction的函数。x_range (Sequence[float] | None) – 曲线沿轴的范围。
x_range = [x_min, x_max, x_step].use_vectorized (bool) – 是否将生成的t值数组传递给函数。仅在您的函数支持时使用此选项。 输出应为形状为
[y_0, y_1, ...]的numpy数组kwargs (Any) – 传递给
ParametricFunction的额外参数。
- Returns:
绘制的曲线。
- Return type:
警告
此方法可能无法生成准确的图形,因为Manim目前依赖于曲线均匀间隔样本之间的插值,而不是智能绘图。 请参阅下面的示例以了解此问题的一些解决方案。
示例
示例:PlotExample ¶

from manim import * class PlotExample(Scene): def construct(self): # construct the axes ax_1 = Axes( x_range=[0.001, 6], y_range=[-8, 2], x_length=5, y_length=3, tips=False, ) ax_2 = ax_1.copy() ax_3 = ax_1.copy() # position the axes ax_1.to_corner(UL) ax_2.to_corner(UR) ax_3.to_edge(DOWN) axes = VGroup(ax_1, ax_2, ax_3) # create the logarithmic curves def log_func(x): return np.log(x) # a curve without adjustments; poor interpolation. curve_1 = ax_1.plot(log_func, color=PURE_RED) # disabling interpolation makes the graph look choppy as not enough # inputs are available curve_2 = ax_2.plot(log_func, use_smoothing=False, color=ORANGE) # taking more inputs of the curve by specifying a step for the # x_range yields expected results, but increases rendering time. curve_3 = ax_3.plot( log_func, x_range=(0.001, 6, 0.001), color=PURE_GREEN ) curves = VGroup(curve_1, curve_2, curve_3) self.add(axes, curves)
class PlotExample(Scene): def construct(self): # construct the axes ax_1 = Axes( x_range=[0.001, 6], y_range=[-8, 2], x_length=5, y_length=3, tips=False, ) ax_2 = ax_1.copy() ax_3 = ax_1.copy() # position the axes ax_1.to_corner(UL) ax_2.to_corner(UR) ax_3.to_edge(DOWN) axes = VGroup(ax_1, ax_2, ax_3) # create the logarithmic curves def log_func(x): return np.log(x) # a curve without adjustments; poor interpolation. curve_1 = ax_1.plot(log_func, color=PURE_RED) # disabling interpolation makes the graph look choppy as not enough # inputs are available curve_2 = ax_2.plot(log_func, use_smoothing=False, color=ORANGE) # taking more inputs of the curve by specifying a step for the # x_range yields expected results, but increases rendering time. curve_3 = ax_3.plot( log_func, x_range=(0.001, 6, 0.001), color=PURE_GREEN ) curves = VGroup(curve_1, curve_2, curve_3) self.add(axes, curves)
- plot_antiderivative_graph(graph, y_intercept=0, samples=50, use_vectorized=False, **kwargs)[来源]¶
绘制一个反导数图。
- Parameters:
graph (ParametricFunction) – 将为其找到反导数的图形。
y_intercept (float) – 图形与y轴相交处的y值。
samples (int) – 用于计算图形下面积的点的数量。
use_vectorized (bool) – 是否使用反导数的向量化版本。这意味着将生成的t值数组传递给函数。只有在你的函数支持时才使用此选项。 输出应该是一个形状为
[y_0, y_1, ...]的numpy数组。kwargs (Any) –
ParametricFunction的任何有效关键字参数。
- Returns:
反导数的曲线。
- Return type:
注意
此图是根据参考图下的面积值绘制的。 如果参考图包含从x=0开始的不可计算区域,结果可能不理想。
示例
示例:不定积分示例 ¶
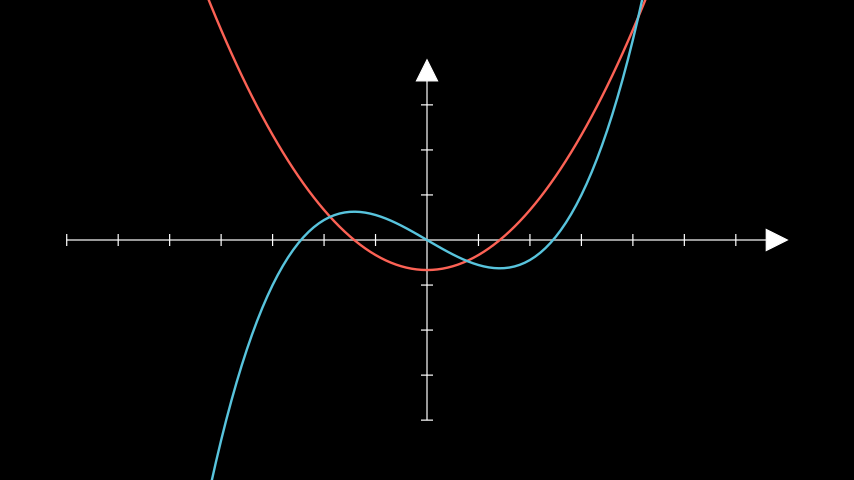
from manim import * class AntiderivativeExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() graph1 = ax.plot( lambda x: (x ** 2 - 2) / 3, color=RED, ) graph2 = ax.plot_antiderivative_graph(graph1, color=BLUE) self.add(ax, graph1, graph2)
class AntiderivativeExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() graph1 = ax.plot( lambda x: (x ** 2 - 2) / 3, color=RED, ) graph2 = ax.plot_antiderivative_graph(graph1, color=BLUE) self.add(ax, graph1, graph2)
- plot_derivative_graph(graph, color=ManimColor('#83C167'), **kwargs)[source]¶
返回传递图形的导数曲线。
- Parameters:
graph (ParametricFunction) – 将为其找到导数的图形。
color (ParsableManimColor) – 导数曲线的颜色。
kwargs –
ParametricFunction的任何有效关键字参数。
- Returns:
导数的曲线。
- Return type:
示例
示例:DerivativeGraphExample ¶
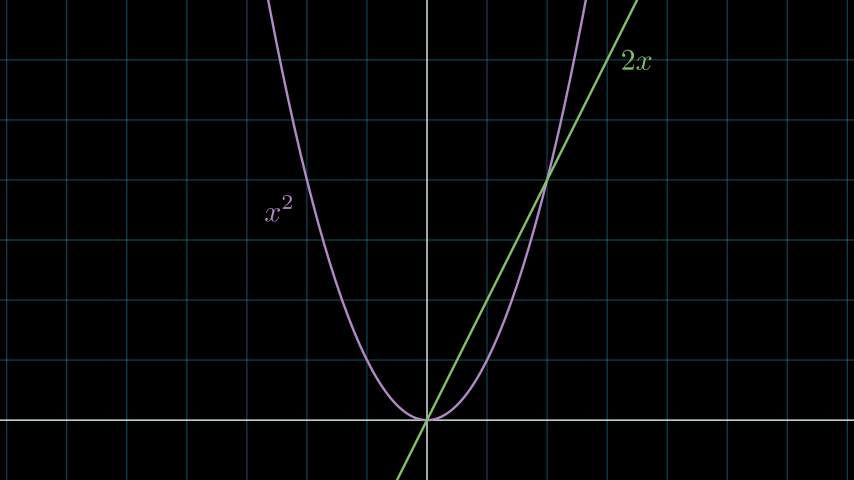
from manim import * class DerivativeGraphExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = NumberPlane(y_range=[-1, 7], background_line_style={"stroke_opacity": 0.4}) curve_1 = ax.plot(lambda x: x ** 2, color=PURPLE_B) curve_2 = ax.plot_derivative_graph(curve_1) curves = VGroup(curve_1, curve_2) label_1 = ax.get_graph_label(curve_1, "x^2", x_val=-2, direction=DL) label_2 = ax.get_graph_label(curve_2, "2x", x_val=3, direction=RIGHT) labels = VGroup(label_1, label_2) self.add(ax, curves, labels)
class DerivativeGraphExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = NumberPlane(y_range=[-1, 7], background_line_style={"stroke_opacity": 0.4}) curve_1 = ax.plot(lambda x: x ** 2, color=PURPLE_B) curve_2 = ax.plot_derivative_graph(curve_1) curves = VGroup(curve_1, curve_2) label_1 = ax.get_graph_label(curve_1, "x^2", x_val=-2, direction=DL) label_2 = ax.get_graph_label(curve_2, "2x", x_val=3, direction=RIGHT) labels = VGroup(label_1, label_2) self.add(ax, curves, labels)
- plot_implicit_curve(func, min_depth=5, max_quads=1500, **kwargs)[source]¶
创建一个隐式函数的曲线。
- Parameters:
func (Callable[[float, float], float]) – 要绘制的函数,形式为 f(x, y) = 0。
min_depth (int) – 要计算的函数的最小深度。
max_quads (int) – 使用的最大四边形数量。
kwargs (Any) – 传递给
ImplicitFunction的额外参数。
- Return type:
示例
示例:ImplicitExample ¶
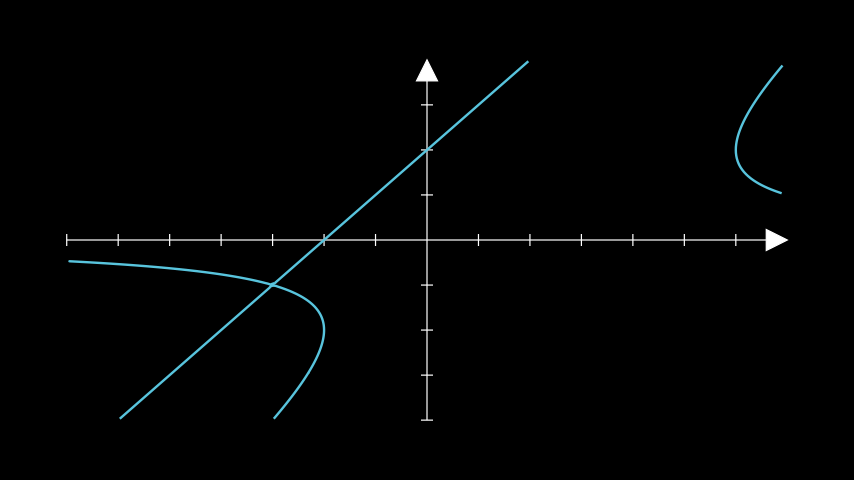
from manim import * class ImplicitExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() a = ax.plot_implicit_curve( lambda x, y: y * (x - y) ** 2 - 4 * x - 8, color=BLUE ) self.add(ax, a)
class ImplicitExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() a = ax.plot_implicit_curve( lambda x, y: y * (x - y) ** 2 - 4 * x - 8, color=BLUE ) self.add(ax, a)
- plot_parametric_curve(function, use_vectorized=False, **kwargs)[来源]¶
参数曲线。
- Parameters:
function (Callable[[float], ndarray]) – 一个将数字映射到坐标系中某点的参数化函数。
use_vectorized (bool) – 是否将生成的t值数组传递给函数。仅在您的函数支持时使用此选项。
kwargs (Any) – 任何进一步的关键字参数都会传递给
ParametricFunction。
- Return type:
示例
示例:ParametricCurveExample ¶
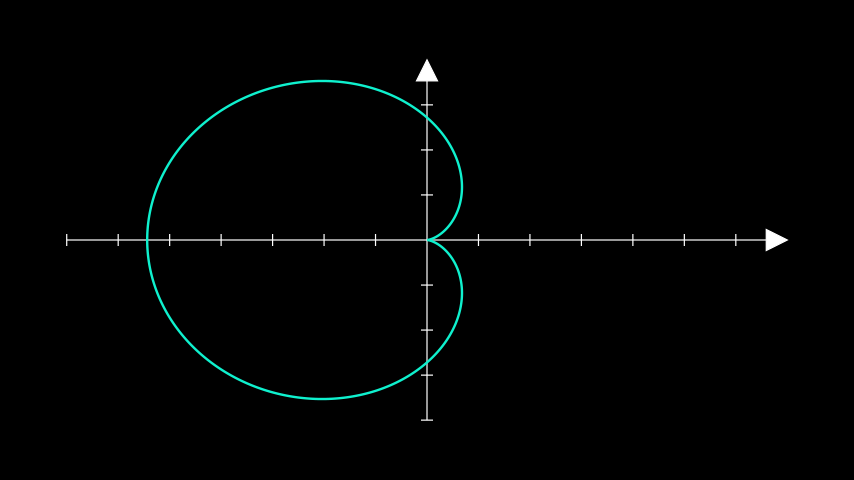
from manim import * class ParametricCurveExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() cardioid = ax.plot_parametric_curve( lambda t: np.array( [ np.exp(1) * np.cos(t) * (1 - np.cos(t)), np.exp(1) * np.sin(t) * (1 - np.cos(t)), 0, ] ), t_range=[0, 2 * PI], color="#0FF1CE", ) self.add(ax, cardioid)
class ParametricCurveExample(Scene): def construct(self): ax = Axes() cardioid = ax.plot_parametric_curve( lambda t: np.array( [ np.exp(1) * np.cos(t) * (1 - np.cos(t)), np.exp(1) * np.sin(t) * (1 - np.cos(t)), 0, ] ), t_range=[0, 2 * PI], color="#0FF1CE", ) self.add(ax, cardioid)
- plot_polar_graph(r_func, theta_range=None, **kwargs)[来源]¶
一个极坐标图。
- Parameters:
r_func (Callable[[float], float]) – 关于theta的函数r。
theta_range (Sequence[float] | None) – theta的范围为
theta_range = [theta_min, theta_max, theta_step]。kwargs (Any) – 传递给
ParametricFunction的附加参数。
- Return type:
示例
示例:PolarGraphExample ¶
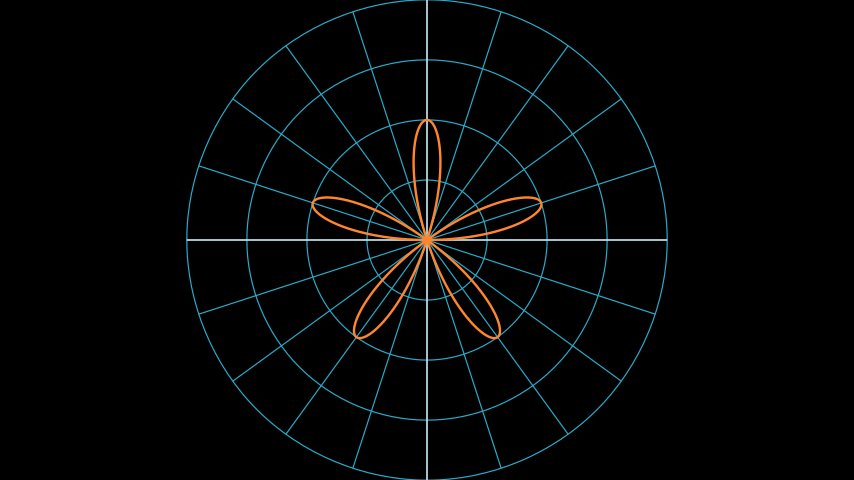
from manim import * class PolarGraphExample(Scene): def construct(self): plane = PolarPlane() r = lambda theta: 2 * np.sin(theta * 5) graph = plane.plot_polar_graph(r, [0, 2 * PI], color=ORANGE) self.add(plane, graph)
class PolarGraphExample(Scene): def construct(self): plane = PolarPlane() r = lambda theta: 2 * np.sin(theta * 5) graph = plane.plot_polar_graph(r, [0, 2 * PI], color=ORANGE) self.add(plane, graph)参考文献:
PolarPlane
- plot_surface(function, u_range=None, v_range=None, colorscale=None, colorscale_axis=2, **kwargs)[source]¶
基于函数生成一个表面。
- Parameters:
function (Callable[[float], float]) – 用于构造
Surface的函数。u_range (Sequence[float] | None) –
u变量的范围:(u_min, u_max)。v_range (Sequence[float] | None) –
v变量的范围:(v_min, v_max)。colorscale (Sequence[ParsableManimColor] | Sequence[tuple[ParsableManimColor, float]] | None) – 曲面的颜色。传递颜色列表将根据z值对曲面进行着色。 传递形式为
(color, pivot)的元组列表允许用户定义颜色过渡的枢轴点。colorscale_axis (int) – 定义应用颜色比例的轴(0 = x,1 = y,2 = z),默认是z轴(2)。
kwargs (Any) – 传递给
Surface的额外参数。
- Returns:
绘制的表面。
- Return type:
示例
示例:PlotSurfaceExample ¶
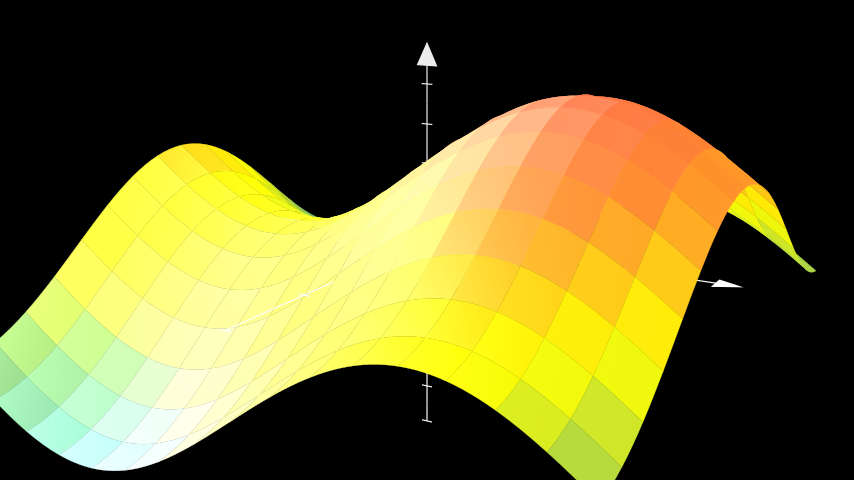
from manim import * class PlotSurfaceExample(ThreeDScene): def construct(self): resolution_fa = 16 self.set_camera_orientation(phi=75 * DEGREES, theta=-60 * DEGREES) axes = ThreeDAxes(x_range=(-3, 3, 1), y_range=(-3, 3, 1), z_range=(-5, 5, 1)) def param_trig(u, v): x = u y = v z = 2 * np.sin(x) + 2 * np.cos(y) return z trig_plane = axes.plot_surface( param_trig, resolution=(resolution_fa, resolution_fa), u_range = (-3, 3), v_range = (-3, 3), colorscale = [BLUE, GREEN, YELLOW, ORANGE, RED], ) self.add(axes, trig_plane)
class PlotSurfaceExample(ThreeDScene): def construct(self): resolution_fa = 16 self.set_camera_orientation(phi=75 * DEGREES, theta=-60 * DEGREES) axes = ThreeDAxes(x_range=(-3, 3, 1), y_range=(-3, 3, 1), z_range=(-5, 5, 1)) def param_trig(u, v): x = u y = v z = 2 * np.sin(x) + 2 * np.cos(y) return z trig_plane = axes.plot_surface( param_trig, resolution=(resolution_fa, resolution_fa), u_range = (-3, 3), v_range = (-3, 3), colorscale = [BLUE, GREEN, YELLOW, ORANGE, RED], ) self.add(axes, trig_plane)
- point_to_polar(point)[source]¶
从点获取极坐标。
- Parameters:
点 (ndarray) – 该点。
- Returns:
坐标半径(\(r\))和坐标方位角(\(\theta\))。
- Return type:
元组[
float,float]
- polar_to_point(radius, azimuth)[来源]¶
从极坐标获取一个点。
- Parameters:
radius (float) – 坐标半径 (\(r\)).
azimuth (float) – 坐标方位角 (\(\theta\))。
- Returns:
重点。
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
示例
示例:PolarToPointExample ¶
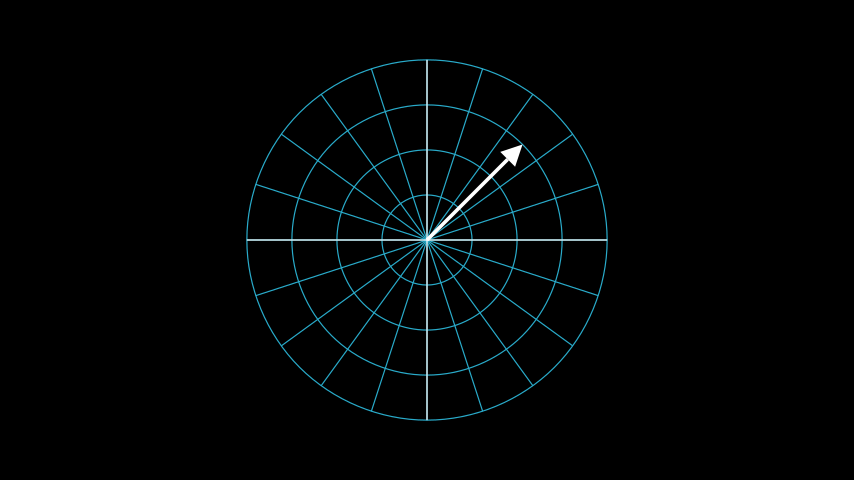
from manim import * class PolarToPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): polarplane_pi = PolarPlane(azimuth_units="PI radians", size=6) polartopoint_vector = Vector(polarplane_pi.polar_to_point(3, PI/4)) self.add(polarplane_pi) self.add(polartopoint_vector)
class PolarToPointExample(Scene): def construct(self): polarplane_pi = PolarPlane(azimuth_units="PI radians", size=6) polartopoint_vector = Vector(polarplane_pi.polar_to_point(3, PI/4)) self.add(polarplane_pi) self.add(polartopoint_vector)参考文献:
PolarPlaneVector
- slope_of_tangent(x, graph, **kwargs)[source]¶
返回在特定x值处绘制曲线的切线斜率。
- Parameters:
x (float) – 切线与曲线接触的x值。
graph (ParametricFunction) – 用于计算切线的
ParametricFunction。kwargs (任意)
- Returns:
切线与x轴的斜率。
- Return type:
float
示例
ax = Axes() curve = ax.plot(lambda x: x**2) ax.slope_of_tangent(x=-2, graph=curve) # -3.5000000259052038